All Exams >
Class 9 >
Science Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of The Fundamental Unit of Life for Class 9 Exam
Living cells were discovered by- a)Robert Hooke
- b)Purkinje
- c)Leeuwenhoek
- d)Robert Brown
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Living cells were discovered by
a)
Robert Hooke
b)
Purkinje
c)
Leeuwenhoek
d)
Robert Brown
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Robert Hooke, a scientist, was the first person to discover the existence of cells with the help of a microscope in 1665 but they were dead cells.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek, in 1674 with the improved microscope, discovered free-living cells of algae Spirogyra in pond water for the first time.
Which organelle is called the suicide bag of the cell- a)Golgi bodies
- b)Centrosome
- c)Chloroplast
- d)Lysosome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which organelle is called the suicide bag of the cell
a)
Golgi bodies
b)
Centrosome
c)
Chloroplast
d)
Lysosome
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
Lysosomes are called suicide bags of the cells because they contain digestive enzymes to digest the food taken by cell and if these enzymes spread in the cell or the membrane of lysosomes break down then the digestive enzymes digest the whole cell and the cell dies
so they are called suicide bags of the cell
Which of the following substance is not present in the cell?- a)Soil
- b)Water
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)Proteins
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following substance is not present in the cell?
a)
Soil
b)
Water
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
Proteins
|
|
Avani Shah answered |
Explanation:
- Soil: Soil is not present in the cell. It is a mixture of organic and inorganic materials found on the surface of the Earth.
- Water: Water is a major component of the cell. It is essential for various metabolic activities and helps in maintaining the shape and structure of the cell.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are one of the main types of nutrients found in the cell. They provide energy to the cell and are involved in various cellular processes.
- Proteins: Proteins are another important component of the cell. They perform a wide range of functions such as enzyme catalysis, structural support, and signaling.
Which of the following is known as “physical basis of life”?- a)Nucleolus
- b)Gene
- c)Protoplasm
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is known as “physical basis of life”?
a)
Nucleolus
b)
Gene
c)
Protoplasm
d)
Mitochondria

|
Prasenjit Kulkarni answered |
The physical basis of life is protoplasm which contains all the cell organelles present in the cell.
Which statement is false with respect to multi-cellular organisms?- a)Multicellular organisms show division of labour.
- b)In multi-cellular organisms, groups of cells perform specific roles.
- c)Different groups of cells are inter-dependent on each other for their continued existence.
- d)All the cells perform the same function in a multi-cellular organism.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is false with respect to multi-cellular organisms?
a)
Multicellular organisms show division of labour.
b)
In multi-cellular organisms, groups of cells perform specific roles.
c)
Different groups of cells are inter-dependent on each other for their continued existence.
d)
All the cells perform the same function in a multi-cellular organism.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Unicellular organisms are made up of only one cell that carries out all the functions needed by the organism, while multicellular organisms use many different cells to function. Multicellular organisms are composed of more than one cell, with groups of cells differentiating to take on specialized functions
Which of the following organelles is smallest in size?- a)Ribosome
- b)Mitochondrial
- c)Chloroplast
- d)Lysosome
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organelles is smallest in size?
a)
Ribosome
b)
Mitochondrial
c)
Chloroplast
d)
Lysosome
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Ribosomes are primary site of protein synthesis or translation and measure 20 nm.
Lysosomes or "suicidal bags" of the cell measure 200 nm.
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell are site of cellular respiration measures 3000 nm
Chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis and measures 5000 nm.
Therefore, ribosomes are smallest of all.
Lysosomes or "suicidal bags" of the cell measure 200 nm.
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell are site of cellular respiration measures 3000 nm
Chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis and measures 5000 nm.
Therefore, ribosomes are smallest of all.
Animal cells do not show the presence of- a)Cell membrane
- b)Cytoplam
- c)Cell wall
- d)Nucleus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Animal cells do not show the presence of
a)
Cell membrane
b)
Cytoplam
c)
Cell wall
d)
Nucleus

|
Mukund Narayan answered |
Yes because animal does not need the upper part of capsule found in cell wall
The cell organelles (other than the nucleus) which contain DNA are- a)plastids and lysosomes
- b)mitochondria and Golgi apparatus
- c)Golgi apparatus and lysosomes
- d)plastids and mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell organelles (other than the nucleus) which contain DNA are
a)
plastids and lysosomes
b)
mitochondria and Golgi apparatus
c)
Golgi apparatus and lysosomes
d)
plastids and mitochondria

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Both mitochondria and plastids possess their own genetic material and ribosomes .
The mitochondria DNA and plastid DNA possess genes which produce the proteins necessary for the functioning of mitochondria and plastids respectively.
Match the following with the correct response.
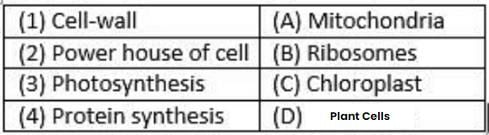
- a)1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
- b)1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
- c)1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- d)1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following with the correct response.

a)
1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
b)
1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
c)
1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
d)
1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Cell wall - Plant Cells
Power house of cell - Mitochondria
Photosynthesis - Chloroplast
Protein synthesis Ribosomes
Power house of cell - Mitochondria
Photosynthesis - Chloroplast
Protein synthesis Ribosomes
Following are a few definitions of osmosis. Read carefully and select the correct definition. - a)Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
- b)Movement of solvent molecules from its higher concentration to lower concentration
- c)Movement of solvent molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration of solution through a permeable membrane
- d)Movement of solute molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration of solution through a semipermeable membrane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Following are a few definitions of osmosis. Read carefully and select the correct definition.
a)
Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
b)
Movement of solvent molecules from its higher concentration to lower concentration
c)
Movement of solvent molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration of solution through a permeable membrane
d)
Movement of solute molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration of solution through a semipermeable membrane
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Osmosis is the passive movement of water or any other solvent molecules from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a semipermeable membrane. This brings both the solutions separated by the semipermeable membrane to the equilibrium. Therefore, option A is correct.
A prokaryotic cell does not possess- a)cell membrane
- b)cell wall
- c)nuclear membrane
- d)both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A prokaryotic cell does not possess
a)
cell membrane
b)
cell wall
c)
nuclear membrane
d)
both (a) and (c)
|
|
Moonlight Stargirl answered |
Prokaryotic cells have no nuclear membrane thus there nucleus is considered not well defined
The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by- a)rough endoplasmic reticulum
- b)Golgi apparatus
- c)plasma membrane
- d)mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by
a)
rough endoplasmic reticulum
b)
Golgi apparatus
c)
plasma membrane
d)
mitochondria

|
Keshav Kapoor answered |
Yes because ribosomes are sites are protein manufacture and they are found attached to the rough ER
If a plant cell is kept in a hypotonic solution, it will
- a)Increase in its volume
- b)Maintain the same volume
- c)Decrease in its volume
- d)Burst
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a plant cell is kept in a hypotonic solution, it will
a)
Increase in its volume
b)
Maintain the same volume
c)
Decrease in its volume
d)
Burst
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When the plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution , it takes up water by osmosis and starts to swell, but the cell wall prevents it from bursting.
Nucleoid is a feature of- a)Bacteria
- b)Amoeba
- c)Humans
- d)Birds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleoid is a feature of
a)
Bacteria
b)
Amoeba
c)
Humans
d)
Birds

|
Bartta Dutta answered |
Bacterium is a prokaryotic cell. pro means primitive and karyon means nucleus . Hence a prokaryotic cell like bacteria contains amembrenous ( without membrane) nuclear material called nucleoid which remains scattered in the cytoplasm.
Cell wall is mainly made up of- a)Maltose
- b)Cellulose
- c)Sucrose
- d)Fructose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall is mainly made up of
a)
Maltose
b)
Cellulose
c)
Sucrose
d)
Fructose
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
In the primary (growing) plant cell wall, the major carbohydrates are cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. The cellulose microfibrils are linked via hemicellulosic tethers to form the cellulose-hemicellulose network, which is embedded in the pectin matrix.
The only cell organelle present in prokaryotic cell is - a)mitochondria
- b)ribosome
- c)plastids
- d)lysosome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The only cell organelle present in prokaryotic cell is
a)
mitochondria
b)
ribosome
c)
plastids
d)
lysosome
|
|
Lokesh Kumar answered |
Ribosomes are a cell structure that makes protein. Protein is needed for many cell functions such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes. Ribosomes can be found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Which term describes the entire content of a living cell, including the cytoplasm and the nucleus, and is often referred to as the living substance of the cell?
- a)Protoplasm
- b)Ooplasm
- c)Nucleoplasm
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which term describes the entire content of a living cell, including the cytoplasm and the nucleus, and is often referred to as the living substance of the cell?
a)
Protoplasm
b)
Ooplasm
c)
Nucleoplasm
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
The term used to describe the entire content of a living cell, including the cytoplasm and the nucleus, is "protoplasm." Protoplasm is often referred to as the living substance of the cell.
A cell will swell up if- a)the concentration of water molecules in the cell is higher than the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium
- b)the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium is higher than water molecules concentration in the cell
- c)the concentration of water molecules is same in the cell and in the surrounding medium
- d)concentration of water molecules does not matter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell will swell up if
a)
the concentration of water molecules in the cell is higher than the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium
b)
the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium is higher than water molecules concentration in the cell
c)
the concentration of water molecules is same in the cell and in the surrounding medium
d)
concentration of water molecules does not matter
|
|
Madhu answered |
Option b
Engulfing of food materials or foreign bodies by cells like Amoeba is called- a)diffusion
- b)endocytosis
- c)osmosis
- d)plasmolysis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Engulfing of food materials or foreign bodies by cells like Amoeba is called
a)
diffusion
b)
endocytosis
c)
osmosis
d)
plasmolysis
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Organisms like Amoeba have flexible cell membrane due to which they can take in food material or engulf foreign bodies through the process called endocytosis.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The presence of various cell organelles within the cell helps in- A:Larger size of the cell
- B:Decoration of the cell
- C:Crowding of the cell
- D:Division of labour
The answer is d.
The presence of various cell organelles within the cell helps in
A:
Larger size of the cell
B:
Decoration of the cell
C:
Crowding of the cell
D:
Division of labour

|
Rohini Seth answered |
In order for cells to function and survive, their organelles work together to carry out specific tasks and perform specific roles. Each organelle has its own role that contributes to the survival of the cell. This is called thr Division of labour.
Find out the correct sentence. - a)Enzymes packed in lysosomes are made through RER
- b)Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum produce lipid and protein respectively
- c)Endoplasmic reticulum is related to the destruction of plasma membrane
- d)Nucleoid is present inside the nucleoplasm of eukaryotic nucleus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the correct sentence.
a)
Enzymes packed in lysosomes are made through RER
b)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum produce lipid and protein respectively
c)
Endoplasmic reticulum is related to the destruction of plasma membrane
d)
Nucleoid is present inside the nucleoplasm of eukaryotic nucleus
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Option B: Rough endoplasmic reticulum produce proteins and smooth endoplasmic reticulum produce lipids. Hence, given statement is wrong.
Option C: Endoplasmic reticulum is related with the making of plasma membrane. It makes the proteins (with the help of ribosomes) and lipids which are used for membrane synthesis. Hence, given statement is false.
Option D: Nuclear material of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single chromosome which is not membrane bound and lies naked in cytoplasm. Such, nuclear region of cytoplasm is called as nucleoid. Hence, given statement is wrong.
Option A: Lysosomal enzymes are made by rough endoplasmic reticulum. The ribosomes present on rough endoplasmic reticulum are involved in protein synthesis. Almost all enzymes are proteins
So, the correct answer is 'Enzymes packed in lysosomes are made through RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum)'
Animal cell lacking nuclei would also lack in- a)Endoplasmic reticulum
- b)Chromosome
- c)Lysosome
- d)Ribosome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Animal cell lacking nuclei would also lack in
a)
Endoplasmic reticulum
b)
Chromosome
c)
Lysosome
d)
Ribosome
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
Animal cell lacking nuclei would also lack in chromosome. As nucleus of a non-dividing cell contains chromatin which is uncoiled thread-like material of chromosome. Chromatin contains a DNA molecule and almost equal amount of basic histone proteins. Chromosomes occur during cell division and they are formed due to coiling and folding of chromatin.
Which of the following acts as garbage disposal system of the cell?- a)Golgi body
- b)Vacuole
- c)Peroxisome
- d)Lysosome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following acts as garbage disposal system of the cell?
a)
Golgi body
b)
Vacuole
c)
Peroxisome
d)
Lysosome

|
Keerthana Chavan answered |
Lysosomes present in the cytoplasm of cell contain very strong enzymes that can breakdown the all organic wastes produced in the cell. So, lysosome is called as garbage disposal system of the cell.
70-80 % of volume of a mature plant cell is occupied by- a)endoplasmic reticulum
- b)nucleus
- c)cytoplasm
- d)vacuole
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
70-80 % of volume of a mature plant cell is occupied by
a)
endoplasmic reticulum
b)
nucleus
c)
cytoplasm
d)
vacuole
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The mature cell has simple tissues rather than meristematic tissues so they will not divide and plant cell needs vacuole to make itself rigid and various excretion and storage works are also done by the vacuoles.
So, the vacuoles perform majority of the tasks of the plant cell and hence this is the reason, a mature plant cell has 70-80% of vacuoles in them.
The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell is - a)mitochondria
- b)ribosomes
- c)plastids
- d)lysosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell is
a)
mitochondria
b)
ribosomes
c)
plastids
d)
lysosomes
|
|
Aradhiya Gupta answered |
Ribosome because it is membraneless organelles and also prokaryoted are those having not nuclear membrane
The membrane of Golgi apparatus has connections with those of- a)nuclear membrane
- b)endoplasmic reticulum
- c)cell membrane
- d)mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The membrane of Golgi apparatus has connections with those of
a)
nuclear membrane
b)
endoplasmic reticulum
c)
cell membrane
d)
mitochondria
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The Golgi apparatus receives proteins and lipids (fats) from the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
It modifies some of them and sorts, concentrates and packs them into sealed droplets called vesicles.
Which organelle releases energy?- a)Golgi Apparatus
- b)Chloroplast
- c)Ribosome
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which organelle releases energy?
a)
Golgi Apparatus
b)
Chloroplast
c)
Ribosome
d)
Mitochondria

|
Sandeep Saini answered |
Mitochondria are called as power house of the cell because it contain enzymes for cellular respiration in which energy is released in form of ATP.
Find the incorrect statement regarding cell organelles from the following:- a)A cell functions because of its organelles.
- b)The organelles help in division of labour in the cell.
- c)Cell organelles are present outside each cell.
- d)Each kind of cell organelle performs a special function.
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the incorrect statement regarding cell organelles from the following:
a)
A cell functions because of its organelles.
b)
The organelles help in division of labour in the cell.
c)
Cell organelles are present outside each cell.
d)
Each kind of cell organelle performs a special function.

|
sujal singhal answered |
Many of the organelles found in cells are made up of or are surrounded by membrane and, therefore,would not be found in prokaryotic cells. cytoplasmType of cell: both plant and animalLocation: found inside the cell membrane but outside the nucleusDescription: clear, thick, jellylike material; contains a large amount of water (about 70%) and chemicals;may sometimes appear to be grainy (this grainy appearance comes from the organelles floating in it)Function: contains all the organelles outside of the nucleusOther: the cytoplasm is constantly moving or “streaming” through the cell.
Match the following with correct response.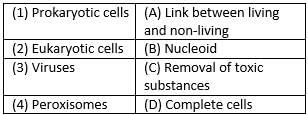
- a)1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
- b)1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- c)1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
- d)1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following with correct response.

a)
1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
b)
1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
c)
1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
d)
1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Prokaryotes lack nucleus and thus they are called nucleoid.
Eukaryotes contain nucleus and thus they are referred as complete cell.
Viruses act both as living and non- living.
Peroxisomes helps in removal of toxic substances.
Eukaryotes contain nucleus and thus they are referred as complete cell.
Viruses act both as living and non- living.
Peroxisomes helps in removal of toxic substances.
Which of the following lacks nucleus-- a)WBC
- b)RBC
- c)Nerve cell.
- d)Muscle cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following lacks nucleus-
a)
WBC
b)
RBC
c)
Nerve cell.
d)
Muscle cell
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
RBCs in humans lack nucleus. Absence of nucleus in cells reduces the O2 consumption in the various cellular activities. Thus the cell is able to send maximum O2 to other cells of the body.It does not have the nucleus. As a result of it, it needs continuous production from the bone marrow.
Which is the control centre of the cell?- a)Protoplasm
- b)Nucleus
- c)Cell membrane
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the control centre of the cell?
a)
Protoplasm
b)
Nucleus
c)
Cell membrane
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
Nucleus is called the control center of the cell.
This is because it performs 2 main functions:
1. Contains genetic information for structure, reproduction , development, metabolism and behaviour. The genetic information is replicated and passed on to daughter cells.
2. Controls cellular activities through directing synthesis of particular proteins and enzymes.
Which plastids are colourless?- a)Chromoplasts
- b)Chloroplast
- c)Leucoplasts
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plastids are colourless?
a)
Chromoplasts
b)
Chloroplast
c)
Leucoplasts
d)
All of the above
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
- The chloroplast is a type of plastid which produces green coloured pigment. The chloroplast is involved in carrying out photosynthesis. It gives a green colour to leaves.
- Chromoplasts are a type of plastids which are responsible for the characteristic colour of flower and fruit. They are involved in attracting insects, various vectors for pollination and for fruit dispersal.
- Leucoplasts are colourless plastids and mainly help in storage of food compounds like starch, proteins or fats. Such colourless plastids are present in underground roots, stems.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Cell wall is mainly made up of
- A:
Maltose
- B:
Cellulose
- C:
Sucrose
- D:
Fructose
The answer is b.
Cell wall is mainly made up of
Maltose
Cellulose
Sucrose
Fructose

|
Arzoo Sharma answered |
Cellulose which is a complex substance ( fibrous polysaccharide ) which provides structural strength to plants
Choose the correctly matched pair.- a)Hypertonic solution - Cell swells up
- b)Hypotonic solution - Cell shrinks
- c)Isotonic solution - No net movement of water
- d)Diffusion - Movement of water molecules
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correctly matched pair.
a)
Hypertonic solution - Cell swells up
b)
Hypotonic solution - Cell shrinks
c)
Isotonic solution - No net movement of water
d)
Diffusion - Movement of water molecules

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
- Option A: Hypertonic solution - Cell swells up
Incorrect. In a hypertonic solution, the outside solution has a higher solute concentration than inside the cell, causing the cell to lose water and shrink, not swell up.
- Option B: Hypotonic solution - Cell shrinks
Incorrect. In a hypotonic solution, the outside solution has a lower solute concentration than inside the cell, causing the cell to gain water and swell up, not shrink.
- Option C: Isotonic solution - No net movement of water
Correct. In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is the same as inside the cell, resulting in no net movement of water across the cell membrane. Thus, the cell maintains its shape and size.
- Option D: Diffusion - Movement of water molecules
Incorrect. Diffusion is the movement of molecules (excluding water molecules) from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. The movement of water molecules specifically through a selectively permeable membrane is known as osmosis.
Incorrect. In a hypertonic solution, the outside solution has a higher solute concentration than inside the cell, causing the cell to lose water and shrink, not swell up.
- Option B: Hypotonic solution - Cell shrinks
Incorrect. In a hypotonic solution, the outside solution has a lower solute concentration than inside the cell, causing the cell to gain water and swell up, not shrink.
- Option C: Isotonic solution - No net movement of water
Correct. In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is the same as inside the cell, resulting in no net movement of water across the cell membrane. Thus, the cell maintains its shape and size.
- Option D: Diffusion - Movement of water molecules
Incorrect. Diffusion is the movement of molecules (excluding water molecules) from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. The movement of water molecules specifically through a selectively permeable membrane is known as osmosis.
Which of the following statements about the structure of chromosomes is correct?- a)Chromosomes are present inside the mitochondria.
- b)Chromosomes are thread-like structures present inside the nucleus.
- c)Chromosomes are made only of proteins.
- d)Chromosomes are found only in plant cells.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the structure of chromosomes is correct?
a)
Chromosomes are present inside the mitochondria.
b)
Chromosomes are thread-like structures present inside the nucleus.
c)
Chromosomes are made only of proteins.
d)
Chromosomes are found only in plant cells.

|
Deepak Yadav answered |
Understanding Chromosomes
Chromosomes are essential structures within the cells of living organisms, playing a crucial role in genetics and heredity. The correct statement about the structure of chromosomes is option 'B': "Chromosomes are thread-like structures present inside the nucleus."
Key Features of Chromosomes:
- Location:
Chromosomes are primarily located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells (cells with a true nucleus), where they house the genetic material (DNA).
- Structure:
They appear as thread-like structures during cell division. When cells are not dividing, chromosomes are less condensed and exist as chromatin, which can be uncoiled to facilitate gene expression.
- Composition:
Chromosomes consist of DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones. This combination of DNA and proteins is essential for the organization, protection, and regulation of the genetic material.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
- Option A:
While mitochondria have their own DNA, they do not contain complete chromosomes like those found in the nucleus.
- Option C:
Chromosomes are not made only of proteins; they are primarily made of DNA and proteins, emphasizing the importance of both components.
- Option D:
Chromosomes are found in both plant and animal cells, making this option inaccurate.
In summary, chromosomes are vital for genetic inheritance and are located within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding their structure is fundamental to the study of biology and genetics.
Chromosomes are essential structures within the cells of living organisms, playing a crucial role in genetics and heredity. The correct statement about the structure of chromosomes is option 'B': "Chromosomes are thread-like structures present inside the nucleus."
Key Features of Chromosomes:
- Location:
Chromosomes are primarily located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells (cells with a true nucleus), where they house the genetic material (DNA).
- Structure:
They appear as thread-like structures during cell division. When cells are not dividing, chromosomes are less condensed and exist as chromatin, which can be uncoiled to facilitate gene expression.
- Composition:
Chromosomes consist of DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones. This combination of DNA and proteins is essential for the organization, protection, and regulation of the genetic material.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
- Option A:
While mitochondria have their own DNA, they do not contain complete chromosomes like those found in the nucleus.
- Option C:
Chromosomes are not made only of proteins; they are primarily made of DNA and proteins, emphasizing the importance of both components.
- Option D:
Chromosomes are found in both plant and animal cells, making this option inaccurate.
In summary, chromosomes are vital for genetic inheritance and are located within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding their structure is fundamental to the study of biology and genetics.
What is the main function of the cytoplasm in a cell?- a)To store genetic material
- b)To provide structure and support
- c)To house organelles and facilitate cellular processes
- d)To protect the cell from external damage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To store genetic material
b)
To provide structure and support
c)
To house organelles and facilitate cellular processes
d)
To protect the cell from external damage

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
The cytoplasm is the fluid inside the cell membrane that contains various organelles and facilitates cellular processes. It acts as a medium where essential functions, such as metabolism and the movement of materials, occur. The cytoplasm's role is crucial for maintaining cell function and organization. Interestingly, the term "cytoplasm" comes from the Greek words "kytos" meaning "cell" and "plasma" meaning "form or substance," reflecting its fundamental role in cell structure.
The passage of water from a region of higher water concentration through a semi – permeable membrane to region of low water concentration is- a)Diffusion
- b)osmosis
- c)Both a and b
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The passage of water from a region of higher water concentration through a semi – permeable membrane to region of low water concentration is
a)
Diffusion
b)
osmosis
c)
Both a and b
d)
None of these.
|
|
C K Academy answered |
The passage of water from a region of higher water concentration to lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane is called osmosis.
What is the outermost covering of a cell that regulates the entry and exit of materials known as?- a)Nucleus
- b)Cytoplasm
- c)Cell wall
- d)Plasma membrane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the outermost covering of a cell that regulates the entry and exit of materials known as?
a)
Nucleus
b)
Cytoplasm
c)
Cell wall
d)
Plasma membrane

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
The plasma membrane, also referred to as the cell membrane, is the outermost covering of a cell that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining cellular functions and homeostasis.
Which of the following are the main constituents of cell wall?- a)Cellulose
- b)Pectin
- c)Starch.
- d)Protein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the main constituents of cell wall?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Pectin
c)
Starch.
d)
Protein
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
In the primary (growing) plant cell wall, the major carbohydrates are cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. The cellulose microfibrils are linked via hemicellulosic tethers to form the cellulose-hemicellulose network, which is embedded in the pectin matrix.
Which of the following statements about vacuoles is correct?- a)Vacuoles are only found in plant cells and not in animal cells.
- b)The central vacuole in some plant cells can occupy 50-90% of the cell volume.
- c)Plant cells generally have smaller vacuoles than animal cells.
- d)Vacuoles are large and centrally located in animal cells.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about vacuoles is correct?
a)
Vacuoles are only found in plant cells and not in animal cells.
b)
The central vacuole in some plant cells can occupy 50-90% of the cell volume.
c)
Plant cells generally have smaller vacuoles than animal cells.
d)
Vacuoles are large and centrally located in animal cells.
|
|
Bassam Al-Khalidi answered |
Understanding Vacuoles
Vacuoles are essential cellular structures found in many types of cells, including plant and animal cells. They serve various functions, most notably in storage and maintaining cell structure.
Why Option B is Correct
- The central vacuole, particularly in plant cells, is a large membrane-bound organelle that plays a crucial role in maintaining turgor pressure.
- In some plant cells, this central vacuole can indeed occupy 50-90% of the cell volume, which is vital for:
- Water storage: Helps in maintaining hydration.
- Nutrient storage: Stores essential substances for the plant.
- Waste management: Sequesters waste products.
- This significant volume helps the plant cells maintain their shape and structural integrity, aiding in overall plant health.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option A: Vacuoles are present in both plant and animal cells, although they are generally larger and more prominent in plant cells.
- Option C: Plant cells typically have larger vacuoles compared to animal cells, which often contain smaller vacuoles used for various functions.
- Option D: In animal cells, vacuoles are usually smaller and more numerous, not large and centrally located like in plant cells.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of the central vacuole in plant cells highlights its importance in cellular function and overall plant vitality. Option B accurately reflects this crucial aspect of plant cell biology.
Vacuoles are essential cellular structures found in many types of cells, including plant and animal cells. They serve various functions, most notably in storage and maintaining cell structure.
Why Option B is Correct
- The central vacuole, particularly in plant cells, is a large membrane-bound organelle that plays a crucial role in maintaining turgor pressure.
- In some plant cells, this central vacuole can indeed occupy 50-90% of the cell volume, which is vital for:
- Water storage: Helps in maintaining hydration.
- Nutrient storage: Stores essential substances for the plant.
- Waste management: Sequesters waste products.
- This significant volume helps the plant cells maintain their shape and structural integrity, aiding in overall plant health.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option A: Vacuoles are present in both plant and animal cells, although they are generally larger and more prominent in plant cells.
- Option C: Plant cells typically have larger vacuoles compared to animal cells, which often contain smaller vacuoles used for various functions.
- Option D: In animal cells, vacuoles are usually smaller and more numerous, not large and centrally located like in plant cells.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of the central vacuole in plant cells highlights its importance in cellular function and overall plant vitality. Option B accurately reflects this crucial aspect of plant cell biology.
Choose the correctly matched pair.- a)Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - Protein Synthesis
- b)Golgi Apparatus - Formation of Lysosomes
- c)Lysosomes - Photosynthesis
- d)Mitochondrion - Detoxification of Drugs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correctly matched pair.
a)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - Protein Synthesis
b)
Golgi Apparatus - Formation of Lysosomes
c)
Lysosomes - Photosynthesis
d)
Mitochondrion - Detoxification of Drugs

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
- Option A: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - Protein Synthesis
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is primarily involved in the synthesis of lipids and detoxification of drugs and poisons, not protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER). Therefore, this pair is incorrectly matched.
- Option B: Golgi Apparatus - Formation of Lysosomes
The Golgi Apparatus is involved in the formation of lysosomes. It packages and dispatches materials within the cell and is essential for the synthesis of complex sugars and the formation of lysosomes from simple vesicles. Therefore, this pair is correctly matched.
- Option C: Lysosomes - Photosynthesis
Lysosomes are responsible for digesting cellular waste and foreign materials within the cell. Photosynthesis is a process carried out by chloroplasts in plant cells. Therefore, this pair is incorrectly matched.
- Option D: Mitochondrion - Detoxification of Drugs
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell, involved in energy production through cellular respiration. Detoxification of drugs is a function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, not mitochondria. Therefore, this pair is incorrectly matched.
Thus, the correctly matched pair is Option B: Golgi Apparatus - Formation of Lysosomes.
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is primarily involved in the synthesis of lipids and detoxification of drugs and poisons, not protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER). Therefore, this pair is incorrectly matched.
- Option B: Golgi Apparatus - Formation of Lysosomes
The Golgi Apparatus is involved in the formation of lysosomes. It packages and dispatches materials within the cell and is essential for the synthesis of complex sugars and the formation of lysosomes from simple vesicles. Therefore, this pair is correctly matched.
- Option C: Lysosomes - Photosynthesis
Lysosomes are responsible for digesting cellular waste and foreign materials within the cell. Photosynthesis is a process carried out by chloroplasts in plant cells. Therefore, this pair is incorrectly matched.
- Option D: Mitochondrion - Detoxification of Drugs
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell, involved in energy production through cellular respiration. Detoxification of drugs is a function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, not mitochondria. Therefore, this pair is incorrectly matched.
Thus, the correctly matched pair is Option B: Golgi Apparatus - Formation of Lysosomes.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Prokaryotic cell contains:
- A:
Two chromosomes
- B:
Three chromosomes
- C:
Single chromosome
- D:
Variable number of chromosomes
The answer is c.
Prokaryotic cell contains:
Two chromosomes
Three chromosomes
Single chromosome
Variable number of chromosomes
|
|
Pankaj Chawla answered |
Prokaryotic cell contains a single chromosome.
Prokaryotic cells are a type of cells that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are typically single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and archaea. Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells do not have a well-defined nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is located in a region of the cell called the nucleoid.
Structure of a prokaryotic chromosome:
The chromosome in a prokaryotic cell is a circular DNA molecule that is compacted and folded to fit inside the nucleoid region. The DNA molecule contains all the genetic information necessary for the cell's survival and reproduction. It carries the instructions for the synthesis of proteins and other molecules needed by the cell.
Functions of the prokaryotic chromosome:
The prokaryotic chromosome plays a vital role in the cell's functions:
1. Genetic information: The chromosome carries all the genes that are responsible for the cell's traits and characteristics.
2. Replication: The chromosome is replicated during the cell division process, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a copy of the genetic material.
3. Gene expression: The chromosome contains the regulatory sequences that control the expression of genes, allowing the cell to respond to its environment and carry out specific functions.
4. Transmission of genetic information: The chromosome is passed on to the next generation during cell division, ensuring the continuity of genetic information.
Comparison with eukaryotic cells:
In contrast to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have multiple linear chromosomes located within a membrane-bound nucleus. The chromosomes in eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, containing not only protein-coding genes but also non-coding regions that regulate gene expression.
Conclusion:
In summary, a prokaryotic cell contains a single chromosome, which is a circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid region. This chromosome carries all the genetic information necessary for the cell's functions and is responsible for the cell's traits and characteristics.
Prokaryotic cells are a type of cells that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are typically single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and archaea. Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells do not have a well-defined nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is located in a region of the cell called the nucleoid.
Structure of a prokaryotic chromosome:
The chromosome in a prokaryotic cell is a circular DNA molecule that is compacted and folded to fit inside the nucleoid region. The DNA molecule contains all the genetic information necessary for the cell's survival and reproduction. It carries the instructions for the synthesis of proteins and other molecules needed by the cell.
Functions of the prokaryotic chromosome:
The prokaryotic chromosome plays a vital role in the cell's functions:
1. Genetic information: The chromosome carries all the genes that are responsible for the cell's traits and characteristics.
2. Replication: The chromosome is replicated during the cell division process, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a copy of the genetic material.
3. Gene expression: The chromosome contains the regulatory sequences that control the expression of genes, allowing the cell to respond to its environment and carry out specific functions.
4. Transmission of genetic information: The chromosome is passed on to the next generation during cell division, ensuring the continuity of genetic information.
Comparison with eukaryotic cells:
In contrast to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have multiple linear chromosomes located within a membrane-bound nucleus. The chromosomes in eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, containing not only protein-coding genes but also non-coding regions that regulate gene expression.
Conclusion:
In summary, a prokaryotic cell contains a single chromosome, which is a circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid region. This chromosome carries all the genetic information necessary for the cell's functions and is responsible for the cell's traits and characteristics.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membrane-bound tubes and sheets. It looks like long tubules or round or oblong bags (vesicles). The ER membrane is similar in structure to the ______ membrane.- a)Nuclear
- b)Plasma
- c)Cell
- d)Ribosomal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membrane-bound tubes and sheets. It looks like long tubules or round or oblong bags (vesicles). The ER membrane is similar in structure to the ______ membrane.
a)
Nuclear
b)
Plasma
c)
Cell
d)
Ribosomal

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
The ER membrane is structurally similar to the plasma membrane, which is a crucial feature of the endoplasmic reticulum.
“All cells arise from pre - existing cells” who said this?
- a)Robert hook
- b)Robert Brown
- c)Virchow
- d)Purkinje
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
“All cells arise from pre - existing cells” who said this?
a)
Robert hook
b)
Robert Brown
c)
Virchow
d)
Purkinje

|
Ishita Roy answered |
R. Virchow in 1855 presented the idea that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This was modification in the earlier cell theory.
The term protoplasm was coined by- a)Haeckel
- b)Robert hook
- c)J. E. Purkinje
- d)Kholl and Ruska
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term protoplasm was coined by
a)
Haeckel
b)
Robert hook
c)
J. E. Purkinje
d)
Kholl and Ruska
|
|
Hrishikesh Saha answered |
Introduction to Protoplasm
Protoplasm is a fundamental substance that constitutes the living matter of cells. The term is essential in biology as it refers to the jelly-like material within cells where organelles are suspended.
Origin of the Term
The term "protoplasm" was coined by:
Significance of Protoplasm
Understanding protoplasm is crucial in the study of biology for several reasons:
Historical Context
When J. E. Purkinje introduced the term, it marked a significant step in cell biology:
Conclusion
In summary, J. E. Purkinje's introduction of the term "protoplasm" has had a lasting impact on our understanding of biology, emphasizing the importance of this substance in the study of life and cellular function.
Protoplasm is a fundamental substance that constitutes the living matter of cells. The term is essential in biology as it refers to the jelly-like material within cells where organelles are suspended.
Origin of the Term
The term "protoplasm" was coined by:
- J. E. Purkinje - A Czech physiologist who introduced the term in 1840.
Significance of Protoplasm
Understanding protoplasm is crucial in the study of biology for several reasons:
- Cell Structure: Protoplasm is the site where cellular processes occur, and it is essential for maintaining the cell's structure.
- Life Processes: It plays a vital role in processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
- Composition: Protoplasm is composed of water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, making it a complex mixture vital for life.
Historical Context
When J. E. Purkinje introduced the term, it marked a significant step in cell biology:
- Cell Theory: His work contributed to the development of cell theory, which states that all living organisms are composed of cells.
- Impact on Science: The concept of protoplasm paved the way for further research into cellular structure and function.
Conclusion
In summary, J. E. Purkinje's introduction of the term "protoplasm" has had a lasting impact on our understanding of biology, emphasizing the importance of this substance in the study of life and cellular function.
Choose the correctly matched pair.- a)Prokaryotic Cell - Membrane-bound cell organelles present
- b)Eukaryotic Cell - Single chromosome
- c)Prokaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
- d)Eukaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correctly matched pair.
a)
Prokaryotic Cell - Membrane-bound cell organelles present
b)
Eukaryotic Cell - Single chromosome
c)
Prokaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
d)
Eukaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
- Option A: Prokaryotic Cell - Membrane-bound cell organelles present
Incorrect. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound cell organelles. They lack structures such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum, which are found in eukaryotic cells.
- Option B: Eukaryotic Cell - Single chromosome
Incorrect. Eukaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes contained within a well-defined nucleus, unlike prokaryotic cells which typically have a single, circular chromosome.
- Option C: Prokaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
Correct. Prokaryotic cells have a nuclear region that is not well defined and is known as the nucleoid. This region is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
- Option D: Eukaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
Incorrect. Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nuclear region that is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells.
The correct answer, therefore, is Option C: Prokaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined.
Incorrect. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound cell organelles. They lack structures such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum, which are found in eukaryotic cells.
- Option B: Eukaryotic Cell - Single chromosome
Incorrect. Eukaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes contained within a well-defined nucleus, unlike prokaryotic cells which typically have a single, circular chromosome.
- Option C: Prokaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
Correct. Prokaryotic cells have a nuclear region that is not well defined and is known as the nucleoid. This region is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
- Option D: Eukaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined
Incorrect. Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nuclear region that is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells.
The correct answer, therefore, is Option C: Prokaryotic Cell - Nuclear region not well defined.
What is the process called when a plant cell loses water through osmosis and the cell contents shrink away from the cell wall?- a)Plasmolysis
- b)Endocytosis
- c)Diffusion
- d)Exocytosis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Plasmolysis
b)
Endocytosis
c)
Diffusion
d)
Exocytosis

|
Priya Nair answered |
Understanding Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is a crucial biological process that occurs in plant cells when they lose water through osmosis. This phenomenon can significantly affect the cell’s structure and function.
What is Plasmolysis?
- Plasmolysis refers to the shrinking of the protoplast (cell contents) away from the cell wall due to the loss of water.
- This occurs when a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, where the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside.
How Does Osmosis Work?
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
- In a hypertonic environment, water moves out of the cell, leading to a decrease in turgor pressure.
Effects of Plasmolysis
- As water leaves the cell, the vacuole shrinks, causing the cell membrane to pull away from the rigid cell wall.
- This can lead to wilting in plants, as the loss of turgor pressure makes it difficult for the plant to maintain its structure.
Importance of Plasmolysis
- Understanding plasmolysis is essential in fields like agriculture and horticulture, as it helps in managing plant hydration.
- Proper water balance is crucial for plant health, growth, and productivity.
In summary, plasmolysis is an important process illustrating how osmotic balance affects plant cell integrity. Recognizing this can help in better understanding plant physiology and care.
Plasmolysis is a crucial biological process that occurs in plant cells when they lose water through osmosis. This phenomenon can significantly affect the cell’s structure and function.
What is Plasmolysis?
- Plasmolysis refers to the shrinking of the protoplast (cell contents) away from the cell wall due to the loss of water.
- This occurs when a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, where the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside.
How Does Osmosis Work?
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
- In a hypertonic environment, water moves out of the cell, leading to a decrease in turgor pressure.
Effects of Plasmolysis
- As water leaves the cell, the vacuole shrinks, causing the cell membrane to pull away from the rigid cell wall.
- This can lead to wilting in plants, as the loss of turgor pressure makes it difficult for the plant to maintain its structure.
Importance of Plasmolysis
- Understanding plasmolysis is essential in fields like agriculture and horticulture, as it helps in managing plant hydration.
- Proper water balance is crucial for plant health, growth, and productivity.
In summary, plasmolysis is an important process illustrating how osmotic balance affects plant cell integrity. Recognizing this can help in better understanding plant physiology and care.
What is the consequence of a ruptured plasma membrane for a cell?- a)The cell will continue to function normally.
- b)The cell will lose its contents and eventually die.
- c)The cell will rapidly produce new membrane materials.
- d)The cell will become more efficient in nutrient absorption.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The cell will continue to function normally.
b)
The cell will lose its contents and eventually die.
c)
The cell will rapidly produce new membrane materials.
d)
The cell will become more efficient in nutrient absorption.
|
|
Nidhi Khanna answered |
Consequences of a Ruptured Plasma Membrane
When a cell's plasma membrane ruptures, it leads to significant consequences that affect its viability. Here’s a detailed explanation of why option 'B' is correct:
Loss of Cellular Integrity
- The plasma membrane serves as a barrier that separates the interior of the cell from its external environment.
- A rupture compromises this barrier, allowing the uncontrolled flow of substances in and out of the cell.
Loss of Cellular Contents
- Essential components such as cytoplasm, organelles, and various biomolecules leak out of the cell.
- This loss disrupts metabolic processes and cellular functions, leading to a decline in the cell's ability to perform essential tasks.
Cell Death
- Without the necessary components and structural integrity, the cell cannot maintain homeostasis.
- The cell will ultimately undergo necrosis or apoptosis (programmed cell death) due to the inability to sustain life.
Inability to Repair
- While cells can sometimes repair minor membrane damages, a complete rupture generally exceeds their repair capabilities.
- The resources required for membrane synthesis may also be depleted following rupture, further preventing recovery.
In summary, a ruptured plasma membrane leads to the loss of cellular contents and ultimately results in cell death. This highlights the critical role of the plasma membrane in maintaining cellular health and functionality.
When a cell's plasma membrane ruptures, it leads to significant consequences that affect its viability. Here’s a detailed explanation of why option 'B' is correct:
Loss of Cellular Integrity
- The plasma membrane serves as a barrier that separates the interior of the cell from its external environment.
- A rupture compromises this barrier, allowing the uncontrolled flow of substances in and out of the cell.
Loss of Cellular Contents
- Essential components such as cytoplasm, organelles, and various biomolecules leak out of the cell.
- This loss disrupts metabolic processes and cellular functions, leading to a decline in the cell's ability to perform essential tasks.
Cell Death
- Without the necessary components and structural integrity, the cell cannot maintain homeostasis.
- The cell will ultimately undergo necrosis or apoptosis (programmed cell death) due to the inability to sustain life.
Inability to Repair
- While cells can sometimes repair minor membrane damages, a complete rupture generally exceeds their repair capabilities.
- The resources required for membrane synthesis may also be depleted following rupture, further preventing recovery.
In summary, a ruptured plasma membrane leads to the loss of cellular contents and ultimately results in cell death. This highlights the critical role of the plasma membrane in maintaining cellular health and functionality.
Chapter doubts & questions for The Fundamental Unit of Life - Science Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The Fundamental Unit of Life - Science Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Class 9
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










