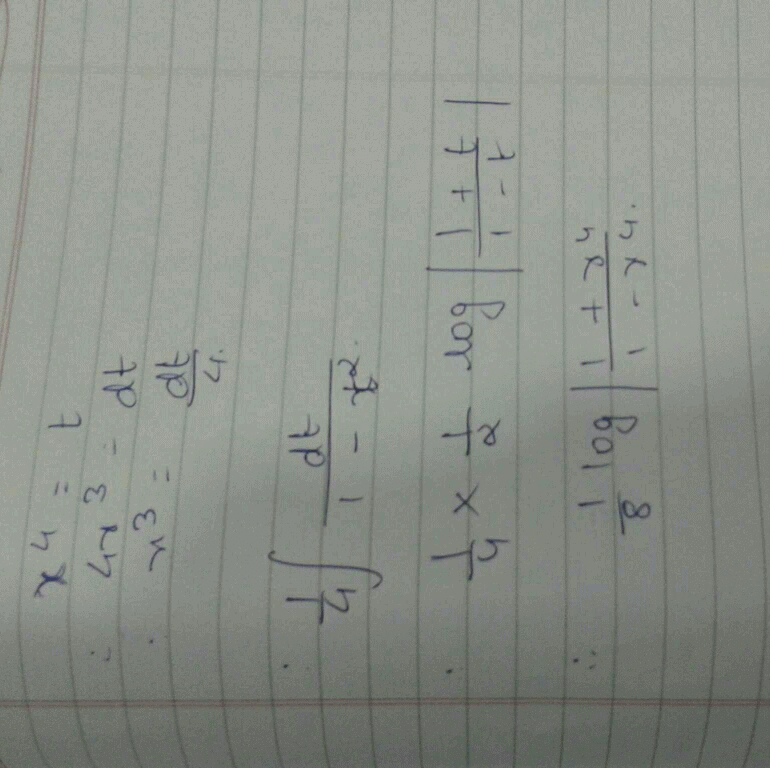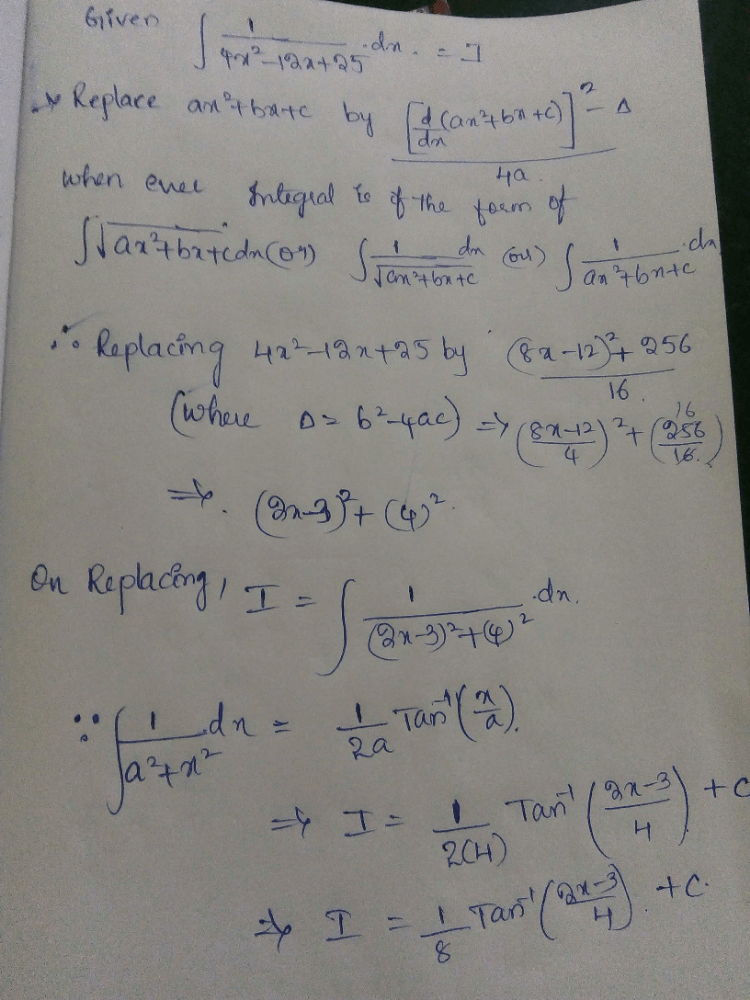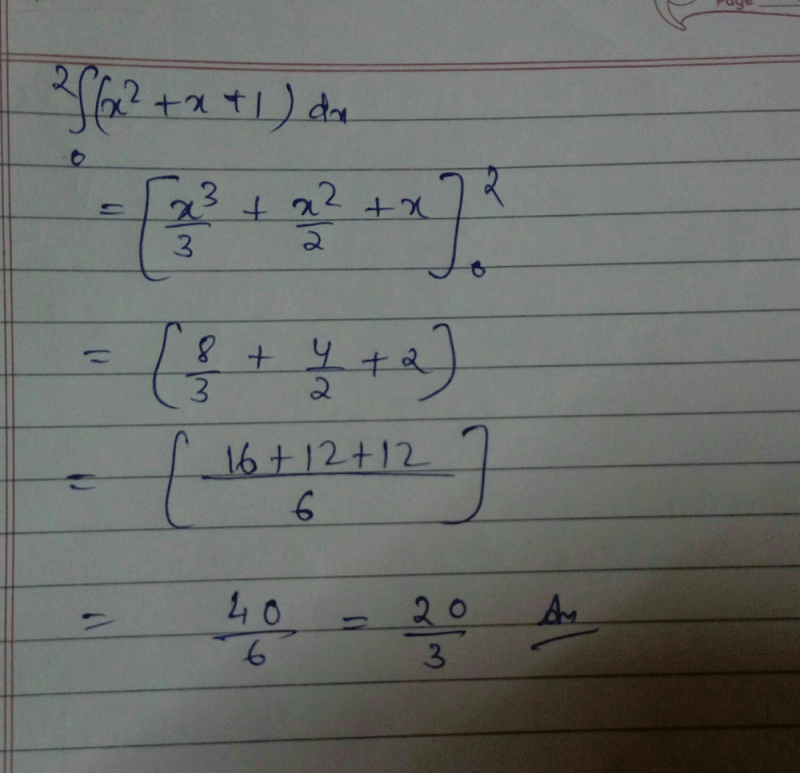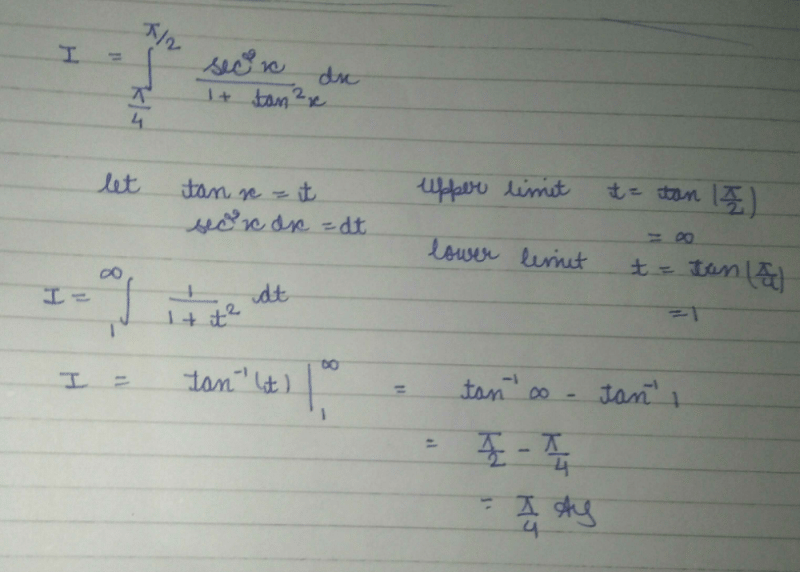All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Integration for EmSAT Achieve Exam
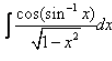
- a)cos(sin-1x) + c
- b)sin-1x + c
- c)sin(cos-1x) + c
- d)x + c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
cos(sin-1x) + c
b)
sin-1x + c
c)
sin(cos-1x) + c
d)
x + c

|
Divey Sethi answered |
cos(sin-1x)/(1-x2)½……………….(1)
t = sin-1 x
dt = dx/(1-x2)½
Put the value of dt in eq(1)
= ∫cost dt
= sint + c
= sin(sin-1 x) + c
⇒ x + c
t = sin-1 x
dt = dx/(1-x2)½
Put the value of dt in eq(1)
= ∫cost dt
= sint + c
= sin(sin-1 x) + c
⇒ x + c
Integral of sin5x.cos2x is: - a)
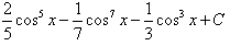
- b)
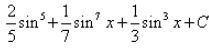
- c)
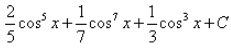
- d)
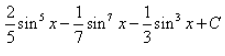
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Integral of sin5x.cos2x is:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Learners Habitat answered |
So Looking at this integral, we have
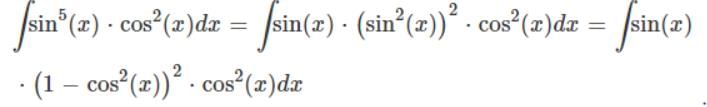

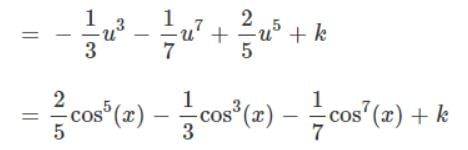
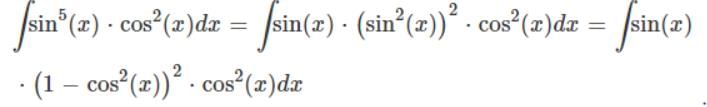

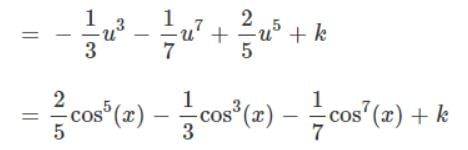
Evaluate: 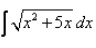
- a)
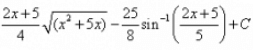
- b)
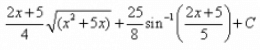
- c)
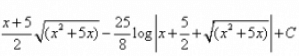
- d)
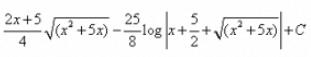
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 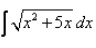
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Leelu Bhai answered |
I = ∫√(x² + 5x)dx= ∫√(x² + 5x + 25/4 - 25/4)= ∫√{(x + 5/2)² - (5/2)²}={1/2(x+5/2)(√x² + 5x)} - {25/8 log{(x + 5/2)+√x²+ 5x}}= {(2x + 5)/4 (√x² + 5x)} - {25/8 log{(x + 5/2)+√x²+ 5x}}Thus, option D is correct...
Evaluate: 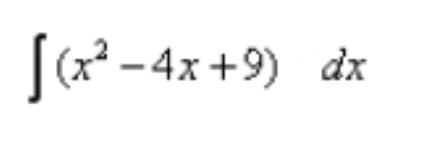
- a)
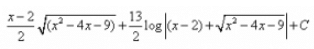
- b)1/√3 arc tan[(x-2)/√5] + C
- c)
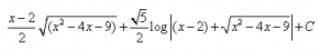
- d)
%7D%7D%7D%2B%7BC%7D)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 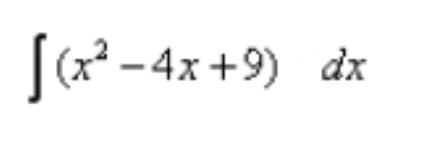
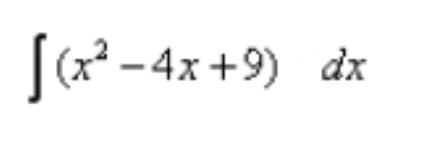
a)
b)
1/√3 arc tan[(x-2)/√5] + C
c)
d)
|
|
Deepak Kapoor answered |
Let's apply the integral substitution,
substitute 
Now use the standard integral :}}})
substitute back u=(x-2) and add a constant C to the solution,
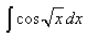
- a)
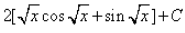 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant - b)
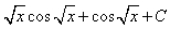 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant - c)
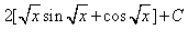 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant - d)
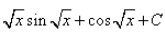 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
q = √x, dq = dx/2√x
⇒ dx = 2q dq
so the integral is 2∫qcosqdq
integration by parts using form
∫uv' = uv − ∫u'v
here u = q, u'= 1 and v'= cosq, v=sinq
so we have 2(qsinq −∫sinqdq)
= 2(qsinq + cosq + C)
= 2(√xsin√x + cos√x + C)
⇒ dx = 2q dq
so the integral is 2∫qcosqdq
integration by parts using form
∫uv' = uv − ∫u'v
here u = q, u'= 1 and v'= cosq, v=sinq
so we have 2(qsinq −∫sinqdq)
= 2(qsinq + cosq + C)
= 2(√xsin√x + cos√x + C)
Evaluate: 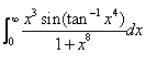
- a)1/2
- b)1/4
- c)1
- d)1/8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 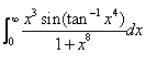
a)
1/2
b)
1/4
c)
1
d)
1/8

|
Sumair Sadiq answered |
This is maths questions I can explain it but you know it is not possible here because this app is not allow to take photo but try it ok let tan inverce 4x =t diff both side wrt x 4x³/1+x⁴ Ka square
x cube / 1+ x8 =dt/4 I = £ 0 se pie by 2 (because when x= 0 t = pie by 2and x = infinity then t = 0 )
I = 1/4 £ 0 se pie by 2 sin t l = 1/4 (- cos t limit 0 se pie by 2 )l = 1/4 ( - cos pie by 2 + cos 0) l = 1/4 ( 0+ 1) l= 1/4 × 1l= 1/4
use my WhatsApp number for further questions but only for study 7060398771
x cube / 1+ x8 =dt/4 I = £ 0 se pie by 2 (because when x= 0 t = pie by 2and x = infinity then t = 0 )
I = 1/4 £ 0 se pie by 2 sin t l = 1/4 (- cos t limit 0 se pie by 2 )l = 1/4 ( - cos pie by 2 + cos 0) l = 1/4 ( 0+ 1) l= 1/4 × 1l= 1/4
use my WhatsApp number for further questions but only for study 7060398771
Evaluate: 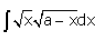
- a)
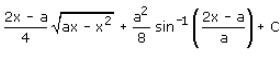
- b)
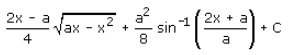
- c)
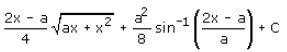
- d)
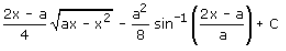
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 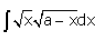
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
(x)½ (a - x)½ dx
= ∫(ax - x2)½ dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax)½} dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax + a2/4 - a2/4)½} dx
= ∫{-(x - a/2)2 - a2/4} dx
= ∫{(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} dx
= ½(x - a/2) {(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} + (a2/4) (½ sin-1(x - a)/a2)
= {(2x - a)/4 (ax - x2)½} + {a2/8 sin-1(2x - a)/a} + c
= ∫(ax - x2)½ dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax)½} dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax + a2/4 - a2/4)½} dx
= ∫{-(x - a/2)2 - a2/4} dx
= ∫{(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} dx
= ½(x - a/2) {(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} + (a2/4) (½ sin-1(x - a)/a2)
= {(2x - a)/4 (ax - x2)½} + {a2/8 sin-1(2x - a)/a} + c
The integration of the function ex.cos3x is:- a)
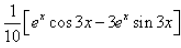
- b)
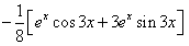
- c)
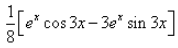
- d)
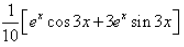
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The integration of the function ex.cos3x is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Let I = ∫ex . cos 3x dx
⇒ I = cos 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫[d/dx(cos 3x) × ∫ex dx]dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x − ∫(− 3 sin 3x . ex)dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3∫sin 3x . ex dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫{ddx(sin 3x) × ∫ex dx}dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x . ex − ∫3 cos 3x . ex dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9∫ex . cos 3x dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9I
⇒ 10I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x
⇒ I = 1/10[ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x] + C
⇒ I = cos 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫[d/dx(cos 3x) × ∫ex dx]dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x − ∫(− 3 sin 3x . ex)dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3∫sin 3x . ex dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫{ddx(sin 3x) × ∫ex dx}dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x . ex − ∫3 cos 3x . ex dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9∫ex . cos 3x dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9I
⇒ 10I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x
⇒ I = 1/10[ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x] + C
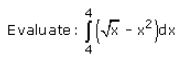
- a)-1
- b)zero
- c)1
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
-1
b)
zero
c)
1
d)
2

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
∫(0 to 4)(x)1/2 - x2 dx
= [[(x)3/2]/(3/2) - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2x3/2]/3 - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2(0)3/2]/3 - (0)2]] - [[2(4)3/2]/3 - (4)2]]
= 0-0
= 0
= [[(x)3/2]/(3/2) - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2x3/2]/3 - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2(0)3/2]/3 - (0)2]] - [[2(4)3/2]/3 - (4)2]]
= 0-0
= 0
The value of the integral 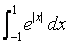 is:
is:- a)2e – 1
- b)2e + 1
- c)2e
- d)2(e – 1)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of the integral 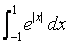 is:
is:
a)
2e – 1
b)
2e + 1
c)
2e
d)
2(e – 1)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Correct Answer : d
Explanation : ∫(-1 to 1) e|x| dx
∫(-1 to 0) e|x|dx + ∫(0 to 1) e|x|dx
e1 -1 + e1 - 1
=> 2(e - 1)
The value of 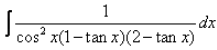
- a)
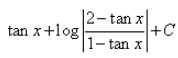
- b)
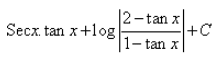
- c)
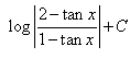
- d)
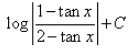
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of 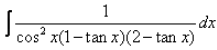
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Shubham Rajput answered |
I have got correct answer as d please confirm me anyone
Evaluate: 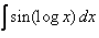
- a)
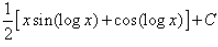
- b)
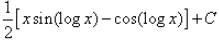
- c)
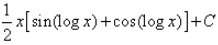
- d)
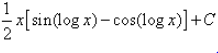
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 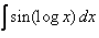
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
I=∫sin(logx)×1dx
= sin(logx) × x−∫cos(logx) × (1/x)×xdx
= xsin(logx)−∫cos(logx) × 1dx
= xsin(logx)−[cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx) × (1/x) × xdx]
∴ I=xsin(logx)−cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx)dx
2I=x[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
∴ I=(x/2)[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
= sin(logx) × x−∫cos(logx) × (1/x)×xdx
= xsin(logx)−∫cos(logx) × 1dx
= xsin(logx)−[cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx) × (1/x) × xdx]
∴ I=xsin(logx)−cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx)dx
2I=x[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
∴ I=(x/2)[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
If 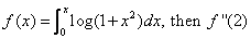 is
is- a)2/3
- b)4/5
- c)1
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If 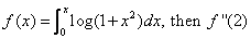 is
is
a)
2/3
b)
4/5
c)
1
d)
None of these

|
Arjun Singh answered |
F'(x)=log(1+x^-2) then differentiate it one time to get f''(x)
Integrate 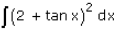
- a)3x – 4 log |sec x| + tan x + C
- b)3x + 4 log |sec x| + tan x
- c)3x + 4 log |sec X| + tan x + C
- d)3x + 4 log |sec x| – tan x + C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Integrate 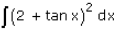
a)
3x – 4 log |sec x| + tan x + C
b)
3x + 4 log |sec x| + tan x
c)
3x + 4 log |sec X| + tan x + C
d)
3x + 4 log |sec x| – tan x + C
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
∫(2+tan x)2dx
= ∫(4 + tan2 x + 4tan x)dx
= ∫4 dx + ∫tan2 x dx + 4∫tan x dx
= 4x + ∫(sec2 x - 1)dx + 4(log|sec x|)
= 4x + tanx - x + 4(log|sec x|)
3x + tanx + 4(log|sec x|) + c
= ∫(4 + tan2 x + 4tan x)dx
= ∫4 dx + ∫tan2 x dx + 4∫tan x dx
= 4x + ∫(sec2 x - 1)dx + 4(log|sec x|)
= 4x + tanx - x + 4(log|sec x|)
3x + tanx + 4(log|sec x|) + c
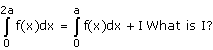
- a)
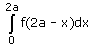
- b)
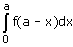
- c)
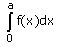
- d)
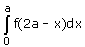
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Option d is correct, because it is the property of definite integral
∫02a f(x) dx = ∫0a f(x) dx + ∫0a f(2a – x) dx
∫02a f(x) dx = ∫0a f(x) dx + ∫0a f(2a – x) dx
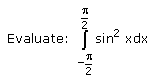
- a)π
- b)π/2
- c)2π
- d)π/4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
π
b)
π/2
c)
2π
d)
π/4

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
For sin2(X), we will use the cos double angle formula:
cos(2X) = 1 - 2sin2(X)
The above formula can be rearranged to make sin2(X) the subject:
sin2(X) = 1/2(1 - cos(2X))
You can now rewrite the integration:
∫sin2(X)dX = ∫1/2(1 - cos(2X))dX
Because 1/2 is a constant, we can remove it from the integration to make the calculation simpler. We are now integrating:
1/2 x ∫(1 - cos(2X)) dX
= 1/2 x (X - 1/2sin(2X)) + C]-pi/4 to pi/4
∫sin2(X) dX = [1/2X - 1/4sin(2X)]-pi/4 to pi/4 + C
½[-pi/2] - 1/4sin(2(-pi/4)] - ½[pi/2] - 1/4sin(2(pi/4)]
= π/2
cos(2X) = 1 - 2sin2(X)
The above formula can be rearranged to make sin2(X) the subject:
sin2(X) = 1/2(1 - cos(2X))
You can now rewrite the integration:
∫sin2(X)dX = ∫1/2(1 - cos(2X))dX
Because 1/2 is a constant, we can remove it from the integration to make the calculation simpler. We are now integrating:
1/2 x ∫(1 - cos(2X)) dX
= 1/2 x (X - 1/2sin(2X)) + C]-pi/4 to pi/4
∫sin2(X) dX = [1/2X - 1/4sin(2X)]-pi/4 to pi/4 + C
½[-pi/2] - 1/4sin(2(-pi/4)] - ½[pi/2] - 1/4sin(2(pi/4)]
= π/2
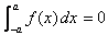
- a)if f(2a – x) = – f(x)
- b)if f(2a – x) = f(x)
- c)if f(- x) = f(x)
- d)if f(- x) = – f(x)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
if f(2a – x) = – f(x)
b)
if f(2a – x) = f(x)
c)
if f(- x) = f(x)
d)
if f(- x) = – f(x)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∫(-a to a)f(x)dx
= ∫(0 to a) [f(x) + f(-x)] if f(x) is an odd function
⇒ f(-x) = -f(x)
= ∫(0 to a) [f(x) + f(-x)] if f(x) is an odd function
⇒ f(-x) = -f(x)
Evaluate: 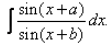
- a)(x + b) cos(a – b) – sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
- b)(x + b) cos(b – a) – sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
- c)(x + b) cos(b – a) + sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
- d)(x + b) cos(a – b) + sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 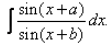
a)
(x + b) cos(a – b) – sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
b)
(x + b) cos(b – a) – sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
c)
(x + b) cos(b – a) + sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
d)
(x + b) cos(a – b) + sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Create ((X+B) + (A-B)) in numerator and then apply Sin(a+b) formula then you will be able to solve it.
Evaluate: 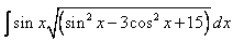
- a)
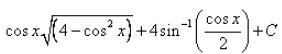
- b)
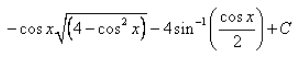
- c)
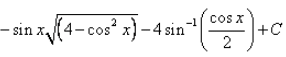
- d)
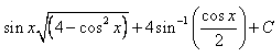
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 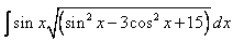
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
sin2x = 1 - cos2x
∫sinx(sin2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
Put cos2x = t
∫sinx(1 - cos2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
= ∫sinx (16 - 4cos2x)dx
Put t = cosx, differentiate with respect to x, we get
dt/dx = -sinx
= - ∫ [(16 - 4t2)]1/2dt
= -2 ∫ [(2)2 - (t)2]½
= -2{[(2)2 - (t)2]½ + 2sin-1(t/2)} + c
= - cosx {[4 - (cos)2x]½ - 4sin-1(cosx/2)} + c
∫sinx(sin2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
Put cos2x = t
∫sinx(1 - cos2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
= ∫sinx (16 - 4cos2x)dx
Put t = cosx, differentiate with respect to x, we get
dt/dx = -sinx
= - ∫ [(16 - 4t2)]1/2dt
= -2 ∫ [(2)2 - (t)2]½
= -2{[(2)2 - (t)2]½ + 2sin-1(t/2)} + c
= - cosx {[4 - (cos)2x]½ - 4sin-1(cosx/2)} + c
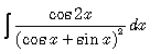
- a)log(sin x + cos x) +C
- b)sin 2x + cos 2x + C
- c)log(sin x - cos x) +C
- d)sin 2x - cos 2x + C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
log(sin x + cos x) +C
b)
sin 2x + cos 2x + C
c)
log(sin x - cos x) +C
d)
sin 2x - cos 2x + C
|
|
Om Desai answered |
I = ∫cos2x/(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫cos2x−sin2x(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫[(cosx+sinx)(cosx−sinx)]/(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫(cosx−sinx)/(sinx+cosx)dx
Let sinx+cosx = t
(cosx−sinx)dx = dt
Then, I = ∫dt/t
I = log|t|+c
I = log|sinx + cosx| + c
⇒I = ∫cos2x−sin2x(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫[(cosx+sinx)(cosx−sinx)]/(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫(cosx−sinx)/(sinx+cosx)dx
Let sinx+cosx = t
(cosx−sinx)dx = dt
Then, I = ∫dt/t
I = log|t|+c
I = log|sinx + cosx| + c
The value of 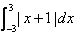 is:
is:- a)10
- b)17/2
- c)7/2
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of 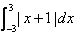 is:
is:
a)
10
b)
17/2
c)
7/2
d)
5

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
∫(-3 to 3) (x+1)dx
= ∫(-3 to -1) (x+1)dx + ∫(-1 to 3) (x+1) dx
= [x2 + x](-3 to -1) + [x2 + x](-1 to 3)
= [½ - 1 - (9/2 - 3)] + [9/2 + 3 - (½ - 1)]
= -[-4 + 2] + [4 + 4]
= -[-2] + [8]
= 10
If 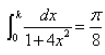 then the value of k is:
then the value of k is:- a)7/8
- b)5/8
- c)1/2
- d)3/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If 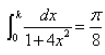 then the value of k is:
then the value of k is:
a)
7/8
b)
5/8
c)
1/2
d)
3/2

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Let I=∫(0 to k) 1/[1 + 4x2]dx = π8
Now, ∫(0 to k) 1/[4(1/4 + x2)]dx
= 2/4[tan−1 2x]0 to k
= 1/2tan-1 2k − 0 = π/8
1/2tan−1 2k = π8
⇒ tan−1 2k = π/4
⇒ 2k = 1
∴ k = 1/2
Now, ∫(0 to k) 1/[4(1/4 + x2)]dx
= 2/4[tan−1 2x]0 to k
= 1/2tan-1 2k − 0 = π/8
1/2tan−1 2k = π8
⇒ tan−1 2k = π/4
⇒ 2k = 1
∴ k = 1/2
Evaluate: 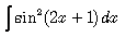
- a)
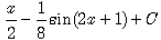
- b)
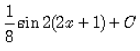
- c)
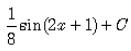
- d)
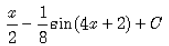
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 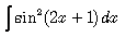
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∫sin2(2x+1) dx
Put t = 2x+1
dt = 2dx
dx= dt/2
= 1/2∫sin2 t dt
=1/2∫(1-cos2t)/2 dt
= 1/4∫(1-cos2t) dt
= ¼[(t - (sin2t)/2]dt
= t/4 - sin2t/8 + c
= (2x+1)/4 - ⅛(sin(4x+2)) + c
= x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + ¼ + c
As ¼ is also a constant, so eq is = x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + c
Put t = 2x+1
dt = 2dx
dx= dt/2
= 1/2∫sin2 t dt
=1/2∫(1-cos2t)/2 dt
= 1/4∫(1-cos2t) dt
= ¼[(t - (sin2t)/2]dt
= t/4 - sin2t/8 + c
= (2x+1)/4 - ⅛(sin(4x+2)) + c
= x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + ¼ + c
As ¼ is also a constant, so eq is = x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + c
The integral of tan4x is:- a)
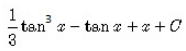
- b)
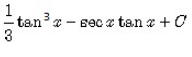
- c)
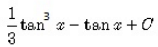
- d)
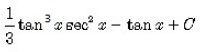
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The integral of tan4x is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Begin by rewriting ∫tan4xdx as ∫tan2xtan2xdx.
Now we can apply the Pythagorean Identity, tan2x+1=sec2x, or tan2x=sec2x−1
∫tan2x tan2x dx = ∫(sec2x−1)tan2xdx
Distributing the tan2x:
= ∫sec2xtan2x − tan2xdx
Applying the sum rule:
= ∫sec2xtan2xdx − ∫tan2xdx
We'll evaluate these integrals one by one.
First Integral
This one is solved using a
Let u = tanx
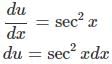
Applying the substitution,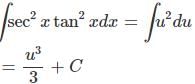
Because u = tanx,
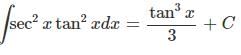
This one is solved using a

Let u = tanx
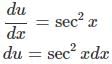
Applying the substitution,
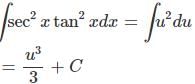
Because u = tanx,
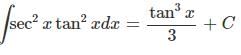
Second Integral
Since we don't really know what ∫tan2xdx is by just looking at it, try applying the tan2x = sec2x−1
Since we don't really know what ∫tan2xdx is by just looking at it, try applying the tan2x = sec2x−1
identity again:
∫tan2xdx = ∫(sec2x−1)dx
Using the sum rule, the integral boils down to:
∫sec2xdx − ∫1dx
∫sec2xdx − ∫1dx
The first of these, ∫sec2xdx, is just tanx + C.
The second one, the so-called "perfect integral", is simply x+C.
Putting it all together, we can say:
∫tan2xdx = tanx + C − x + C
∫tan2xdx = tanx + C − x + C
And because C+C is just another arbitrary constant, we can combine it into a general constant C:
∫tan2xdx = tanx − x + C
∫tan2xdx = tanx − x + C
Combining the two results, we have:
∫tan4xdx=∫sec2xtan2xdx−∫tan2xdx
∫tan4xdx=∫sec2xtan2xdx−∫tan2xdx
=(tan3x/3 + C) − (tanx − x + C)
=tan3x/3 − tanx + x + C
Again, because C+C is a constant, we can join them into one C.
The value of 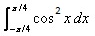 is:
is:- a)
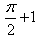
- b)
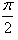
- c)
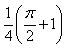
- d)
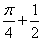
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of 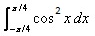 is:
is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Samyak Jain answered |
1/2(cos π/2 + 1 -[cos(π/2-π/4)+1])=1/2+π/4
The integral of 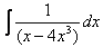 is:
is:- a)
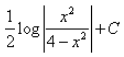
- b)
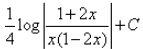
- c)
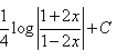
- d)
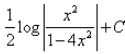
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The integral of 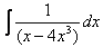 is:
is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
∫dx/x3(x-2 -4).............(1)
= ∫x-3 dx/(x-2 - 4)
Let t = (x-2 - 4)
dt = -2x-3 dx
x-3 = -dt/2
Put the value of x-3 in eq(1)
= -½ ∫dt/t
= -½ log t + c
= -½ log(x-2 - 4) + c
= -½ log(1-4x2)/x2 + c
= ½ log(x2/(1 - 4x2)) + c
= ∫x-3 dx/(x-2 - 4)
Let t = (x-2 - 4)
dt = -2x-3 dx
x-3 = -dt/2
Put the value of x-3 in eq(1)
= -½ ∫dt/t
= -½ log t + c
= -½ log(x-2 - 4) + c
= -½ log(1-4x2)/x2 + c
= ½ log(x2/(1 - 4x2)) + c
Evaluate: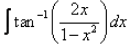
- a)
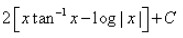
- b)
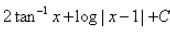
- c)
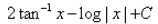
- d)
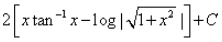
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: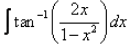
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Let x=tanθ , so that θ=tan−1x , dx=sec2θdθ
Then the given integral is equivalent to
∫tan−1(2x/(1−x2)dx
=∫tan−1 (2tanθ/(1−tan2θ))⋅sec2θdθ
=∫tan−1tan2θ⋅sec2θdθ
=2×∫θsec2θdθ
(integrate by parts)
=2θ⋅∫sec2θdθ −2⋅∫1⋅(∫sec2θdθ)dθ
=2θtanθ−2⋅∫tanθdθ
=2θtanθ−2loge secθ+c
=2xtan−1x−2loge√1+x2+c
=2xtan−1x−loge(1+x2)+c
Then the given integral is equivalent to
∫tan−1(2x/(1−x2)dx
=∫tan−1 (2tanθ/(1−tan2θ))⋅sec2θdθ
=∫tan−1tan2θ⋅sec2θdθ
=2×∫θsec2θdθ
(integrate by parts)
=2θ⋅∫sec2θdθ −2⋅∫1⋅(∫sec2θdθ)dθ
=2θtanθ−2⋅∫tanθdθ
=2θtanθ−2loge secθ+c
=2xtan−1x−2loge√1+x2+c
=2xtan−1x−loge(1+x2)+c
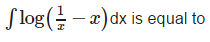
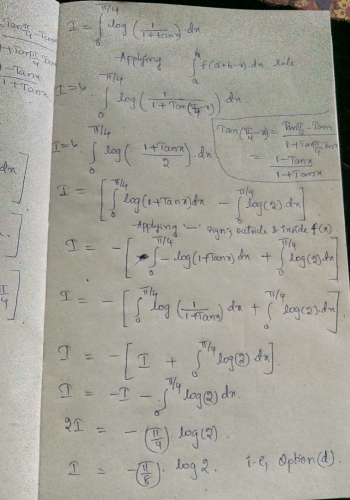
- a)log 2
- b)0
- c)
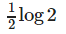
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
log 2
b)
0
c)
d)
none of these

|
Shilpa Saha answered |
∫ log(1-x) dx - ∫ log x dx = 0
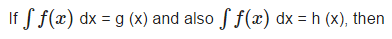
- a)g (x) h (s) = constant
- b)g (x) = h (x).
- c)g (x) - h (x) = constant
- d)h (x) + g (x) = constant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
g (x) h (s) = constant
b)
g (x) = h (x).
c)
g (x) - h (x) = constant
d)
h (x) + g (x) = constant

|
Seblewongel Girma answered |
Integration of a function can have many possibility by adding variable C.
for instance :
take integral of X^2=X^3/3 +C
integral of X^2 can be X^3/3 +1, X^3/3 +2.....
their d/CE is a constant.
for instance :
take integral of X^2=X^3/3 +C
integral of X^2 can be X^3/3 +1, X^3/3 +2.....
their d/CE is a constant.
Chapter doubts & questions for Integration - Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Integration - Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve
146 videos|222 docs|220 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup