All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Acids, Bases and Salts for Class 10 Exam
Which of the following does not conduct electricity?- a)Sodium hydroxide
- b)Rain water
- c)Hydrochloric acid
- d)Distilled water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not conduct electricity?
a)
Sodium hydroxide
b)
Rain water
c)
Hydrochloric acid
d)
Distilled water
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Distilled water do not conduct electricity. The reason is that a liquid conducts electricity is by the positively or negatively charged ions that are actually moving from one of the electrodes to the other, carrying charge (electricity) with them.
Identify ‘X’ in the reaction: 2HCl + CuO → X + H2O- a)CuCl
- b)Cu(OH)2
- c)CuCl2
- d)HOCl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify ‘X’ in the reaction: 2HCl + CuO → X + H2O
a)
CuCl
b)
Cu(OH)2
c)
CuCl2
d)
HOCl
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
When copper oxide and dilute hydrochloric acid are mixed the blue green solution is formed.
The reaction is :-
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
The reaction is :-
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
The colour of phenolphthalein in acids is:- a)Colourless
- b)Red
- c)Pink
- d)Blue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The colour of phenolphthalein in acids is:
a)
Colourless
b)
Red
c)
Pink
d)
Blue
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Phenolphthalein is often used as an indicator in acid–base titrations. For this application, it turns colourless in acidic solutions and magenta in basic solutions.
Carbon dioxide is an example of:- a)Amphoteric oxide
- b)Acidic oxide
- c)Basic oxide
- d)Neutral oxide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon dioxide is an example of:
a)
Amphoteric oxide
b)
Acidic oxide
c)
Basic oxide
d)
Neutral oxide
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Acid oxides is a complex chemical substance oxides, which form a salt with the chemical reactions with bases or basic oxides and do not react with acidic oxides.
Examples of acidic oxides can be:
CO2 (all known carbon dioxide), P2O5 - oxide of phosphorus (formed in air if burns white phosphorus), SO3 - oxide of sulfur (VI) is a substance used for sulfuric acid.
Examples of acidic oxides can be:
CO2 (all known carbon dioxide), P2O5 - oxide of phosphorus (formed in air if burns white phosphorus), SO3 - oxide of sulfur (VI) is a substance used for sulfuric acid.
Identify the type of reaction: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O- a)Combination reaction
- b)Double decomposition reaction
- c)Decomposition reaction
- d)Neutralisation reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the type of reaction: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
a)
Combination reaction
b)
Double decomposition reaction
c)
Decomposition reaction
d)
Neutralisation reaction
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Reaction of a strong acid with strong base is called neutralization reaction which produces salt and water,
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
This equation is already balanced.
Aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus:- a)Red
- b)No change
- c)Colourless
- d)Pink
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus:
a)
Red
b)
No change
c)
Colourless
d)
Pink

|
Sagar Rane answered |
Since Sodium hydroxide is a base and thus it has no effect on a blue litmus paper but it changes red litmus to blue.
Which of the following is an olfactory indicator?- a)Litmus
- b)Phenolphthalein
- c)Onion
- d)Methyl orange
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an olfactory indicator?
a)
Litmus
b)
Phenolphthalein
c)
Onion
d)
Methyl orange
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
An olfactory indicator is a material whose smell varies reliant on whether it is mixed with an acidic or basic solution. Olfactory indicators mainly used in laboratory to test whether a solution is a base or an acid. Onion is an example of olfactory indicators.
Red cabbage indicator turns _______ in basic solutions.- a)Pink
- b)Green
- c)Blue
- d)Red
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Red cabbage indicator turns _______ in basic solutions.
a)
Pink
b)
Green
c)
Blue
d)
Red

|
Ruba answered |
This is a natural indicator which are found in the nature of the plants
Marble chips reacts with a solution to produce a gas which turns lime water milky. So the solution contains:
- a)Na2SO4
- b)H2SO4
- c)K2SO4
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Marble chips reacts with a solution to produce a gas which turns lime water milky. So the solution contains:
a)
Na2SO4
b)
H2SO4
c)
K2SO4
d)
none of these
|
|
Rajiv Gupta answered |
Marble chips are the substances that have the formula CaCO3
Calcium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid to form calcium sulphate and carbon dioxide which turns lime water milky.
Calcium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid to form calcium sulphate and carbon dioxide which turns lime water milky.
CaCO3 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Acids turn blue litmus :- a)Blue
- b)Red
- c)colourless
- d)Pink
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acids turn blue litmus :
a)
Blue
b)
Red
c)
colourless
d)
Pink

|
Ameya Rane answered |
Blue litmus paper turns red under acidic conditions and red litmus paper turns blue under basic or alkaline conditions
Assertion : Weak acids have low electrical conductivity.Reason : Strong acids and weak acids have equal concentration of hydrogen ions in their solutions.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : Weak acids have low electrical conductivity.
Reason : Strong acids and weak acids have equal concentration of hydrogen ions in their solutions.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
Acids change the colour of methyl orange to:- a)Colourless
- b)Pink/Red
- c)Blue
- d)Purple
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acids change the colour of methyl orange to:
a)
Colourless
b)
Pink/Red
c)
Blue
d)
Purple
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
Methyl orange is a pH indicator frequently used in titration because of its clear and distinct colour variance at different pH values. Methyl orange shows pink colour in acidic medium and yellow colour in basic medium. Because it changes colour at the pH of a mid strength acid, it is usually used in titration for acids. Unlike a universal indicator, methyl orange does not have a full spectrum of colour change, but it has a sharp end point.
Which of the following compound can turn blue litmus solution red?- a)CH3CHO
- b)NaOH
- c)CH3OCH3
- d)CH3COOH
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compound can turn blue litmus solution red?
a)
CH3CHO
b)
NaOH
c)
CH3OCH3
d)
CH3COOH
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Acid convert blue litmus solution to Red. HCHO, CH3CHO are aldehydes. HCOOH, CH3COOH are carboxylic acids. CH3OH and C2H5OH are alcohols. Out of these only carboxyhc acids would turn blue litmus solution red. So HCOOH and CH3COOH would turn blue litmus solution red.
Which gas is released when acids react with metal carbonates?- a)O2
- b)CO2
- c)CO
- d)H2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which gas is released when acids react with metal carbonates?
a)
O2
b)
CO2
c)
CO
d)
H2

|
Siddharth answered |
It is the property acid that ..... when acid react with metal carbonates ....acid + metal carbonates -------> salt +carbon dioxide + water .... so option B is correct.......
Assertion : When zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen is given off.
Reason : Hydrogen chloride molecules contain hydrochloric acid and hydrogen atoms.
- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- c)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : When zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen is given off.
Reason : Hydrogen chloride molecules contain hydrochloric acid and hydrogen atoms.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
c)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The correct answer is b) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
Explanation:
-
Assertion (A): When zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen is indeed given off. This is a chemical reaction where zinc displaces hydrogen from hydrochloric acid, producing zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
-
Reason (R): The statement that "Hydrogen chloride molecules contain hydrochloric acid and hydrogen atoms" is misleading. Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is a compound consisting of hydrogen and chlorine, but it doesn't accurately explain why hydrogen gas is evolved when zinc reacts with dilute HCl.
Therefore, the assertion is true, but the reason does not correctly explain it.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: After white washing the walls, a shiny white finish on walls is obtained after two to three days.Reason: Calcium Oxide reacts with Carbon dioxide to form Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate which gives shiny white finish.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: After white washing the walls, a shiny white finish on walls is obtained after two to three days.
Reason: Calcium Oxide reacts with Carbon dioxide to form Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate which gives shiny white finish.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Calcium hydroxide is obtained by reaction of calcium oxide and water.
Assertion : Phenolphthalein gives pink colour in basic solution.Reason : Phenolphthalein is a natural indicator.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : Phenolphthalein gives pink colour in basic solution.
Reason : Phenolphthalein is a natural indicator.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
Assertion : The acidity of Mg(OH)2 is two.
Reason : The acidity of a base is equal to the number of hydroxyl ions.
- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : The acidity of Mg(OH)2 is two.
Reason : The acidity of a base is equal to the number of hydroxyl ions.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The number of replaceable hydroxyl (OH−) Ions in a base is called the acidity of that base. Magnesium hydroxide has 2 replaceable hydroxyl ions, therefore it's acidity is 2. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A)
Assertion : If the pH inside the mouth decreases below5.5, the decay of tooth enamel begins.Reason : The bacteria present in the mouth degrades the sugar and left over food particles and produce acids that remain in the mouth after eating.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : If the pH inside the mouth decreases below5.5, the decay of tooth enamel begins.
Reason : The bacteria present in the mouth degrades the sugar and left over food particles and produce acids that remain in the mouth after eating.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Assertion (A): Baking soda creates acidity in the stomach.Reason (R): Baking soda is alkaline.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Baking soda creates acidity in the stomach.
Reason (R): Baking soda is alkaline.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Baking soda, being alkaline, neutralises the acidity in the stomach and removes it.
Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.

|
Avi Mukherjee answered |
Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
The correct answer is option 'A': Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Explanation:
When sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is added to dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), a reaction takes place resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. This reaction is represented by the following chemical equation:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
This reaction is a type of double displacement reaction, where sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce sodium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
Now, let's analyze the given assertion and reason:
Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
This assertion is true. When sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, effervescence occurs, and gas bubbles are observed. This is evident in the reaction mentioned above, where carbon dioxide gas is produced.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
This reason is also true and it explains why gas bubbles are observed. During the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas is given off as a product. This gas evolution leads to the formation of gas bubbles.
Hence, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the occurrence of gas bubbles. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
The correct answer is option 'A': Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Explanation:
When sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is added to dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), a reaction takes place resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. This reaction is represented by the following chemical equation:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
This reaction is a type of double displacement reaction, where sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce sodium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
Now, let's analyze the given assertion and reason:
Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
This assertion is true. When sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, effervescence occurs, and gas bubbles are observed. This is evident in the reaction mentioned above, where carbon dioxide gas is produced.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction.
This reason is also true and it explains why gas bubbles are observed. During the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas is given off as a product. This gas evolution leads to the formation of gas bubbles.
Hence, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the occurrence of gas bubbles. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Turmeric, a natural indicator in presence of bases turns:
- a)Reddish brown
- b)Blue
- c)No change
- d)Orange
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Turmeric, a natural indicator in presence of bases turns:
a)
Reddish brown
b)
Blue
c)
No change
d)
Orange
|
|
Manoj Choudhury answered |
**Turmeric as a Natural Indicator**
Turmeric, a commonly used spice in cooking, can also be used as a natural indicator to detect the presence of bases. The active compound in turmeric responsible for this property is called curcumin. When curcumin comes into contact with bases, it undergoes a chemical reaction that results in a change in color. In the presence of bases, turmeric turns bright red.
**Explanation**
Turmeric contains a class of compounds known as polyphenols, which are responsible for its vibrant yellow color. Curcumin, one of the polyphenols present in turmeric, acts as a pH indicator. pH indicators are substances that change color depending on the acidity or alkalinity (basicity) of a solution.
Bases are substances that can accept protons or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) in a chemical reaction. When a base is added to a solution of turmeric, the curcumin molecules react with the base, resulting in the formation of a new compound. This new compound has a different structure and absorbs light in a different range of wavelengths, giving rise to a change in color.
In the case of turmeric, the reaction with bases leads to the formation of a red compound. This compound is responsible for the bright red color observed when turmeric comes into contact with bases. The exact mechanism of this reaction is complex and involves multiple steps, including the deprotonation of curcumin and the formation of a conjugated system.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, turmeric can be used as a natural indicator to detect the presence of bases. When turmeric is exposed to bases, it undergoes a chemical reaction that results in a change in color. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, reacts with bases to form a red compound, giving turmeric a bright red color in the presence of bases.
Turmeric, a commonly used spice in cooking, can also be used as a natural indicator to detect the presence of bases. The active compound in turmeric responsible for this property is called curcumin. When curcumin comes into contact with bases, it undergoes a chemical reaction that results in a change in color. In the presence of bases, turmeric turns bright red.
**Explanation**
Turmeric contains a class of compounds known as polyphenols, which are responsible for its vibrant yellow color. Curcumin, one of the polyphenols present in turmeric, acts as a pH indicator. pH indicators are substances that change color depending on the acidity or alkalinity (basicity) of a solution.
Bases are substances that can accept protons or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) in a chemical reaction. When a base is added to a solution of turmeric, the curcumin molecules react with the base, resulting in the formation of a new compound. This new compound has a different structure and absorbs light in a different range of wavelengths, giving rise to a change in color.
In the case of turmeric, the reaction with bases leads to the formation of a red compound. This compound is responsible for the bright red color observed when turmeric comes into contact with bases. The exact mechanism of this reaction is complex and involves multiple steps, including the deprotonation of curcumin and the formation of a conjugated system.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, turmeric can be used as a natural indicator to detect the presence of bases. When turmeric is exposed to bases, it undergoes a chemical reaction that results in a change in color. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, reacts with bases to form a red compound, giving turmeric a bright red color in the presence of bases.
Assertion : HCl produces hydronium ions (H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl-) in aqueous solution.Reason : In presence of water, bases give H+ ions.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : HCl produces hydronium ions (H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl-) in aqueous solution.
Reason : In presence of water, bases give H+ ions.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
- Assertion (A): HCl produces hydronium ions (H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl-) in aqueous solution.
- This statement is true. When hydrogen chloride (HCl) dissolves in water, it dissociates completely into hydronium ions (H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl-). The reaction can be represented as:
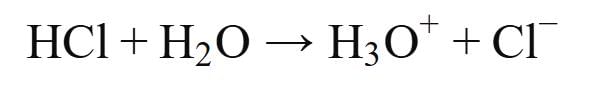
- This statement is true. When hydrogen chloride (HCl) dissolves in water, it dissociates completely into hydronium ions (H3O+) and chloride ions (Cl-). The reaction can be represented as:
- Reason (R): In presence of water, bases give H+ ions.
- This statement is false. Bases do not give H+ ions in water; they give OH- ions instead. The presence of OH- ions characterizes a basic solution, not H+ ions.
Assertion (A): Ammonia solution is an alkali.Reason (R): Ammonia solution turns blue litmus paper red.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Ammonia solution is an alkali.
Reason (R): Ammonia solution turns blue litmus paper red.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Ammonia solution, which is alkaline, turns the red litmus paper blue.
What does the "p" in the pH scale stand for, and what does the scale measure?- a)Potential; measures temperature variations.
- b)Power; measures the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
- c)Percentage; measures the basic nature of a solution.
- d)Pressure; measures the acidity of a liquid.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the "p" in the pH scale stand for, and what does the scale measure?
a)
Potential; measures temperature variations.
b)
Power; measures the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
c)
Percentage; measures the basic nature of a solution.
d)
Pressure; measures the acidity of a liquid.

|
Ankita Basak answered |
What Does the "p" in pH Stand For?
The "p" in pH stands for "power." This designation is derived from the German word "Potenz," which translates to "power" or "potential."
Understanding pH Scale
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, where:
- A pH of 7 is considered neutral (pure water).
- A pH less than 7 indicates acidity (higher hydrogen ion concentration).
- A pH greater than 7 indicates basicity (lower hydrogen ion concentration).
Measurement of Hydrogen Ion Concentration
The pH scale specifically measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. This is crucial because:
- Acidic Solutions: Higher concentrations of H+ ions lead to lower pH values. For example, lemon juice has a pH of around 2, indicating high acidity.
- Basic Solutions: Lower concentrations of H+ ions correspond to higher pH values. For instance, bleach has a pH of around 12, indicating it is basic.
Importance of pH
Understanding pH is essential in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: It helps in determining the nature of chemical reactions.
- Biology: Enzyme activity and metabolic processes are pH-dependent.
- Environmental Science: pH affects aquatic life and soil health.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' because the pH scale effectively measures the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, which determines its acidity or basicity.
The "p" in pH stands for "power." This designation is derived from the German word "Potenz," which translates to "power" or "potential."
Understanding pH Scale
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, where:
- A pH of 7 is considered neutral (pure water).
- A pH less than 7 indicates acidity (higher hydrogen ion concentration).
- A pH greater than 7 indicates basicity (lower hydrogen ion concentration).
Measurement of Hydrogen Ion Concentration
The pH scale specifically measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. This is crucial because:
- Acidic Solutions: Higher concentrations of H+ ions lead to lower pH values. For example, lemon juice has a pH of around 2, indicating high acidity.
- Basic Solutions: Lower concentrations of H+ ions correspond to higher pH values. For instance, bleach has a pH of around 12, indicating it is basic.
Importance of pH
Understanding pH is essential in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: It helps in determining the nature of chemical reactions.
- Biology: Enzyme activity and metabolic processes are pH-dependent.
- Environmental Science: pH affects aquatic life and soil health.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' because the pH scale effectively measures the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, which determines its acidity or basicity.
Assertion (A): Plaster of Paris is used by doctors for setting fractured bones.Reason (R): When Plaster of Paris is mixed with water and applied around the fractured limbs, it sets into a hard mass.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Plaster of Paris is used by doctors for setting fractured bones.
Reason (R): When Plaster of Paris is mixed with water and applied around the fractured limbs, it sets into a hard mass.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Plaster of Paris when mixed with water and applied around the fractured limbs, it sets into a hard mass and keeps the bone joints in a fixed position. So, it is commonly used for setting fractured bones.
Assertion : During electrolysis of concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen is produced at anode and chlorine gas is produced at cathode.Reason : Ions get attracted to oppositely charged electrodes.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : During electrolysis of concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen is produced at anode and chlorine gas is produced at cathode.
Reason : Ions get attracted to oppositely charged electrodes.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Assertion : On adding H2SO4 to water the resulting aqueous solution gets corrosive.Reason: Hydronium ions are responsible for corrosive action.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : On adding H2SO4 to water the resulting aqueous solution gets corrosive.
Reason: Hydronium ions are responsible for corrosive action.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Because H2SO4 is a strong acid, it readily forms hydronium ions when dissolved in water which are responsible for its corrosive action.
What is the primary result when a base reacts with an acid?- a)Formation of Salt and Hydrogen
- b)No Reaction
- c)Formation of Salt and Carbon Dioxide
- d)Formation of Salt and Water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary result when a base reacts with an acid?
a)
Formation of Salt and Hydrogen
b)
No Reaction
c)
Formation of Salt and Carbon Dioxide
d)
Formation of Salt and Water

|
Neha Sharma answered |
Understanding Acid-Base Reactions
When an acid reacts with a base, the primary result is the formation of salt and water. This reaction is commonly known as a neutralization reaction.
Key Components of the Reaction
- Acids: Substances that donate protons (H+) in a solution.
- Bases: Substances that accept protons (H+) or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution.
Neutralization Reaction
- When an acid and a base interact, they undergo a neutralization process.
- The acidic component (H+) from the acid combines with the basic component (OH-) from the base to form water (H2O).
Formation of Salt
- The remaining ions from the acid and base combine to form a salt.
- For example, if hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the products will be sodium chloride (NaCl) and water.
General Reaction Equation
- The general form of the neutralization reaction can be expressed as:
Acid + Base → Salt + Water.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'D' because the primary products of an acid-base reaction are indeed salt and water. This fundamental concept is crucial in understanding many chemical reactions and applications in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
When an acid reacts with a base, the primary result is the formation of salt and water. This reaction is commonly known as a neutralization reaction.
Key Components of the Reaction
- Acids: Substances that donate protons (H+) in a solution.
- Bases: Substances that accept protons (H+) or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution.
Neutralization Reaction
- When an acid and a base interact, they undergo a neutralization process.
- The acidic component (H+) from the acid combines with the basic component (OH-) from the base to form water (H2O).
Formation of Salt
- The remaining ions from the acid and base combine to form a salt.
- For example, if hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the products will be sodium chloride (NaCl) and water.
General Reaction Equation
- The general form of the neutralization reaction can be expressed as:
Acid + Base → Salt + Water.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'D' because the primary products of an acid-base reaction are indeed salt and water. This fundamental concept is crucial in understanding many chemical reactions and applications in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
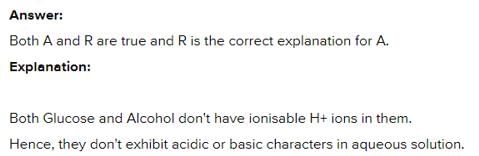
Assertion : The aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not show acidic character. Reason : Aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not give H+ ions.
- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : The aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not show acidic character. Reason : Aqueous solutions of glucose and alcohol do not give H+ ions.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Which of the following base is used in the manufacture of bleaching powder?- a)Magnesium hydroxide
- b)Sodium hydroxide
- c)Potassium hydroxide
- d)Calcium hydroxide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following base is used in the manufacture of bleaching powder?
a)
Magnesium hydroxide
b)
Sodium hydroxide
c)
Potassium hydroxide
d)
Calcium hydroxide

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Bleaching powder is prepared by passing chlorine gas over dry slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
Chemical Equation:
Cl2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Here,
- Ca(OH)2 = Calcium hydroxide (slaked lime)
- Cl2 = Chlorine
- CaOCl2 = Bleaching powder
- H2O = Water
So, the base used is Calcium hydroxide.
Assertion: HCl gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper.
Reason: HCl gas dissolves in the water present in wet litmus paper to from H+ ions.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: HCl gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper.
Reason: HCl gas dissolves in the water present in wet litmus paper to from H+ ions.
Reason: HCl gas dissolves in the water present in wet litmus paper to from H+ ions.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Prabhat pandey answered |
Assertion and Reason Overview
The assertion states that HCl gas does not change the color of dry blue litmus paper, while the reason explains that HCl gas dissolves in the water present in wet litmus paper to form H+ ions.
Analysis of the Assertion (A)
- Dry Blue Litmus Paper:
- Dry litmus paper does not contain any water.
- Without moisture, HCl gas cannot dissolve or dissociate into H+ ions.
- Color Change:
- Since there are no H+ ions from HCl in dry conditions, there will be no color change in the blue litmus paper.
Analysis of the Reason (R)
- Dissolution of HCl:
- HCl is a strong acid and readily dissolves in water, producing H+ ions.
- This dissolution occurs only in the presence of moisture.
- Correct Explanation:
- While the reason correctly states the behavior of HCl in wet litmus paper, it does not explain why dry litmus paper remains unchanged.
Conclusion
- Both Statements:
- Both the assertion (A) and reason (R) are true statements.
- However, reason (R) does not logically explain the assertion (A) since the absence of moisture in dry litmus paper prevents any interaction with HCl gas.
Thus, the correct option is B: Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
The assertion states that HCl gas does not change the color of dry blue litmus paper, while the reason explains that HCl gas dissolves in the water present in wet litmus paper to form H+ ions.
Analysis of the Assertion (A)
- Dry Blue Litmus Paper:
- Dry litmus paper does not contain any water.
- Without moisture, HCl gas cannot dissolve or dissociate into H+ ions.
- Color Change:
- Since there are no H+ ions from HCl in dry conditions, there will be no color change in the blue litmus paper.
Analysis of the Reason (R)
- Dissolution of HCl:
- HCl is a strong acid and readily dissolves in water, producing H+ ions.
- This dissolution occurs only in the presence of moisture.
- Correct Explanation:
- While the reason correctly states the behavior of HCl in wet litmus paper, it does not explain why dry litmus paper remains unchanged.
Conclusion
- Both Statements:
- Both the assertion (A) and reason (R) are true statements.
- However, reason (R) does not logically explain the assertion (A) since the absence of moisture in dry litmus paper prevents any interaction with HCl gas.
Thus, the correct option is B: Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Assertion : pH = 7 signifies pure water.
Reason : At this pH, [H+] = [OH-]= 10-7.
- a)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : pH = 7 signifies pure water.
Reason : At this pH, [H+] = [OH-]= 10-7.
a)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Let's evaluate the assertion and reason provided:
-
Assertion (A): pH = 7 signifies pure water.
- This statement is true. Pure water at 25°C has a neutral pH of 7, which is a result of the equal concentrations of hydrogen ions [H+][H^+][H+] and hydroxide ions [OH−][OH^-][OH−].
-
Reason (R): At this pH, [H+] = [OH-] = 10^-7.
- This statement is also true. In pure water at 25°C, the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+][H^+][H+] and hydroxide ions [OH−][OH^-][OH−] are both 10−710^{-7}10−7 M, leading to a pH of 7.
Conclusion:
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
4. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Direction: In the Following Questions, A Statement of Assertion (A) Is Followed by A Statement of Reason (R). Mark The Correct Choice As:Assertion: While dissolving an acid or base in water, the acids must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring.Reason: Dissolving an acid on a base in water in a highly exothermic reaction.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the Following Questions, A Statement of Assertion (A) Is Followed by A Statement of Reason (R). Mark The Correct Choice As:
Assertion: While dissolving an acid or base in water, the acids must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring.
Reason: Dissolving an acid on a base in water in a highly exothermic reaction.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
e)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A) : The acid must always be added to water with constant stirring.
Reason (R) : Mixing of an acid with water decreases the concentration of H+ ions per unit volume.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d) A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A) : The acid must always be added to water with constant stirring.
Reason (R) : Mixing of an acid with water decreases the concentration of H+ ions per unit volume.
Assertion (A) : The acid must always be added to water with constant stirring.
Reason (R) : Mixing of an acid with water decreases the concentration of H+ ions per unit volume.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
- Assertion (A): True. Acid should be added to water with stirring to prevent exothermic reactions from causing splashes or eruptions.
- Reason (R): True. Adding acid to water decreases the concentration of H⁺ ions per unit volume as the solution becomes more diluted.
- The reason (R) correctly explains the safety aspect of dilution rather than the procedural necessity of adding acid to water.
- Correct choice: B. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- Reason (R): True. Adding acid to water decreases the concentration of H⁺ ions per unit volume as the solution becomes more diluted.
- The reason (R) correctly explains the safety aspect of dilution rather than the procedural necessity of adding acid to water.
- Correct choice: B. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Assertion: Common salt is an important raw material for the production of various materials like sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.Reasoning: Common salt is processed to obtain different substances, and each of these substances plays a crucial role in daily use, such as in cleaning, cooking, and chemical processes.- a)Both assertion and reasoning are true, and the reasoning is the correct explanation for the assertion.
- b)Both assertion and reasoning are true, but the reasoning is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
- c)The assertion is true, but the reasoning is false.
- d)The assertion is false, but the reasoning is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: Common salt is an important raw material for the production of various materials like sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
Reasoning: Common salt is processed to obtain different substances, and each of these substances plays a crucial role in daily use, such as in cleaning, cooking, and chemical processes.
a)
Both assertion and reasoning are true, and the reasoning is the correct explanation for the assertion.
b)
Both assertion and reasoning are true, but the reasoning is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
c)
The assertion is true, but the reasoning is false.
d)
The assertion is false, but the reasoning is true.
|
|
Naman gupta answered |
Assertion: Importance of Common Salt
- Common salt (sodium chloride) is essential as a raw material for producing various important chemicals.
- These chemicals include:
- Sodium hydroxide (used in soap and detergents)
- Baking soda (used in cooking and cleaning)
- Washing soda (used in laundry and cleaning)
- Bleaching powder (used for disinfecting and bleaching)
Reasoning: Processing of Common Salt
- Common salt is processed through chemical reactions to obtain these substances.
- Each product derived from common salt plays a significant role in daily life:
- Cleaning agents
- Cooking ingredients
- Components in numerous industrial processes
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option A)
- Both the assertion and reasoning are true.
- The assertion highlights the importance of common salt in producing various chemicals used in everyday applications.
- The reasoning accurately explains how common salt is transformed into these substances and emphasizes their significance in daily tasks such as cleaning and cooking.
Conclusion
- Since both statements are true and the reasoning correctly supports the assertion, the answer is option 'A': both assertion and reasoning are true, and the reasoning is the correct explanation for the assertion.
- Common salt (sodium chloride) is essential as a raw material for producing various important chemicals.
- These chemicals include:
- Sodium hydroxide (used in soap and detergents)
- Baking soda (used in cooking and cleaning)
- Washing soda (used in laundry and cleaning)
- Bleaching powder (used for disinfecting and bleaching)
Reasoning: Processing of Common Salt
- Common salt is processed through chemical reactions to obtain these substances.
- Each product derived from common salt plays a significant role in daily life:
- Cleaning agents
- Cooking ingredients
- Components in numerous industrial processes
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option A)
- Both the assertion and reasoning are true.
- The assertion highlights the importance of common salt in producing various chemicals used in everyday applications.
- The reasoning accurately explains how common salt is transformed into these substances and emphasizes their significance in daily tasks such as cleaning and cooking.
Conclusion
- Since both statements are true and the reasoning correctly supports the assertion, the answer is option 'A': both assertion and reasoning are true, and the reasoning is the correct explanation for the assertion.
In addition to sculpting and art, where else is Plaster of Paris commonly used?
- a)Automotive industry
- b)Healthcare industry
- c)Food industry
- d)Home decoration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer??
In addition to sculpting and art, where else is Plaster of Paris commonly used?
a)
Automotive industry
b)
Healthcare industry
c)
Food industry
d)
Home decoration
|
|
Rounak Joshi answered |
Plaster of Paris in Home Decoration
Plaster of Paris is a versatile material commonly used in various applications, including home decoration. Here are some key uses in this context:
1. Decorative Molding
- Plaster of Paris is frequently used to create intricate decorative molding and cornices for ceilings and walls.
- These moldings add elegance and character to a room, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
2. Wall Finishes
- It can be applied as a smooth finish on walls, providing a clean and polished look.
- Textured finishes can also be created using Plaster of Paris, adding dimension and style.
3. Sculptures and Art Pieces
- While it is known for sculpting, Plaster of Paris is also used to create standalone art pieces and decorative sculptures that can be displayed in homes.
- These sculptures can be customized to fit various interior design styles.
4. Ceiling Medallions
- Ceiling medallions made from Plaster of Paris serve as decorative accents around light fixtures or chandeliers.
- They create a focal point and can be found in various designs, from classical to modern.
5. DIY Projects
- Many homeowners use Plaster of Paris for DIY home decor projects, such as making personalized decorative items.
- It is easy to mold and shape, making it a favorite among craft enthusiasts.
In conclusion, Plaster of Paris serves as an essential material in home decoration, offering both functionality and artistic expression. Its various applications contribute significantly to enhancing the beauty and charm of living spaces.
Plaster of Paris is a versatile material commonly used in various applications, including home decoration. Here are some key uses in this context:
1. Decorative Molding
- Plaster of Paris is frequently used to create intricate decorative molding and cornices for ceilings and walls.
- These moldings add elegance and character to a room, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
2. Wall Finishes
- It can be applied as a smooth finish on walls, providing a clean and polished look.
- Textured finishes can also be created using Plaster of Paris, adding dimension and style.
3. Sculptures and Art Pieces
- While it is known for sculpting, Plaster of Paris is also used to create standalone art pieces and decorative sculptures that can be displayed in homes.
- These sculptures can be customized to fit various interior design styles.
4. Ceiling Medallions
- Ceiling medallions made from Plaster of Paris serve as decorative accents around light fixtures or chandeliers.
- They create a focal point and can be found in various designs, from classical to modern.
5. DIY Projects
- Many homeowners use Plaster of Paris for DIY home decor projects, such as making personalized decorative items.
- It is easy to mold and shape, making it a favorite among craft enthusiasts.
In conclusion, Plaster of Paris serves as an essential material in home decoration, offering both functionality and artistic expression. Its various applications contribute significantly to enhancing the beauty and charm of living spaces.
What can be said about the pH of a salt formed by a weak acid and a weak base?
- a)The pH will always be exactly 7.
- b)The pH will always be less than 7.
- c)The pH will always be greater than 7.
- d)The pH cannot be predicted.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer??
What can be said about the pH of a salt formed by a weak acid and a weak base?
a)
The pH will always be exactly 7.
b)
The pH will always be less than 7.
c)
The pH will always be greater than 7.
d)
The pH cannot be predicted.
|
|
Parag chakraborty answered |
Understanding pH of Salts from Weak Acids and Bases
When a salt is formed from a weak acid and a weak base, predicting its pH can be complex. Here's why:
Nature of the Components
- Weak Acid: A weak acid only partially dissociates in water, meaning it does not release all its hydrogen ions (H+).
- Weak Base: A weak base also partially dissociates, producing hydroxide ions (OH-) to a limited extent.
Hydrolysis Reaction
- When the salt dissolves in water, hydrolysis occurs. The anions from the weak acid and the cations from the weak base can react with water, affecting the pH.
Factors Influencing pH
- Strength of Acid and Base: The degree of dissociation of both the weak acid and weak base plays a critical role. If one is significantly weaker than the other, it will dominate the pH outcome.
- Concentration: The concentrations of the salt solution also influence how much the salt will hydrolyze and thus the resulting pH.
Conclusion
- Since the pH depends on the relative strengths of the weak acid and weak base, it can be less than, greater than, or equal to 7.
- Therefore, without specific information about the acid and base involved, it is impossible to predict the pH of the resulting salt solution accurately.
This complexity leads to the conclusion that the pH cannot be predicted definitively, which is why option 'D' is the correct answer.
When a salt is formed from a weak acid and a weak base, predicting its pH can be complex. Here's why:
Nature of the Components
- Weak Acid: A weak acid only partially dissociates in water, meaning it does not release all its hydrogen ions (H+).
- Weak Base: A weak base also partially dissociates, producing hydroxide ions (OH-) to a limited extent.
Hydrolysis Reaction
- When the salt dissolves in water, hydrolysis occurs. The anions from the weak acid and the cations from the weak base can react with water, affecting the pH.
Factors Influencing pH
- Strength of Acid and Base: The degree of dissociation of both the weak acid and weak base plays a critical role. If one is significantly weaker than the other, it will dominate the pH outcome.
- Concentration: The concentrations of the salt solution also influence how much the salt will hydrolyze and thus the resulting pH.
Conclusion
- Since the pH depends on the relative strengths of the weak acid and weak base, it can be less than, greater than, or equal to 7.
- Therefore, without specific information about the acid and base involved, it is impossible to predict the pH of the resulting salt solution accurately.
This complexity leads to the conclusion that the pH cannot be predicted definitively, which is why option 'D' is the correct answer.
What happens when excess carbon dioxide is passed through lime water?
- a)The lime water turns milky.
- b)The lime water turns green.
- c)The lime water turns yellow.
- d)The lime water milkiness disappears.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer??
What happens when excess carbon dioxide is passed through lime water?
a)
The lime water turns milky.
b)
The lime water turns green.
c)
The lime water turns yellow.
d)
The lime water milkiness disappears.
|
|
Alpana dubey answered |
Understanding Lime Water Reaction with Carbon Dioxide
When excess carbon dioxide is passed through lime water (a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide), a series of chemical reactions occur that ultimately lead to the observed outcomes.
Initial Reaction
- Lime water is clear due to the presence of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- When carbon dioxide (CO2) is introduced, it reacts with calcium hydroxide to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Formation of Calcium Carbonate
- The reaction can be summarized as follows:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
- Calcium carbonate is insoluble in water, leading to the formation of a white precipitate, which can make the lime water appear milky.
Excess Carbon Dioxide Impact
- If an excess amount of carbon dioxide is passed through the lime water, the following reaction takes place:
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
- This reaction converts the precipitate (calcium carbonate) back into calcium bicarbonate (calcium hydrogen carbonate), which is soluble in water.
Final Observation
- As a result of this reaction, the initial milkiness of the lime water disappears, leading to a clear solution again.
- This explains why the correct answer is option 'D': The milkiness of the lime water disappears when excess carbon dioxide is passed through it.
In summary, the initial reaction creates a milky solution due to calcium carbonate formation, but excess CO2 causes the precipitation to dissolve, restoring the clarity of the lime water.
When excess carbon dioxide is passed through lime water (a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide), a series of chemical reactions occur that ultimately lead to the observed outcomes.
Initial Reaction
- Lime water is clear due to the presence of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- When carbon dioxide (CO2) is introduced, it reacts with calcium hydroxide to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Formation of Calcium Carbonate
- The reaction can be summarized as follows:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
- Calcium carbonate is insoluble in water, leading to the formation of a white precipitate, which can make the lime water appear milky.
Excess Carbon Dioxide Impact
- If an excess amount of carbon dioxide is passed through the lime water, the following reaction takes place:
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
- This reaction converts the precipitate (calcium carbonate) back into calcium bicarbonate (calcium hydrogen carbonate), which is soluble in water.
Final Observation
- As a result of this reaction, the initial milkiness of the lime water disappears, leading to a clear solution again.
- This explains why the correct answer is option 'D': The milkiness of the lime water disappears when excess carbon dioxide is passed through it.
In summary, the initial reaction creates a milky solution due to calcium carbonate formation, but excess CO2 causes the precipitation to dissolve, restoring the clarity of the lime water.
What is the chemical formula of bleaching powder?
- a)Ca(ClO)2
- b)CaOCl2
- c)CaClO
- d)CaOCl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer??
What is the chemical formula of bleaching powder?
a)
Ca(ClO)2
b)
CaOCl2
c)
CaClO
d)
CaOCl

|
Ishani Sengupta answered |
Chemical Composition of Bleaching Powder
Bleaching powder is a widely used chemical in various applications, primarily for its bleaching and disinfecting properties. Its chemical formula is essential for understanding its composition and usage.
Correct Answer: Ca(OCl)2
The correct option for the chemical formula of bleaching powder is:
- Ca(OCl)2 (or equivalently, CaOCl2)
Explanation of the Components
- Calcium (Ca): This element is a metal that forms the basis of the compound. It is essential for many chemical reactions and contributes to the stability of the compound.
- Hypochlorite Ion (OCl-): The hypochlorite ion is responsible for the bleaching and disinfecting properties of the compound. It releases chlorine when dissolved in water, which is effective for killing bacteria and other pathogens.
Structure and Properties
- Molecular Structure: In bleaching powder, one calcium ion is bonded to two hypochlorite ions. This results in a stable compound that can be used effectively in various applications.
- Uses: Bleaching powder is commonly used in water treatment, textile industry, and for disinfecting surfaces. Its ability to release chlorine makes it an excellent agent for purifying water.
Conclusion
In summary, the chemical formula of bleaching powder is correctly represented by option b (CaOCl2). Understanding its composition helps in appreciating its applications and effectiveness as a bleaching and disinfecting agent.
Bleaching powder is a widely used chemical in various applications, primarily for its bleaching and disinfecting properties. Its chemical formula is essential for understanding its composition and usage.
Correct Answer: Ca(OCl)2
The correct option for the chemical formula of bleaching powder is:
- Ca(OCl)2 (or equivalently, CaOCl2)
Explanation of the Components
- Calcium (Ca): This element is a metal that forms the basis of the compound. It is essential for many chemical reactions and contributes to the stability of the compound.
- Hypochlorite Ion (OCl-): The hypochlorite ion is responsible for the bleaching and disinfecting properties of the compound. It releases chlorine when dissolved in water, which is effective for killing bacteria and other pathogens.
Structure and Properties
- Molecular Structure: In bleaching powder, one calcium ion is bonded to two hypochlorite ions. This results in a stable compound that can be used effectively in various applications.
- Uses: Bleaching powder is commonly used in water treatment, textile industry, and for disinfecting surfaces. Its ability to release chlorine makes it an excellent agent for purifying water.
Conclusion
In summary, the chemical formula of bleaching powder is correctly represented by option b (CaOCl2). Understanding its composition helps in appreciating its applications and effectiveness as a bleaching and disinfecting agent.
Chapter doubts & questions for Acids, Bases and Salts - Science Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Acids, Bases and Salts - Science Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









