All questions of Theory of Consumer Behaviour for Humanities/Arts Exam
A budget constraint line is a result of?- a)Market price of commodity X
- b)Market price of commodity Y
- c)Income of the consumer
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The want satisfying power of a commodity is known as:- a)Utility
- b)Consumption
- c)Supply
- d)Demand
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
One factor that causes a leftward shift of the demand curve out of the following is- a) Rise in income
- b) Fall in the price of substitute goods
- c) Rise in the price of complementary goods
- d) Fall in income
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, _________?- a)Additional consumption always yields extra utility
- b)Additional consumption leads to lower average total utility
- c)Additional consumption always yields negative utility
- d)After a point any addition in the consumption causes a reduction in total utility.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Which of the following curve has a negative slope and cannot interest each other?- a)Isoquants
- b)Demand and supply curves
- c)Indifference curves
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Each indifference curve is convex to the origin, and no two indifference curves ever intersect.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - Theory of Consumer Behaviour of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?
- A:
It helps consumers to make choices.
- B:
Utility is always measurable.
- C:
It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
- D:
It is purely a subjective entity.
The answer is B.
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - Theory of Consumer Behaviour of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?
It helps consumers to make choices.
Utility is always measurable.
It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
It is purely a subjective entity.

|
Priyanka Ravichandran answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Indifference curve represents?
- A:
Four commodities
- B:
Less than two commodities
- C:
Only two commodities
- D:
More than two commodities
The answer is C.
Indifference curve represents?
Four commodities
Less than two commodities
Only two commodities
More than two commodities
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
The coefficient of price elasticity of demand is always- a)Zero
- b)Undefined
- c)Positive
- d)Negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Utility is measured in terms of?- a)Centimeter
- b)Seconds
- c)Gram
- d)Utils
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Consumer’s surplus is also known as?- a)Buyer’s surplus
- b)Elasticity of demand
- c)Differential surplus
- d) Indifference surplus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
At what point does total utility starts diminishing?- a)When marginal utility is negative
- b)When marginal utility remains constant
- c)When marginal utility is increasing
- d)When marginal utility is postive
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Arya Reddy answered |
Which of the following will have inelastic demand?- a)Fruits
- b)ice-cream
- c)petrol
- d)Medicine
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
A curve which first moves upwards then downwards is__________?- a)Total utility curve
- b)Demand curve
- c)Indifference curve
- d)Marginal utility curve
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Which of the following curve has a negative slope and cannot interest each other?- a)None of above
- b)Indifference curves
- c)Demand and supply curves
- d)Isoquants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:What is called point of satiety?
- A:
The point where marginal utility becomes less than zero
- B:
The point where marginal utility becomes greater than zero
- C:
The point where marginal utility becomes zero.
- D:
None of above
The answer is C.
What is called point of satiety?
The point where marginal utility becomes less than zero
The point where marginal utility becomes greater than zero
The point where marginal utility becomes zero.
None of above
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
At what point does total utility starts diminishing?- a)When marginal utility remains constant
- b)When marginal utility is increasing
- c) When marginal utility is negative
- d)When marginal utility is negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Total utility curve:- a)First falls and then rises
- b)Always falls
- c)Always rises
- d)First rises at an increasing rate, then rises at a decreasing rate and falls after reaching its maximum.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The concept of marginal utility was developed by?- a)Paul Samuelson
- b)Alfred Marshall
- c)Hicks & Allen
- d)Robbins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Which of the following utility approach is based on the theory of Alfred Marshall?- a)None of these
- b) Ordinal utility approach
- c) Independent variable approach
- d) Cardinal utility approach
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Om Desai answered |
It was Alfred Marshall who first discussed the role played by the theory of utility in the theory of value. In Marshall's theory, the concept of utility is cardinal.
When the total utility is increasing at an increasing rate, marginal utility is___________?- a)Increasing
- b)Constant
- c)Negative
- d)Decreasing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?- a)Utility is always measurable.
- b) It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
- c) It helps consumers to make choices.
- d) It is purely a subjective entity.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
_____________ is defined as the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay for a product and what he actually pays?- a)Consumer surplus
- b)Price gap
- c)Consumer burden
- d)Optimum price
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Devansh Goyal answered |
The slope of price line throughout its length?- a)Remains the same
- b)Is equal on the other side of the mid points
- c)Differs from point to point
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Which of the following utility approach is based on the theory of Alfred Marshall?- a)Independent variable approach
- b)Cardinal utility approach
- c)Ordinal utility approach
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Marginal utility curve of a given consumer is also his?- a)Demand curve
- b)Supply curve
- c)Indifference curve
- d)Total utility curve
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
One factor that causes a movement along the demand curve of a commodity- a)Fall in price of the good
- b)Rise in income
- c)Fall in the price of substitute goods
- d)Rise in the price of complementary goods
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
_____________ is defined as the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay for a product and what he actually pays?- a)Consumer burden
- b)Consumer surplus
- c)Price gap
- d) Optimum price
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Consumer surplus always increases as the price of a good falls and decreases as the price of a good rises.
A consumer reaches equilibrium when?- a)
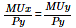
- b)
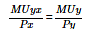
- c)
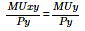
- d)
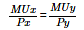
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Shashank Kr. Sarraf answered |
Which of the following is not true?- a)Indifference curves cannot intersect each other
- b)Two indifference curve can be tangent to each other
- c)Indifference curves are convex to the origin
- d)Indifference curves slopes downward to the right
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Which of the following statements regarding ordinal utility is true?- a)Utility can be measured, but cannot be ranked in order of preferences.
- b)Utility can neither be measured nor can be ranked in order of preferences.
- c)Utility can be measured and can also be ranked in order of preferences.
- d)Utility cannot be measured, but can be ranked in order of preferences.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
For example, we prefer a BMW car to a Nissan car, but we don’t say by how much.
Which of the following will have elastic demand?- a)Fruits
- b)Salt
- c)School uniform
- d)Medicine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Which of the following utility approach suggests that utility is a measurable and quantifiable entity?- a)Ordinal approach
- b)Cardinal approach
- c)Both cardinal & ordinal
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
_____________ is the addition to total utility by the consumption of one additional unit of the commodity?- a)Average utility
- b)Ordinal utility
- c)Marginal utility
- d)Total utility
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Which of the following assumption is not necessary for the cardinal utility theory?- a)Perfectly competitive market
- b)Constant marginal utility of money
- c)Rationality of the consumer
- d)Cardinal measurability of utility
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - Theory of Consumer Behaviour of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinationsQ Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?- a)It helps consumers to make choices.
- b)Utility is always measurable.
- c)It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
- d)It is purely a subjective entity.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Consumer’s surplus is also known as?- a)Elasticity of demand
- b)Indifference surplus
- c)Buyer’s surplus
- d) Differential surplus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rashi Bose answered |
____________ shows various combinations of two goods that give same amount of satisfaction to the consumer?- a)Isocost curve
- b)Marginal utility curve
- c)Indifference curve
- d)Isoquant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
In case of relatively more elastic, demand curve is:- a)Horizontal
- b)Vertical
- c)Steeper
- d)Flatter
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Due to a rise in the price of a good by Rs.5, its demand decreases from 100 units to 95 units. Its price elasticity of demand is 1.2. Calculate the price before the change.
- a)Rs. 20
- b)Rs. 100
- c)Rs. 120
- d)Rs. 240
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Consumer surplus is more in the case of______________?- a)Inferior goods
- b)Necessities
- c)Luxuries
- d)Comforts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, _________?- a)Additional consumption always yields extra utility
- b)Additional consumption leads to lower average total utility
- c)After a point any addition in the consumption causes a reduction in total utility.
- d)Additional consumption always yields negative utility
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghav Shah answered |
MU1 + MU2 + ……..MUn represents?- a)Total utility of a commodity
- b)Total marginal utility
- c)Total average utility
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Utility of a good can be explained as a?- a)Monetary value a consumer gains from consuming a particular good
- b)Difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and actually pays
- c)Desire to consume
- d)Satisfaction that a consumer derives from the consumption of a particular good.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Yuvraj Bhardwaj answered |
What is called point of satiety?- a)The point where marginal utility becomes less than zero
- b)The point where marginal utility becomes greater than zero
- c)The point where marginal utility becomes zero.
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Kaavya Mukherjee answered |
Due to a 10 percent fall in the price of a good, its demand rises from 400 units to 450 units. Calculate its price elasticity of demand.- a) 3.25.
- b)3.25.
- c)25. 2.
- d)1.25
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Pranavi Das answered |
Given data:
Initial demand = 400 units
Final demand = 450 units
Percentage change in price = -10%
Using the formula for calculating price elasticity of demand:
Price elasticity of demand = (Percentage change in quantity demanded) / (Percentage change in price)
Percentage change in quantity demanded = ((Final demand - Initial demand) / Initial demand) x 100%
= ((450 - 400) / 400) x 100%
= 12.5%
Percentage change in price = -10%
Price elasticity of demand = (12.5% / -10%) = -1.25
Since price elasticity of demand is a positive value, we take the absolute value of -1.25, which is 1.25. Therefore, the correct answer is option D) 1.25.
MU1 + MU2 + ……..MUn represents?- a)Total marginal utility
- b)Total utility of a commodity
- c)Total average utility
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
According to Marshall, the law of diminishing marginal utility applies on ___________?- a)All commodities except money
- b)Bank money
- c)Money in the same manner as it applies on the commodity
- d)Cash but not on bank money
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The value of elasticity in case of a horizontal line will be- a)One
- b)Greater than one
- c)Infinity
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sai Mishra answered |
An indifference curve indicates, ceteris paribus?- a)Combinations of goods which yield to a producer different levels of satisfaction
- b)Combinations of goods which yield to a consumer equal degrees of satisfaction
- c)Combinations of goods which yield to a consumer different levels of satisfaction
- d)A consumer’s preference for any two goods
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Chapter doubts & questions for Theory of Consumer Behaviour - Economics Practice Tests: CUET Preparation 2024 is part of Humanities/Arts exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Humanities/Arts 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|










