All Exams >
Grade 9 >
Biology for Grade 9 >
All Questions
All questions of DNA for Grade 9 Exam
Synthesis of protein is controlled by:- a)Nucleotide
- b)RNA
- c)DNA
- d)Nucleoside
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Synthesis of protein is controlled by:
a)
Nucleotide
b)
RNA
c)
DNA
d)
Nucleoside
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
RNA can directly control the synthesis of proteins, hence can easily express the characters. DNA, however, is dependent on RNA for synthesis of proteins. The protein synthesising machinery has evolved around RNA.
Alpha helix is found in- a)RNA
- b)Lipid
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)secondary proteins
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Alpha helix is found in
a)
RNA
b)
Lipid
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
secondary proteins
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O. group of the amino acid located three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence.
Name the RNA molecules which is used to carry genetic information copied from DNA?- a)tRNA
- b)mRNA
- c)rRNA
- d)snRNA
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the RNA molecules which is used to carry genetic information copied from DNA?
a)
tRNA
b)
mRNA
c)
rRNA
d)
snRNA
|
|
Raushani Praween answered |
Because mRNA is called messanger RNA, which carries the information from DNA to synthesis of protein and other essential products in cell.
Process which leads to the synthesis of RNA is called- a)Termination
- b)Replication
- c)Transcription
- d)Translation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Process which leads to the synthesis of RNA is called
a)
Termination
b)
Replication
c)
Transcription
d)
Translation

|
Srishti Raghuwanshi answered |
DNA TO DNA - replication
DNA TO RNA-transcription
RNA TO PROTEIN-translation
DNA TO RNA-transcription
RNA TO PROTEIN-translation
Purine derivative among the following bases is:- a)Uracil
- b)Cytosine
- c)Guanine
- d)Thymine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Purine derivative among the following bases is:
a)
Uracil
b)
Cytosine
c)
Guanine
d)
Thymine
|
|
Shail Chawla answered |
Purine is a type of nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA molecules. The purine bases are adenine and guanine. Among the given options, the purine derivative is:
c) Guanine
Explanation:
- Purine and pyrimidine are two types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA molecules.
- Purine bases are larger and have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidine bases are smaller and have a single-ring structure.
- Adenine and guanine are purine bases, while cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidine bases.
- Therefore, among the given options, the purine derivative is guanine.
c) Guanine
Explanation:
- Purine and pyrimidine are two types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA molecules.
- Purine bases are larger and have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidine bases are smaller and have a single-ring structure.
- Adenine and guanine are purine bases, while cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidine bases.
- Therefore, among the given options, the purine derivative is guanine.
Nucleoside differs from nucleotide with the absence of:- a)Pentose sugar and Nitrogenous base
- b)Nitrogenous base
- c)Phosphoric acid
- d)Pentose sugar
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleoside differs from nucleotide with the absence of:
a)
Pentose sugar and Nitrogenous base
b)
Nitrogenous base
c)
Phosphoric acid
d)
Pentose sugar
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
The structure of nucleotide and nucleoside units are distinguished primarily by the presence (or lack thereof) of this phosphate group. Deoxyribose in DNA differs from the ribose found in RNA in that it has only a hydrogen atom in the same position that ribose has a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
Nucleotides are joined together by 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar. The linkage is known as:
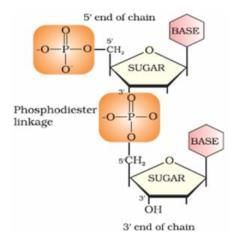
- a)Glycosidic
- b)Peptide
- c)Hydrogen
- d)Phoshodiester
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleotides are joined together by 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar. The linkage is known as:

a)
Glycosidic
b)
Peptide
c)
Hydrogen
d)
Phoshodiester
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar.
Which of the following base is not found in DNA?- a)Uracil
- b)Guanine
- c)Cytosine
- d)Adenine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following base is not found in DNA?
a)
Uracil
b)
Guanine
c)
Cytosine
d)
Adenine
|
|
Ritu Pal answered |
Uracil is not found in DNA , as it Uracil has more base pair affinity to adenine , guanine and cytosine. Instead thymine is present in DNA.
RNA is different from DNA because RNA contains:
- a)Ribose sugar and thymine
- b)Deoxyribose sugar and thymine
- c)Ribose sugar and uracil
- d)Deoxyribose sugar and uracil
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RNA is different from DNA because RNA contains:
a)
Ribose sugar and thymine
b)
Deoxyribose sugar and thymine
c)
Ribose sugar and uracil
d)
Deoxyribose sugar and uracil
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
RNA is ribonucliec acid, it contains ribose sugar and uracil. In DNA molecules, the sugar is 2-deoxyribose. In DNA, four bases have been found. They are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). The first three of these bases are found in RNA also but the fourth is uracil (U).
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is _______- a)ligase
- b)lipase
- c)DNase
- d)RNase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is _______
a)
ligase
b)
lipase
c)
DNase
d)
RNase
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is DNase. It catalyzes the breakdown of phosphodiester linkages of DNA. It is a type of endonuclease. Ligases are the enzymes used in the joining of two strands.
What is the purpose of treating bacterial cells or plant/animal tissue with enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, or chitinase in the process of recombinant DNA technology?- a)To release DNA from cells
- b)To remove proteins
- c)To isolate RNA
- d)To precipitate DNA with ethanol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the purpose of treating bacterial cells or plant/animal tissue with enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, or chitinase in the process of recombinant DNA technology?
a)
To release DNA from cells
b)
To remove proteins
c)
To isolate RNA
d)
To precipitate DNA with ethanol

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, and chitinase are used to break down cell walls and release DNA from cells.
The plant cells can be lysed by using ______ enzyme.- a)lipase
- b)chitinase
- c)ligase
- d)cellulase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant cells can be lysed by using ______ enzyme.
a)
lipase
b)
chitinase
c)
ligase
d)
cellulase
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Cellulase is the enzyme used for the lysis of plant cells. It catalyzes cellulolysis, which is the breakdown of cellulose. Cellulase acts on the glycosidic linkages of cellulose. Cellulose is mostly found in plant cell walls along with other components.
Which technique is employed to check the progression of a restriction enzyme digestion in recombinant DNA technology?- a)PCR
- b)DNA ligation
- c)Agarose gel electrophoresis
- d)Reverse transcription
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which technique is employed to check the progression of a restriction enzyme digestion in recombinant DNA technology?
a)
PCR
b)
DNA ligation
c)
Agarose gel electrophoresis
d)
Reverse transcription

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Agarose gel electrophoresis is used to check the progress of a restriction enzyme digestion by separating DNA fragments based on size.
In DNA the complementary bases are:- a)adenine and guanine; thymine and cytosine
- b)adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
- c)uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
- d)adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In DNA the complementary bases are:
a)
adenine and guanine; thymine and cytosine
b)
adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
c)
uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
d)
adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil

|
Aditya Sen answered |
Each nucleotide base can hydrogen-bond with a specific partner base in a process known as complementary base pairing: Cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine.
The enzyme which cleaves RNA is _______- a)DNase
- b)ribonuclease
- c)ligase
- d)protease
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which cleaves RNA is _______
a)
DNase
b)
ribonuclease
c)
ligase
d)
protease
|
|
Shilpa Iyer answered |
Introduction:
RNA cleavage is a crucial process in various cellular activities such as gene expression, RNA degradation, and RNA processing. The enzyme responsible for cleaving RNA is called ribonuclease (RNase).
Explanation:
Ribonuclease (RNase):
- Ribonuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of RNA molecules.
- It plays a vital role in various biological processes, including RNA degradation and turnover, RNA processing, and regulation of gene expression.
- There are different types of ribonucleases that have evolved to perform specific functions in different cellular contexts.
DNase:
- DNase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA molecules, not RNA.
- It is responsible for degrading DNA and plays a role in DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and other DNA-related processes.
Ligase:
- Ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules by forming a covalent bond between them.
- It is involved in DNA repair, DNA replication, and other processes that require the joining of DNA or RNA fragments.
Protease:
- Protease is an enzyme that cleaves peptide bonds in proteins, not RNA.
- It is responsible for protein degradation, protein processing, and regulation of protein function.
Conclusion:
The enzyme that cleaves RNA is ribonuclease (RNase). It is specifically designed to recognize and cleave RNA molecules, playing essential roles in RNA degradation, processing, and gene expression regulation. DNase cleaves DNA, ligase joins molecules, and protease cleaves peptide bonds in proteins.
RNA cleavage is a crucial process in various cellular activities such as gene expression, RNA degradation, and RNA processing. The enzyme responsible for cleaving RNA is called ribonuclease (RNase).
Explanation:
Ribonuclease (RNase):
- Ribonuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of RNA molecules.
- It plays a vital role in various biological processes, including RNA degradation and turnover, RNA processing, and regulation of gene expression.
- There are different types of ribonucleases that have evolved to perform specific functions in different cellular contexts.
DNase:
- DNase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA molecules, not RNA.
- It is responsible for degrading DNA and plays a role in DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and other DNA-related processes.
Ligase:
- Ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules by forming a covalent bond between them.
- It is involved in DNA repair, DNA replication, and other processes that require the joining of DNA or RNA fragments.
Protease:
- Protease is an enzyme that cleaves peptide bonds in proteins, not RNA.
- It is responsible for protein degradation, protein processing, and regulation of protein function.
Conclusion:
The enzyme that cleaves RNA is ribonuclease (RNase). It is specifically designed to recognize and cleave RNA molecules, playing essential roles in RNA degradation, processing, and gene expression regulation. DNase cleaves DNA, ligase joins molecules, and protease cleaves peptide bonds in proteins.
A cloning vector has two antibiotic resistance genes- for tetracycline and ampicillin. A foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline gene. Non-recombinants would survive on the medium containing :- a)ampicillin but not tetracycline
- b)tetracycline but not ampicillin
- c)both tetracycline and ampicillin
- d)neither tetracycline nor ampicillin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cloning vector has two antibiotic resistance genes- for tetracycline and ampicillin. A foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline gene. Non-recombinants would survive on the medium containing :
a)
ampicillin but not tetracycline
b)
tetracycline but not ampicillin
c)
both tetracycline and ampicillin
d)
neither tetracycline nor ampicillin

|
Lead Academy answered |
Normally, the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline or kanamycin, etc., are considered useful selectable markers for E. coli.
The restriction enzyme needs to be in _____ form to cut the DNA.- a)impure
- b)pure
- c)mixed
- d)hybrid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The restriction enzyme needs to be in _____ form to cut the DNA.
a)
impure
b)
pure
c)
mixed
d)
hybrid
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The restriction enzyme needs to be in pure form to cut the DNA. The restriction enzymes are molecular scissors that cleave the DNA at specific recognition sites. Restriction enzymes are also known as restriction endonucleases or restrictase.
What term is used to collectively refer to the separation and purification processes of a product in recombinant DNA technology?- a)Upstream processing
- b)Downstream processing
- c)Gene amplification
- d)PCR
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What term is used to collectively refer to the separation and purification processes of a product in recombinant DNA technology?
a)
Upstream processing
b)
Downstream processing
c)
Gene amplification
d)
PCR

|
Top Rankers answered |
Downstream processing involves the separation and purification of the product before it is ready for marketing.
In recombinant DNA technology, what is the purpose of a bioreactor in the large-scale production of desired proteins?- a)To amplify genes of interest
- b)To isolate recombinant DNA
- c)To maintain cells in the log/exponential phase
- d)To perform agarose gel electrophoresis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In recombinant DNA technology, what is the purpose of a bioreactor in the large-scale production of desired proteins?
a)
To amplify genes of interest
b)
To isolate recombinant DNA
c)
To maintain cells in the log/exponential phase
d)
To perform agarose gel electrophoresis

|
Top Rankers answered |
A bioreactor is used to provide optimal conditions for cell growth, ensuring cells are in their physiologically most active phase.
What is the purpose of using a selectable marker gene like ampicillin resistance in recombinant DNA technology?- a)To enhance DNA ligation
- b)To amplify the gene of interest
- c)To select transformed cells
- d)To extract the desired product
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the purpose of using a selectable marker gene like ampicillin resistance in recombinant DNA technology?
a)
To enhance DNA ligation
b)
To amplify the gene of interest
c)
To select transformed cells
d)
To extract the desired product
|
|
Aditi Nair answered |
Introduction:
In recombinant DNA technology, selectable marker genes are used to distinguish transformed cells from non-transformed cells. These marker genes provide a selective advantage to the cells that have taken up the recombinant DNA, allowing for their identification and isolation.
Explanation:
Selectable marker genes, such as ampicillin resistance, are commonly used in recombinant DNA technology for the following reasons:
1. Selective advantage:
Selectable marker genes provide a selective advantage to the transformed cells that have successfully incorporated the recombinant DNA. In the case of ampicillin resistance, the gene encodes for an enzyme called β-lactamase, which confers resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. Therefore, only the cells that have taken up the recombinant DNA containing the selectable marker gene will be able to grow and survive in the presence of ampicillin.
2. Selection of transformed cells:
By including the selectable marker gene in the recombinant DNA construct, researchers can selectively grow and isolate only those cells that have successfully taken up the desired gene or DNA fragment of interest. This allows for the identification and selection of transformed cells from a population of non-transformed cells.
3. Identification of successful transformation:
The presence of the selectable marker gene, such as ampicillin resistance, allows researchers to easily identify successful transformations. Transformed cells will be able to grow on selective media containing ampicillin, while non-transformed cells will not survive. This simplifies the screening process and confirms the presence of the desired gene or DNA fragment in the transformed cells.
Conclusion:
The purpose of using a selectable marker gene like ampicillin resistance in recombinant DNA technology is to provide a selective advantage to the transformed cells, allowing for their identification and isolation. This marker gene helps in distinguishing transformed cells from non-transformed cells and facilitates the selection of cells that have successfully taken up the desired gene or DNA fragment of interest.
In recombinant DNA technology, selectable marker genes are used to distinguish transformed cells from non-transformed cells. These marker genes provide a selective advantage to the cells that have taken up the recombinant DNA, allowing for their identification and isolation.
Explanation:
Selectable marker genes, such as ampicillin resistance, are commonly used in recombinant DNA technology for the following reasons:
1. Selective advantage:
Selectable marker genes provide a selective advantage to the transformed cells that have successfully incorporated the recombinant DNA. In the case of ampicillin resistance, the gene encodes for an enzyme called β-lactamase, which confers resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. Therefore, only the cells that have taken up the recombinant DNA containing the selectable marker gene will be able to grow and survive in the presence of ampicillin.
2. Selection of transformed cells:
By including the selectable marker gene in the recombinant DNA construct, researchers can selectively grow and isolate only those cells that have successfully taken up the desired gene or DNA fragment of interest. This allows for the identification and selection of transformed cells from a population of non-transformed cells.
3. Identification of successful transformation:
The presence of the selectable marker gene, such as ampicillin resistance, allows researchers to easily identify successful transformations. Transformed cells will be able to grow on selective media containing ampicillin, while non-transformed cells will not survive. This simplifies the screening process and confirms the presence of the desired gene or DNA fragment in the transformed cells.
Conclusion:
The purpose of using a selectable marker gene like ampicillin resistance in recombinant DNA technology is to provide a selective advantage to the transformed cells, allowing for their identification and isolation. This marker gene helps in distinguishing transformed cells from non-transformed cells and facilitates the selection of cells that have successfully taken up the desired gene or DNA fragment of interest.
Chapter doubts & questions for DNA - Biology for Grade 9 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of DNA - Biology for Grade 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 9
50 videos|96 docs|27 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









