All Exams >
MCAT >
Biochemistry for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Carbohydrates for MCAT Exam
The compound which gives red colour with Fehling’s solution?- a)Cellulose
- b)Benzaldehyde
- c)Cane sugar
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which gives red colour with Fehling’s solution?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Benzaldehyde
c)
Cane sugar
d)
Glucose

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Fehling's solution to make difference between carbohydrate and ketone functional grp and also used for differentiate reducing and non reducing sugar and as u know glucose is a reducing sugar so it will give red colour with fehling's solution (all monosachharides are reducing sugar).
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:- a)The presence of -CHO group
- b)The presence of alkaline group
- c)The presence of acidic group
- d)The presence of keto group
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:
a)
The presence of -CHO group
b)
The presence of alkaline group
c)
The presence of acidic group
d)
The presence of keto group
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Glucose gives silver mirror test with Tollens reagent. It shows the presence of aldehyde group.
Also, mild oxidation of glucose with bromine water gives gluconic acid which shows the presence of aldehyde group.
Also, mild oxidation of glucose with bromine water gives gluconic acid which shows the presence of aldehyde group.
Glucose and fructose are:- a)Position isomers
- b)Functional isomers
- c)Chain isomers
- d)Optical isomers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose and fructose are:
a)
Position isomers
b)
Functional isomers
c)
Chain isomers
d)
Optical isomers
|
|
Tanvi Bose answered |
Glucose and fructose are functional isomers of each other Because they have same molecular formula that is C6H12O6 But different functional group in their chemical formula. Glucose has aldehyde group while fructose has ketone as functional group.
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?- a)Cellulose
- b)Lactose
- c)Mannose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Lactose
c)
Mannose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Lactose intolerance is the inability to break down a type of natural sugar called lactose. Lactose is commonly found in dairy products, such as milk and yogurt. A person becomes lactose intolerant when his or her small intestine stops making enough of the enzyme lactase to digest and break down the lactose.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:- a)Hydration
- b)Inversion
- c)Esterification
- d)Saponification
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:
a)
Hydration
b)
Inversion
c)
Esterification
d)
Saponification

|
Sahana Savalagi answered |
Hydrolysis of sucrose is inversion because the angle of specific rotation of the plane polarized light changes from positive to negative value due to the presence of optical isomers of mixture of glucose and fructose sugar...
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:- a)Monoacetate
- b)Diacetate
- c)Pentaacetate
- d) Hexaacetate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:
a)
Monoacetate
b)
Diacetate
c)
Pentaacetate
d)
Hexaacetate
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
It forms glucose pentaacetate. The acetic anhydride esterifies with all the alcohol groups on the glucose ring.
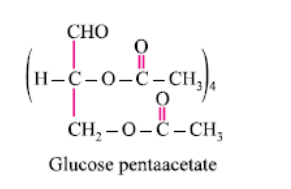

The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:- a)Carboxylic linkage
- b)Carbonyl linkage
- c)Peptide linkage
- d)Glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:
a)
Carboxylic linkage
b)
Carbonyl linkage
c)
Peptide linkage
d)
Glycosidic linkage

|
Aleena Mathew answered |
All sacchrides /carbohydrates form glycosidic bond by eliminating water molecule
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:- a)The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
- b)Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
- c)On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
- d)Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:
a)
The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
b)
Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
c)
On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
d)
Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
|
|
Gowri Menon answered |
Glucose and C2 of fructose, which does not have a free aldehyde or ketone group to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:- a)All carbohydrates
- b)Sucrose
- c)Fructose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:
a)
All carbohydrates
b)
Sucrose
c)
Fructose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The Molisch test uses concentrated sulphuric acid as the dehydrating acid. This acid dehydrates all carbohydrates, so the test is used to distinguish between carbohydrates and non-carbohydrates.
On hydrolysis maltose gives:- a)One molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose
- b)Two molecules of fructose
- c)One molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose
- d)Two molecules of glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On hydrolysis maltose gives:
a)
One molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose
b)
Two molecules of fructose
c)
One molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose
d)
Two molecules of glucose
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
On hydrolysis, maltose gives glucose with the help of maltase enzyme which works as a catalysis of the hydrolysis of the glycoside bond.
Maltase is a disaccharide which will reduce sugar giving two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis.
It will give alpha-D-glucose and alpha-D-glucose.
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?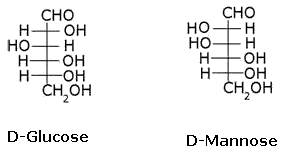
- a)Epimers
- b)Enatiomers
- c)Structural isomers
- d)Anomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?
a)
Epimers
b)
Enatiomers
c)
Structural isomers
d)
Anomers

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The pairs of optical isomers which differ in configuration around any other C atom other than C1 atom are called epimers. D-glucose and D-mannose are C2 epimers.
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?- a)Sucrose
- b)Maltose
- c)Lactose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Maltose
c)
Lactose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Non-reducing sugars do not have an OH group attached to the anomeric carbon so they cannot reduce other compounds. All monosaccharides such as glucose are reducing sugars. A disaccharide can be a reducing sugar or a non-reducing sugar. Maltose and lactose are reducing sugars, while sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
The commonest disaccharide have the molecular formula:- a)C10H20O10
- b)C12H22O11
- c)C10H18O9
- d)C11H22O11
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The commonest disaccharide have the molecular formula:
a)
C10H20O10
b)
C12H22O11
c)
C10H18O9
d)
C11H22O11

|
Sanjeev Kumar answered |
Because it is in the ratio of 1:2:1
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?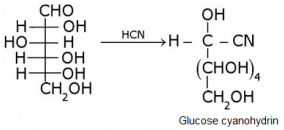
- a)It shows the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
- b)It shows the presence of primary alcoholic group in glucose.
- c)It shows the presence of ring structure in glucose.
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?
a)
It shows the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
b)
It shows the presence of primary alcoholic group in glucose.
c)
It shows the presence of ring structure in glucose.
d)
none
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Glucose gets oxidized to cyanohydrin in reaction with HCN . This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.
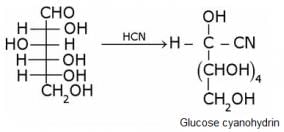
Glucose gets oxidized to cyanohydrin in reaction with HCN . This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.

The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?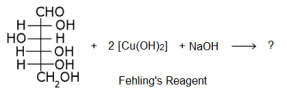
- a)Glucose will not react with Fehling’s reagent.
- b)Grey precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
- c)Red precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
- d)Saccharic acid will be formed when glucose will react with Fehling’s reagent.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?
a)
Glucose will not react with Fehling’s reagent.
b)
Grey precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
c)
Red precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
d)
Saccharic acid will be formed when glucose will react with Fehling’s reagent.

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Because it is the chemical property of aliphatic aldehyde to give red precipitate with fehling solution.
RCHO + 2 CuO -----------> Cu2O. + RCOOH
Fehling reagents is aq. alkaline CuSO4 solution along with Rochelle salt Na-K tartrate.
And glucose molecule consists of aldehydic group at first position and hence it is also a aldehyde and thus give this characteristic test.
RCHO + 2 CuO -----------> Cu2O. + RCOOH
Fehling reagents is aq. alkaline CuSO4 solution along with Rochelle salt Na-K tartrate.
And glucose molecule consists of aldehydic group at first position and hence it is also a aldehyde and thus give this characteristic test.
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?- a)Sucrose
- b)Fructose
- c)Glucose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Fructose
c)
Glucose
d)
Cellulose

|
Sanjeevini Angadi answered |
It is called invert sugar because the angle of the specific rotation of the plain polarized light changes from a positive to a negative value due to the presence of the optical isomers of the mixture of glucose and fructosesugars.
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?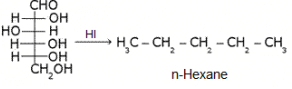
- a)Shows the presence of -CHO group
- b)Shows the presence of C=O group
- c)Shows the presence of six carbons linked linearly
- d)Shows the presence of ring structure of glucose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?
a)
Shows the presence of -CHO group
b)
Shows the presence of C=O group
c)
Shows the presence of six carbons linked linearly
d)
Shows the presence of ring structure of glucose
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
It shows that glucose exists as n-hexane...i.e. it has straight linear chain...
Which of the following is the simplest form of carbohydrates?- a)Carboxyl groups.
- b)Aldehyde and ketone groups.
- c)Alcohol and carboxyl groups.
- d)Hydroxyl groups and hydrogen groups.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the simplest form of carbohydrates?
a)
Carboxyl groups.
b)
Aldehyde and ketone groups.
c)
Alcohol and carboxyl groups.
d)
Hydroxyl groups and hydrogen groups.

|
Orion Classes answered |
The simplest form of carbohydrates consists of aldehyde and ketone groups. These functional groups are present in monosaccharides, the basic building blocks of carbohydrates.
Which of the following is true regarding carbohydrates?- a)Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
- b)Carbohydrates are primarily found in animal tissues.
- c)Carbohydrates are classified as lipids and proteins.
- d)Carbohydrates are insoluble in water.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true regarding carbohydrates?
a)
Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
b)
Carbohydrates are primarily found in animal tissues.
c)
Carbohydrates are classified as lipids and proteins.
d)
Carbohydrates are insoluble in water.
|
|
Carter Mitchell answered |
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are one of the three main macronutrients, along with proteins and lipids, and are essential for providing energy to the body.
Composition of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The general formula for carbohydrates is (CH2O)n, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. This formula indicates that carbohydrates are composed of carbon and water (H2O).
Primary Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are primarily found in plant tissues. Plants produce carbohydrates through photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight into energy. Common sources of carbohydrates in the human diet include fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and dairy products.
Classification of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are a distinct group of compounds and are not classified as lipids or proteins. They have their own classification system, which includes monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are single sugar units, while disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharide units joined together. Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked together.
Solubility of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are generally soluble in water. This solubility is due to the presence of hydroxyl groups (-OH) in their structure, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, some carbohydrates, such as insoluble fiber, may be partially or completely insoluble in water.
Summary
In summary, carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are primarily found in plant tissues and are not classified as lipids or proteins. Carbohydrates are generally soluble in water, although some types may be insoluble.
Carbohydrates are organic compounds that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are one of the three main macronutrients, along with proteins and lipids, and are essential for providing energy to the body.
Composition of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The general formula for carbohydrates is (CH2O)n, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. This formula indicates that carbohydrates are composed of carbon and water (H2O).
Primary Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are primarily found in plant tissues. Plants produce carbohydrates through photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight into energy. Common sources of carbohydrates in the human diet include fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and dairy products.
Classification of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are a distinct group of compounds and are not classified as lipids or proteins. They have their own classification system, which includes monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are single sugar units, while disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharide units joined together. Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked together.
Solubility of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are generally soluble in water. This solubility is due to the presence of hydroxyl groups (-OH) in their structure, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, some carbohydrates, such as insoluble fiber, may be partially or completely insoluble in water.
Summary
In summary, carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are primarily found in plant tissues and are not classified as lipids or proteins. Carbohydrates are generally soluble in water, although some types may be insoluble.
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharide is called:- a)peptide linkage
- b)glycogen linkage
- c)nucleosidic linkage
- d)glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharide is called:
a)
peptide linkage
b)
glycogen linkage
c)
nucleosidic linkage
d)
glycosidic linkage
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Monosaccharides such as glucose can be linked together in condensation reactions. For example, sucrose (table sugar) is formed from one molecule of glucose and one of fructose, as shown below. Molecules composed of two monosaccharides are called disaccharides.
Which of the following carbohydrates is called milk sugar?- a)Glucose
- b)Galactose
- c)Lactose
- d)Maltose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called milk sugar?
a)
Glucose
b)
Galactose
c)
Lactose
d)
Maltose

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Lactose is the carbohydrate that is commonly known as milk sugar. It is a disaccharide composed of two sugar molecules, galactose and glucose, linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose is found in the milk of mammals, including humans, and is an important source of energy for infants.
Here is a detailed explanation of why lactose is called milk sugar:
Lactose in Milk:
- Lactose is primarily found in the milk of mammals. It is the main carbohydrate present in milk, accounting for about 4-5% of its composition.
- It provides energy for the growing infant and is essential for their development.
- As mammals produce milk to nourish their young, lactose is present in varying amounts in the milk of different species, including humans.
Structure of Lactose:
- Lactose is a disaccharide, which means it is composed of two sugar molecules linked together.
- It consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
- The glucose and galactose molecules are joined by a β-glycosidic bond, which is a specific type of chemical bond between the two sugars.
Digestion of Lactose:
- Lactose is digested by the enzyme lactase, which is produced in the small intestine.
- Lactase breaks down lactose into its individual sugar components, glucose and galactose.
- These simple sugars can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
Intolerance to Lactose:
- Some individuals have a reduced ability to produce lactase, resulting in lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance is characterized by symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming milk or dairy products.
- This occurs because undigested lactose reaches the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and other byproducts.
In conclusion, lactose is called milk sugar because it is the main carbohydrate found in milk. It consists of glucose and galactose linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose provides energy for infants and is digested by the enzyme lactase. Lactose intolerance can occur when there is a reduced ability to produce lactase, leading to digestive symptoms after consuming milk or dairy products.
Here is a detailed explanation of why lactose is called milk sugar:
Lactose in Milk:
- Lactose is primarily found in the milk of mammals. It is the main carbohydrate present in milk, accounting for about 4-5% of its composition.
- It provides energy for the growing infant and is essential for their development.
- As mammals produce milk to nourish their young, lactose is present in varying amounts in the milk of different species, including humans.
Structure of Lactose:
- Lactose is a disaccharide, which means it is composed of two sugar molecules linked together.
- It consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
- The glucose and galactose molecules are joined by a β-glycosidic bond, which is a specific type of chemical bond between the two sugars.
Digestion of Lactose:
- Lactose is digested by the enzyme lactase, which is produced in the small intestine.
- Lactase breaks down lactose into its individual sugar components, glucose and galactose.
- These simple sugars can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
Intolerance to Lactose:
- Some individuals have a reduced ability to produce lactase, resulting in lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance is characterized by symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming milk or dairy products.
- This occurs because undigested lactose reaches the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and other byproducts.
In conclusion, lactose is called milk sugar because it is the main carbohydrate found in milk. It consists of glucose and galactose linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose provides energy for infants and is digested by the enzyme lactase. Lactose intolerance can occur when there is a reduced ability to produce lactase, leading to digestive symptoms after consuming milk or dairy products.
Aldonic acids are compounds that:- a)can be oxidized, and therefore act as reducing agents.
- b)can be reduced, and therefore act as reducing agents.
- c)have been oxidized, and have acted as reducing agents.
- d)have been oxidized, and have acted as oxidizing agents.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Aldonic acids are compounds that:
a)
can be oxidized, and therefore act as reducing agents.
b)
can be reduced, and therefore act as reducing agents.
c)
have been oxidized, and have acted as reducing agents.
d)
have been oxidized, and have acted as oxidizing agents.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Aldonic acids form after the aldehyde group on a reducing sugar reduces another compound, becoming oxidized in the process.
Identify the following compound: 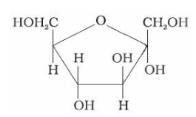
- a)β – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
- b)α – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
- c)α – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
- d)β – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the following compound:

a)
β – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
b)
α – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
c)
α – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
d)
β – D – (+) – Glucopyranose

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The given compound is a five-membered ring with:
- An oxygen atom in the ring → furanose ring
- Two –CH₂OH groups (on carbon-1 and carbon-4)
- Multiple –OH groups on the ring
This matches the structure of β-D-fructofuranose, the cyclic form of fructose.
The cyclic forms of monosaccharides are:
I. hemiacetals.
II. hemiketals.
III. acetals.- a)I only
- b)III only
- c)I and II only
- d)I, II, and III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cyclic forms of monosaccharides are:
I. hemiacetals.
II. hemiketals.
III. acetals.
I. hemiacetals.
II. hemiketals.
III. acetals.
a)
I only
b)
III only
c)
I and II only
d)
I, II, and III

|
Orion Classes answered |
Monosaccharides can exist as hemiacetals or hemiketals, depending on whether they are aldoses or ketoses. When a monosaccharide is in its cyclic form, the anomeric carbon is attached to the oxygen in the ring and a hydroxyl group. Hence, it is only a hemiacetal or hemiketal because an acetal or ketal would require the –OH group to be converted to another –OR group.
Which of the following is digestible by humans and is made up of only one type of monosaccharide?- a)Lactose
- b)Sucrose
- c)Maltose
- d)Cellobiose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is digestible by humans and is made up of only one type of monosaccharide?
a)
Lactose
b)
Sucrose
c)
Maltose
d)
Cellobiose

|
Orion Classes answered |
While maltose and cellobiose both have the same glucose subunits, only maltose is digestible by humans because β-glycosidic linkages cannot be cleaved in the human body.
When glucose is in a straight-chain formation, it:- a)is an aldoketose.
- b)is a pentose.
- c)has five chiral carbons.
- d)is one of a group of 16 stereoisomers.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When glucose is in a straight-chain formation, it:
a)
is an aldoketose.
b)
is a pentose.
c)
has five chiral carbons.
d)
is one of a group of 16 stereoisomers.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Glucose is an aldohexose, meaning that it has one aldehyde group and six carbons. Given this information, choices (A) and (B) can be eliminated. In aldose sugars, each nonterminal carbon is chiral. Therefore, glucose has four chiral centers, not five, as mentioned in choice (C). The number of stereoisomers possible for a chiral molecule is 2n, where n is the number of chiral carbons. Because glucose has four chiral centers, there are 24 = 16 possible stereoisomers.
Ketose sugars may have the ability to act as reducing sugars. Which process explains this?- a)Ketose sugars undergo tautomerization.
- b)The ketone group is oxidized directly.
- c)Ketose sugars undergo anomerization.
- d)The ketone group is reduced directly.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ketose sugars may have the ability to act as reducing sugars. Which process explains this?
a)
Ketose sugars undergo tautomerization.
b)
The ketone group is oxidized directly.
c)
Ketose sugars undergo anomerization.
d)
The ketone group is reduced directly.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Ketose sugars undergo tautomerization, a rearrangement of bonds, to undergo keto-enol shifts. This forms an aldose, which then allows them to act as reducing sugars. A ketone group alone cannot be oxidized. Anomerization, mentioned in choice (C), refers to ring closure of a monosaccharide, creating an anomeric carbon.
Which of the following is an example of a monosaccharide?- a)Glucose
- b)Sucrose
- c)Cellulose
- d)Starch
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of a monosaccharide?
a)
Glucose
b)
Sucrose
c)
Cellulose
d)
Starch

|
Orion Classes answered |
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and cannot be further hydrolyzed into smaller units. Glucose is a common monosaccharide and an important energy source in biological systems.
Why is the α-anomer of d-glucose less likely to form than the β-anomer?- a)The β-anomer is preferred for metabolism.
- b)The β-anomer undergoes less electron repulsion.
- c)The α-anomer is the more stable anomer.
- d)The α-anomer forms more in l-glucose.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is the α-anomer of d-glucose less likely to form than the β-anomer?
a)
The β-anomer is preferred for metabolism.
b)
The β-anomer undergoes less electron repulsion.
c)
The α-anomer is the more stable anomer.
d)
The α-anomer forms more in l-glucose.

|
Orion Classes answered |
The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon of the β-anomer is equatorial, thereby creating less steric hindrance than the α-anomer, which has the hydroxyl group of the anomeric carbon in axial position.
Which of the following enzymes cleaves polysaccharide chains and yields maltose exclusively?- a)α-Amylase
- b)β-Amylase
- c)Debranching enzyme
- d)Glycogen phosphorylase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following enzymes cleaves polysaccharide chains and yields maltose exclusively?
a)
α-Amylase
b)
β-Amylase
c)
Debranching enzyme
d)
Glycogen phosphorylase

|
Orion Classes answered |
β-Amylase cleaves amylose at the nonreducing end of the polymer to yield maltose exclusively, while α-amylase, choice (A), cleaves amylose anywhere along the chain to yield short polysaccharides, maltose, and glucose. Debranching enzyme, choice (C), removes oligosaccharides from a branch in glycogen or starches, while glycogen phosphorylase, choice (D), yields glucose 1-phosphate.
Chapter doubts & questions for Carbohydrates - Biochemistry for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Carbohydrates - Biochemistry for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Biochemistry for MCAT
138 videos|21 docs|26 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









