All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Reflection for EmSAT Achieve Exam
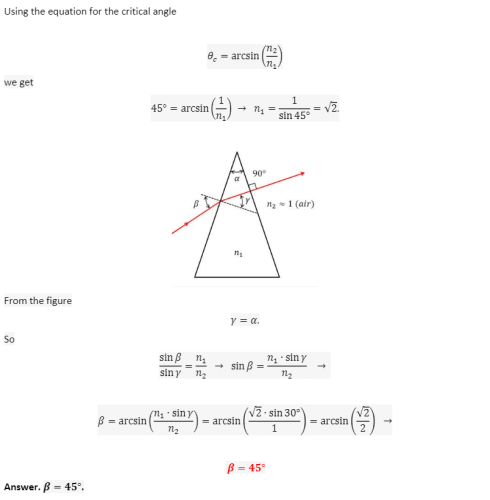
The critical angle for the material of a prism is 45° and its refracting angle is 30°. A monochromatic ray goes out perpendicular to the surface of emergence from the prism. What is the angle of incidence on the prism?- a)60°
- b)75°
- c)30°
- d)45°
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The critical angle for the material of a prism is 45° and its refracting angle is 30°. A monochromatic ray goes out perpendicular to the surface of emergence from the prism. What is the angle of incidence on the prism?
a)
60°
b)
75°
c)
30°
d)
45°

|
Sanchita Iyer answered |
Light is confined within the core of a simple optical fiber by:- a)total internal reflection at the outer edge of the cladding.
- b)reflection from the fiber’s plastic coating.
- c)total internal reflection at the core cladding boundary.
- d)refraction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Light is confined within the core of a simple optical fiber by:
a)
total internal reflection at the outer edge of the cladding.
b)
reflection from the fiber’s plastic coating.
c)
total internal reflection at the core cladding boundary.
d)
refraction
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Light remains confined within the core of simple optical fibre because of Total internal reflection from core cladding boundary.
Light is confined within the core of a simple optical fiber by. If light hits a boundary of a material of lower refractive index at a steep enough angle, it cannot get out and it's reflected back into the high index medium, as in the figure below.
An optical fibre is a thin rod of high-quality glass. Very little light is absorbed by the glass.Optical fibres can carry more information than an ordinary cable of the same thickness. The signals in optical fibres do not weaken as much over long distances as the signals in ordinary cables.
Total internal reflection. When light traveling in an optically dense medium hits a boundary at a steep angle (larger than the critical angle for the boundary), the light is completely reflected. This effect is used in optical fibers to confine light in the core.
The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core (hallway) by constantly bouncing from the cladding (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances.
Light is confined within the core of a simple optical fiber by. If light hits a boundary of a material of lower refractive index at a steep enough angle, it cannot get out and it's reflected back into the high index medium, as in the figure below.
An optical fibre is a thin rod of high-quality glass. Very little light is absorbed by the glass.Optical fibres can carry more information than an ordinary cable of the same thickness. The signals in optical fibres do not weaken as much over long distances as the signals in ordinary cables.
Total internal reflection. When light traveling in an optically dense medium hits a boundary at a steep angle (larger than the critical angle for the boundary), the light is completely reflected. This effect is used in optical fibers to confine light in the core.
The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core (hallway) by constantly bouncing from the cladding (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances.
Total internal reflection occurs when- a)Angle of incidence is equal to critical angle
- b)Angle of incidence is greater than critical angle
- c)Total internal reflection doesn’t depend on angle of incidence or critical angle
- d)Angle of incidence is less than critical angle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Total internal reflection occurs when
a)
Angle of incidence is equal to critical angle
b)
Angle of incidence is greater than critical angle
c)
Total internal reflection doesn’t depend on angle of incidence or critical angle
d)
Angle of incidence is less than critical angle

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
Total internal reflection is the phenomenon which occurs when a propagated wave strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface.The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal reflection occurs.
Critical angle is- a)The angle of refraction in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of incidence in the rarer medium is 90°.
- b)The angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 0°.
- c)The angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90°.
- d)The angle of incidence in the rarer medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the denser medium is 90°
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Critical angle is
a)
The angle of refraction in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of incidence in the rarer medium is 90°.
b)
The angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 0°.
c)
The angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90°.
d)
The angle of incidence in the rarer medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the denser medium is 90°
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The Critical Angle
In the previous part of Lesson 3, the phenomenon of total internal reflection was introduced. Total internal reflection (TIR) is the phenomenon that involves the reflection of all the incident light off the boundary. TIR only takes place when both of the following two conditions are met:
a light ray is in the more dense medium and approaching the less dense medium.
the angle of incidence for the light ray is greater than the so-called critical angle.
In our introduction to TIR, we used the example of light traveling through water towards the boundary with a less dense material such as air. When the angle of incidence in water reaches a certain critical value, the refracted ray lies along the boundary, having an angle of refraction of 90-degrees. This angle of incidence is known as the critical angle; it is the largest angle of incidence for which refraction can still occur. For any angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, light will undergo total internal reflection.
What is the relation between critical angle and refractive index?- a)μ = cosC
- b)μ = 1/cosC
- c)μ = 1/sinC
- d)μ = sinC
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relation between critical angle and refractive index?
a)
μ = cosC
b)
μ = 1/cosC
c)
μ = 1/sinC
d)
μ = sinC
|
|
Aravind Rane answered |
The critical angle is related to the refractive index by the following equation:
critical angle = sin^(-1)(1/n),
where n is the refractive index of the medium.
critical angle = sin^(-1)(1/n),
where n is the refractive index of the medium.
Total internal reflecting mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors because- a)They do not absorb any light
- b)They produce sharp images
- c)They do not produce ghost image
- d)Both a and c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Total internal reflecting mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors because
a)
They do not absorb any light
b)
They produce sharp images
c)
They do not produce ghost image
d)
Both a and c
|
|
Anagha Mukherjee answered |
Total internal reflecting mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors because they do not absorb any light and do not produce ghost images.
1. Absorption of Light:
Total internal reflecting (TIR) mirrors are made of materials with high reflectivity, such as glass or plastic coated with a thin layer of metal. Unlike plane mirrors, TIR mirrors do not absorb any light. When light falls on a TIR mirror, it undergoes total internal reflection at the interface between the mirror and the surrounding medium. This means that all the incident light is reflected back, resulting in minimal loss of light energy. On the other hand, plane mirrors absorb a small amount of light, leading to some energy loss. Therefore, TIR mirrors are preferred when maximum reflection efficiency is desired.
2. Production of Sharp Images:
TIR mirrors are designed in such a way that light rays undergo multiple internal reflections before emerging from the mirror surface. This property allows TIR mirrors to produce sharp and well-defined images. In contrast, plane mirrors produce images that are not as sharp due to the presence of various imperfections, such as surface irregularities and slight distortions. TIR mirrors are commonly used in optical systems where high image quality is required, such as in telescopes, microscopes, and laser systems.
3. Absence of Ghost Images:
Ghost images are unwanted secondary images that can appear in optical systems due to reflections or scattering of light. Plane mirrors are more prone to producing ghost images compared to TIR mirrors. This is because plane mirrors reflect light at a single interface, while TIR mirrors utilize multiple internal reflections to achieve total reflection. The multiple internal reflections in TIR mirrors reduce the chance of ghost images by minimizing the amount of light that can escape or scatter within the mirror. As a result, TIR mirrors offer superior image quality by eliminating or significantly reducing ghost images.
Overall, total internal reflecting mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors because they do not absorb any light, produce sharp images, and do not produce ghost images. These features make TIR mirrors ideal for applications requiring high reflectivity and image quality, such as in optical instruments and systems.
1. Absorption of Light:
Total internal reflecting (TIR) mirrors are made of materials with high reflectivity, such as glass or plastic coated with a thin layer of metal. Unlike plane mirrors, TIR mirrors do not absorb any light. When light falls on a TIR mirror, it undergoes total internal reflection at the interface between the mirror and the surrounding medium. This means that all the incident light is reflected back, resulting in minimal loss of light energy. On the other hand, plane mirrors absorb a small amount of light, leading to some energy loss. Therefore, TIR mirrors are preferred when maximum reflection efficiency is desired.
2. Production of Sharp Images:
TIR mirrors are designed in such a way that light rays undergo multiple internal reflections before emerging from the mirror surface. This property allows TIR mirrors to produce sharp and well-defined images. In contrast, plane mirrors produce images that are not as sharp due to the presence of various imperfections, such as surface irregularities and slight distortions. TIR mirrors are commonly used in optical systems where high image quality is required, such as in telescopes, microscopes, and laser systems.
3. Absence of Ghost Images:
Ghost images are unwanted secondary images that can appear in optical systems due to reflections or scattering of light. Plane mirrors are more prone to producing ghost images compared to TIR mirrors. This is because plane mirrors reflect light at a single interface, while TIR mirrors utilize multiple internal reflections to achieve total reflection. The multiple internal reflections in TIR mirrors reduce the chance of ghost images by minimizing the amount of light that can escape or scatter within the mirror. As a result, TIR mirrors offer superior image quality by eliminating or significantly reducing ghost images.
Overall, total internal reflecting mirrors are preferred over plane mirrors because they do not absorb any light, produce sharp images, and do not produce ghost images. These features make TIR mirrors ideal for applications requiring high reflectivity and image quality, such as in optical instruments and systems.
Which of the following phenomena takes place inside an optical fiber ?- a)Reflection
- b)Dispersion
- c)Total Internal Reflection
- d)Scattering
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following phenomena takes place inside an optical fiber ?
a)
Reflection
b)
Dispersion
c)
Total Internal Reflection
d)
Scattering

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
In fibre optics ,a optical phenomenon known as total internal reflection is used to transmit light rays. In case of the simplest form of optical fiber, light entering one end of the fiber strikes the boundary of the fiber and is reflected inward.
Carbon disulfide (n = 1.63) is poured into a container made of crown glass (n = 1.52). What is the critical angle for internal reflection of a ray in the liquid when it is incident on the liquid-to-glass surface?- a)4.0 degrees
- b)68.8 degrees
- c)89.0 degrees
- d)21.2 degrees
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon disulfide (n = 1.63) is poured into a container made of crown glass (n = 1.52). What is the critical angle for internal reflection of a ray in the liquid when it is incident on the liquid-to-glass surface?
a)
4.0 degrees
b)
68.8 degrees
c)
89.0 degrees
d)
21.2 degrees
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Refractive index of glass with respect to liquid:
n = 1.52/1.63 = 0.9325
thus critical angle, i = sin^-1(n) = 68.8 degrees
Mirage is caused due to- a)Scattering of light by the various layers of air
- b)Dispersion of light by the various layers of air
- c)Total Internal Reflection of light by the various layers of air
- d)Both b and c
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mirage is caused due to
a)
Scattering of light by the various layers of air
b)
Dispersion of light by the various layers of air
c)
Total Internal Reflection of light by the various layers of air
d)
Both b and c

|
Akshay Shah answered |
When appearing on roads due to the hot asphalt, it is often referred to as a highway mirage. Convection causes the temperature of the air to vary, and the variation between the hot air at the surface of the road and the denser cool air above it creates a gradient in the refractive index of the air.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reflection - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reflection - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









