All Exams >
Commerce >
Accountancy CUET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of Dissolution of a Partnership Firm for Commerce Exam
Unrecorded liability will be shown in:- a)Credit side of Realisation A/c
- b)Debit side of partners’ capital A/c
- c)Debit side of Realisation A/c
- d)Debit side of cash A/c
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Unrecorded liability will be shown in:
a)
Credit side of Realisation A/c
b)
Debit side of partners’ capital A/c
c)
Debit side of Realisation A/c
d)
Debit side of cash A/c
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Unrecorded liabilities are those liabilities that are not shown in the Balance Sheet but they still exist in the business. Although these liabilities are not shown in the books, they still need to the discharged off at the time of dissolution and hence are debited to the Realisation account.
Money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets is debited to the _________- a)Balance Sheet
- b)Revaluation Account
- c)Partners capital account
- d)Cash Account
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets is debited to the _________
a)
Balance Sheet
b)
Revaluation Account
c)
Partners capital account
d)
Cash Account

|
Sounak Chaudhary answered |
Debiting the Cash Account for the money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets
When a business sells an unrecorded asset, it receives cash in exchange. This cash receipt needs to be recorded in the accounting system to ensure accurate financial reporting. The money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets is debited to the Cash Account because it represents an increase in the business's cash balance.
Importance of recording the sale of unrecorded assets
The sale of unrecorded assets can have an impact on the financial statements of a business. If the sale is not recorded, it can lead to incorrect financial reporting and misrepresent the financial position of the business. For example, if the business sells a valuable asset for a significant amount of cash, but fails to record the sale, its cash balance will be understated, and its assets will be overstated. This can lead to inaccurate financial ratios, such as the current ratio, and mislead stakeholders about the business's ability to meet its short-term obligations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets should be debited to the Cash Account to ensure accurate financial reporting and prevent misrepresentation of the business's financial position. It is important to record all transactions accurately and in a timely manner to maintain the integrity of the accounting system.
When a business sells an unrecorded asset, it receives cash in exchange. This cash receipt needs to be recorded in the accounting system to ensure accurate financial reporting. The money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets is debited to the Cash Account because it represents an increase in the business's cash balance.
Importance of recording the sale of unrecorded assets
The sale of unrecorded assets can have an impact on the financial statements of a business. If the sale is not recorded, it can lead to incorrect financial reporting and misrepresent the financial position of the business. For example, if the business sells a valuable asset for a significant amount of cash, but fails to record the sale, its cash balance will be understated, and its assets will be overstated. This can lead to inaccurate financial ratios, such as the current ratio, and mislead stakeholders about the business's ability to meet its short-term obligations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the money realised from the sale of unrecorded assets should be debited to the Cash Account to ensure accurate financial reporting and prevent misrepresentation of the business's financial position. It is important to record all transactions accurately and in a timely manner to maintain the integrity of the accounting system.
If a partner agreed to pay the unrecorded liability then ______- a)Realisation account is credited and concerned partner’s account debited
- b)Only Realisation account is credited
- c)Realisation account is debited and concerned partner’s capital account is credited.
- d)Concerned partner’s account is debited
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a partner agreed to pay the unrecorded liability then ______
a)
Realisation account is credited and concerned partner’s account debited
b)
Only Realisation account is credited
c)
Realisation account is debited and concerned partner’s capital account is credited.
d)
Concerned partner’s account is debited

|
Sai Mishra answered |
When a partner agreed to pay any unrecorded liability, in such a case, realization account should be debited and concerned partner’s capital account should be credited. No effect on cash account.
Debtors given in the balance sheet ?17,000. In additional information bad debts of ?2,000 given and it is also given that debtors have paid their money in full and final settlement after 10% discount. How much amount is received from debtors?- a)15,000
- b)17,000
- c)15,300
- d)13,500
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Debtors given in the balance sheet ?17,000. In additional information bad debts of ?2,000 given and it is also given that debtors have paid their money in full and final settlement after 10% discount. How much amount is received from debtors?
a)
15,000
b)
17,000
c)
15,300
d)
13,500

|
Ashwini Majumdar answered |
Amount received from debtors:
Total amount due ?17,000
Bad debts ?2,000
Final amount received = 17,000 – 2,000 = 15,000 – 10% = 13,500
Total amount due ?17,000
Bad debts ?2,000
Final amount received = 17,000 – 2,000 = 15,000 – 10% = 13,500
A partnership deed usually contain the particulars relating to- a)Name of firm and partners.
- b)Nature of business and duration of firm.
- c)Capital contribution, profit/loss sharing ration and other agreed terms.
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A partnership deed usually contain the particulars relating to
a)
Name of firm and partners.
b)
Nature of business and duration of firm.
c)
Capital contribution, profit/loss sharing ration and other agreed terms.
d)
All of these.

|
Anjali Reddy answered |
Particulars in Partnership Deed
A partnership deed is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions of a partnership and the roles and responsibilities of each partner. It is a crucial document that helps to avoid misunderstandings and conflicts between partners in the future. The particulars that are usually included in a partnership deed are:
1. Name of the firm and partners:
The name of the partnership firm should be unique and should not be similar to any existing firm. The names of all partners along with their addresses and contact details should be mentioned in the deed.
2. Nature of business and duration of the firm:
The partnership deed should clearly state the nature of the business that the firm will engage in. It should also mention the duration for which the partnership will exist. The duration can be for a fixed period or until the completion of a particular project.
3. Capital contribution, profit/loss sharing ratio, and other agreed terms:
The partnership deed should specify the amount of capital that each partner will contribute to the business. It should also mention the profit/loss sharing ratio among the partners. Other terms that may be included are the salaries or drawings that partners are entitled to, the method of accounting to be used, and the procedures for admitting or expelling partners.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a partnership deed is a crucial document that outlines the terms and conditions of a partnership. It should include the name of the firm and partners, the nature of business and duration of the firm, capital contribution, profit/loss sharing ratio, and other agreed terms. A well-drafted partnership deed can help to avoid misunderstandings and conflicts between partners and ensure the smooth running of the business.
A partnership deed is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions of a partnership and the roles and responsibilities of each partner. It is a crucial document that helps to avoid misunderstandings and conflicts between partners in the future. The particulars that are usually included in a partnership deed are:
1. Name of the firm and partners:
The name of the partnership firm should be unique and should not be similar to any existing firm. The names of all partners along with their addresses and contact details should be mentioned in the deed.
2. Nature of business and duration of the firm:
The partnership deed should clearly state the nature of the business that the firm will engage in. It should also mention the duration for which the partnership will exist. The duration can be for a fixed period or until the completion of a particular project.
3. Capital contribution, profit/loss sharing ratio, and other agreed terms:
The partnership deed should specify the amount of capital that each partner will contribute to the business. It should also mention the profit/loss sharing ratio among the partners. Other terms that may be included are the salaries or drawings that partners are entitled to, the method of accounting to be used, and the procedures for admitting or expelling partners.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a partnership deed is a crucial document that outlines the terms and conditions of a partnership. It should include the name of the firm and partners, the nature of business and duration of the firm, capital contribution, profit/loss sharing ratio, and other agreed terms. A well-drafted partnership deed can help to avoid misunderstandings and conflicts between partners and ensure the smooth running of the business.
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :₹Sundry Creditors 27,000Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000Cash in hand 6,000Bank Loan 20,000Bills Payable 5,000Sundry Assets 1,98,000Capital A/cs :Mehta 1,12,000Menon 48,000Additional information :(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.Q. The loss on the realisation transferred to Menon’s Capital Account is:- a)₹31,465
- b)₹13,485
- c)₹44,950
- d)₹15,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :
₹
Sundry Creditors 27,000
Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000
Cash in hand 6,000
Bank Loan 20,000
Bills Payable 5,000
Sundry Assets 1,98,000
Capital A/cs :
Mehta 1,12,000
Menon 48,000
Additional information :
(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.
(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.
(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.
(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.
(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.
Q. The loss on the realisation transferred to Menon’s Capital Account is:
a)
₹31,465
b)
₹13,485
c)
₹44,950
d)
₹15,000

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
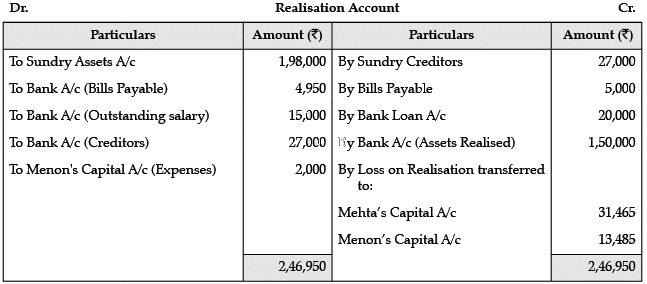
At the time of dissolution, how would you treat the loss shown by Profit and Loss A/c in the Balance Sheet?- a)Dr. Side of Partners capital account
- b)Credit side of partners’ capital account
- c)Cash Account
- d)Realisation Account
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At the time of dissolution, how would you treat the loss shown by Profit and Loss A/c in the Balance Sheet?
a)
Dr. Side of Partners capital account
b)
Credit side of partners’ capital account
c)
Cash Account
d)
Realisation Account

|
Manisha Patel answered |
Profit and Loss (Dr. balance) given in the balance sheet will be transferred to the debit side of partners capital account in their respective profit sharing ratio. It should not be transferred to the realization account.
If a liability is assumed (to be paid) by a partner such partner capital account is ___- a)No effect on capital account
- b)Debited
- c)Credited
- d)Both Credited and Debited
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a liability is assumed (to be paid) by a partner such partner capital account is ___
a)
No effect on capital account
b)
Debited
c)
Credited
d)
Both Credited and Debited

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
If a partner is agreed to pay off any liability at the time of dissolution of a partnership firm, in such a case following entry should be recorded in the books: Journal Entry: Realisation A/c Dr.
To Partner’s Capital A/c
To Partner’s Capital A/c
Asset taken over by partner will be shown in:- a)Debit side of Cash A/c
- b)Debit side of Realisation A/c
- c)Credit side of Cash A/c
- d)Credit side of Realisation A/c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Asset taken over by partner will be shown in:
a)
Debit side of Cash A/c
b)
Debit side of Realisation A/c
c)
Credit side of Cash A/c
d)
Credit side of Realisation A/c

|
Mansi Chopra answered |
Any asset taken by a partner will be shown in the credit side of realization account and in partner’s capital account.
All the assets of the firm are _____ and all outsiders’ liabilities and partners’ loan and partners capitals are ___ at the time of dissolution of firm.- a)Paid , Disposed Off
- b)Realised , Paid
- c)Disposed Off , Acquired
- d)Acquired , Paid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All the assets of the firm are _____ and all outsiders’ liabilities and partners’ loan and partners capitals are ___ at the time of dissolution of firm.
a)
Paid , Disposed Off
b)
Realised , Paid
c)
Disposed Off , Acquired
d)
Acquired , Paid

|
Sai Mishra answered |
At the time of dissolution of a partnership firm, all assets available in the business will be realized (sold) and all liabilities will be paid off.
When Asset is taken over by a creditor:- a)Debit side of Realisation A/c
- b)Only in Cash A/c
- c)Credit side of Realisation A/c
- d)No Entry in this case
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When Asset is taken over by a creditor:
a)
Debit side of Realisation A/c
b)
Only in Cash A/c
c)
Credit side of Realisation A/c
d)
No Entry in this case

|
Simran Mishra answered |
Any asset taken over by the creditor at the time of dissolution of partnership firm, will not be shown separately or no separate entry will be recorded for the same.
If creditors given in the balance sheet ?30,000. Stock costing ?10,000 taken over by creditors at market price of ?8,000 at the time of dissolution of partnership firm and balance amount paid in cash after deducting a discount of 10%. How much amount is paid in cash?- a)19,800
- b)18,000
- c)30,000
- d)22,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If creditors given in the balance sheet ?30,000. Stock costing ?10,000 taken over by creditors at market price of ?8,000 at the time of dissolution of partnership firm and balance amount paid in cash after deducting a discount of 10%. How much amount is paid in cash?
a)
19,800
b)
18,000
c)
30,000
d)
22,000
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Calculation of the amount payable to the creditors:
Total amount payable to the creditors ?30,000
Asset taken over by creditors at market price ?8,000.
Now amount due to the creditors is ?22,000 (30,000 – 8,000)
Final payment to creditors in cash = 22,000 – 2,200 (discount) = 19,800
Total amount payable to the creditors ?30,000
Asset taken over by creditors at market price ?8,000.
Now amount due to the creditors is ?22,000 (30,000 – 8,000)
Final payment to creditors in cash = 22,000 – 2,200 (discount) = 19,800
When realized value of goodwill is given in adjustment, it indicates that ________
- a) Goodwill is taken over by creditors.
- b) Goodwill is written off by the old partners
- c) Goodwill is sold
- d) Goodwill is purchased
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When realized value of goodwill is given in adjustment, it indicates that ________
a)
Goodwill is taken over by creditors.b)
Goodwill is written off by the old partnersc)
Goodwill is soldd)
Goodwill is purchased|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Goodwill is a premium paid over the fair value of assets during the purchase of a company. Hence, it is tagged to a company or business and cannot be sold or purchased independently, whereas other intangible assets like licenses, patents, etc. can be sold and purchased independently.
Which of the following Reserve or fund is not transferred to the Realisation Account?- a)Contingency Reserve
- b)Investment Fluctuation Reserve
- c)Reserve for doubtful debts
- d)Employee Provident Fund
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following Reserve or fund is not transferred to the Realisation Account?
a)
Contingency Reserve
b)
Investment Fluctuation Reserve
c)
Reserve for doubtful debts
d)
Employee Provident Fund
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Contingency Reserves is a free reserve which is not transferred to the Realisation account at the time of dissolution of a partnership firm. Other reserves or funds (given in the above question) will be transferred to the Realisation account.
Accumulated losses are transfer to ______ in ________ ratio- a)Capital account , Profit sharing ratio
- b)Capital account , Gaining ratio
- c)Realisation account, Gaining sharing ratio
- d)Realisation account , Profit sharing ratio
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Accumulated losses are transfer to ______ in ________ ratio
a)
Capital account , Profit sharing ratio
b)
Capital account , Gaining ratio
c)
Realisation account, Gaining sharing ratio
d)
Realisation account , Profit sharing ratio

|
Raghav Chakraborty answered |
At the time of dissolution all accumulated profits and losses should be transferred to the partners capital account in their profit sharing ratio.
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:₹Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000Contingency Reserve 7,000On the date of dissolution of the firm:(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.Q. How much loan amount will be paid to Raina?- a)₹15,000
- b)₹15,500
- c)₹500
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:
Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.
On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:
₹
Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)
Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)
Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)
Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000
Contingency Reserve 7,000
On the date of dissolution of the firm:
(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.
(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.
(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.
(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Q. How much loan amount will be paid to Raina?
a)
₹15,000
b)
₹15,500
c)
₹500
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Loan amount paid = ₹15,000 + ₹500 = ₹15,500
Unrecorded asset when realised (in cash) will be _________- a)Credited to partners capital account
- b)Debited to Realisation Account
- c)Debited to Partners capital account
- d)Credited to Realisation Account
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Unrecorded asset when realised (in cash) will be _________
a)
Credited to partners capital account
b)
Debited to Realisation Account
c)
Debited to Partners capital account
d)
Credited to Realisation Account

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Unrecorded asset (if any) given in the additional information, which is realized (sold) at the time of dissolution, should be shown in the credit side of Realisation Account because realized value of all the assets is recorded in the credit side of Realisation Account.
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:₹Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000Contingency Reserve 7,000On the date of dissolution of the firm:(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.Q. The contingency fund will be debited or credited to which account?- a)Partners’ Capital Account
- b)Realisation Account
- c)Profit and Loss Account
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:
Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.
On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:
₹
Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)
Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)
Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)
Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000
Contingency Reserve 7,000
On the date of dissolution of the firm:
(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.
(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.
(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.
(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Q. The contingency fund will be debited or credited to which account?
a)
Partners’ Capital Account
b)
Realisation Account
c)
Profit and Loss Account
d)
None of the above
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Contingency funds will be credited to Partners’ Capital Account in the profit sharing ratio.
All _____ liabilities are transferred to the ____ side of Realisation account- a)Internal , Debit
- b)Capitals of the partner, Credit
- c)Internal , Credit
- d)External , Credit
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All _____ liabilities are transferred to the ____ side of Realisation account
a)
Internal , Debit
b)
Capitals of the partner, Credit
c)
Internal , Credit
d)
External , Credit

|
Sai Mishra answered |
All external liabilities are transferred to the credit side of realization account at the time of dissolution and same will be paid off in the debit side of realization account.
If Creditors are given ?20,000 in the balance sheet. But nothing is mentioned under additional information about the payment of the same. How much amount will be paid to the creditors?- a)No Payment to Creditors
- b)Payment after 10% Discount
- c)Full Amount ?20,000
- d)Half Amount Rs.10,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If Creditors are given ?20,000 in the balance sheet. But nothing is mentioned under additional information about the payment of the same. How much amount will be paid to the creditors?
a)
No Payment to Creditors
b)
Payment after 10% Discount
c)
Full Amount ?20,000
d)
Half Amount Rs.10,000

|
Sai Mishra answered |
All liabilities will be paid at the time of dissolution of a partnership firm. Whether some information is given or not about the payment of the same. In this case nothing is mentioned about the payment of creditors but it is mandatory to pay the full amount ?20,000 to the creditors.
In the absence of any contract to the contrary, capital profit on the dissolution of a Partnership Firm is shared among partners in:- a)Equal ratio
- b)Capital ratio
- c)Profit-sharing ratio
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Equal ratio
b)
Capital ratio
c)
Profit-sharing ratio
d)
None of these

|
KP Classes answered |
In the event of the dissolution of a partnership firm, capital profit (surplus) is shared among the partners in their profit-sharing ratio unless stated otherwise in a partnership agreement. According to Section 48 of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, the surplus remaining after settling liabilities, advances, and capital contributions is distributed among the partners in their agreed profit-sharing ratio. If no agreement exists, the default rule is to use the profit-sharing ratio.
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:₹Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000Contingency Reserve 7,000On the date of dissolution of the firm:(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.Q. The amount of Profit and Loss Account to be transferred to the Partner’s Capital Account is:- a)₹5,000 each
- b)₹6,000 Raina and ₹4,000 Meena
- c)₹4,000 Raina and ₹6,000 Meena
- d)Insufficient data
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:
Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.
On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:
₹
Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)
Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)
Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)
Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000
Contingency Reserve 7,000
On the date of dissolution of the firm:
(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.
(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.
(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.
(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Q. The amount of Profit and Loss Account to be transferred to the Partner’s Capital Account is:
a)
₹5,000 each
b)
₹6,000 Raina and ₹4,000 Meena
c)
₹4,000 Raina and ₹6,000 Meena
d)
Insufficient data
|
|
Amita Das answered |
S they share profit and losses equally so the undistributed loss will be debited to their capital account equally.
Read the following information and answer the given questions:Vibhuti, Tiwari and Happu were partners in a partnership firm sharing profits and losses in their capital ratio, i.e., 1 : 2 : 3. On 31st March 2020, they decided to dissolve the partnership firm. The following information is given to you on the dissolution of the firm: The firm had total assets of ₹ 12,00,000 that realized ₹ 10,80,000. The creditors were settled at 90% by paying them ₹54,000. There was an unrecorded asset in the books of the firm which was taken by Vibhuti for ₹ 12,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000 and were paid by Tiwari on behalf of the firm. There was a general reserve in the books of the company of ₹ 21,000. The capitals of the partners were in the proportion of their profit sharing ratio. Their balance sheet also showed a cash balance of ₹ 81,000.Q. What will be the final amount to be paid to Happu?- a)₹6,05,000
- b)₹52,000
- c)₹5,52,500
- d)₹6,08,500
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:
Vibhuti, Tiwari and Happu were partners in a partnership firm sharing profits and losses in their capital ratio, i.e., 1 : 2 : 3. On 31st March 2020, they decided to dissolve the partnership firm. The following information is given to you on the dissolution of the firm: The firm had total assets of ₹ 12,00,000 that realized ₹ 10,80,000. The creditors were settled at 90% by paying them ₹54,000. There was an unrecorded asset in the books of the firm which was taken by Vibhuti for ₹ 12,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000 and were paid by Tiwari on behalf of the firm. There was a general reserve in the books of the company of ₹ 21,000. The capitals of the partners were in the proportion of their profit sharing ratio. Their balance sheet also showed a cash balance of ₹ 81,000.
Q. What will be the final amount to be paid to Happu?
a)
₹6,05,000
b)
₹52,000
c)
₹5,52,500
d)
₹6,08,500

|
Samridhi Kaur answered |
Calculation of the Final Amount to be paid to Happu:
The first step in calculating the final amount to be paid to Happu is to determine the total amount available for distribution after settling the liabilities of the firm.
1. Calculation of Total Realization Amount:
Total Assets of the firm = ₹12,00,000
Realization Amount = ₹10,80,000
2. Settlement of Creditors:
Creditors settled at 90% = ₹54,000
Remaining amount for distribution = Total Realization Amount - Creditors settled = ₹10,80,000 - ₹54,000 = ₹10,26,000
3. Unrecorded Asset taken by Vibhuti:
Unrecorded Asset taken by Vibhuti = ₹12,000
4. Realization Expenses:
Realization Expenses paid by Tiwari = ₹2,000
5. General Reserve in the books of the firm:
General Reserve = ₹21,000
6. Calculation of Final Amount to be paid to Happu:
Total amount available for distribution = Remaining amount for distribution - Unrecorded Asset - Realization Expenses - General Reserve
= ₹10,26,000 - ₹12,000 - ₹2,000 - ₹21,000
= ₹9,91,000
Happu's share in the profit sharing ratio = 3/6 (as per the capital ratio)
= 1/2
Final amount to be paid to Happu = ₹9,91,000 x 1/2
= ₹4,95,500
Therefore, the final amount to be paid to Happu is ₹5,52,500 (Option C).
The first step in calculating the final amount to be paid to Happu is to determine the total amount available for distribution after settling the liabilities of the firm.
1. Calculation of Total Realization Amount:
Total Assets of the firm = ₹12,00,000
Realization Amount = ₹10,80,000
2. Settlement of Creditors:
Creditors settled at 90% = ₹54,000
Remaining amount for distribution = Total Realization Amount - Creditors settled = ₹10,80,000 - ₹54,000 = ₹10,26,000
3. Unrecorded Asset taken by Vibhuti:
Unrecorded Asset taken by Vibhuti = ₹12,000
4. Realization Expenses:
Realization Expenses paid by Tiwari = ₹2,000
5. General Reserve in the books of the firm:
General Reserve = ₹21,000
6. Calculation of Final Amount to be paid to Happu:
Total amount available for distribution = Remaining amount for distribution - Unrecorded Asset - Realization Expenses - General Reserve
= ₹10,26,000 - ₹12,000 - ₹2,000 - ₹21,000
= ₹9,91,000
Happu's share in the profit sharing ratio = 3/6 (as per the capital ratio)
= 1/2
Final amount to be paid to Happu = ₹9,91,000 x 1/2
= ₹4,95,500
Therefore, the final amount to be paid to Happu is ₹5,52,500 (Option C).
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Partner ’s loan account is prepared before partners’ capital accounts.Reason (R): At the time of dissolution, capitals are paid off, only if any balance is left after payment of the partner ’s loan.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Partner ’s loan account is prepared before partners’ capital accounts.
Reason (R): At the time of dissolution, capitals are paid off, only if any balance is left after payment of the partner ’s loan.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.

|
Kunal Pillai answered |
Assertion (A): Partner's loan account is prepared before partners' capital accounts.
Reason (R): At the time of dissolution, capitals are paid off, only if any balance is left after payment of the partner's loan.
Explanation:
When a partnership firm is dissolved, the assets and liabilities are settled among the partners. The process of settlement involves the preparation of various accounts, including partner's loan account and partner's capital account.
Partner's Loan Account:
- In a partnership, partners may lend money to the firm for various reasons, such as initial capital contribution or additional funds required by the firm.
- The partner's loan account records the amount of money lent by each partner to the firm.
- This account reflects a liability for the partnership firm as it represents the amount owed to the partner.
- During the dissolution of the partnership, the partner's loan is repaid before the partner's capital is settled. This is because the partner's loan is considered a priority liability that needs to be cleared before distributing the remaining capital among the partners.
Partner's Capital Account:
- The partner's capital account represents the partner's ownership interest in the partnership.
- It records the initial capital contribution made by the partner, as well as any additional investments or withdrawals.
- At the time of dissolution, the partner's capital account is settled by distributing the remaining capital among the partners after clearing the partner's loan.
Explanation of Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
- Assertion (A) states that the partner's loan account is prepared before partners' capital accounts, which is true.
- Reason (R) states that at the time of dissolution, capitals are paid off only if any balance is left after payment of the partner's loan, which is also true.
- The reason for preparing the partner's loan account before partners' capital accounts is that the loan represents a liability that needs to be settled first.
- If there is any remaining capital after clearing the loan, it is then distributed among the partners based on their capital contributions.
Conclusion:
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Reason (R): At the time of dissolution, capitals are paid off, only if any balance is left after payment of the partner's loan.
Explanation:
When a partnership firm is dissolved, the assets and liabilities are settled among the partners. The process of settlement involves the preparation of various accounts, including partner's loan account and partner's capital account.
Partner's Loan Account:
- In a partnership, partners may lend money to the firm for various reasons, such as initial capital contribution or additional funds required by the firm.
- The partner's loan account records the amount of money lent by each partner to the firm.
- This account reflects a liability for the partnership firm as it represents the amount owed to the partner.
- During the dissolution of the partnership, the partner's loan is repaid before the partner's capital is settled. This is because the partner's loan is considered a priority liability that needs to be cleared before distributing the remaining capital among the partners.
Partner's Capital Account:
- The partner's capital account represents the partner's ownership interest in the partnership.
- It records the initial capital contribution made by the partner, as well as any additional investments or withdrawals.
- At the time of dissolution, the partner's capital account is settled by distributing the remaining capital among the partners after clearing the partner's loan.
Explanation of Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
- Assertion (A) states that the partner's loan account is prepared before partners' capital accounts, which is true.
- Reason (R) states that at the time of dissolution, capitals are paid off only if any balance is left after payment of the partner's loan, which is also true.
- The reason for preparing the partner's loan account before partners' capital accounts is that the loan represents a liability that needs to be settled first.
- If there is any remaining capital after clearing the loan, it is then distributed among the partners based on their capital contributions.
Conclusion:
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :₹Sundry Creditors 27,000Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000Cash in hand 6,000Bank Loan 20,000Bills Payable 5,000Sundry Assets 1,98,000Capital A/cs :Mehta 1,12,000Menon 48,000Additional information :(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.Consider the following Accounts:(i) Mehta’s Capital Account(ii) Menon’s Capital Account(iii) Realisation Account(iv) Profit and Loss AccountQ. Which account will be affected by the realisation expenses paid by Menon?- a)(i) only
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :
₹
Sundry Creditors 27,000
Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000
Cash in hand 6,000
Bank Loan 20,000
Bills Payable 5,000
Sundry Assets 1,98,000
Capital A/cs :
Mehta 1,12,000
Menon 48,000
Additional information :
(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.
(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.
(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.
(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.
(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.
Consider the following Accounts:
(i) Mehta’s Capital Account
(ii) Menon’s Capital Account
(iii) Realisation Account
(iv) Profit and Loss Account
Q. Which account will be affected by the realisation expenses paid by Menon?
a)
(i) only
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Realisation A /c Dr. 5,600
To Menon’s Capital A /c 5,600
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :₹Sundry Creditors 27,000Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000Cash in hand 6,000Bank Loan 20,000Bills Payable 5,000Sundry Assets 1,98,000Capital A/cs :Mehta 1,12,000Menon 48,000Additional information :(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.Q. The amount of Bills payable paid is:- a)₹5,000
- b)₹4,950
- c)₹4,500
- d)₹5,150
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :
₹
Sundry Creditors 27,000
Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000
Cash in hand 6,000
Bank Loan 20,000
Bills Payable 5,000
Sundry Assets 1,98,000
Capital A/cs :
Mehta 1,12,000
Menon 48,000
Additional information :
(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.
(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.
(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.
(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.
(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.
Q. The amount of Bills payable paid is:
a)
₹5,000
b)
₹4,950
c)
₹4,500
d)
₹5,150
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
₹5 000 x 6 / 100 x 2 / 12 = ₹4,950
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:₹Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000Contingency Reserve 7,000On the date of dissolution of the firm:(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.Q. The unrecorded asset taken by Meena will be:- a)Debited to Meena’s Capital Account
- b)Credited to Realisation Account
- c)Both (A) and (B)
- d)In the balance sheet
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follow:
Raina and Meena were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. They dissolved their firm on 31st March, 2018.
On this date, the Balance Sheet of the firm, apart from realizable assets and outside liabilities showed the following:
₹
Raina's Capital 40,000 (Cr.)
Meena's Capital 20,000 (Dr.)
Profit & Loss Account 10,000 (Dr.)
Raina’s loan to the firm 15,000
Contingency Reserve 7,000
On the date of dissolution of the firm:
(a) Raina’s loan was repaid by the firm along with interest of ₹ 500.
(b) The dissolution expenses of ₹ 1,000 were paid by the firm on behalf of Raina who had to bear these expenses.
(c) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 was taken over by Meena while Raina discharged an unrecorded liability of ₹ 3,000.
(d) The dissolution resulted in a loss of 60,000 from the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Q. The unrecorded asset taken by Meena will be:
a)
Debited to Meena’s Capital Account
b)
Credited to Realisation Account
c)
Both (A) and (B)
d)
In the balance sheet
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Unrecorded assets are those assets which had forgotten to record in book like unrecorded investment, goods given by new partner etc. It arises at the time of balancing of balance sheet.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Rajiv and Vinod, who share the profit and losses in the ratio 2:3, are dissolving the firm. There is a general reserve in the balance of Rs.60,000 in the balance sheet. The accountant transferred Rs.24,000 in Rajiv’s Capital and Rs.36,000 in Vinod’s Capital Accounts.Reason (R): The undistributed profits and losses and reserves are always transferred to partners’ capital accounts in their profit sharing ratio and not to the realisation account.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Rajiv and Vinod, who share the profit and losses in the ratio 2:3, are dissolving the firm. There is a general reserve in the balance of Rs.60,000 in the balance sheet. The accountant transferred Rs.24,000 in Rajiv’s Capital and Rs.36,000 in Vinod’s Capital Accounts.
Reason (R): The undistributed profits and losses and reserves are always transferred to partners’ capital accounts in their profit sharing ratio and not to the realisation account.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Amita Das answered |
These undistributed profits belong to old partners. Therefore, these undistributed profits are transferred to the old partners' account in their old profit sharing ratio before the admission of a new partner. After these adjustments, the general reserve or undistributed losses do not appear in the Balance Sheet.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Realisation account is prepared in the dissolution of the firm.Reason (R): Dissolution of partnership involves the partners selling the assets and settling the liabilities. Thus, various amounts are recovered or paid to partners.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Realisation account is prepared in the dissolution of the firm.
Reason (R): Dissolution of partnership involves the partners selling the assets and settling the liabilities. Thus, various amounts are recovered or paid to partners.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
In dissolution of the partnership firm, a realisation account is prepared as the liabilities are to be settled as against the assets of the firm and to find the surplus that the partners get or the deficit they need to bring in order for the process of dissolution.
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion (A): Dissolution of partnership is different from the dissolution of the Partnership firm.Reason (R): Dissolution of partnership doesn’t dissolve the firm but the firm is dissolved in the partnership firm.- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
- d)Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Dissolution of partnership is different from the dissolution of the Partnership firm.
Reason (R): Dissolution of partnership doesn’t dissolve the firm but the firm is dissolved in the partnership firm.
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false .
d)
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Priyanka Khatri answered |
Dissolution of partnership means reconstitution of the firm due to change in the profit sharing ratio among existing partners, admission of a new partner, retirement of a partner, death of a partner, insolvency of a partner and the firm continues as before. However, the dissolution of partnership does not lead to the dissolution of the firm.
Rohan, Mohan, and Sohan were partners, sharing profits equally. At the time of the dissolution of the partnership firm, Rohan’s loan to the firm will be:- a)Debited to Rohan’s Capital Account
- b)Debited to Realisation Account
- c)Credited to Realisation Account
- d)Credited to Bank Account
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Debited to Rohan’s Capital Account
b)
Debited to Realisation Account
c)
Credited to Realisation Account
d)
Credited to Bank Account

|
KP Classes answered |
When a partner has given a loan to the firm, this loan is treated as a liability of the firm at the time of dissolution. The loan amount is settled by paying it through the Bank Account. Thus, Rohan's loan to the firm will be credited to the Bank Account when the loan is repaid.
In the event of dissolution, assets are transferred to the Realization Account:- a)At Book Value
- b)At Market Value
- c)Cost or Market Value, whichever is lower
- d)More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
At Book Value
b)
At Market Value
c)
Cost or Market Value, whichever is lower
d)
More than one of the above

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
At the time of dissolution of a partnership firm, all assets (except cash and bank) are transferred to the Realization Account at their Book Value. The Realization Account is a nominal account prepared to record the realization (sale) of assets and payment of liabilities. Assets are debited to the Realization Account at their book value, and the actual proceeds from the sale of these assets are credited. The resulting balance, which is the profit or loss on realization, is transferred to the Partners' Capital Accounts in their profit-sharing ratio.
Read the following information and answer the given questions:Vibhuti, Tiwari and Happu were partners in a partnership firm sharing profits and losses in their capital ratio, i.e., 1 : 2 : 3. On 31st March 2020, they decided to dissolve the partnership firm. The following information is given to you on the dissolution of the firm: The firm had total assets of ₹ 12,00,000 that realized ₹ 10,80,000. The creditors were settled at 90% by paying them ₹54,000. There was an unrecorded asset in the books of the firm which was taken by Vibhuti for ₹ 12,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000 and were paid by Tiwari on behalf of the firm. There was a general reserve in the books of the company of ₹ 21,000. The capitals of the partners were in the proportion of their profit sharing ratio. Their balance sheet also showed a cash balance of ₹ 81,000.Q. What was the capital of Tiwari before the dissolution of the firm?- a)₹2,00,000
- b)₹4,00,000
- c)₹6,00,000
- d)₹8,00,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:
Vibhuti, Tiwari and Happu were partners in a partnership firm sharing profits and losses in their capital ratio, i.e., 1 : 2 : 3. On 31st March 2020, they decided to dissolve the partnership firm. The following information is given to you on the dissolution of the firm: The firm had total assets of ₹ 12,00,000 that realized ₹ 10,80,000. The creditors were settled at 90% by paying them ₹54,000. There was an unrecorded asset in the books of the firm which was taken by Vibhuti for ₹ 12,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000 and were paid by Tiwari on behalf of the firm. There was a general reserve in the books of the company of ₹ 21,000. The capitals of the partners were in the proportion of their profit sharing ratio. Their balance sheet also showed a cash balance of ₹ 81,000.
Q. What was the capital of Tiwari before the dissolution of the firm?
a)
₹2,00,000
b)
₹4,00,000
c)
₹6,00,000
d)
₹8,00,000
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
In a balance sheet
Total of Assets side = Total of liabilities side
As per the case, total of assets side = ₹ 12,00,000 + ₹ 81,000 = ₹ 12,81,000
Total of Liabilities side = Creditors + General reserve + Capitals of partners
(as per the given question)
₹ 12,81,000 = ₹ 60,000 + 21,000 + Capital of partners
Capitals of partners = ₹12,81,000 –₹ 81,000 = ₹12,00,000
Capital of Tiwari = ₹12,00,00 x 2 / 6 = ₹4,00,000
Read the following information and answer the given questions:Vibhuti, Tiwari and Happu were partners in a partnership firm sharing profits and losses in their capital ratio, i.e., 1 : 2 : 3. On 31st March 2020, they decided to dissolve the partnership firm. The following information is given to you on the dissolution of the firm: The firm had total assets of ₹ 12,00,000 that realized ₹ 10,80,000. The creditors were settled at 90% by paying them ₹54,000. There was an unrecorded asset in the books of the firm which was taken by Vibhuti for ₹ 12,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000 and were paid by Tiwari on behalf of the firm. There was a general reserve in the books of the company of ₹ 21,000. The capitals of the partners were in the proportion of their profit sharing ratio. Their balance sheet also showed a cash balance of ₹ 81,000.Q. __________ account will be debited for the treatment of unrecorded assets given in case study.- a)Vibhuti’s Capital
- b)Tiwari’s Capital
- c)Happu’s Capital
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the given questions:
Vibhuti, Tiwari and Happu were partners in a partnership firm sharing profits and losses in their capital ratio, i.e., 1 : 2 : 3. On 31st March 2020, they decided to dissolve the partnership firm. The following information is given to you on the dissolution of the firm: The firm had total assets of ₹ 12,00,000 that realized ₹ 10,80,000. The creditors were settled at 90% by paying them ₹54,000. There was an unrecorded asset in the books of the firm which was taken by Vibhuti for ₹ 12,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000 and were paid by Tiwari on behalf of the firm. There was a general reserve in the books of the company of ₹ 21,000. The capitals of the partners were in the proportion of their profit sharing ratio. Their balance sheet also showed a cash balance of ₹ 81,000.
Q. __________ account will be debited for the treatment of unrecorded assets given in case study.
a)
Vibhuti’s Capital
b)
Tiwari’s Capital
c)
Happu’s Capital
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Vibhuti’s Capital account will be debited for the treatment of unrecorded assets given in case study.
Unrecorded assets and liabilities of the firm are brought into the books of the firm. The actual position of the firm is calculated. Profit and loss arriving on account of such revaluation up to the date of admission of a new partner may be adjusted in the partner's capital accounts in their old profit sharing ratio.
How is Goodwill treated at the time of dissolution of a partnership firm?- a)Not recorded anywhere
- b)Recorded in realisation account like any other asset
- c)Distributed among partners in old ratio
- d)More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Not recorded anywhere
b)
Recorded in realisation account like any other asset
c)
Distributed among partners in old ratio
d)
More than one of the above

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
→ At the time of dissolution, Goodwill is treated as a regular asset.
→ It is recorded in the Realisation Account along with other assets of the firm.
→ The firm sells Goodwill to realize its value, and the proceeds are used to:
Pay liabilities.
Settle outstanding amounts with partners.
→ This ensures Goodwill is accounted for properly during the closure of the partnership firm.
→ It is recorded in the Realisation Account along with other assets of the firm.
→ The firm sells Goodwill to realize its value, and the proceeds are used to:
Pay liabilities.
Settle outstanding amounts with partners.
→ This ensures Goodwill is accounted for properly during the closure of the partnership firm.
Realisation Account is differ from Revaluation Account as- a)prepared at a number of times during the life of a firm
- b)prepared at three times during the life of a firm
- c)Prepared only twice during the life of a firm
- d)Prepared only once during the life of a firm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Realisation Account is differ from Revaluation Account as
a)
prepared at a number of times during the life of a firm
b)
prepared at three times during the life of a firm
c)
Prepared only twice during the life of a firm
d)
Prepared only once during the life of a firm

|
Navya Sengupta answered |
Realisation Account vs Revaluation Account
Realisation Account and Revaluation Account are both important accounts used in accounting, but they serve different purposes and are prepared at different times during the life of a firm. Let's understand the key differences between the two:
Realisation Account
- Realisation Account is prepared only once during the life of a firm.
- It is used to record the sale of assets and liabilities when a firm is being dissolved or when there is a change in the constitution of the firm.
- The main purpose of the Realisation Account is to determine the profit or loss on the realisation of assets and settlement of liabilities.
- It helps in distributing the final profits or losses among the partners of the firm.
Revaluation Account
- Revaluation Account is prepared at different times during the life of a firm, typically when there is a change in the partnership or when the firm wants to revalue its assets and liabilities.
- It is used to record any increase or decrease in the value of assets and liabilities of the firm.
- The main purpose of the Revaluation Account is to adjust the capital accounts of the partners based on the revalued amounts of assets and liabilities.
- It helps in maintaining the accuracy of the capital accounts and reflecting the true financial position of the firm.
In conclusion, while Realisation Account is prepared only once during the life of a firm to determine the final profit or loss, Revaluation Account is prepared at different times to adjust the values of assets and liabilities and to maintain the accuracy of the capital accounts.
Realisation Account and Revaluation Account are both important accounts used in accounting, but they serve different purposes and are prepared at different times during the life of a firm. Let's understand the key differences between the two:
Realisation Account
- Realisation Account is prepared only once during the life of a firm.
- It is used to record the sale of assets and liabilities when a firm is being dissolved or when there is a change in the constitution of the firm.
- The main purpose of the Realisation Account is to determine the profit or loss on the realisation of assets and settlement of liabilities.
- It helps in distributing the final profits or losses among the partners of the firm.
Revaluation Account
- Revaluation Account is prepared at different times during the life of a firm, typically when there is a change in the partnership or when the firm wants to revalue its assets and liabilities.
- It is used to record any increase or decrease in the value of assets and liabilities of the firm.
- The main purpose of the Revaluation Account is to adjust the capital accounts of the partners based on the revalued amounts of assets and liabilities.
- It helps in maintaining the accuracy of the capital accounts and reflecting the true financial position of the firm.
In conclusion, while Realisation Account is prepared only once during the life of a firm to determine the final profit or loss, Revaluation Account is prepared at different times to adjust the values of assets and liabilities and to maintain the accuracy of the capital accounts.
How would you treat investment fluctuation reserve given in the balance sheet at the time of dissolution?- a)Debit side of Realisation Account
- b)Cash Account credit side
- c)Debit side of partners’ capital account
- d)Credit side of Realisation Account
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How would you treat investment fluctuation reserve given in the balance sheet at the time of dissolution?
a)
Debit side of Realisation Account
b)
Cash Account credit side
c)
Debit side of partners’ capital account
d)
Credit side of Realisation Account

|
Sai Mishra answered |
At the time of dissolution, investment fluctuation reserve should be transferred to the credit side of revaluation account. It should not be distributed as free reserve.
In the absence of any contract to the contrary, capital profit on the dissolution of a Partnership Firm is shared among partners in:- a)Equal ratio
- b)Capital ratio
- c)Profit-sharing ratio
- d)More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Equal ratio
b)
Capital ratio
c)
Profit-sharing ratio
d)
More than one of the above

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
→ At the time of dissolution of a partnership firm, capital profit (surplus) is shared among partners according to their profit-sharing ratio unless specified otherwise in a contract.
→ As per Section 48 of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932:
Losses, including capital deficiencies, are settled first out of profits, then capital, and lastly by partners in their profit-sharing ratio.
Surplus or capital profit (if any) remaining after paying all liabilities, advances, and capital contributions is divided among partners in their profit-sharing ratio.
Identify which account is prepared at last in the process of firm’s dissolution:
Option A: Realization Account
Option B: Partner’s Capital Accounts
Option C: Cash Account
Option D: More than one of the above
Answer: Option C: Cash Account
→ As per Section 48 of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932:
Losses, including capital deficiencies, are settled first out of profits, then capital, and lastly by partners in their profit-sharing ratio.
Surplus or capital profit (if any) remaining after paying all liabilities, advances, and capital contributions is divided among partners in their profit-sharing ratio.
Identify which account is prepared at last in the process of firm’s dissolution:
Option A: Realization Account
Option B: Partner’s Capital Accounts
Option C: Cash Account
Option D: More than one of the above
Answer: Option C: Cash Account
When a partner takes over an unrecorded asset during dissolution, the following is credited:- a)Capital Account of the Partner
- b)Cash Account
- c)Asset Account
- d)Realization Account
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Capital Account of the Partner
b)
Cash Account
c)
Asset Account
d)
Realization Account

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
At the time of dissolution, if a partner takes over an unrecorded asset, the Realization Account is credited with the value of the asset. The Realization Account is a nominal account used to close the firm's books, record the sale of assets, payment of liabilities, and transfer of unrecorded assets. The partner’s capital account is then adjusted accordingly.
A partner paid 700 for the firm's realization expenses when the firm was dissolved. - a)Cash Account
- b)Realization Account
- c)Capital Account of the Partner
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A partner paid 700 for the firm's realization expenses when the firm was dissolved.
a)
Cash Account
b)
Realization Account
c)
Capital Account of the Partner
d)
None of the above

|
KP Classes answered |
Realization Account:
- The nature of the Realization account is a Nominal Account. The purpose of preparing a Realization account is to close the dissolved firm's books of accounts and determine profit or loss on the Realization of assets and payment of liabilities. It is put together by:
- Transferring all assets, except cash and bank accounts, to the account's debit side.
- Transferring all liabilities to the credit side of the account except the Partner's Loan Account and the Partners' Capital Accounts.
- Crediting the asset sale receipt to the account.
- Debiting the account for the payment of liabilities.
- Deducting the firm's dissolution expenses.
- The account balance can be either profit or loss. This balance is transferred to the Partners' Capital Accounts in their profit-sharing ratio.
The assets of the Partnership firm, including any sums contributed by the partners to make up deficiencies of capital at the time of dissolution, shall be applied in the following manner and order:
(A) In paying each partner rateably what is due to him for advances as distinguished from capital.
(B) In paying to each partner rateably what is due to him on account of capital.
(C) In paying the debts of the firm to third parties.
(D) Dividing among the partners in the proportion in which they were entitled to share profits.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)(C), (A), (B), (D)
- b)(C), (B), (A), (D)
- c)(A), (B), (C), (D)
- d)(B), (C), (A), (D)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
(A) In paying each partner rateably what is due to him for advances as distinguished from capital.
(B) In paying to each partner rateably what is due to him on account of capital.
(C) In paying the debts of the firm to third parties.
(D) Dividing among the partners in the proportion in which they were entitled to share profits.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
(C), (A), (B), (D)
b)
(C), (B), (A), (D)
c)
(A), (B), (C), (D)
d)
(B), (C), (A), (D)

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
At the time of dissolution of a partnership firm, the assets are applied in the following order:
- In paying the debts of the firm to third parties (C).
- In paying each partner rateably for their advances as distinguished from capital (A).
- In paying each partner rateably what is due to them on account of capital (B).
- The remaining surplus, if any, is divided among the partners in their profit-sharing ratio (D).
- In paying the debts of the firm to third parties (C).
- In paying each partner rateably for their advances as distinguished from capital (A).
- In paying each partner rateably what is due to them on account of capital (B).
- The remaining surplus, if any, is divided among the partners in their profit-sharing ratio (D).
When a partnership dissolves, the balance of a partner's capital account on the assets side of a balance sheet is transferred to:- a)On the Debit of Realization Account
- b)On the Credit of Realization Account
- c)On the Debit of Partner’s Capital Account
- d)On the Credit of Cash Account
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a partnership dissolves, the balance of a partner's capital account on the assets side of a balance sheet is transferred to:
a)
On the Debit of Realization Account
b)
On the Credit of Realization Account
c)
On the Debit of Partner’s Capital Account
d)
On the Credit of Cash Account

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
At the time of dissolution, if a partner's capital account balance appears on the assets side of the balance sheet, it indicates that the partner owes the firm. This balance is transferred to the debit side of the Partner's Capital Account to adjust for the outstanding amount.
The Realization Account is used to close the books of accounts by transferring assets and liabilities, but the balance owed by a partner is adjusted through the Partner’s Capital Account. Hence, the correct treatment is to transfer it to the debit of the Partner's Capital Account.
The Realization Account is used to close the books of accounts by transferring assets and liabilities, but the balance owed by a partner is adjusted through the Partner’s Capital Account. Hence, the correct treatment is to transfer it to the debit of the Partner's Capital Account.
Which one of the following rights is usually not available to a partner consequent to the dissolution of a firm?- a)Right of equitable distribution of firm's property
- b)Right to return of premium on premature winding up
- c)Right to be consulted
- d)Right to restrain any partner or his representatives from the use of firm name or firm property
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Right of equitable distribution of firm's property
b)
Right to return of premium on premature winding up
c)
Right to be consulted
d)
Right to restrain any partner or his representatives from the use of firm name or firm property

|
KP Classes answered |
After the dissolution of a partnership firm, the rights of the partners are mainly related to the settlement of the firm's affairs, repayment of debts, and distribution of any surplus assets. Partners also have the right to restrain other partners from misusing the firm’s name or property and the right to receive the return of the premium if the dissolution is premature.
However, the right to be consulted ceases to exist after the dissolution because the partnership no longer operates as a business entity. The main focus shifts to the settlement of accounts and winding up the firm’s affairs. Therefore, the right to be consulted is not available to a partner after the dissolution of the firm.
However, the right to be consulted ceases to exist after the dissolution because the partnership no longer operates as a business entity. The main focus shifts to the settlement of accounts and winding up the firm’s affairs. Therefore, the right to be consulted is not available to a partner after the dissolution of the firm.
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :₹Sundry Creditors 27,000Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000Cash in hand 6,000Bank Loan 20,000Bills Payable 5,000Sundry Assets 1,98,000Capital A/cs :Mehta 1,12,000Menon 48,000Additional information :(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.Q. What will be the amount of past loss transferred to Mehta’s Account?- a)₹5,600
- b)₹2,400
- c)₹2,500
- d)₹5,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information and answer the questions that follows: Mehta and Menon were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. They decided to dissolve firm on 31st March, 2016 on that date, their books showed the following ledger account balances :
₹
Sundry Creditors 27,000
Profit & Loss A/c (Dr.) 8,000
Cash in hand 6,000
Bank Loan 20,000
Bills Payable 5,000
Sundry Assets 1,98,000
Capital A/cs :
Mehta 1,12,000
Menon 48,000
Additional information :
(i) Bills payable falling due on 31st May, 2016 retired on the date of dissolution of the firm at a rebate of 6% per annum.
(ii) The bankers accepted the furniture (included in sundry assets) having a book value of ₹18,000 in full settlement of the loan given by them.
(iii) Remaining assets were sold for ₹ 1,50,000.
(iv) Liability on account of outstanding salary not recorded in the books, amounting to ₹15,000 was met.
(v) Menon agreed to take over the responsibility of completing the dissolution work to bear all expenses of realization at an agreed remuneration of ₹2,000. The actual realization expenses were ₹1,500 which were paid by the firm on behalf of Menon.
Q. What will be the amount of past loss transferred to Mehta’s Account?
a)
₹5,600
b)
₹2,400
c)
₹2,500
d)
₹5,000
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
7 / 10 × 8, 000= ₹ 5, 600
Section 41 of the Partnership Act 1932 deals with which type of dissolution of a firm?- a)By mutual agreement
- b)Compulsory dissolution
- c)By notice
- d)By order of court
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
By mutual agreement
b)
Compulsory dissolution
c)
By notice
d)
By order of court

|
KP Classes answered |
Section 41 of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, deals with compulsory dissolution of a partnership firm. A firm is dissolved compulsorily in the following circumstances:
- When all the partners, or all but one, become insolvent, making them incapable of signing a contract.
- When the firm's business becomes illegal due to changes in law.
- When an event occurs that makes it illegal for partners to continue the business, such as one partner becoming an alien enemy due to war with their country.
This dissolution under Section 41 is termed compulsory dissolution as it arises due to legal or unavoidable conditions.
- When all the partners, or all but one, become insolvent, making them incapable of signing a contract.
- When the firm's business becomes illegal due to changes in law.
- When an event occurs that makes it illegal for partners to continue the business, such as one partner becoming an alien enemy due to war with their country.
This dissolution under Section 41 is termed compulsory dissolution as it arises due to legal or unavoidable conditions.
Chapter doubts & questions for Dissolution of a Partnership Firm - Accountancy CUET Preparation 2025 is part of Commerce exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Dissolution of a Partnership Firm - Accountancy CUET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Commerce exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Accountancy CUET Preparation
46 videos|7 docs|83 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









