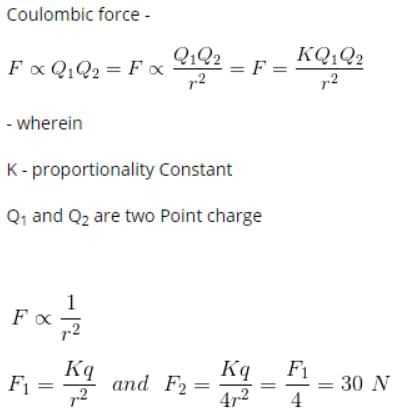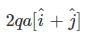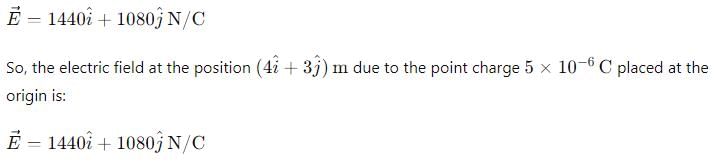All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Electric Charge for EmSAT Achieve Exam
The total negative charge in 1 mol of helium (atomic number 2, atomic mass 4) is:- a)

- b)
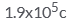
- c)
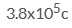
- d)
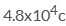
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The total negative charge in 1 mol of helium (atomic number 2, atomic mass 4) is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Isha Rane answered |
He atom has 2 electrons. so 1 mole of He has 2*N(N is Avohadro's no.) electrons. then total -ve charge in 1 mole He gas is 2*N*charge of 1 electron. calculating we will get about 1.9*10^5 C.
Two identical point charges are placed at a separation of l.P is a point on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from any one charge. The field at P is E. E is plotted against x for values of x from close to zero to slightly less than l. Which of the following best represents the resulting curve ?- a)
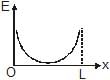
- b)
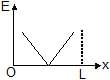
- c)
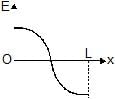
- d)
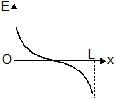
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical point charges are placed at a separation of l.P is a point on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from any one charge. The field at P is E. E is plotted against x for values of x from close to zero to slightly less than l. Which of the following best represents the resulting curve ?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Imk Pathsala answered |

At point P,
E=E1−E2 rightward
⟹E=(kq/x2)−(kq/(l−x)2) where k=1/4πϵo
⟹E=kq (l(l−2x)/x2(l−x)2)
From graph we can see that it can't be straight line and E=0 at x=l/2
At x=0 ,,E→∞ and at x=l, E→−∞
Hence, from the shown graphs the correct answer is (D).
If Q =2 coloumb and force on it is F=100 newtons , Then the value of field intensity will be- a)100 N/C
- b)50 N/C
- c)200 N/C
- d)10 N/C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If Q =2 coloumb and force on it is F=100 newtons , Then the value of field intensity will be
a)
100 N/C
b)
50 N/C
c)
200 N/C
d)
10 N/C
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Electric force on a charge q placed in a region o electric field intensity is E and it is given by F = qE.
In this case, F = 100 N and q = 2 C.
So, E=F/q=100N/2C=50 N/C.
Hence, the value of field intensity will be 50 N/C.
In this case, F = 100 N and q = 2 C.
So, E=F/q=100N/2C=50 N/C.
Hence, the value of field intensity will be 50 N/C.
If body is positively or negatively charged leaves of electroscope will- a)diverge
- b)converge
- c)stay still
- d)shrink
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If body is positively or negatively charged leaves of electroscope will
a)
diverge
b)
converge
c)
stay still
d)
shrink
|
|
Raghavendra Rane answered |
Explanation:
When a body is charged, it gains either positive or negative charge. This charge is transferred to the leaves of an electroscope. The leaves of an electroscope are made of a thin metal foil that is suspended from a metal rod. When the charged body is brought near the electroscope, the charge on the body induces a charge of the opposite sign in the leaves of the electroscope. This causes the leaves to either diverge or converge. The direction of divergence or convergence depends on the type of charge on the charged body.
When the body is positively charged, the leaves of the electroscope diverge. This is because the positive charge on the body repels the positive charge in the leaves, causing them to move away from each other.
When the body is negatively charged, the leaves of the electroscope also diverge. This is because the negative charge on the body repels the negative charge in the leaves, causing them to move away from each other.
In both cases, the movement of the leaves indicates the presence of a charge on the body. The greater the charge on the body, the greater the divergence of the leaves.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', which states that the leaves of the electroscope will diverge when the body is positively or negatively charged.
When a body is charged, it gains either positive or negative charge. This charge is transferred to the leaves of an electroscope. The leaves of an electroscope are made of a thin metal foil that is suspended from a metal rod. When the charged body is brought near the electroscope, the charge on the body induces a charge of the opposite sign in the leaves of the electroscope. This causes the leaves to either diverge or converge. The direction of divergence or convergence depends on the type of charge on the charged body.
When the body is positively charged, the leaves of the electroscope diverge. This is because the positive charge on the body repels the positive charge in the leaves, causing them to move away from each other.
When the body is negatively charged, the leaves of the electroscope also diverge. This is because the negative charge on the body repels the negative charge in the leaves, causing them to move away from each other.
In both cases, the movement of the leaves indicates the presence of a charge on the body. The greater the charge on the body, the greater the divergence of the leaves.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', which states that the leaves of the electroscope will diverge when the body is positively or negatively charged.
Electric potential is a -- a)Vector quantity
- b)Scalar quantity
- c) Neither vector Nor scalar
- d)Fictious quantity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Electric potential is a -
a)
Vector quantity
b)
Scalar quantity
c)
Neither vector Nor scalar
d)
Fictious quantity
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Electric potential is a pure Scalar quantity, The reason is as follows.
The Electric Potential is defined as the amount of work-done per unit positive charge to bring from infinity to that point under the influence of the primary charge only.
U=W/q
And work done is defined as the dot product of force and displacement which is a scalar quantity.
W=F.S
Thus Electric potential is a scalar quantity.
The Electric Potential is defined as the amount of work-done per unit positive charge to bring from infinity to that point under the influence of the primary charge only.
U=W/q
And work done is defined as the dot product of force and displacement which is a scalar quantity.
W=F.S
Thus Electric potential is a scalar quantity.
Both the leaves of the electroscope carry- a)Same charges
- b)zero charge
- c)opposite charge
- d)always negative charge
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Both the leaves of the electroscope carry
a)
Same charges
b)
zero charge
c)
opposite charge
d)
always negative charge
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
When the metal terminal is touched with a charged object, the gold leaves spread apart in a 'V'. This is because some of the charge on the object is conducted through the terminal and metal rod to the leaves. Since they receive the same sign charge they repel each other and thus diverge.
The quantization of charge has little practical consequence and can be ignored at the- a)microscopic level
- b)macroscopic level
- c)all levels
- d)information given is insufficient to decide
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The quantization of charge has little practical consequence and can be ignored at the
a)
microscopic level
b)
macroscopic level
c)
all levels
d)
information given is insufficient to decide
|
|
Roshni Desai answered |
Gain or loss of charge in terms of few electrons each carrying very small charge is unobservable at macroscopic level.
A charged particle having some mass is resting in equilibrium at a height H above the centre of a uniformly charged non-conducting horizontal ring of radius R. The force of gravity acts downwards. The equilibrium of the particle will be stable -- a)For all values of H
- b)Only if H >
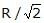
- c)Only if H <
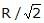
- d)Only if H =
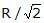
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A charged particle having some mass is resting in equilibrium at a height H above the centre of a uniformly charged non-conducting horizontal ring of radius R. The force of gravity acts downwards. The equilibrium of the particle will be stable -
a)
For all values of H
b)
Only if H > 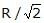
c)
Only if H < 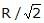
d)
Only if H = 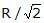

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
electric field due to non-conducting ring along its axis is given by,
E=kqz/(Z2+r2)3/2
where z is the separation between point of observation to the centre of the ring, q is the charge on the ring and r is the radius of the ring.
We know, electric field will be maximum only when z = R/√2, meaning at this point the value of force must be maximum. and if we increase the value of z from R/√2 it will decrease and if we decrease the value of z from R/√2 , it will increase.
condition of stable equilibrium,
A small vertical displacement upwards should cause the resultant force on the particle to be downwards, to return it or a small vertical displacement downward should cause the resultant force on the particle to be downward.
hence, at z > R/√2 or, h > R/√2 system will be in stable equilibrium.
E=kqz/(Z2+r2)3/2
where z is the separation between point of observation to the centre of the ring, q is the charge on the ring and r is the radius of the ring.
We know, electric field will be maximum only when z = R/√2, meaning at this point the value of force must be maximum. and if we increase the value of z from R/√2 it will decrease and if we decrease the value of z from R/√2 , it will increase.
condition of stable equilibrium,
A small vertical displacement upwards should cause the resultant force on the particle to be downwards, to return it or a small vertical displacement downward should cause the resultant force on the particle to be downward.
hence, at z > R/√2 or, h > R/√2 system will be in stable equilibrium.
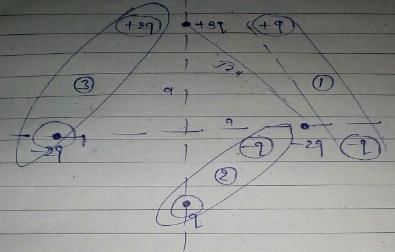
Two fixed charges 4Q (positive) and Q (negative) are located at A and B, the distance AB being 3 m. 
- a)The point P where the resultant field due to both is zero is on AB outside AB.
- b)The point P where the resultant field due to both is zero is on AB inside AB.
- c) If a positive charge is placed at P and displaced slightly along AB it will execute oscillations.
- d) If a negative charge is placed at P and displaced slightly along AB it will execute oscillation.
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two fixed charges 4Q (positive) and Q (negative) are located at A and B, the distance AB being 3 m.
a)
The point P where the resultant field due to both is zero is on AB outside AB.
b)
The point P where the resultant field due to both is zero is on AB inside AB.
c)
If a positive charge is placed at P and displaced slightly along AB it will execute oscillations.
d)
If a negative charge is placed at P and displaced slightly along AB it will execute oscillation.

|
Gopal Gupta answered |
A and C
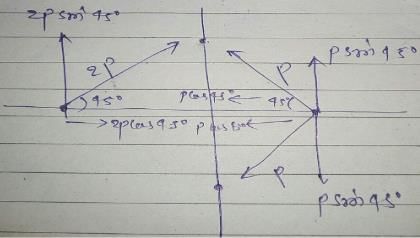
The direction (q) of at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be -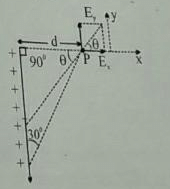
- a)At angle 30° from x-axis
- b)45° from x-axis
- c)60° from x-axis
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The direction (q) of at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be -
a)
At angle 30° from x-axis
b)
45° from x-axis
c)
60° from x-axis
d)
None of these

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The angle suspended by the finite line charge at P=60°
So, the resultant electric field due to line charge will be at 60/2⇒30° since we can assume the charge concentrated at the centre of finite line charge.
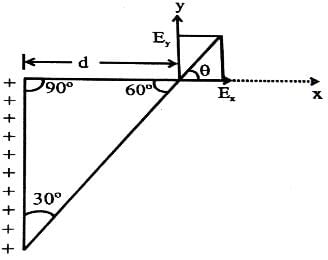
So, the resultant electric field due to line charge will be at 60/2⇒30° since we can assume the charge concentrated at the centre of finite line charge.

The total negative charge in 1 mol of helium (atomic number 2, atomic mass 4) is:- a)

- b)
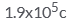
- c)
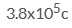
- d)
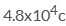
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The total negative charge in 1 mol of helium (atomic number 2, atomic mass 4) is:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Tejas Desai answered |
He atom has 2 electrons. so 1 mole of He has 2*N(N is Avohadro's no.) electrons. then total -ve charge in 1 mole He gas is 2*N*charge of 1 electron. calculating we will get about 1.9*10^5 C.
If a body contains n1 electrons and n2 protons, the total amount of charge on the body is- a)(n2 x n1) e
- b)(n2 / n1) e
- c)(n2-n1)e
- d)(n2 + n1) e
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a body contains n1 electrons and n2 protons, the total amount of charge on the body is
a)
(n2 x n1) e
b)
(n2 / n1) e
c)
(n2-n1)e
d)
(n2 + n1) e
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Correct Answer :- A
Explanation :
Line charge density = λ
radius, r=R
length of wire inside the sphere is 2 R
Now, λdl=dθ
for total charge enclosed by radius R, ∫(O to R)Q = ∫(O to R)λdl
Qinc = λ2R
Now, ϕ = Qinc/ε0
= λ2R/ε0
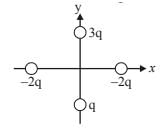
Four equal but like charge are placed at four corners of a square. The electric field intensity at the center of the square due to any one charge is E, then the resultant electric field intensity at centre of square will be- a)Zero
- b)4E
- c)E
- d)1/2E
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Four equal but like charge are placed at four corners of a square. The electric field intensity at the center of the square due to any one charge is E, then the resultant electric field intensity at centre of square will be
a)
Zero
b)
4E
c)
E
d)
1/2E
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
As the components of electric field intensity at diagonal are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, thus the intensity of electric field will be zero.
Hence the correct answer would be option A.
Hence the correct answer would be option A.
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown in a region where uniform gravitational field and electric field are present. The path of particle- a)May be a straight line
- b)May be a circle
- c)May be a parabola
- d)May be a hyperbola
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown in a region where uniform gravitational field and electric field are present. The path of particle
a)
May be a straight line
b)
May be a circle
c)
May be a parabola
d)
May be a hyperbola
|
|
Rajesh Chatterjee answered |
Explanation:
When a particle of mass m and charge q is thrown in a region where uniform gravitational field and electric field are present, its path can be determined by considering the forces acting on it.
Forces acting on the particle:
Possible paths of the particle:
Therefore, the correct answer is options A and C - the path of the particle may be a straight line or a parabola.
When a particle of mass m and charge q is thrown in a region where uniform gravitational field and electric field are present, its path can be determined by considering the forces acting on it.
Forces acting on the particle:
- Gravitational force (Fg) = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity
- Electric force (Fe) = qE, where E is the electric field strength
Possible paths of the particle:
- Straight line: If the electric and gravitational forces are in the same direction, the particle will move in a straight line with constant acceleration. The path will be a straight line.
- Parabola: If the electric and gravitational forces are perpendicular to each other, the particle will move in a parabolic path. This happens when the particle is thrown at an angle to the electric field. The path will be a parabola.
- Circle: If the electric force is perpendicular to the gravitational force, the particle will move in a circular path. This happens when the particle is thrown in a direction perpendicular to the electric field. The path will be a circle.
Therefore, the correct answer is options A and C - the path of the particle may be a straight line or a parabola.
Magnitude of electric charge on a single electron is:- a)1.6 x 10-18 coulomb
- b)1.6 x 10-10 coulomb
- c)1.6 x 10-16 coulomb
- d)1.6 x 10-19 coulomb
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Magnitude of electric charge on a single electron is:
a)
1.6 x 10-18 coulomb
b)
1.6 x 10-10 coulomb
c)
1.6 x 10-16 coulomb
d)
1.6 x 10-19 coulomb
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
One Coulomb is equal to 6.25 x 10^18 proton's worth or electron's worth of charge (depending on whether it's positive or negative charge). So one electron has -1.6 x 10^-19 Coulombs of charge and one proton has +1.6 x 10^-19 Coulombs of charge. We will use “C” to represent Coulombs.
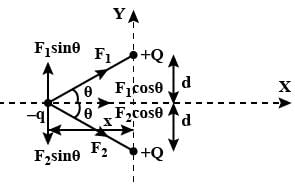
Two small balls having equal positive charge Q (Coulomb) on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length 'L' metre, from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite in to space where there is no gravity (state of weight lessness) Then the angle (q) between the two strings is- a)0º
- b)90º
- c)180º
- d)0º < q < 180º
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two small balls having equal positive charge Q (Coulomb) on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length 'L' metre, from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite in to space where there is no gravity (state of weight lessness) Then the angle (q) between the two strings is
a)
0º
b)
90º
c)
180º
d)
0º < q < 180º
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
There is a condition of weightlessness in a satellite.
Therefore, mg=0
Due to electrostatic force of repulsion between the balls, the string would become horizontal.
Therefore, angle between the string =180
Therefore, mg=0
Due to electrostatic force of repulsion between the balls, the string would become horizontal.
Therefore, angle between the string =180
If mica and woolen cloth are rubbed together, then mica gets- a)positively charged
- b)negatively charged
- c)remains neutral
- d)dual charged
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If mica and woolen cloth are rubbed together, then mica gets
a)
positively charged
b)
negatively charged
c)
remains neutral
d)
dual charged
|
|
Nisha Pillai answered |
Woolen cloth has +ve charge and when mica is rubbed on it , mica gets +vely charged due to (conduction) - flow of charge from wool to mica
Quantization of charge means that- a)the charge on a body is a fraction of electronic charge, e
- b)The charge on a body is an integral multiple of electronic charge, e
- c)the net charge on a body is always zero
- d)the total charge on a body is always conserved
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Quantization of charge means that
a)
the charge on a body is a fraction of electronic charge, e
b)
The charge on a body is an integral multiple of electronic charge, e
c)
the net charge on a body is always zero
d)
the total charge on a body is always conserved
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Charge quantization, then, means that charge cannot take any arbitrary values, but only values that are integral multiples of the fundamental charge (charge of proton/electron). For example, in a hydrogen ion, we usually denote it with a positive sign to indicate that there's one proton more than there are electrons.
The charge on a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk is called positive:- a)so that the proton charge will be positive
- b)because like charges repel
- c)to conform to the conventions adopted for G and m in Newton’s law of gravitation
- d)by arbitrary convention
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The charge on a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk is called positive:
a)
so that the proton charge will be positive
b)
because like charges repel
c)
to conform to the conventions adopted for G and m in Newton’s law of gravitation
d)
by arbitrary convention

|
Aravind Mehra answered |
When the point is on the diameter and away from the centre of hemisphere which is charged uniformly and positively, the component of electric field intensity parallel to the diameter cancel out. So the electric field is perpendicular to the diameter.
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
- a)8 mC
- b)2 mC
- c)5 mC
- d)7 μC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
a)
8 mC
b)
2 mC
c)
5 mC
d)
7 μC
|
|
Srestha Chopra answered |
° with an electric field of magnitude 500 N/C. The dipole moment is 2 C.m. Find the torque experienced by the dipole.
The torque experienced by an electric dipole in an electric field is given by the formula:
τ = p E sinθ
where τ is the torque, p is the dipole moment, E is the electric field, and θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Substituting the given values, we get:
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × sin30°
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × 0.5
τ = 500 N.m
Therefore, the torque experienced by the dipole is 500 N.m.
The torque experienced by an electric dipole in an electric field is given by the formula:
τ = p E sinθ
where τ is the torque, p is the dipole moment, E is the electric field, and θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Substituting the given values, we get:
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × sin30°
τ = (2 C.m) × (500 N/C) × 0.5
τ = 500 N.m
Therefore, the torque experienced by the dipole is 500 N.m.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electric Charge - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electric Charge - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
215 videos|402 docs|221 tests
|