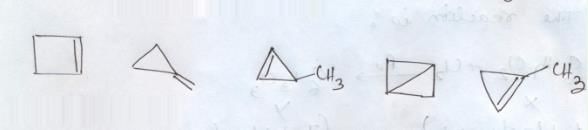All Exams >
Chemistry >
Topicwise Question Bank for IIT JAM/CSIR/GATE Chemistry >
All Questions
All questions of Basic Concepts in Organic Chemistry and Stereochemistry for Chemistry Exam
The acidity order for the following compound follows the order: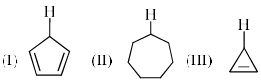
- a)I > II > III
- b)II > III > I
- c)I > III > II
- d)III > I > II
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The acidity order for the following compound follows the order:
a)
I > II > III
b)
II > III > I
c)
I > III > II
d)
III > I > II

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
Acidity of a compound depends upon the stability of the conjugate base. Here after protonation the conjugate base of 1 will gain stability due to aromatic character similarly conjugate base of 3 will be highly unstable due to anti aromatic character. Thus the order of the stability of conjugate base - 1>2>3. Thus the order of acidity is: 1>2>3 which is option 'a'.
Stability order of the following resonating structure will be: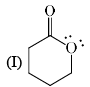
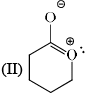
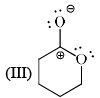
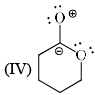
- a)I > II > III > IV
- b)II > I > III > IV
- c)III > II > I > IV
- d)I > III > II > IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stability order of the following resonating structure will be:
a)
I > II > III > IV
b)
II > I > III > IV
c)
III > II > I > IV
d)
I > III > II > IV

|
Dipanjan Sharma answered |
-1st is uncharged so it is the most stable among the following options.
-2nd one is charged but have more no of covalent bonds than 3rd and 4th so it is more stable than 3rd and 4th.
-Between 3rd and 4th follow the electronegativity rulle which means more electronegative atom bears negative charge. In 4th the positive charge on oxygen atom is against the electronegative prinicple . So it will like to have negative charge rather than positive chargee. So 3rd is more stable tha 4th.
Therefore the order will be 1>2>3>4
-2nd one is charged but have more no of covalent bonds than 3rd and 4th so it is more stable than 3rd and 4th.
-Between 3rd and 4th follow the electronegativity rulle which means more electronegative atom bears negative charge. In 4th the positive charge on oxygen atom is against the electronegative prinicple . So it will like to have negative charge rather than positive chargee. So 3rd is more stable tha 4th.
Therefore the order will be 1>2>3>4
The most stable conformations of 1,2-difluoroethane and dl-2, 3-butanediol are:
- a)
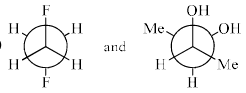
- b)
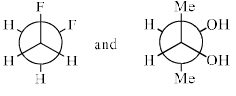
- c)
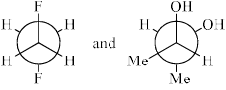
- d)
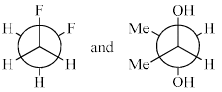
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable conformations of 1,2-difluoroethane and dl-2, 3-butanediol are:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
1,2-Difluoroethane:
1,2-Difluoroethane has two fluorine atoms attached to adjacent carbons in an ethane backbone. The most stable conformation generally minimizes steric repulsion and maximizes favorable interactions such as hyperconjugation and the anomeric effect (if applicable).
For 1,2-difluoroethane, the anti conformation (where the two fluorine atoms are 180 degrees apart) is generally the most stable due to minimized steric repulsion and torsional strain.
dl-2,3-Butanediol:
dl-2,3-Butanediol has hydroxyl groups on the second and third carbons of a butane backbone. The most stable conformation minimizes steric hindrance between the hydroxyl groups and other substituents.
For dl-2,3-butanediol, the gauche conformation (where the two hydroxyl groups are 60 degrees apart) is often the most stable due to the hydrogen bonding between the -OH groups.
Given the information above, we can analyze the provided options:
- Option A:
- 1,2-difluoroethane is in the anti conformation.
- dl-2,3-butanediol is in the gauche conformation.
- Option B:
- 1,2-difluoroethane is in a gauche conformation.
- dl-2,3-butanediol is in the anti conformation.
- Option C:
- 1,2-difluoroethane is in the gauche conformation.
- dl-2,3-butanediol is in the gauche conformation.
- Option D:
- 1,2-difluoroethane is in the anti conformation.
- dl-2,3-butanediol is in the anti conformation.
Based on the stability analysis:
- The anti conformation is most stable for 1,2-difluoroethane.
- The gauche conformation is most stable for dl-2,3-butanediol.
Therefore, the correct option is:
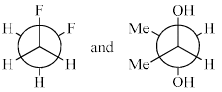
Increasing order of pKa values (pKa = –log Ka) of H2O, CH3OH and C6H5OH is:- a) H2O < CH3OH < C6H5OH
- b)CH3OH < H2O < C6H5OH
- c)C6H5OH < H2O < CH3OH
- d) C6H5OH < CH3OH < H2O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Increasing order of pKa values (pKa = –log Ka) of H2O, CH3OH and C6H5OH is:
a)
H2O < CH3OH < C6H5OH
b)
CH3OH < H2O < C6H5OH
c)
C6H5OH < H2O < CH3OH
d)
C6H5OH < CH3OH < H2O

|
Saikat Ghoshal answered |
The pKa of water is 14
The pKa of methanol (CH3OH) is 15.5
The pKa of Phenol (C6H5OH) is 9.88
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following is most basic?
- A:
- B:
- C:
- D:
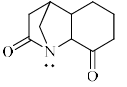
The answer is c.
Which of the following is most basic?

|
Yashdeep Maurya answered |
In option A,B,D the the loan pair of nitrogen atom is in conjugation with double bond of Oxygen atom... .so somewhat electron will be reduced or we can say diverted ...but in Option C there is no conjunction so it will be giving heighest quantity of electron ....and hence most basic...
Among the following dibromocyclohexanes, the one that reacts fastest with sodium iodide to give cyclohexene is:- a)
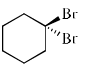
- b)
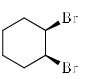
- c)
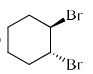
- d)
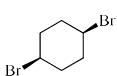
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following dibromocyclohexanes, the one that reacts fastest with sodium iodide to give cyclohexene is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
- The above reaction is an example of E2 elimination.
- For E2 elimination both the leaving group must be anti w.r.t each other in the adjacent carbon atoms.
- In option C, we get this requirement of anti geometry of the Br atoms, so it undergoes reaction.
Which is the correct structure of D-Glyceraldehyde:- a)
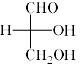
- b)
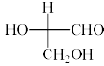
- c)
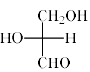
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the correct structure of D-Glyceraldehyde:
a)
b)
c)
d)
All of these.

|
Asf Institute answered |
All the options A, B and C are same
- When A is rotated by 90 degrees two times i.e. 180 degrees in plane of your screen then compound C will be obtained
- Now by switching A two times or ‘even’ switch compound B will be obtained and configuration remained same as the switch was even
Hence all are the same, so, D is correct.
Among the following compounds, which is the correct order of % enol content?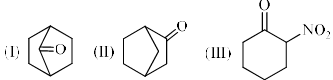
- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I
- c)II > III > I
- d)I > III > II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds, which is the correct order of % enol content?
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I
c)
II > III > I
d)
I > III > II
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
In the 1st compound the double bond is at the bridgehead carbon , as a result this compound cannot exist in enol form because such conformation would give an impossibility strained ring .Such dis stabilizing effect is absent in 2 nd compound . Whereas the 3 rd compound exclusively exist in enol form due to the formation of intramolecular hydrogen bonding
According to britz's rule at bridge head position -ve charge is unstable so; 3>2>1
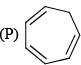
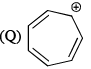
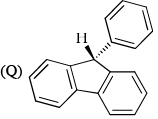
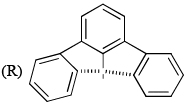
Which of the following are aromatic?

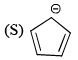
- a)P and Q
- b)Q and R
- c)R and S
- d)Q and S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are aromatic?
a)
P and Q
b)
Q and R
c)
R and S
d)
Q and S

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
Correct answer is. Q and S.
Which of the following reaction undergoes in the forward direction:- a)C2H5OH + OH- → C2H5O- + OH2
- b)H2S + OH- → HS- + OH2
- c)CH3CHO + OH- → CH2- — CHO + OH2
- d)
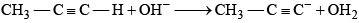
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reaction undergoes in the forward direction:
a)
C2H5OH + OH- → C2H5O- + OH2
b)
H2S + OH- → HS- + OH2
c)
CH3CHO + OH- → CH2- — CHO + OH2
d)
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Negative charge over S atom gets additional stability by conjugation through vacent 3d orbital of S ,so HS- is the most stable species and the reaction undergoes in the forward direction.
Which of the following compounds are non-aromatic?- a)
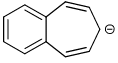
- b)
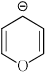
- c)
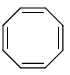
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds are non-aromatic?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
C and D are non-aromatic because C is nonplanar and D is having one carbon without hybridization.
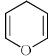
How many compounds become aromatic after deprotonation?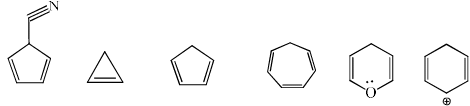
- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many compounds become aromatic after deprotonation?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
Compound which gives an stable conjugate base deprotonation will deprotonate easily.
so, 1,3 and 6 will become aromatic after deprotonation.
Which of the following term best describes the pair of compound shown:a) Enantiomers.b) Diastereomers.c) Mesomersd) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Dam answered |
If u have confusion in determining these type of problems look at the R and S configuration ...
if the compounds have opposite configuration then enantiomers ...if same identical...
still doubt ???
if the compounds have opposite configuration then enantiomers ...if same identical...
still doubt ???
Hyperconjugation is best described as:- a)Delocalization of p electrons into a nearby empty orbital
- b)Delocalization of sigma electrons into a nearby empty orbital
- c)The effect of alkyl groups donating a small amount of electron densit y induct ively into a carbocation
- d)The migration of a carbon or hydrogen from one carbocation to another
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hyperconjugation is best described as:
a)
Delocalization of p electrons into a nearby empty orbital
b)
Delocalization of sigma electrons into a nearby empty orbital
c)
The effect of alkyl groups donating a small amount of electron densit y induct ively into a carbocation
d)
The migration of a carbon or hydrogen from one carbocation to another

|
Om Desai answered |
Hyperconjugation is the stabilising interaction that results from the interaction of the electrons in a σ-bond (usually C-H or C-C) with an adjacent empty or partially filled p-orbital or a π-orbital to give an extended molecular orbital that increases the stability of the system.
Select the compounds which is/are anti-aromatic?- a)
- b)
- c)
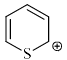
- d)
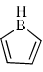
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the compounds which is/are anti-aromatic?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Corect Answer : a,d
For aromatic-compound should be cyclic, sp2 hybridised, planar, (4n+2)πe- for anti-aromatic-compound should be cyclic, sp2 hybridised, planar, (4n)πe-
Hence compound A and D has anti-aromatic character.
Hence compound A and D has anti-aromatic character.
Identify the correct C-O bond length order: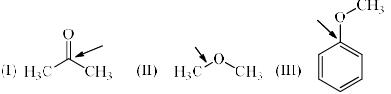
- a)I > II > III
- b)II > III > I
- c)I > III > II
- d)III > I > II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct C-O bond length order:
a)
I > II > III
b)
II > III > I
c)
I > III > II
d)
III > I > II

|
Rohan Desai answered |
Double bonds are shorter than single bond. In 1 there is double bond so it's bond length will be least.
Now we have to compare between 2 and 3. In 3 the lonepair over the Oxygen atom is involve in conjugation so it has partial double bond character, means bond length is lesser than single bond but greater than double bond. so bond length of 3 is greater than 2.
So the option 'B' is correct.
Now we have to compare between 2 and 3. In 3 the lonepair over the Oxygen atom is involve in conjugation so it has partial double bond character, means bond length is lesser than single bond but greater than double bond. so bond length of 3 is greater than 2.
So the option 'B' is correct.
Which of the following molecules, in pure form, is (are) unstable at room temperature:- a)
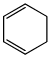
- b)
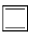
- c)
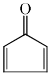
- d)
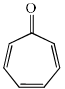
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecules, in pure form, is (are) unstable at room temperature:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Asf Institute answered |
Correct Answer :- b,c
Explanation : (B) Cyclobutadiene follows Huckel's criteria for anti-aromaticity [(4n)−π electrons], hence unstable.
(C) Follows Huckel's criteria for anti-aromaticity [(4n)−π electrons], hence, unstable.
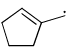
Which of the following systems are resonance contributors of the radical shown below?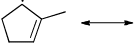
- a)
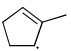
- b)
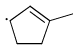
- c)
- d)
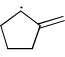
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following systems are resonance contributors of the radical shown below?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Option A is the contributor of the radical as it is the only structure going in delocalization.
Which one is strongest acid among following options?
- a)CH2FCOOH
- b)CHF2COOH
- c)CHCl2COOH
- d)CH2ClCOOH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is strongest acid among following options?
a)
CH2FCOOH
b)
CHF2COOH
c)
CHCl2COOH
d)
CH2ClCOOH
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
CHF2−COOH. Difluoroacetic acid is strongest because presence of two F atoms increases its acidic nature.
Which of the following is anti-aromatic?
- a)
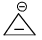
- b)
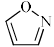
- c)
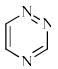
- d)
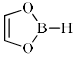
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is anti-aromatic?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Vishal Thakur answered |
In all other option we have 6pi electrons whereas in case of structure a we only have 4 pi electrons hence it is antiaromatic....
Arrange the following in the correct order of acidity of the hydrogen indicated in bold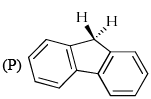
- a)P > Q > R
- b)R > Q > P
- c)Q > R > P
- d)P > R > Q
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following in the correct order of acidity of the hydrogen indicated in bold
a)
P > Q > R
b)
R > Q > P
c)
Q > R > P
d)
P > R > Q

|
Asf Institute answered |
Correct Answer :- b
Explanation : In R negative charge delocalised into two rings make them aromatic which are further stabilized by 3 benzene rings. while in P and Q negative charge delocalised to one ring make it aromatic which are further stabilized by two benzene rings. but Q have extra resonance in compare to P
Which of the following has (have) (4n + 2) π-electrons but not aromatic?- a)
- b)
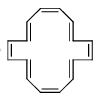
- c)
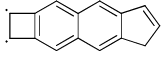
- d)
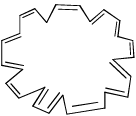
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has (have) (4n + 2) π-electrons but not aromatic?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
A and D have 4n+2 electrons but are not aromatic as they are non-planar.
Identify the correct acidic strength order in the following compounds.
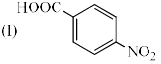
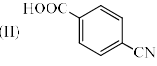
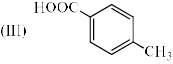
- a)I > II > III
- b)II > III > I
- c)I > III > II
- d)III > I > II
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct acidic strength order in the following compounds.
a)
I > II > III
b)
II > III > I
c)
I > III > II
d)
III > I > II
|
|
Bittoo Jangra answered |
Acidic strength is directly proportional to -I effect. -I effect order -NO2>CN>CH3.
The value of ‘n’ for the following molecule according to Hucke’s rule is
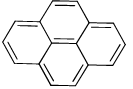
- a)16
- b)4
- c)3
- d)14
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of ‘n’ for the following molecule according to Hucke’s rule is
a)
16
b)
4
c)
3
d)
14

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
Correct Answer :- c
Explanation : According to Hucckel’s rule
We take pi bonds only on the periphery and do not count one not on boundaries or periphery.
4n + 2 = 14
4n = 12
n = 3
The most stable conformation of ethylene glycol is:- a)Anti
- b)Gauche
- c)Partially eclipsed
- d)Gully eclipsed
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable conformation of ethylene glycol is:
a)
Anti
b)
Gauche
c)
Partially eclipsed
d)
Gully eclipsed
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
- Fully eclipsed conformation: the rotation of the gauge conformation to 60 degrees results in the gauge conformation and it is the least stable conformation of all.
- Hence, the most stable conformation of ethylene glycol is gauche conformation.
Which of the following resonance structures contributes the most to the resonance hybrid?
- a)
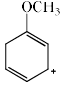
- b)
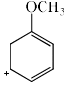
- c)
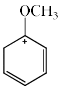
- d)
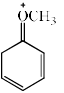
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following resonance structures contributes the most to the resonance hybrid?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Akanksha Choudhary answered |
Most stable structure contributes more in the resonance hybrid. Here we can see that option 'D' has 3 double bonds in it it which means that it is the most stable among all. So it will be the most contributing structure in resonance hybrid than others.
The compound that is anti-aromatic is:- a)
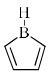
- b)
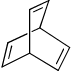
- c)
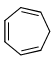
- d)
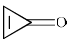
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound that is anti-aromatic is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Rima Das answered |
Because A satisfies the following conditions.It is cyclic,planer,continuous conjugation occurs through vacent 2p orbital of B and it has 4n number of electrons (n=1)
Arrange the following compounds in order of Ca—Cb bond length: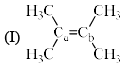
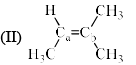
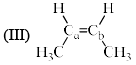
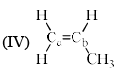
- a)I > II > III > IV
- b)IV > III > II > I
- c)I > III > II > IV
- d)III > II > IV > I
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following compounds in order of Ca—Cb bond length:
a)
I > II > III > IV
b)
IV > III > II > I
c)
I > III > II > IV
d)
III > II > IV > I
|
|
Rima Das answered |
The alekenes are stabilized by hyperconjugation.On moving from 1 to 4 the number of alpha hydrogen decreases so number of hyperconjugative structure decreases. 1 has the highest no of hyperconjugative structure so the double bond in 1 has the maximum tendency to attain single bond character. And from 1 to 4 as the no of hyperconjugative structure decreases the tendency of the double bond to have single bond character also decreases , means bond length decreases.
The number of sigma and pi-bonds in 1-butene 3-yne are- a) 5 sigma and 5 pi
- b) 7 sigma and 3 pi
- c) 8 sigma and 2 pi
- d) 6 sigma and 4 pi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of sigma and pi-bonds in 1-butene 3-yne are
a)
5 sigma and 5 pi
b)
7 sigma and 3 pi
c)
8 sigma and 2 pi
d)
6 sigma and 4 pi

|
Swara Dasgupta answered |
CH2 = CH – C ≡ CH;
No of σ bonds = 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 / 1 + 1 = 7;
No of π bonds = 1 + 2 = 3
Which one of the following statement is true?a)Diastereomers are a pair of isomers related spatially as object and mirror image.b)Diastereomers can often be separated by fractional crystallization ion.c)Diastereomers have identical physical and chemical properties.d)Diastereomers rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarization light to an equal but opposite extent.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomers that have different configurations at one or more stereocenters but are not mirror images of each other. They have different physical and chemical properties and can often be separated by fractional crystallization.
Explanation:
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that have different configurations at one or more stereocenters, which are carbon atoms that have four different substituents attached to them. Unlike enantiomers, which are mirror images of each other and have identical physical and chemical properties, diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties. This is because diastereomers have different spatial arrangements of their atoms and functional groups.
Fractional crystallization is a technique used to separate diastereomers. It involves slowly cooling a solution containing the diastereomers, causing one diastereomer to crystallize out before the other. This technique works because diastereomers have different solubilities in different solvents, and their crystals have different shapes and sizes.
In conclusion, the statement "Diastereomers can often be separated by fractional crystallization" is true because diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties and can be separated based on these differences using techniques such as fractional crystallization.
Explanation:
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that have different configurations at one or more stereocenters, which are carbon atoms that have four different substituents attached to them. Unlike enantiomers, which are mirror images of each other and have identical physical and chemical properties, diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties. This is because diastereomers have different spatial arrangements of their atoms and functional groups.
Fractional crystallization is a technique used to separate diastereomers. It involves slowly cooling a solution containing the diastereomers, causing one diastereomer to crystallize out before the other. This technique works because diastereomers have different solubilities in different solvents, and their crystals have different shapes and sizes.
In conclusion, the statement "Diastereomers can often be separated by fractional crystallization" is true because diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties and can be separated based on these differences using techniques such as fractional crystallization.
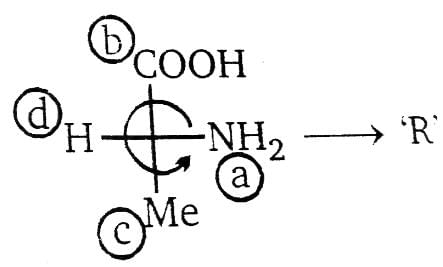
Amongst the following amino acids, the (S)–enantiomer is represented by:
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Amongst the following amino acids, the (S)–enantiomer is represented by:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Rishabh Mehta answered |
When the highest priority substituent to the lowest priority substituent are arranged in a clockwise manner the then the stereocenter is labeled R ("Rectus" Latin= "right"). In an amino acid the highest priority group is NH2 then COOH and then CH3. In option C the amino acid has right handed configuration of substituents and therefore is R− enantiomer.
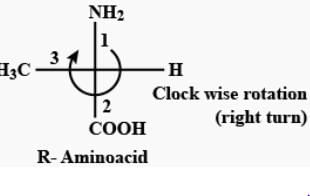
Which of the following compounds is/are aromatic?
- a)
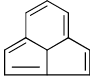
- b)
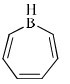
- c)
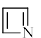
- d)
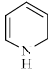
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds is/are aromatic?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Correct Answer :- a,b
Explanation : The term aromaticity is used to describe a cyclic, planar molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms.
Only the peripheral pie electrons are considered! doesn't matter whether that central carbon is sp2 or not.
A,B have all sp2 carbon atoms and follow (4n+2)pie electron rule so are aromatic.
Chapter doubts & questions for Basic Concepts in Organic Chemistry and Stereochemistry - Topicwise Question Bank for IIT JAM/CSIR/GATE Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Basic Concepts in Organic Chemistry and Stereochemistry - Topicwise Question Bank for IIT JAM/CSIR/GATE Chemistry in English & Hindi are available as part of Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.