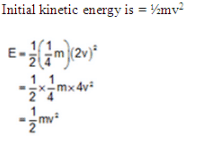All Exams >
Grade 6 >
Science for Grade 6 >
All Questions
All questions of Energy for Grade 6 Exam
If a light bulb is switched on for 20 s and it consumes 2400 J of electrical energy then it's power is- a)60 W
- b)70 W
- c)80 W
- d)90 W
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a light bulb is switched on for 20 s and it consumes 2400 J of electrical energy then it's power is
a)
60 W
b)
70 W
c)
80 W
d)
90 W
|
|
Gayatri bajaj answered |
Power = Energy /Time
Power = 2400/20
Power = 120w
Power = 2400/20
Power = 120w
A diesel engine supplies 25,000 J of energy in 50 seconds. Power of engine would be- a)7500 W
- b)250 W
- c)25000 W
- d)500 W
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A diesel engine supplies 25,000 J of energy in 50 seconds. Power of engine would be
a)
7500 W
b)
250 W
c)
25000 W
d)
500 W
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Power = Work done / Time
= 25000 / 50
= 500J/s or 500W
= 25000 / 50
= 500J/s or 500W
A coolie was standing with 2 suitcases on his head and 2 bags in his hand. The luggage exerted a force of 159 N on him. What is the amount of work done by him?- a)79.5 J
- b)318 J
- c)0 J
- d)159 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A coolie was standing with 2 suitcases on his head and 2 bags in his hand. The luggage exerted a force of 159 N on him. What is the amount of work done by him?
a)
79.5 J
b)
318 J
c)
0 J
d)
159 J
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Work done is zero, since there is no displacement of the coolie.
Calculate the distance between the man and the box when the work done to move the box was 100 J with a force of 15 N.- a)6 m
- b)16.6 m
- c)26.6 m
- d)6.6 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the distance between the man and the box when the work done to move the box was 100 J with a force of 15 N.
a)
6 m
b)
16.6 m
c)
26.6 m
d)
6.6 m
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
As given, W = 100 J, F = 15 N
We know, W = Fs
⇒ s = W/ F
⇒ s = 100 / 15
⇒ s = 6.6 m
We know, W = Fs
⇒ s = W/ F
⇒ s = 100 / 15
⇒ s = 6.6 m
Newton-metre is the unit of- a)power
- b)work
- c)momentum
- d)gravitational intensity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Newton-metre is the unit of
a)
power
b)
work
c)
momentum
d)
gravitational intensity
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Work=Force*Displacement (N-m)
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A force a body of mass 3 kg producing a displacement of 10 m in it. The work done by force is of 6 N acts on
- A:
30 J
- B:
60 J
- C:
18 J
- D:
36 J
The answer is a.
A force a body of mass 3 kg producing a displacement of 10 m in it. The work done by force is of 6 N acts on
30 J
60 J
18 J
36 J

|
Sonal Sinha answered |
Here,
work done(W)=fdcos60degree
W=6×10×1/2
w=60/2
w=30j(Ans).
work done(W)=fdcos60degree
W=6×10×1/2
w=60/2
w=30j(Ans).
To lift 700 kg of water, through a height of 10 m we use a pump. The work done in operating the pump is;
Take g = 10 m/s2.- a)7 kilo joules
- b)7 x 106 J
- c)700 J
- d)70000 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To lift 700 kg of water, through a height of 10 m we use a pump. The work done in operating the pump is;
Take g = 10 m/s2.
Take g = 10 m/s2.
a)
7 kilo joules
b)
7 x 106 J
c)
700 J
d)
70000 J
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Work done = mgh
= 700 kg x 10m/s x 10m = 70000 joule
= 700 kg x 10m/s x 10m = 70000 joule
How fast should a person with mass 50kg walk so that his kinetic energy is 625 J ?- a)15 km/s
- b)0.5 m/s
- c)5 m/s
- d)5 Km/s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How fast should a person with mass 50kg walk so that his kinetic energy is 625 J ?
a)
15 km/s
b)
0.5 m/s
c)
5 m/s
d)
5 Km/s

|
Soumya answered |
K.E = 0.5mv²
v = √(2K.E / m)
= √(2 × 625 Joule / 50 kg)
= √(625 Joule / 25 kg)
= 5 m/s...
v = √(2K.E / m)
= √(2 × 625 Joule / 50 kg)
= √(625 Joule / 25 kg)
= 5 m/s...
The winners of long jump each weighing 56 Kg, 40 Kg and 45 Kg stand on the podium. What is the work done by them on the podium while they receive the medals?- a)250 J
- b)0 J
- c)282 J
- d)141 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The winners of long jump each weighing 56 Kg, 40 Kg and 45 Kg stand on the podium. What is the work done by them on the podium while they receive the medals?
a)
250 J
b)
0 J
c)
282 J
d)
141 J
|
|
Aayush Kumar answered |
The winners of long jump each weighing 56kg,40kg and 45 kg stand on podium.Work done by them is 0 Ioule because there is no displacement and if the displacement is 0 then work done will be also 0.
What is the commercial unit of energy?- a)electron volt
- b)W/s
- c)kW h
- d)joule
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the commercial unit of energy?
a)
electron volt
b)
W/s
c)
kW h
d)
joule

|
Rajesh Seervi answered |
C is correct answer because energy consumed in commercial use in per unit time and which is defined as power and power has unit watt . We take kWh because energy consumed in commercial use have high value so kWh is taken.
Two bodies of unequal masses are dropped from a cliff. At any instant, they have equal- a)momentum
- b)acceleration
- c)potential energy
- d)kinetic energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two bodies of unequal masses are dropped from a cliff. At any instant, they have equal
a)
momentum
b)
acceleration
c)
potential energy
d)
kinetic energy
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
They will have the same acceleration due to gravity because it is independent of mass.
A stone weighing 1 kg is dropped from rest from a height of 4 metres above the ground. When it has free-fallen 1 metre its total energy with respect to the ground is- a)15 J
- b)40 J
- c)20 J
- d)30 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone weighing 1 kg is dropped from rest from a height of 4 metres above the ground. When it has free-fallen 1 metre its total energy with respect to the ground is
a)
15 J
b)
40 J
c)
20 J
d)
30 J
|
|
Gitanjali Mukherjee answered |
**Explanation:**
When an object is dropped from a height, it undergoes free fall. During free fall, the only force acting on the object is the force of gravity. As the object falls, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
**Step 1: Calculate the potential energy at a height of 4 metres.**
The potential energy (PE) of an object at a certain height is given by the equation:
PE = mgh
where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height.
Given:
m = 1 kg (mass of the stone)
g = 9.8 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity)
h = 4 m (height)
PE = (1 kg)(9.8 m/s²)(4 m) = 39.2 J
So, the potential energy of the stone at a height of 4 metres is 39.2 J.
**Step 2: Calculate the potential energy at a height of 1 metre.**
Using the same formula, we can calculate the potential energy at a height of 1 metre.
Given:
m = 1 kg (mass of the stone)
g = 9.8 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity)
h = 1 m (height)
PE = (1 kg)(9.8 m/s²)(1 m) = 9.8 J
So, the potential energy of the stone at a height of 1 metre is 9.8 J.
**Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy at a height of 1 metre.**
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object is given by the equation:
KE = 0.5mv²
where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
Since the stone is dropped from rest, its initial velocity is 0 m/s.
Given:
m = 1 kg (mass of the stone)
v = 0 m/s (initial velocity)
KE = 0.5(1 kg)(0 m/s)² = 0 J
So, the kinetic energy of the stone at a height of 1 metre is 0 J.
**Step 4: Calculate the total energy at a height of 1 metre.**
The total energy (TE) of an object is the sum of its potential energy and kinetic energy.
TE = PE + KE
TE = 9.8 J + 0 J = 9.8 J
So, the total energy of the stone at a height of 1 metre is 9.8 J.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B) 40 J.
When an object is dropped from a height, it undergoes free fall. During free fall, the only force acting on the object is the force of gravity. As the object falls, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
**Step 1: Calculate the potential energy at a height of 4 metres.**
The potential energy (PE) of an object at a certain height is given by the equation:
PE = mgh
where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height.
Given:
m = 1 kg (mass of the stone)
g = 9.8 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity)
h = 4 m (height)
PE = (1 kg)(9.8 m/s²)(4 m) = 39.2 J
So, the potential energy of the stone at a height of 4 metres is 39.2 J.
**Step 2: Calculate the potential energy at a height of 1 metre.**
Using the same formula, we can calculate the potential energy at a height of 1 metre.
Given:
m = 1 kg (mass of the stone)
g = 9.8 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity)
h = 1 m (height)
PE = (1 kg)(9.8 m/s²)(1 m) = 9.8 J
So, the potential energy of the stone at a height of 1 metre is 9.8 J.
**Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy at a height of 1 metre.**
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object is given by the equation:
KE = 0.5mv²
where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
Since the stone is dropped from rest, its initial velocity is 0 m/s.
Given:
m = 1 kg (mass of the stone)
v = 0 m/s (initial velocity)
KE = 0.5(1 kg)(0 m/s)² = 0 J
So, the kinetic energy of the stone at a height of 1 metre is 0 J.
**Step 4: Calculate the total energy at a height of 1 metre.**
The total energy (TE) of an object is the sum of its potential energy and kinetic energy.
TE = PE + KE
TE = 9.8 J + 0 J = 9.8 J
So, the total energy of the stone at a height of 1 metre is 9.8 J.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B) 40 J.
9800 joule of energy was spent to raise a mass of 50kg, the mass was raised to a height of- a)20m
- b)980m
- c)10m
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
9800 joule of energy was spent to raise a mass of 50kg, the mass was raised to a height of
a)
20m
b)
980m
c)
10m
d)
none of these
|
|
Ramya sengupta answered |
Potential energy = mgh, here, RE = 9800 j. mass = 50kg, g = 9.8m/s2. Therefore, 9800 = 50 x 9.8 x h, h= 9800/50 x 9.8 = 20m.
A lamp consumes 1000J of energy in 10s, what is its power?- a)100 W
- b)100000 W
- c)1k W
- d)1000 W
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A lamp consumes 1000J of energy in 10s, what is its power?
a)
100 W
b)
100000 W
c)
1k W
d)
1000 W
|
|
Isha Isha answered |
Power =Work/time =1000 J /10 sec =100 WBecause SI unit of energy is watt .
Work done by a body is- a)negative, positive or zero
- b)always positive
- c)always zero
- d)always negative
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by a body is
a)
negative, positive or zero
b)
always positive
c)
always zero
d)
always negative
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Positive Work
- If a force displaces the object in its direction, then the work done is positive
So, W=Fd
The example of this kind of work done is motion of ball falling towards ground where displacement of ball is in the direction of force of gravity.
Negative work
- If the force and the displacement are in opposite directions, then the work is said to be negative. For example if a ball is thrown in upwards direction, its displacement would be in upwards direction but the force due to earth’s gravity is in the downward direction.
So here in this case gravity is doing negative work when you throw the ball upwards. Hence the work done by gravitational force is negative. Mathematically when displacement is opposite to the force work done is given by
- Negative work just means that the force and the displacement act in opposite directions.
Case of zero work done
- If the directions of force and the displacement are perpendicular to each other, the work done by the force on the object is zero.
For example, when we push hard against a wall, the force we are exerting on the wall does no work, because in this case the displacement of the wall is d = 0. However, in this process, our muscles are using our internal energy and as a result we get tired.
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with an acceleration of 5 ms-2 gets a displacement of 2m, the work done by the force is:- a)75 J
- b)25 J
- c)100 J
- d)50 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with an acceleration of 5 ms-2 gets a displacement of 2m, the work done by the force is:
a)
75 J
b)
25 J
c)
100 J
d)
50 J
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
We know, F = ma
F = 5 * 5
F = 25
We, also know;
W = F. s
= 25 * 2
W = 50 J
F = 5 * 5
F = 25
We, also know;
W = F. s
= 25 * 2
W = 50 J
Scientifically, work is said to be done in which of the following cases- a)Manish pulls the trolley for a certain distance
- b)Mira studies for her exam
- c)Manoj pushes the wall with no change in the position of wall
- d)Mira pulls the wall with no change in the position of wall
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Scientifically, work is said to be done in which of the following cases
a)
Manish pulls the trolley for a certain distance
b)
Mira studies for her exam
c)
Manoj pushes the wall with no change in the position of wall
d)
Mira pulls the wall with no change in the position of wall

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Manish pulls the trolley for a certain distance:- force is applied and there is displacement also , so work is done.
A freely falling body during its fall will have- a)Kinetic energy
- b)Potential energy
- c)Sound energy
- d)Both kinetic energy and potential energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A freely falling body during its fall will have
a)
Kinetic energy
b)
Potential energy
c)
Sound energy
d)
Both kinetic energy and potential energy
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Object Falling from Rest. As an object falls from rest, its gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Conservation of energy as a tool permits the calculation of the velocity just before it hits the surface. K.E. = J, which is of course equal to its initial potential energy.
A flying aeroplane possesses- a)only potential energy
- b)only kinetic energy
- c)both potential and kinetic energy
- d)neither potential nor kinetic energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A flying aeroplane possesses
a)
only potential energy
b)
only kinetic energy
c)
both potential and kinetic energy
d)
neither potential nor kinetic energy
|
|
Rajat Singh answered |
Correct answer is option c because it is flying above ground level it will posses potential energy and since it is moving with the motion associated through it, it possesses kinetic energy.
Calculate the work done in moving a body of mass 50 Kg through a height of 5 m.(g = 10m/s2)- a)250 J
- b)2500 J
- c)25 x 103 J
- d)2.5 x 105 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the work done in moving a body of mass 50 Kg through a height of 5 m.(g = 10m/s2)
a)
250 J
b)
2500 J
c)
25 x 103 J
d)
2.5 x 105 J

|
Sonal Sinha answered |
W=fd
Force=mg =50×10=500N
W=fd
=500×5=2500j(Ans).
Force=mg =50×10=500N
W=fd
=500×5=2500j(Ans).
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A certain household has consumed 250 units of energy during a month. How much energy is this in joules?
- A:
9 ×106J
- B:
5 × 108 Joule
- C:
10 × 105Joule
- D:
9 ×108J
The answer is d.
A certain household has consumed 250 units of energy during a month. How much energy is this in joules?
9 ×106J
5 × 108 Joule
10 × 105Joule
9 ×108J
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
1 unit of energy is equal to 1 kilowatt hour (kWh).
1 unit = 1 kWh
1 kWh = 3.6 x 10^6J
Therefore, 250 units of energy = 250 x 3.6 x 10^6 = 9 x 10^8 J.
If the velocity of a moving car is halved, its kinetic energy would- a)Double
- b)Become Half
- c)Become one fourth
- d)Remain same
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the velocity of a moving car is halved, its kinetic energy would
a)
Double
b)
Become Half
c)
Become one fourth
d)
Remain same
|
|
Namrata Desai answered |
The kinetic energy of an object is directly proportional to its velocity squared. This means that if the velocity of a moving car is halved, its kinetic energy would decrease significantly.
Explanation:
1. Kinetic Energy Formula: The formula for kinetic energy is KE = 1/2 * m * v^2, where KE is the kinetic energy, m is the mass of the object, and v is the velocity of the object.
2. Halving the Velocity: If the velocity of the car is halved, it means that the new velocity (v') is equal to half of the original velocity (v/2).
3. Calculation: Substituting the new velocity into the kinetic energy formula, we get KE' = 1/2 * m * (v/2)^2 = 1/2 * m * v^2/4 = KE/4.
4. Conclusion: We can see that the new kinetic energy (KE') is equal to one-fourth of the original kinetic energy (KE). Therefore, when the velocity of a moving car is halved, its kinetic energy becomes one-fourth of what it was originally.
Example:
Let's consider an example to illustrate this concept. Suppose a car has a mass of 1000 kg and is initially moving at a velocity of 20 m/s.
- The initial kinetic energy of the car can be calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 * m * v^2 = 1/2 * 1000 kg * (20 m/s)^2 = 200,000 J.
- If the velocity of the car is halved, the new velocity becomes 10 m/s.
- The new kinetic energy can be calculated using the formula KE' = 1/2 * m * (v/2)^2 = 1/2 * 1000 kg * (10 m/s)^2 = 50,000 J.
- Comparing the initial kinetic energy with the new kinetic energy, we can see that the new kinetic energy is one-fourth (1/4) of the original kinetic energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C - the kinetic energy would become one-fourth if the velocity of a moving car is halved.
Explanation:
1. Kinetic Energy Formula: The formula for kinetic energy is KE = 1/2 * m * v^2, where KE is the kinetic energy, m is the mass of the object, and v is the velocity of the object.
2. Halving the Velocity: If the velocity of the car is halved, it means that the new velocity (v') is equal to half of the original velocity (v/2).
3. Calculation: Substituting the new velocity into the kinetic energy formula, we get KE' = 1/2 * m * (v/2)^2 = 1/2 * m * v^2/4 = KE/4.
4. Conclusion: We can see that the new kinetic energy (KE') is equal to one-fourth of the original kinetic energy (KE). Therefore, when the velocity of a moving car is halved, its kinetic energy becomes one-fourth of what it was originally.
Example:
Let's consider an example to illustrate this concept. Suppose a car has a mass of 1000 kg and is initially moving at a velocity of 20 m/s.
- The initial kinetic energy of the car can be calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 * m * v^2 = 1/2 * 1000 kg * (20 m/s)^2 = 200,000 J.
- If the velocity of the car is halved, the new velocity becomes 10 m/s.
- The new kinetic energy can be calculated using the formula KE' = 1/2 * m * (v/2)^2 = 1/2 * 1000 kg * (10 m/s)^2 = 50,000 J.
- Comparing the initial kinetic energy with the new kinetic energy, we can see that the new kinetic energy is one-fourth (1/4) of the original kinetic energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C - the kinetic energy would become one-fourth if the velocity of a moving car is halved.
If 1 newton of force displaces a body by 1 m, the work done is- a)10 joule
- b)5 joule
- c)1 joule
- d)Depends on time
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If 1 newton of force displaces a body by 1 m, the work done is
a)
10 joule
b)
5 joule
c)
1 joule
d)
Depends on time
|
|
Prasad Ghoshal answered |
Explanation:
Work done is defined as the product of force and displacement in the direction of force. Thus, if 1 newton of force displaces a body by 1 m, the work done will be:
Work = Force x Displacement
= 1 N x 1 m
= 1 joule
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
Work done is defined as the product of force and displacement in the direction of force. Thus, if 1 newton of force displaces a body by 1 m, the work done will be:
Work = Force x Displacement
= 1 N x 1 m
= 1 joule
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
If two bodies of different masses have the same K.E. then the relation between momentum and mass will be:- a)
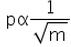
- b)
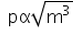
- c)

- d)
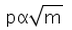
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If two bodies of different masses have the same K.E. then the relation between momentum and mass will be:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
KE = K = 1 /2( mv2)
We know, p = mv
⇒ K = p2 / 2m
p2 = 2Km
As, KE is Same, ie . Constant, momentum would be directly proportional to the square root of mass.
We know, p = mv
⇒ K = p2 / 2m
p2 = 2Km
As, KE is Same, ie . Constant, momentum would be directly proportional to the square root of mass.
An electric lamp of 100w is used for 5 hours per day calculate the units of energy consumed by lamp in one day- a)1 unit
- b)0.5 unit
- c)1.5 units
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric lamp of 100w is used for 5 hours per day calculate the units of energy consumed by lamp in one day
a)
1 unit
b)
0.5 unit
c)
1.5 units
d)
none of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Power of lamp = 100w = 100/1000 = 0.1Kw, time= 5 hrs. Electrical energy = power×timepower×time, E = 0.1kw×5h = 0.5 kw–h. = 0.5 unit.
For what value of .ϕ. is work done maximum?- a)900
- b)00
- c)600
- d)450
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For what value of .ϕ. is work done maximum?
a)
900
b)
00
c)
600
d)
450

|
Jatin Basu answered |
Work done when a body moves at an angle to the direction of force is W=Fcosϕ×s. The value of Cos is maximum for 00. So, work done will be maximum for this angel.
Find the correct statement- a)1 Gigawatt is equal to 109W
- b)power is the rate of doing work
- c)both a and b
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the correct statement
a)
1 Gigawatt is equal to 109W
b)
power is the rate of doing work
c)
both a and b
d)
none of these

|
Ashish Saha answered |
One Giga watt is equal to 109 watt or 106 kilowatt. The rate of doing work is called as power. Hence both statements are correct.
Two masses m and 2m are dropped from certain height ‘h’. Then on reaching the ground,- a)K.E. of them will be equal
- b)K.E. of the heavier is 4 times the K.E. of the lighter
- c)K.E. of the lighter is 4 times the K.E. of the heavier
- d)K.E. of the heavier is more than that of the lighter.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two masses m and 2m are dropped from certain height ‘h’. Then on reaching the ground,
a)
K.E. of them will be equal
b)
K.E. of the heavier is 4 times the K.E. of the lighter
c)
K.E. of the lighter is 4 times the K.E. of the heavier
d)
K.E. of the heavier is more than that of the lighter.
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
- Since the free-falling acceleration is not dependent on mass, the final velocities of both masses are the same.
The kinetic energy = KE = mv2/2 - Hence, the kinetic energy of the heavier mass will be more.
When we throw a rock from the top of a building which equation describes the energy of the body at each point during the fall?
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When we throw a rock from the top of a building which equation describes the energy of the body at each point during the fall?
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D

|
Mehak answered |
It's 'A ' because according to the law of conservation of energy , energy can only be transformed from to form to another , it can neither be created nor destroyed . The total energy before and after the transformation always remains constant.
A fish with weight 35 kg dives and hits the ground (zero height) with kinetic energy equal to 3500J. Find the height through which fish dived. Take g = 10 m/s2
- a)1 km
- b)100 m
- c)10 m
- d)20 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A fish with weight 35 kg dives and hits the ground (zero height) with kinetic energy equal to 3500J. Find the height through which fish dived. Take g = 10 m/s2
a)
1 km
b)
100 m
c)
10 m
d)
20 m
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
We can use the principle of conservation of mechanical energy to solve this problem. According to this principle, the potential energy (PE) at the height is converted into kinetic energy (KE) as the fish dives to the ground.
The formula for potential energy is:
PE=mgh
Where:
- m=35 kg
- g=10 m/s^2
- hhh is the height through which the fish dived (which we need to find)
Given that the kinetic energy when the fish hits the ground is equal to the potential energy it had at the starting height:
KE=PE
3500 J=35×10×h
Now solve for h:
3500=350h
h=3500/350=10 m
So, the height through which the fish dived is 10 meters.
The correct answer is:
3. 10 m.
A force of 10 N displaces a body by 6 m in 3 seconds. The power of the agency applying the force is- a)1.8 W
- b)5 W
- c)180 W
- d)20 W
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A force of 10 N displaces a body by 6 m in 3 seconds. The power of the agency applying the force is
a)
1.8 W
b)
5 W
c)
180 W
d)
20 W
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
We know, Power :-
= force * displacement/Time
Force is 10 N, displacement = 6 m
Time = 3 s
Then, power = 10*6/3 => 10 * 2 ⇒ 20W
= force * displacement/Time
Force is 10 N, displacement = 6 m
Time = 3 s
Then, power = 10*6/3 => 10 * 2 ⇒ 20W
Which of the following produces energy because of temperature difference at various levels in ocean. - a)Tidal energy
- b)Wave energy
- c)Solar energy
- d)Ocean thermal energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following produces energy because of temperature difference at various levels in ocean.
a)
Tidal energy
b)
Wave energy
c)
Solar energy
d)
Ocean thermal energy
|
|
Poulomi Nambiar answered |
The correct option is C.
Both will have the same kinetic energy.
Both will have the same kinetic energy.
Work done by centripetal force is- a)>0
- b)≥0
- c)<0
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by centripetal force is
a)
>0
b)
≥0
c)
<0
d)
0
|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
W = F* d cos (Theta)
W = Tension * displacement * cos (90)
The force is perpendicular to the objects motion (or displacement of the object)
W = T * d * 0
W= 0
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A light body and heavy body have same momentum. Then they also have same kinetic energy.Reason : Kinetic energy depends on mass of the body.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : A light body and heavy body have same momentum. Then they also have same kinetic energy.
Reason : Kinetic energy depends on mass of the body.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but reason is true.

|
Dont Memorise answered |
Kinetic energy of a body of mass m1,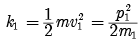
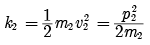
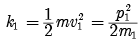
Again, kinetic energy of a body of mass m2,
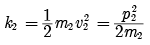
If 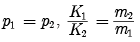
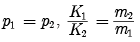
As given m2 > m1
Therefore, K1 > K2 i.e. the kinetic energy of light body will be more than the kinetic energy of heavy body when both have same momentum.
In the SI system, the unit of potential energy is:- a)Newton
- b)Joule
- c)Watt
- d)Metre per second
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the SI system, the unit of potential energy is:
a)
Newton
b)
Joule
c)
Watt
d)
Metre per second
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Potential energy is energy stored in matter. Joule is the SI unit of energy.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : According to law of conservation of mechanical energy, change in potential energy is equal and opposite to the change in kinetic energy.Reason : Mechanical energy is not a conserved quantity.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : According to law of conservation of mechanical energy, change in potential energy is equal and opposite to the change in kinetic energy.
Reason : Mechanical energy is not a conserved quantity.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but reason is true.

|
Dont Memorise answered |
For conservative forces the sum of kinetic and potential energies at any point remains constant throughout the motion. It does not depend upon time. This is known as law of conservation of mechanical energy. According to this rule.
Kinetic energy + Potential energy = E = constant
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : Watt hour has units of energy.Reason : Kilowatt hour (kW h) is the unit of electric power.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Watt hour has units of energy.
Reason : Kilowatt hour (kW h) is the unit of electric power.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but reason is true.
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Kilowatt (1000 watt) is the unit of power. Kilowatt hour is the power consumed in one hour = power x time = energy. One watt is equal to Joule per second. Hence, watt # time has units of energy.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : Energy possessed by a rolling stone is kinetic energy.Reason : Kinetic energy possessed by an object is due to its motion.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Energy possessed by a rolling stone is kinetic energy.
Reason : Kinetic energy possessed by an object is due to its motion.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Dont Memorise answered |
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. Moving objects possess kinetic energy. For example, energy possessed by a rolling stone is kinetic energy.
Which of the following is not an example of potential energy?- a)A compressed spring
- b)Water stored in the reservoir of dam
- c)A stretched rubber band
- d)A moving car
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of potential energy?
a)
A compressed spring
b)
Water stored in the reservoir of dam
c)
A stretched rubber band
d)
A moving car
|
|
Aman Majumdar answered |
A moving car is an example of Kinetic energy whereas water stored in a dam, compressed springs and stretched rubber band are examples of potential energy.
According to the law of conservation of energy, which statement is true?- a)Energy can be created and destroyed.
- b)The total energy before and after transformation remains the same.
- c)Energy transformation always leads to a loss of energy.
- d)Only kinetic energy is conserved, not potential energy.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Energy can be created and destroyed.
b)
The total energy before and after transformation remains the same.
c)
Energy transformation always leads to a loss of energy.
d)
Only kinetic energy is conserved, not potential energy.

|
Let's Tute answered |
The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. The total energy in a closed system remains constant before and after any transformation.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : Work done by the gravitational force through a certain distance is constant irrespective of the fact that the body has a uniform or accelerated motion.Reason : Gravitational force is a conservative force.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Work done by the gravitational force through a certain distance is constant irrespective of the fact that the body has a uniform or accelerated motion.
Reason : Gravitational force is a conservative force.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but reason is true.

|
Dont Memorise answered |
Work done by the gravitational force in moving a body through a certain distance remains the same whether the body moves uniformly or with decreasing acceleration.It is correct statement.
Gravitational forces are conservative forces.It is correct statement But reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion (A): Work is not done when a force is applied to an object, but there is no displacement of the object.Reason (R): According to the scientific definition of work, work is defined as force multiplied by displacement. If there is no displacement, no work is done.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Work is not done when a force is applied to an object, but there is no displacement of the object.
Reason (R): According to the scientific definition of work, work is defined as force multiplied by displacement. If there is no displacement, no work is done.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Hadi Al-Ahmed answered |
Understanding Work in Physics
In physics, the concept of work is crucial for understanding how forces interact with objects. Let's break down the assertion and reason provided.
Assertion (A):
- Work is not done when a force is applied to an object, but there is no displacement of the object.
Reason (R):
- According to the scientific definition of work, work is defined as force multiplied by displacement. If there is no displacement, no work is done.
Explanation of Assertion and Reason:
- The assertion is true because work requires not just a force but also movement. If an object does not move, regardless of the applied force, no work is accomplished.
- The reason is also true as it accurately reflects the definition of work in physics:
- Work = Force x Displacement
- If displacement is zero, then work is zero, regardless of the force applied.
Conclusion:
- Both the assertion and reason are true. Moreover, the reason directly explains why the assertion is correct. Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' because the reason clarifies the assertion effectively.
Key Takeaway:
- Work involves both force and displacement.
- No displacement means no work is done, even if a force is applied.
Understanding these fundamentals helps in grasping more complex concepts in physics as you progress in your studies.
In physics, the concept of work is crucial for understanding how forces interact with objects. Let's break down the assertion and reason provided.
Assertion (A):
- Work is not done when a force is applied to an object, but there is no displacement of the object.
Reason (R):
- According to the scientific definition of work, work is defined as force multiplied by displacement. If there is no displacement, no work is done.
Explanation of Assertion and Reason:
- The assertion is true because work requires not just a force but also movement. If an object does not move, regardless of the applied force, no work is accomplished.
- The reason is also true as it accurately reflects the definition of work in physics:
- Work = Force x Displacement
- If displacement is zero, then work is zero, regardless of the force applied.
Conclusion:
- Both the assertion and reason are true. Moreover, the reason directly explains why the assertion is correct. Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' because the reason clarifies the assertion effectively.
Key Takeaway:
- Work involves both force and displacement.
- No displacement means no work is done, even if a force is applied.
Understanding these fundamentals helps in grasping more complex concepts in physics as you progress in your studies.
When two identical bodies are in motion, the body with a higher velocity has __________.- a)Lower Kinetic Energy
- b)Higher Kinetic Energy
- c)No Kinetic Energy
- d)None of the options
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When two identical bodies are in motion, the body with a higher velocity has __________.
a)
Lower Kinetic Energy
b)
Higher Kinetic Energy
c)
No Kinetic Energy
d)
None of the options

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
- Kinetic energy is given by the formula KE = 1/2 mv2
- When two bodies are identical, they have the same mass.
- The kinetic energy depends on the square of the velocity.
- A higher velocity results in a higher K.E.
- Therefore, the body with a higher velocity has higher kinetic energy.
- Correct answer: B: Higher Kinetic Energy.
- When two bodies are identical, they have the same mass.
- The kinetic energy depends on the square of the velocity.
- A higher velocity results in a higher K.E.
- Therefore, the body with a higher velocity has higher kinetic energy.
- Correct answer: B: Higher Kinetic Energy.
A body is moved through a distance of 3 m in the following different ways. In which case is the maximum work done?- a)when pushed over an inclined plane
- b)when lifted vertically upward
- c)when pushed over smooth rollers
- d)when pushed on a plain horizontal surface
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body is moved through a distance of 3 m in the following different ways. In which case is the maximum work done?
a)
when pushed over an inclined plane
b)
when lifted vertically upward
c)
when pushed over smooth rollers
d)
when pushed on a plain horizontal surface
|
|
Ishita Khanna answered |
Work done= Mgg
Work will be maximum when the change in height is Maximum, thus when it is lifted vertically upward.
Assertion (A): An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line.Reason (R): The work done by the force of gravity on the object in this scenario is zero.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line.
Reason (R): The work done by the force of gravity on the object in this scenario is zero.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
- Assertion's Correctness: The assertion that an object follows a curved path and falls back to the ground with the initial and final points on the same horizontal line is correct for a projectile motion scenario.
- Reason's Correctness: The reason given that the work done by the force of gravity in this situation is zero is incorrect. Gravity does work on the object during its projectile motion, constantly changing its speed and direction.
- Explanation: In projectile motion, gravity constantly acts on the object, causing it to accelerate towards the ground. This acceleration due to gravity affects the object's path, making it follow a curved trajectory. The work done by gravity is not zero, as it continuously affects the object's motion.
- Conclusion: While the assertion is true regarding the path of the object, the reason provided is false since gravity does work on the object during its motion. Therefore, Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
In which of the following activities the work is said to be done?- a)Khushi is pushing a wall of a house but fails to do so
- b)Pinki is walking on a level road with a book on his head.
- c)Shruti is stretching a string.
- d)Harsh is reading a book
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following activities the work is said to be done?
a)
Khushi is pushing a wall of a house but fails to do so
b)
Pinki is walking on a level road with a book on his head.
c)
Shruti is stretching a string.
d)
Harsh is reading a book
|
|
Priya Dasgupta answered |
Understanding Work in Physics
In physics, the concept of work is defined based on the force applied and the movement of an object in the direction of that force. Work is only done when a force causes displacement of an object. Let's analyze each option to determine where work is done.
Option A: Khushi Pushing a Wall
- Khushi is applying force on the wall.
- However, since the wall does not move, there is no displacement.
- Thus, no work is done.
Option B: Pinki Walking on a Level Road
- Pinki is walking and carrying a book on her head.
- While she is exerting force to carry the book, the vertical force (upward) is perpendicular to the direction of her movement (horizontal).
- Therefore, no work is done on the book as it does not move in the direction of the force applied.
Option C: Shruti Stretching a String
- When Shruti stretches the string, she applies a force to it.
- As the string extends, there is a displacement in the direction of the force.
- This means that work is done in stretching the string.
- Hence, work is done in this scenario.
Option D: Harsh Reading a Book
- Harsh is not exerting any force that results in the movement of an object in the direction of that force.
- Therefore, no work is done while reading.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis, the correct answer is option 'C' – Shruti is stretching a string, as it involves both force and displacement, thus fulfilling the condition for work to be done.
In physics, the concept of work is defined based on the force applied and the movement of an object in the direction of that force. Work is only done when a force causes displacement of an object. Let's analyze each option to determine where work is done.
Option A: Khushi Pushing a Wall
- Khushi is applying force on the wall.
- However, since the wall does not move, there is no displacement.
- Thus, no work is done.
Option B: Pinki Walking on a Level Road
- Pinki is walking and carrying a book on her head.
- While she is exerting force to carry the book, the vertical force (upward) is perpendicular to the direction of her movement (horizontal).
- Therefore, no work is done on the book as it does not move in the direction of the force applied.
Option C: Shruti Stretching a String
- When Shruti stretches the string, she applies a force to it.
- As the string extends, there is a displacement in the direction of the force.
- This means that work is done in stretching the string.
- Hence, work is done in this scenario.
Option D: Harsh Reading a Book
- Harsh is not exerting any force that results in the movement of an object in the direction of that force.
- Therefore, no work is done while reading.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis, the correct answer is option 'C' – Shruti is stretching a string, as it involves both force and displacement, thus fulfilling the condition for work to be done.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : The work done during a round trip is always zero.Reason : No force is required to move a body in its round trip.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : The work done during a round trip is always zero.
Reason : No force is required to move a body in its round trip.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but reason is true.
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
The work done by a non-conservative force in a round trip is not zero. Since the body moves, there must be force acting on the body.
Chapter doubts & questions for Energy - Science for Grade 6 2025 is part of Grade 6 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 6 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 6 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Energy - Science for Grade 6 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 6 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Science for Grade 6
101 videos|166 docs|51 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup