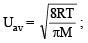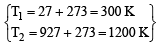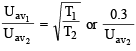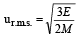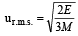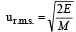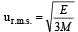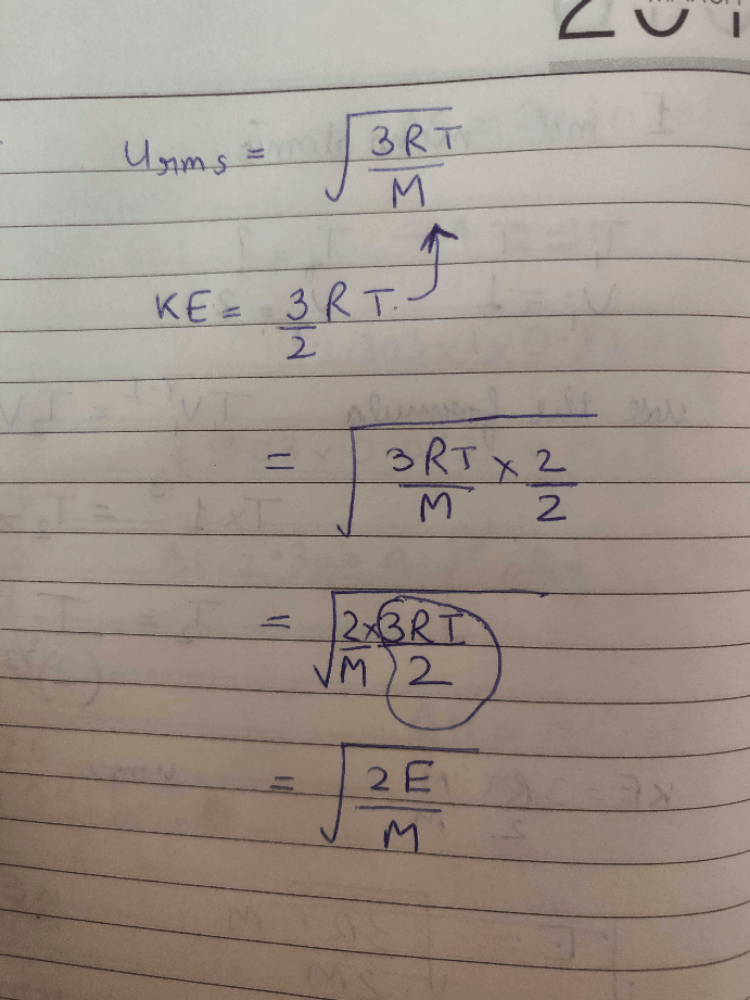All Exams >
JEE >
Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of Liquid state for JEE Exam
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-6) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Which pair of molecules has the strongest dipole-dipole interactions?- a)NH3 and CH4
- b)CH4 and CH4
- c)CO3 and CO2
- d)NH3 and NH3
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-6) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which pair of molecules has the strongest dipole-dipole interactions?
a)
NH3 and CH4
b)
CH4 and CH4
c)
CO3 and CO2
d)
NH3 and NH3
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
NH3 and NH3. Both polar, asymmetric molecules. CH4 is nonpolar. CO2 is symetrical.
A liquid enclosed in 1.0L flask at 298K. The vapour pressure exerted by the liquid is 20.0 mm. when the same liquid is enclosed in a flask of 5L capacity at the same temperature, the vapour pressure of the liquid will be:- a)40mm
- b)20.0mm
- c)10mm
- d)1000mm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A liquid enclosed in 1.0L flask at 298K. The vapour pressure exerted by the liquid is 20.0 mm. when the same liquid is enclosed in a flask of 5L capacity at the same temperature, the vapour pressure of the liquid will be:
a)
40mm
b)
20.0mm
c)
10mm
d)
1000mm
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The vapour pressure of a liquid depends only on the nature of the liquid and the temperature. It does not depend on the volume of the container so it is 20.0mm.
The temperature in Celsius scale can be converted into Kelvin scale- a)By dividing it with 273
- b)By subtracting 273.15 from it
- c)By multiplying it with 273
- d)By adding 273.15 to it
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The temperature in Celsius scale can be converted into Kelvin scale
a)
By dividing it with 273
b)
By subtracting 273.15 from it
c)
By multiplying it with 273
d)
By adding 273.15 to it
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
To convert from Celsius to Kelvin you use the following formula:
Celsius temperature + 273.15 = Kelvin Temperature
For example:
26 °Celsius + 273.15 = 299.15 Kelvin
26 °Celsius + 273.15 = 299.15 Kelvin
The Kelvin temperature scale was designed so that it starts at absolute zero. In Kelvin, absolute zero is equal to 0 degrees. In Celsius, absolute zero is equal to −273.15 degrees.
Therefore, you need to add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature to get to the Kelvin temperature.
Note: Kelvin does not use the degree symbol, °.
Stronger intermolecular forces result in higher boiling point. Strength of London forces increases with number of electrons in the molecule. Boiling point of  Q. Based on the boiling points, predominant force which gives variation of boiling point of HCI < HBr < HI is
Q. Based on the boiling points, predominant force which gives variation of boiling point of HCI < HBr < HI is- a)London interaction
- b)dipole-dipole interaction
- c)hydrogen bonding
- d)dipole-induced dipole interaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stronger intermolecular forces result in higher boiling point. Strength of London forces increases with number of electrons in the molecule. Boiling point of
Q. Based on the boiling points, predominant force which gives variation of boiling point of HCI < HBr < HI is
a)
London interaction
b)
dipole-dipole interaction
c)
hydrogen bonding
d)
dipole-induced dipole interaction
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
(a) HF - Hydrogen bonding HCl,HBr,HI→ Dipole-dipole interaction, London-dispersion force.
Select the correct statement(s).- a)Cohesive forces are the intermolecular forces between like molecules and adhesive forces are between unlike molecules
- b)A drop maintains its shape if cohesive forces are stronger than adhesive forces
- c)If cohesive forces are weak compared to adhesive forces, drop collapses and spreads into film
- d)Cohesive forces in mercury, consiste of metallic bonds between atoms, are strong; thus it does not wet glass
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s).
a)
Cohesive forces are the intermolecular forces between like molecules and adhesive forces are between unlike molecules
b)
A drop maintains its shape if cohesive forces are stronger than adhesive forces
c)
If cohesive forces are weak compared to adhesive forces, drop collapses and spreads into film
d)
Cohesive forces in mercury, consiste of metallic bonds between atoms, are strong; thus it does not wet glass
|
|
Om Desai answered |
a) True, cohesive forces are intermolecular forces between like molecules and adhesive forces between unlike molecules.
b) True, only due to cohesive force, all the molecules of droplets(which are like molecule) are attracted towards each other to form drop
c) True, if the cohesive force becomes weak as to adhesive forces, then there will be no force to bind water molecules and the drop will collapse and spread into film.
d) True, It's only due to cohesive force that mercury doesn’t wet the glass.
b) True, only due to cohesive force, all the molecules of droplets(which are like molecule) are attracted towards each other to form drop
c) True, if the cohesive force becomes weak as to adhesive forces, then there will be no force to bind water molecules and the drop will collapse and spread into film.
d) True, It's only due to cohesive force that mercury doesn’t wet the glass.
Vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mole volatile liquid A and 1 mole volatile liquid B is 350 mm Hg at 50°C. On adding 2 moles of A Into mixture, vapour pressure increases by 25 mm Hg. Thus, vapour pressure of pure components are (in mm Hg)
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mole volatile liquid A and 1 mole volatile liquid B is 350 mm Hg at 50°C. On adding 2 moles of A Into mixture, vapour pressure increases by 25 mm Hg. Thus, vapour pressure of pure components are (in mm Hg)
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
We have from Raoult’s law;-
Pmixture = xaPa+xbPb
350 = 1/2×Pa+1/2×Pb
Pa+Pb = 700
And 375 = 3/4Pa+1/4pb
On solving both equations, we get Pa = 400 and Pb = 300
Pmixture = xaPa+xbPb
350 = 1/2×Pa+1/2×Pb
Pa+Pb = 700
And 375 = 3/4Pa+1/4pb
On solving both equations, we get Pa = 400 and Pb = 300
A student was given Water, Benzene, Orange juice, and Glycerol to pipette out in four different beakers. The liquid that will be relatively difficult to be sucked into the pipette will be:- a)Orange juice
- b)Water
- c)Benzene
- d)Glycerol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A student was given Water, Benzene, Orange juice, and Glycerol to pipette out in four different beakers. The liquid that will be relatively difficult to be sucked into the pipette will be:
a)
Orange juice
b)
Water
c)
Benzene
d)
Glycerol
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Glycerol
The reason behind is that it is a viscous liquid.
The reason behind is that it is a viscous liquid.
A cylinder of V litre capacity contains ammonia gas. This cylinder is inverted over another vessel of V litre capacity containing hydrogen chloride at the same temperature and pressure. The pressure in the cylinder after sometime will- a)Remain same
- b)Become 3/2 of the original pressure
- c)Double
- d)Drop
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylinder of V litre capacity contains ammonia gas. This cylinder is inverted over another vessel of V litre capacity containing hydrogen chloride at the same temperature and pressure. The pressure in the cylinder after sometime will
a)
Remain same
b)
Become 3/2 of the original pressure
c)
Double
d)
Drop
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
As per Gay Lussac’s Law, when pressure and temperature are same V directly proportional to the moles. Let n moles of NH3 and n moles HCl after some time they react and form n moles NH4Cl and hence pressure drops.
The standard boiling point of the liquid is
- a)The boiling point at 2 atm pressure.
- b)The boiling point at 1 bar pressure.
- c)The temperature at which a liquid converts to gas.
- d)The boiling point at 1 atm pressure.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard boiling point of the liquid is
a)
The boiling point at 2 atm pressure.
b)
The boiling point at 1 bar pressure.
c)
The temperature at which a liquid converts to gas.
d)
The boiling point at 1 atm pressure.
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The answer is b.
The normal boiling point of liquid is 99.97 degreeC (211.9 degreeF) at a pressure of 1 atm (i.e., 101.325 kPa).
When one mole of monoatomic ideal gas at T K undergoes adiabatic change under a constant external pressure of 1 atm volume changes from 1 litre to 2 litre. The final temperature in Kelvin would be (2005S)- a)
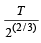
- b)
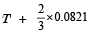
- c)T
- d)
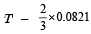
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When one mole of monoatomic ideal gas at T K undergoes adiabatic change under a constant external pressure of 1 atm volume changes from 1 litre to 2 litre. The final temperature in Kelvin would be (2005S)
a)
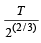
b)
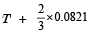
c)
T
d)
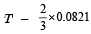
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
TVγ-1 = Constant (Q change is adiabatic) 1
T1V1γ-1= T2V2γ-1
T1V1γ-1= T2V2γ-1
For monoatomic gas γ = 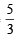
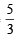
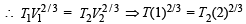
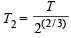
Hence A is correct.
he number of elements that exists in gaseous state under normal atmospheric conditions is- a)15
- b)10
- c)5
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
he number of elements that exists in gaseous state under normal atmospheric conditions is
a)
15
b)
10
c)
5
d)
11
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A look at the periodic table shows us that there are 11 elements in the table that exist in the gaseous state at room temperature. These elements are Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, and Radon.
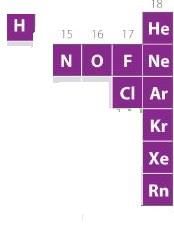
A mono-atomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which the ratio of P to V at any instant is constant and equals to 1.What is the molar heat capacity of the gas- a)
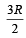
- b)2 R (2006 - 3M; –1)
- c)0
- d)
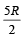
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mono-atomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which the ratio of P to V at any instant is constant and equals to 1.What is the molar heat capacity of the gas
a)
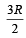
b)
2 R (2006 - 3M; –1)
c)
0
d)
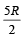
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In general, the molar heat capacity for any process is given by
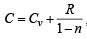 when PVn = constant
when PVn = constantHere 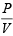 = i.e. PV–1 = constant
= i.e. PV–1 = constant
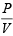 = i.e. PV–1 = constant
= i.e. PV–1 = constantFor monoatomic gas, 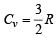
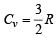
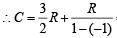
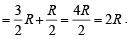
In comparing gases with liquids , gases have ........ compressibility and...........density.- a)greater, smalle
- b)greater, greater
- c)smaller, smaller
- d)smaller, greater
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In comparing gases with liquids , gases have ........ compressibility and...........density.
a)
greater, smalle
b)
greater, greater
c)
smaller, smaller
d)
smaller, greater
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
In a gas, the distance between molecules, whether monatomic or polyatomic, is very large compared with the size of the molecules; thus gases have a low density and are highly compressible.Density: The molecules of a liquid are packed relatively close together. Consequently, liquids are much denser than gases.
Hydrogen bonding reduces the quality of water molecules to
- a)repel
- b)attract
- c)compactly arrange
- d)slide over each other
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding reduces the quality of water molecules to
a)
repel
b)
attract
c)
compactly arrange
d)
slide over each other
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Hydrogen bonding is a type of attractive force that occurs between molecules when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. In water molecules, hydrogen bonding occurs between the positively charged hydrogen atoms of one water molecule and the negatively charged oxygen atoms of another water molecule. These hydrogen bonds cause the water molecules to attract each other and stick together, which gives water many of its unique properties, such as its high surface tension and its ability to act as a solvent. The hydrogen bonds do not cause the water molecules to repel each other or to compactly arrange, but they do make it more difficult for the molecules to slide over each other, which contributes to the high viscosity of water.
Dry O2 is:- a)Same as moist O2
- b)Lighter than moist O2
- c)Lighter than dry air
- d)Heavier than moist O2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dry O2 is:
a)
Same as moist O2
b)
Lighter than moist O2
c)
Lighter than dry air
d)
Heavier than moist O2
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The amount of water vapor in the air also affects the density. Water vapor is a relatively light gas when compared to diatomic Oxygen and diatomic Nitrogen. Thus, when water vapor increases, the amount of Oxygen and Nitrogen decrease per unit volume and thus density decreases because mass is decreasing.
Surface tension of water is 73 dynes cm -1 at 20° C. If surface area is increased by 0.10 m2, work done is- a)7.3 erg
- b)7.3 x 104 erg
- c)7.3 J
- d)0.73 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Surface tension of water is 73 dynes cm -1 at 20° C. If surface area is increased by 0.10 m2, work done is
a)
7.3 erg
b)
7.3 x 104 erg
c)
7.3 J
d)
0.73 J
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Work done = surface tension×Change in area
Surface tension = 73 dyne cm-1 or 73 x 10-3 N/m
Area = 0.10 m2
So, work done = 73×10-3 x 0.10
= 73 x 10-4 J or 73×10-4 x 107 erg
= 7.3×104 erg
Surface tension = 73 dyne cm-1 or 73 x 10-3 N/m
Area = 0.10 m2
So, work done = 73×10-3 x 0.10
= 73 x 10-4 J or 73×10-4 x 107 erg
= 7.3×104 erg
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure (in torr) of a mixture of volatile components A and B is g iven by ptotal = 120 - 75 x B.Hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively are- a)120,75
- b)120,95
- c)120,45
- d)75,45
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure (in torr) of a mixture of volatile components A and B is g iven by ptotal = 120 - 75 x B.
Hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively are
a)
120,75
b)
120,95
c)
120,45
d)
75,45
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
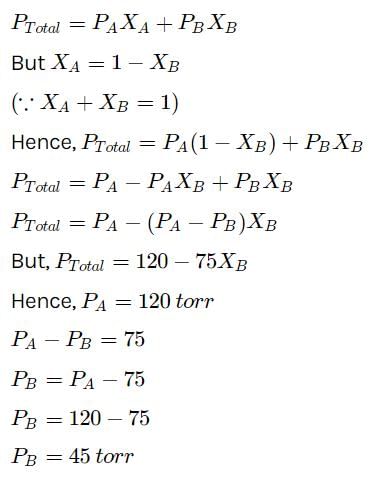
As the temperature is raised from 20°C to 40°C, the average kinetic energy of neon atoms changes by a factor of which of the following ? [AIEEE-2004]- a)
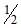
- b)
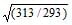
- c)
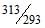
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
As the temperature is raised from 20°C to 40°C, the average kinetic energy of neon atoms changes by a factor of which of the following ? [AIEEE-2004]
a)
b)
c)
d)
2
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Average kinetic energy ∝ Temperature in Kelvin
(KE40) / (KE20) = (3/2 nR * 313)/(3/2 nR*293)
KE40 / KE20 = T2/T1 = 40 + 273 / 20 + 273 = 313/293
If 10–4 dm3 of water is introduced into a 1.0 dm3 flask at 300 K, how many moles of water are in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ? [2010](Given : Vapour pressure of H2O at 300 K is 3170 Pa; R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1)- a)5.56× 10–3 mol
- b)1.53 × 10–2 mol
- c)4.46 × 10–2 mol
- d)1.27 × 10–3 mol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 10–4 dm3 of water is introduced into a 1.0 dm3 flask at 300 K, how many moles of water are in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ? [2010]
(Given : Vapour pressure of H2O at 300 K is 3170 Pa; R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1)
a)
5.56× 10–3 mol
b)
1.53 × 10–2 mol
c)
4.46 × 10–2 mol
d)
1.27 × 10–3 mol
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
From the ideal gas equation :
PV = nRT or n = 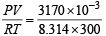 = 1.27 × 10–3
= 1.27 × 10–3
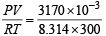 = 1.27 × 10–3
= 1.27 × 10–3Which of the following properties of water can be used to explain the spherical shape of rain droplets?- a)Viscosity
- b)Surface tension
- c)Critical phenomenon
- d)Vapour pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following properties of water can be used to explain the spherical shape of rain droplets?
a)
Viscosity
b)
Surface tension
c)
Critical phenomenon
d)
Vapour pressure
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
A simple way to form a drop is to allow liquid to flow slowly from the lower end of a vertical tube of small diameter. The surface tension of the liquid causes the liquid to hang from the tube, forming a pendant. When the drop exceeds a certain size it is no longer stable and detaches itself. The falling liquid is also a drop held together by surface tension.
The correct value of R is - [aieee-2002]- a)R = 0.082 litre-atm
- b)R = 8.314 × 107 erg K-1 mol-1
- c)R = 2 k-1 mol-1
- d) None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct value of R is - [aieee-2002]
a)
R = 0.082 litre-atm
b)
R = 8.314 × 107 erg K-1 mol-1
c)
R = 2 k-1 mol-1
d)
None
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The different values of R are as follow:-
8.314 J mol-1 K-1, 8.314×107 erg mol-1 K-1, 0.0821 atm-lit mol-1 K-1 or 2 cal mol-1 K-1
8.314 J mol-1 K-1, 8.314×107 erg mol-1 K-1, 0.0821 atm-lit mol-1 K-1 or 2 cal mol-1 K-1
When r, P and M represent rate of diffusion, pressure and molecular mass, respectively, then the ratio of the rates of diffusion (rA/rB) of two gases A and B, is given as - [AIEEE - 2011]- a)(PA/PB) (MB/MA)1/2
- b)(PA/PB)1/2 (MB/MA)
- c)(PA/PB) (MA/MB)1/2
- d)(PA/PB)1/2 (MA/MB)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When r, P and M represent rate of diffusion, pressure and molecular mass, respectively, then the ratio of the rates of diffusion (rA/rB) of two gases A and B, is given as -
[AIEEE - 2011]
a)
(PA/PB) (MB/MA)1/2
b)
(PA/PB)1/2 (MB/MA)
c)
(PA/PB) (MA/MB)1/2
d)
(PA/PB)1/2 (MA/MB)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is option A
Rate of diffusion: r α p

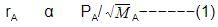
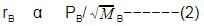
rA/rB = pA/pB.(MB/MA)1/2
Hence, pBpA (MB/MA)1/2 is the answer.
Rate of diffusion: r α p

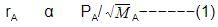
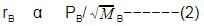
rA/rB = pA/pB.(MB/MA)1/2
Hence, pBpA (MB/MA)1/2 is the answer.
Intermolecular forces can be out of the following.- a)van der Waais' forces
- b)Electrostatic forces existing between two oppositely charged ions
- c)Covalent bond between two like atoms
- d)Gravitational force
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Intermolecular forces can be out of the following.
a)
van der Waais' forces
b)
Electrostatic forces existing between two oppositely charged ions
c)
Covalent bond between two like atoms
d)
Gravitational force
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
In molecular physics, the van der Waals forces, named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, are distance-dependent interactions between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions are not a result of any chemical electronic bond, and they are comparatively weak and more susceptible to being perturbed. Van der Waals forces quickly vanish at longer distances between interacting molecules.
Van der Waals forces play a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. Van der Waals forces also define many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media.
Normal boiling point is- a)The boiling point at 1 bar pressure.
- b)The boiling point at 1 atm pressure.
- c)The boiling point at 2 bar pressure.
- d)The temperature at which a liquid converts to gas.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Normal boiling point is
a)
The boiling point at 1 bar pressure.
b)
The boiling point at 1 atm pressure.
c)
The boiling point at 2 bar pressure.
d)
The temperature at which a liquid converts to gas.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The boiling point of a liquid at 1 atm is also known as the normal boiling point. It has been found that Helium has the lowest normal boiling point (−268.9 °C) because it has very weak intermolecular attractions. Liquids that have high vapour pressures and low boiling points are known to be volatile, which means they evaporate quickly at room temperature. When the temperature increases, molecules start entering the gaseous state, consequently increasing the vapor pressure of the liquid until it comes into equilibrium with the atmospheric pressure.
The root mean square velocity of an ideal gas at constant pressure varies with density (d) as (2001S)- a)d2
- b)d
- c)
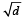
- d)1/
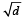
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The root mean square velocity of an ideal gas at constant pressure varies with density (d) as (2001S)
a)
d2
b)
d
c)
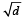
d)
1/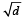
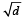
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
URMS = 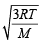 Using ideal gas equation,
Using ideal gas equation,
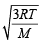 Using ideal gas equation,
Using ideal gas equation,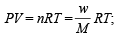
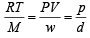 where d is the
where d is thedensity of the gas
∴ URMS = 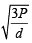 at constant pressure,
at constant pressure, 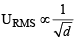
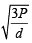 at constant pressure,
at constant pressure, 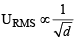
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).Passage IFor a given liquid at a given temperature vapour pressure is given by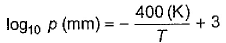 Q. Thus, vapour pressure of the liquid at 400 K is
Q. Thus, vapour pressure of the liquid at 400 K is- a)2 mm
- b)100 mm
- c)103 mm
- d)20 mm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage I
For a given liquid at a given temperature vapour pressure is given by
Q. Thus, vapour pressure of the liquid at 400 K is
a)
2 mm
b)
100 mm
c)
103 mm
d)
20 mm
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Substitute T equal to 400 K in RHS and solve the log.
log(base 10)p = 2
⇒ 10² = p
⇒ p = 100 mm
log(base 10)p = 2
⇒ 10² = p
⇒ p = 100 mm
Van der waals forces include the following except
- a)London forces
- b)dipole - dipole forces
- c)dipole- include dipole forces
- d)chemical bonding forces
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Van der waals forces include the following except
a)
London forces
b)
dipole - dipole forces
c)
dipole- include dipole forces
d)
chemical bonding forces
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Chemical bonding forces are not considered to be part of van der Waals forces. Van der Waals forces include London forces, dipole-dipole forces, and dipole-induced dipole forces.
The mass of 112 ml of N2 at STP on liquefaction is:- a)0.84 g
- b)0.56 g
- c)0.28 g
- d)0.14 g
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of 112 ml of N2 at STP on liquefaction is:
a)
0.84 g
b)
0.56 g
c)
0.28 g
d)
0.14 g
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Number of moles when condition of STP is given by given volume divided by 22400 this will give number of moles and after that number of moles X molecular mass will give the mass of the given sample.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The vapour pressure of benzene C6H6 at 298 K is 95 torr. After 10.00 g of benzene is injected into a 10.0 L bulb at 298 K, how many grams of benzene remain as liquid?
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. The vapour pressure of benzene C6H6 at 298 K is 95 torr. After 10.00 g of benzene is injected into a 10.0 L bulb at 298 K, how many grams of benzene remain as liquid?
|
|
Sanchita Chakraborty answered |
Question Analysis
The question provides the initial conditions of a system (vapour pressure of benzene at 298 K) and asks for the final state of the system (grams of benzene remaining as liquid after injection into a bulb). To solve this problem, we need to apply the concept of vapour pressure and use the ideal gas law.
Solution
Step 1: Calculate the number of moles of benzene
Given:
- Mass of benzene (m) = 10.00 g
- Molar mass of benzene (M) = 78.11 g/mol
Using the formula:
Number of moles (n) = mass / molar mass
Substituting the given values:
n = 10.00 g / 78.11 g/mol
n ≈ 0.128 mol
Step 2: Calculate the initial number of moles of benzene in the vapor phase
Given:
- Total volume of the bulb (V) = 10.0 L
- Vapour pressure of benzene (P) = 95 torr
Using the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
Rearranging the formula:
n = PV / RT
Substituting the given values:
n = (95 torr) * (10.0 L) / (0.0821 L·atm/mol·K) * (298 K)
n ≈ 3.84 mol
Step 3: Calculate the number of moles of benzene in the liquid phase
Given:
- Initial number of moles of benzene = 0.128 mol
- Number of moles of benzene in the vapor phase = 3.84 mol
Using the law of conservation of mass:
Number of moles of benzene in the liquid phase = Initial number of moles - Number of moles in the vapor phase
Substituting the given values:
Number of moles of benzene in the liquid phase = 0.128 mol - 3.84 mol
Number of moles of benzene in the liquid phase ≈ -3.712 mol
Step 4: Calculate the mass of benzene remaining as liquid
Given:
- Molar mass of benzene (M) = 78.11 g/mol
Using the formula:
Mass of benzene remaining as liquid = Number of moles of benzene in the liquid phase * Molar mass of benzene
Substituting the given values:
Mass of benzene remaining as liquid = -3.712 mol * 78.11 g/mol
Mass of benzene remaining as liquid ≈ -289.57 g
Since mass cannot be negative, the negative sign indicates an error in the calculations.
Step 5: Identifying the error and correcting it
The error in the calculations is likely due to the assumption that all the benzene injected into the bulb vaporizes. However, in reality, only a fraction of the benzene will vaporize based on its vapour pressure.
To correct the error, we need to determine the fraction of benzene that vaporizes and subtract it from the initial mass of benzene.
Step 6: Calculate the fraction of benz
If Z is a compressibility factor, van der Waals equation at low pressure can be written as: [JEE M 2014]- a)
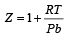
- b)
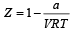
- c)
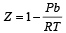
- d)
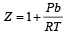
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If Z is a compressibility factor, van der Waals equation at low pressure can be written as: [JEE M 2014]
a)
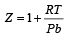
b)
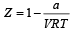
c)
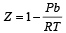
d)
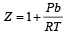
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Compressibility factor (Z) = 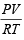
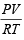
(For one mole of real gas) van der Waals equation
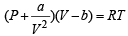
At low pressure, volume is very large and hence correction term b can be neglected in comparison to very large volume of V.
i.e. 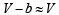
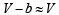
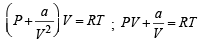
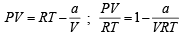
Hence, 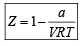
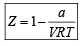
Thermal energy is directly proportional to:- a)Temperature of the surrounding
- b)Temperature of the substance
- c)Density
- d)Pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Thermal energy is directly proportional to:
a)
Temperature of the surrounding
b)
Temperature of the substance
c)
Density
d)
Pressure
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Thermal energy is the sum of all the random kinetic energies of the molecules in a substance, that is, the energy in their motions. The higher the temperature, the greater the thermal energy. On the Kelvin temperature scale, thermal energy is directly proportional to temperature.
If 10-4 dm3 of water is introduced into a 1.0 dm3 flask at 300 K, how many moles of water are in in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ? [aieee-2010](Given : Vapour pressure of H2O at 300 is 3170 pa; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol)- a)1.27 x 10-3 mol
- b)5.56 × 10-3 mol
- c) 1.53 x10-2 mol
- d)4346 × 10-2 mol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 10-4 dm3 of water is introduced into a 1.0 dm3 flask at 300 K, how many moles of water are in in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ? [aieee-2010]
(Given : Vapour pressure of H2O at 300 is 3170 pa; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol)
a)
1.27 x 10-3 mol
b)
5.56 × 10-3 mol
c)
1.53 x10-2 mol
d)
4346 × 10-2 mol
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The volume occupied by water molecules in vapour phase is (1×10−4) dm3, that is approximately (1×10−3) m3.
pvapV = nH2O mol
3170 × 1 × 10−3 = nH2O × 8.314 × 300K
nH2O = 3170 × 1 × 10−3 / 8.314 × 300
= 1.27 × 10−3 mol
pvapV = nH2O mol
3170 × 1 × 10−3 = nH2O × 8.314 × 300K
nH2O = 3170 × 1 × 10−3 / 8.314 × 300
= 1.27 × 10−3 mol
A gaseous hydrocarbon gives upon combustion 0.72 g of water and 3.08 g. of CO2. The empirical formula of the Hydrocarbon is : [Jee(Main) 2013, 3/120]- a) C2H4
- b)C3H4
- c)C6H5
- d)C7H8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A gaseous hydrocarbon gives upon combustion 0.72 g of water and 3.08 g. of CO2. The empirical formula of the Hydrocarbon is : [Jee(Main) 2013, 3/120]
a)
C2H4
b)
C3H4
c)
C6H5
d)
C7H8
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
General equation for combustion of hydrocarbon:
CxHy + (x+ y/4)O2 → xCO2 + (y/2)H2O
Number of moles of CO2 produced = 3.08/44 = 0.07
Number of moles of H2O produced = 0.72/18 = 0.04
SO, x / (y/2) = 0.07/0.04 = 7/4
The formula of hydrocarbon is C7H8
Hence, the correct option is D.
The no. of moles per litre in the equation PV = nRT is expressed by - [aieee-2002]- a)
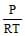
- b)
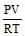
- c)
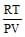
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The no. of moles per litre in the equation PV = nRT is expressed by - [aieee-2002]
a)
b)
c)
d)
None

|
Chinmaykumar811 Rout answered |
See qn . given .....per litre..... that means v=1.Then look at options If any option don't contain V that will be answer otherwise select ...none ...Hence option A correct.
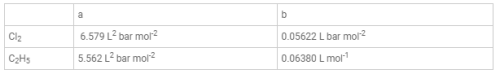
`a' and `b' are Vander Waals' constant for gases. Chlorine is more easily liquefied than ethane because : [aieee-2011]- a) A and b for Cl2 > a and b for C2H6
- b)A and b for Cl2 < a and b for C2H6
- c)A for Cl2 < a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 > b for C2H6
- d)A for Cl2 > a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 < b for C2H6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
`a' and `b' are Vander Waals' constant for gases. Chlorine is more easily liquefied than ethane because : [aieee-2011]
a)
A and b for Cl2 > a and b for C2H6
b)
A and b for Cl2 < a and b for C2H6
c)
A for Cl2 < a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 > b for C2H6
d)
A for Cl2 > a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 < b for C2H6

|
Sanchita Reddy answered |
Vander Waals, constant a is due to force of attraction and b due to the infinite size of molecules. Thus, greater the value a and smaller the value b, larger the liquefaction.

In van der Waals equation of state of the gas law, the constant `b' is a measure of -[AIEEE-2004]- a) Intermolecular repulsions
- b) Intermolecular attraction
- c)Volume occupied by the molecules
- d) Intermolecular collisions per unit volume
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In van der Waals equation of state of the gas law, the constant `b' is a measure of -
[AIEEE-2004]
a)
Intermolecular repulsions
b)
Intermolecular attraction
c)
Volume occupied by the molecules
d)
Intermolecular collisions per unit volume
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
In van der Waals equation of state of the gas law, the constant b is a measure of the volume occupied by the molecules.
It gives the effective size of the gas molecules. The greater value of b indicates a larger size of the molecules and smaller compressible volume.
It gives the effective size of the gas molecules. The greater value of b indicates a larger size of the molecules and smaller compressible volume.
Dipole-dipole interaction energy between stationary polar molecules is proportional to x and that between rotating molecules is proportional to y. Assume distance between polar molecules as r, then x and y are- a)
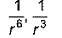
- b)
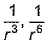
- c)
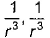
- d)
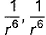
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dipole-dipole interaction energy between stationary polar molecules is proportional to x and that between rotating molecules is proportional to y. Assume distance between polar molecules as r, then x and y are
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Dipole-dipole interaction energy between stationary polar molecules is proportional to 1/ r3 and that between rotating polar molecules is proportional to 1/ r6 where ‘r’ is the distance between polar molecules
Besides dipole - dipole interaction, polar molecules can interact by London forces also.
Atom which must be present in hydrogen bonding is- a)hydrogen
- b)sodium
- c)calcium
- d)sulphur
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Atom which must be present in hydrogen bonding is
a)
hydrogen
b)
sodium
c)
calcium
d)
sulphur
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
A hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge.
The interaction energy of London force is inversely proportional to sixth power of the distance between two interacting particles but their magnitude depends upon- a)charge of interacting particles
- b)mass of interacting particles
- c)strength of permanent dipoles in the particles
- d)polarisability of interacting particles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The interaction energy of London force is inversely proportional to sixth power of the distance between two interacting particles but their magnitude depends upon
a)
charge of interacting particles
b)
mass of interacting particles
c)
strength of permanent dipoles in the particles
d)
polarisability of interacting particles
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The interaction energy of London force is inversely proportional to sixth power of the distance between two interacting particles but their magnitude depends upon. (d) strength of permanent dipoles in the particles.
Based on the following statements I and IS, select the correct answer from the codes given.Statement I Three states of matter are the result of balance between intermolecular forces and thermal energy of the molecules.Statement IIIntermolecular forces tend to keep the molecules together but thermal energy of molecules tends to keep them apart.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement il is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the following statements I and IS, select the correct answer from the codes given.
Statement I
Three states of matter are the result of balance between intermolecular forces and thermal energy of the molecules.
Statement II
Intermolecular forces tend to keep the molecules together but thermal energy of molecules tends to keep them apart.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement il is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Thermal energy is the energy of a body arising from motion of its atoms or molecules. It is directly proportional to the temperature of the substance. It is the measure of average kinetic energy of the particles of the matter and is thus responsible for movement of particles. This movement of particles is called thermal motion. We have already learnt that intermolecular forces tend to keep the molecules together but thermal energy of the molecules tends to keep them apart. Three states of matter are the result of balance between intermolecular forces and the thermal energy of the molecules.
Among the following sentences the one that is false about gases is- a)Gases have low densities
- b)The gases mix evenly and uniformly without any mechanical aid.
- c)The pressure exerted by gases on the walls of the container is equal in all the directions.
- d)Gases are highly compressible because their molecules are very tightly packed.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following sentences the one that is false about gases is
a)
Gases have low densities
b)
The gases mix evenly and uniformly without any mechanical aid.
c)
The pressure exerted by gases on the walls of the container is equal in all the directions.
d)
Gases are highly compressible because their molecules are very tightly packed.
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Gasses are highly compressible because it is less dense than other states of matter. it's intermolecular force of attraction is less and it has more space between the molecules. Therefore, it is easy to compress gas.
While, solids are almost incompressible. This is because the intermolecular force of attraction in solids is greater compared to other states of matter. The moles in solids are tightly packed. Therefore, solids are almost incompressible.
While, solids are almost incompressible. This is because the intermolecular force of attraction in solids is greater compared to other states of matter. The moles in solids are tightly packed. Therefore, solids are almost incompressible.
Choose the correct statement with respect to the vapour pressure of a liquid among the following.- a)Increases linearly with increasing temperature
- b)Increases non-linearly with increasing temperature
- c)Decreases linearly with increasing temperature
- d)Decreases non-linearly with increasing temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement with respect to the vapour pressure of a liquid among the following.
a)
Increases linearly with increasing temperature
b)
Increases non-linearly with increasing temperature
c)
Decreases linearly with increasing temperature
d)
Decreases non-linearly with increasing temperature
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Vapour pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the vapours above the liquid surface in equilibrium with the liquid at a given temperature. The vapour pressure of a liquid increases non-linearly with increasing temperature.
This is because kinetic energy is the function of temperature which means that as the temperature is increased, more molecules will have greater kinetic energies and thus they can escape from the surface of the liquid to the vapour phase resulting in higher vapour pressure.
This is because kinetic energy is the function of temperature which means that as the temperature is increased, more molecules will have greater kinetic energies and thus they can escape from the surface of the liquid to the vapour phase resulting in higher vapour pressure.
Arrange ortho, meta and para-nitrophenols in increasing boiling points- a)para < meta < ortho
- b)ortho < para < meta
- c)ortho = para = meta
- d)ortho < meta < para
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange ortho, meta and para-nitrophenols in increasing boiling points
a)
para < meta < ortho
b)
ortho < para < meta
c)
ortho = para = meta
d)
ortho < meta < para
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Para has max packing efficiency due to its symmetrical structure and it also forms intermolecular H-bonds. Meta derivative has comparatively low packing efficiency but forms intermolecular H-bonds and ortho derivative has the least packing efficiency and does not form intermolecular hydrogen bonds instead it forms intramolecular hydrogen bond which doesn't have any role in increasing the boiling point.
Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially at pressure pi and temperature T1 are connected through a narrow tube of negligible volume as shown in the figure below. The temperature of one of the bulbs is then raised to T2. The final pr essur e pf is : [JEE M 2016]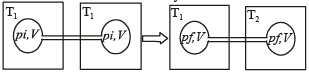
- a)
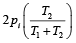
- b)
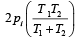
- c)
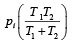
- d)
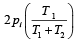
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially at pressure pi and temperature T1 are connected through a narrow tube of negligible volume as shown in the figure below. The temperature of one of the bulbs is then raised to T2. The final pr essur e pf is : [JEE M 2016]

a)
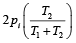
b)
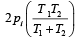
c)
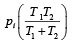
d)
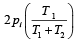
|
|
Vicky Kumar answered |
Kinetic theory of gases proves [2002]- a)only Boyle’s law
- b)only Charles’ law
- c)only Avogadro’s law
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinetic theory of gases proves [2002]
a)
only Boyle’s law
b)
only Charles’ law
c)
only Avogadro’s law
d)
All of these.

|
Avantika Joshi answered |
(d) : Explanation of the Gas Laws on the basis of Kinetic Molecular Model One of the postulates of kinetic theory of gases is
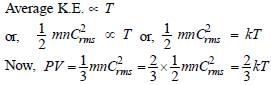
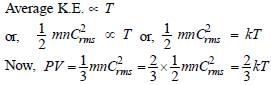
(i) Boyle’s Law :
1. Constant temperature means that the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules remains constant.
1. Constant temperature means that the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules remains constant.
2. This means that the rms velocity of the molecules, Crms remains unchanged.
3. If the rms velocity remains unchanged, but the volume increases, this means that there will be fewer collisions with the container walls over a given time.
4. Therefore, the pressure will decrease
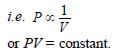
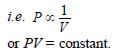
(ii) Charles’ Law :
1. An increase in temperature means an increase in the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules, thus an increase in crms.
1. An increase in temperature means an increase in the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules, thus an increase in crms.
2. There will be more collisions per unit time, furthermore, the momentum of each collision increases (molecules strike the wallharder).
3. Therefore, there will be an increase in pressure.
4. If we allow the volume to change to maintain constant pressure, the volume will increase with increasing temperature (Charles law).
(iii) Avogadro’s Law
It states that under similar conditions of pressure and temperature, equal volume of all gases contain equal number of molecules. Considering
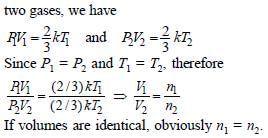
It states that under similar conditions of pressure and temperature, equal volume of all gases contain equal number of molecules. Considering
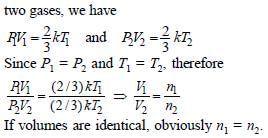
Standard enthalpy of vaporization is taken at:- a)273 K
- b)0°C
- c)25°C
- d)298 K
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Standard enthalpy of vaporization is taken at:
a)
273 K
b)
0°C
c)
25°C
d)
298 K

|
Aditya Sengupta answered |
The problem deals with variation of enthalpy with temperature (Kirchhoff's Law). The standard enthalpy of vaporization of water at 298 K and 1 bar is thus: The heat absorbed to vaporize m = 250 g of water at 298 K and 1 bar: This is the energy content of two slices of dry toast.
Which one will have higher value of enthalpy of vaporization:- a)Liquid having weak hydrogen bonds
- b)Liquid having strong attractive forces
- c)Liquid having no attractive forces
- d)Liquid having weak attractive forces
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one will have higher value of enthalpy of vaporization:
a)
Liquid having weak hydrogen bonds
b)
Liquid having strong attractive forces
c)
Liquid having no attractive forces
d)
Liquid having weak attractive forces
|
|
Anmol Chauhan answered |
Higher value of enthalpy of vaporization means that we need to give high heat for the given liquid to vapour. So this is possible with only option b because with only option b, there is enough strong attractive force which we need to overcome by providing the most amount of heat in all the given cases.
Chapter doubts & questions for Liquid state - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Liquid state - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup