All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Calorimetry and Phase Changes for EmSAT Achieve Exam
5 g of ice at 0° C is mixed with 10 g of water at 10° C. The temperature of the mixture is:- a)2°C
- b)0°C
- c)5°C
- d)2.5°C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
5 g of ice at 0° C is mixed with 10 g of water at 10° C. The temperature of the mixture is:
a)
2°C
b)
0°C
c)
5°C
d)
2.5°C
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Heat absorbed by 5g ice when it converted to at 0° C = 5 x 80 = 400 cal.
Heat liberated by 10g water at 10° C to 0° C = 100 cal
Hence there is 15g water at 0° C and 300 cal needs to be liberated , thus for some amount of water converts into ice, hence the temp of mixture is 0° C.
Heat liberated by 10g water at 10° C to 0° C = 100 cal
Hence there is 15g water at 0° C and 300 cal needs to be liberated , thus for some amount of water converts into ice, hence the temp of mixture is 0° C.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of an ideal mono atomic gas through 2°C at constant pressure is (universal gas constant = R)- a)5R/2
- b)3 R
- c)2R
- d)5 R
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of an ideal mono atomic gas through 2°C at constant pressure is (universal gas constant = R)
a)
5R/2
b)
3 R
c)
2R
d)
5 R
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
At constant pressure
dQ= nCpdT
=1*(5R/2)*2
=5R
dQ= nCpdT
=1*(5R/2)*2
=5R
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Water is used as coolant in automobiles radiators because
- A:
it has high specific heat capacity
- B:
it is easily available
- C:
it is easy to carry
- D:
it is cheap
The answer is a.
Water is used as coolant in automobiles radiators because
it has high specific heat capacity
it is easily available
it is easy to carry
it is cheap
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Water is used as a coolant in automobiles radiators because it has high specific heat capacity. So, it absorbs a large amount of heat for a degree rise in temperature.
Equal masses of three liquids of specific heats C1, C2 and C3 at temperatures t1, t2 and t3 respectively are mixed. If there is no change of state, the temperature of the mixture is- a)(C1t1 + C2t2 + C3t3)/3(C1 + C2 + C1)
- b)(C1t1 + C2t2 + C3t3)/(C1 + C2 + C1)
- c)(t1 + t2 +t3 )/3
- d)3(C1t1 + C2t2 + C3t3)/(C1 + C2 + C1)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Equal masses of three liquids of specific heats C1, C2 and C3 at temperatures t1, t2 and t3 respectively are mixed. If there is no change of state, the temperature of the mixture is
a)
(C1t1 + C2t2 + C3t3)/3(C1 + C2 + C1)
b)
(C1t1 + C2t2 + C3t3)/(C1 + C2 + C1)
c)
(t1 + t2 +t3 )/3
d)
3(C1t1 + C2t2 + C3t3)/(C1 + C2 + C1)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
For the composite system, energy conservation yields no net energy flow in or out of the system.
Let final temperature be T
Then, heat absorbed by A+heat absorbed by B+heat absorbed by C=0
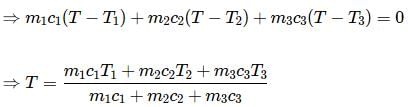
Here in the question m1=m2=m3
Let final temperature be T
Then, heat absorbed by A+heat absorbed by B+heat absorbed by C=0
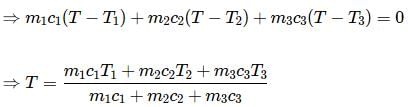
Here in the question m1=m2=m3
Melting point of ice decreases with- a)Decrease in pressure
- b)Increase in temperature
- c)Decrease in temperature
- d)Increase in pressure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Melting point of ice decreases with
a)
Decrease in pressure
b)
Increase in temperature
c)
Decrease in temperature
d)
Increase in pressure
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
When ice melts the volume decreases and an increase in pressure will support this phenomena according to Le Chatalier’s rule.
A piece of iron of mass 100g is kept inside a furnace for a long time and Jthen put in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10g containing 240g of water at 20°C. The mixture attains an equilibrium temperature of 60°C. Find the temperature of the furnace. Specific heat capacity of iron = 470J/kg-°C.- a)500°C
- b)900°C
- c)953.6∘C
- d)706.80 °C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of iron of mass 100g is kept inside a furnace for a long time and Jthen put in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10g containing 240g of water at 20°C. The mixture attains an equilibrium temperature of 60°C. Find the temperature of the furnace. Specific heat capacity of iron = 470J/kg-°C.
a)
500°C
b)
900°C
c)
953.6∘C
d)
706.80 °C
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Mass of Iron = 100g
Water Eq of caloriemeter = 10g
Mass of water = 240g
Let the Temp. of surface = 0ºC
Siron = 470J/kg°C
Water Eq of caloriemeter = 10g
Mass of water = 240g
Let the Temp. of surface = 0ºC
Siron = 470J/kg°C
Total heat gained = Total heat lost.
So,100/1000× 470 × (θ – 60) = 250/1000 × 4200 × (60 – 20)
⇒ 47θ – 47 × 60 = 25 × 42 × 40
⇒ θ = 4200 + 2820/47= 44820/47 =953.61°C
⇒ 47θ – 47 × 60 = 25 × 42 × 40
⇒ θ = 4200 + 2820/47= 44820/47 =953.61°C
According to law of calorimetry, which of the given relation is true?- a)Heat gained ≥ Heat lost
- b)Heat gained = Heat lost
- c)Heat gained > Heat lost
- d)Heat lost > Heat gained
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to law of calorimetry, which of the given relation is true?
a)
Heat gained ≥ Heat lost
b)
Heat gained = Heat lost
c)
Heat gained > Heat lost
d)
Heat lost > Heat gained
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
A principle of calorimetry states that if there is no loss of heat in surrounding the total heat lost by hot body equal to the total heat gained by a cold body.
i.e. heat loss = heat gain
A device in which heat measurement can be made is called- a)Joule meter
- b)Calorimeter
- c)Thermal meter
- d)Gauge meter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A device in which heat measurement can be made is called
a)
Joule meter
b)
Calorimeter
c)
Thermal meter
d)
Gauge meter
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity.
Skating is possible on snow due to the formation of water below the skates. This water below skates comes as result of- a)Increase in temperature between skates and snow
- b)Increase in pressure between skates and snow
- c)Force due to weight of the skater
- d)Decrease in pressure between skates and snow
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Skating is possible on snow due to the formation of water below the skates. This water below skates comes as result of
a)
Increase in temperature between skates and snow
b)
Increase in pressure between skates and snow
c)
Force due to weight of the skater
d)
Decrease in pressure between skates and snow
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
As the pressure increases between the skates and ice, the ice starts melting below 0o C.
The temperature and pressure at which all three phases of a substances coexist is called- a)Fusion point
- b)Triple point
- c)Sublimation point
- d)Melting Point
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The temperature and pressure at which all three phases of a substances coexist is called
a)
Fusion point
b)
Triple point
c)
Sublimation point
d)
Melting Point
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sublimation curve, fusion curve and the vaporisation curve meet.
An increase in temperature in a liquid would cause a phase change to which of the following?- a)Gas
- b)liquid
- c)solid
- d)plasma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An increase in temperature in a liquid would cause a phase change to which of the following?
a)
Gas
b)
liquid
c)
solid
d)
plasma
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Increasing the temperature of liquid, increases the average K.E. of the molecules. The molecules start moving vigorously in all the directions, thereby increasing and the inter-molecular space between them. Thus, the liquid changes into gas.
A student added a drop of red food coloring to 4 beakers of water.Each beaker contained 100 ml of a different temperature water. The student recorded how long it took each beaker to mix completely (without stirring). The following table shows her results:
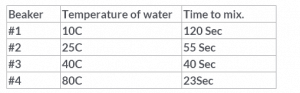 What conclusion should the student make from this experiment? Particles are moving
What conclusion should the student make from this experiment? Particles are moving - a)faster in warm water so they mix faster
- b)slowly in warm water so they mix faster
- c)faster in warm water so they mix slowly
- d)slowly in warm water so they mix slowly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A student added a drop of red food coloring to 4 beakers of water.Each beaker contained 100 ml of a different temperature water. The student recorded how long it took each beaker to mix completely (without stirring). The following table shows her results:


What conclusion should the student make from this experiment? Particles are moving
a)
faster in warm water so they mix faster
b)
slowly in warm water so they mix faster
c)
faster in warm water so they mix slowly
d)
slowly in warm water so they mix slowly
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Adding heat energy to water increases the motion of the water molecules and the molecules of food coloring. The faster moving molecules cause the food coloring to mix into the water faster. The water molecules and food coloring molecules in cold water don't move as quickly as in hot water.
SI unit of latent heat is- a)Cal/ Kg
- b)J Kg
- c)J Kg -2
- d)J/Kg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
SI unit of latent heat is
a)
Cal/ Kg
b)
J Kg
c)
J Kg -2
d)
J/Kg
|
|
Jyoti Dey answered |
The correct answer is option 'D', J/Kg.
Latent heat is the amount of heat energy required or released during a phase change of a substance, such as melting or vaporization, at a constant temperature and pressure. It is a specific type of heat energy associated with the change in the internal energy of a substance, without a change in its temperature.
There are two types of latent heat: latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization. The latent heat of fusion refers to the heat energy required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid state, while the latent heat of vaporization refers to the heat energy required to change a substance from a liquid to a gaseous state.
The SI unit of latent heat is Joule per kilogram (J/Kg). The Joule is the SI unit of energy, and the kilogram is the SI unit of mass. So, when we express the latent heat in the SI unit, we are essentially referring to the amount of energy required or released per unit mass of the substance during a phase change.
The SI unit of latent heat can be derived by considering the equation Q = mL, where Q is the heat energy required or released, m is the mass of the substance, and L is the latent heat. By rearranging the equation, we get L = Q/m. Since Q is in Joules and m is in kilograms, the SI unit of latent heat is J/Kg.
So, option 'D', J/Kg, is the correct answer for the SI unit of latent heat.
Latent heat is the amount of heat energy required or released during a phase change of a substance, such as melting or vaporization, at a constant temperature and pressure. It is a specific type of heat energy associated with the change in the internal energy of a substance, without a change in its temperature.
There are two types of latent heat: latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization. The latent heat of fusion refers to the heat energy required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid state, while the latent heat of vaporization refers to the heat energy required to change a substance from a liquid to a gaseous state.
The SI unit of latent heat is Joule per kilogram (J/Kg). The Joule is the SI unit of energy, and the kilogram is the SI unit of mass. So, when we express the latent heat in the SI unit, we are essentially referring to the amount of energy required or released per unit mass of the substance during a phase change.
The SI unit of latent heat can be derived by considering the equation Q = mL, where Q is the heat energy required or released, m is the mass of the substance, and L is the latent heat. By rearranging the equation, we get L = Q/m. Since Q is in Joules and m is in kilograms, the SI unit of latent heat is J/Kg.
So, option 'D', J/Kg, is the correct answer for the SI unit of latent heat.
What happens to the volume of the substance when the temperature increases?- a)decreases
- b)increases
- c)remains same
- d)not measurable
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens to the volume of the substance when the temperature increases?
a)
decreases
b)
increases
c)
remains same
d)
not measurable
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
In general, liquids tend to get “thinner” when their temperature increases. In general, the liquids tend to expand when their temperature increases. For example, the same mass of boiling water occupies more volume at 100 degrees Celsius than at 20 degrees Celsius. Therefore, increasing temperature decreases density.
Which diagram is the best depiction of the direction of flow of diffusion?- a)
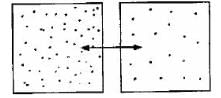
- b)
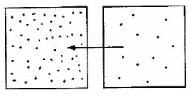
- c)
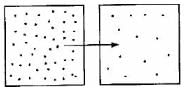
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which diagram is the best depiction of the direction of flow of diffusion?
a)

b)

c)

d)
none of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The net flow of solute is from its higher concentration to lower concentration.
A rigid container of volume 0.5 m³ contains 1.0 kg of water at 120°C (vf = 0.00106 m³/kg, vg = 0.8908 m³/kg). The state of water is- a)Compressed liquid
- b)Saturated liquid
- c)Superheated vapor
- d)A mixture of saturated liquid and saturated vapor
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A rigid container of volume 0.5 m³ contains 1.0 kg of water at 120°C (vf = 0.00106 m³/kg, vg = 0.8908 m³/kg). The state of water is
a)
Compressed liquid
b)
Saturated liquid
c)
Superheated vapor
d)
A mixture of saturated liquid and saturated vapor

|
Ambition Institute answered |
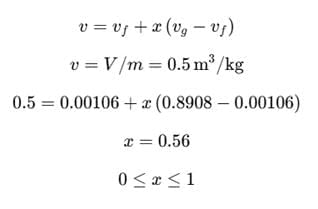
x = 0, Saturated liquid
x = 1, Saturated vapor
x = 1, Saturated vapor
As x value lies between 0 and 1, therefore it is a mixture of saturated liquid and saturated vapor.
Chapter doubts & questions for Calorimetry and Phase Changes - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Calorimetry and Phase Changes - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup