All Exams >
A Level >
Biology A-Level >
All Questions
All questions of Transport in Plants for A Level Exam
Which does not pertain to facilitated transport?- a)Uphill transport
- b)Transport saturation
- c)High selectivity
- d)Requirement of special membrane
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which does not pertain to facilitated transport?
a)
Uphill transport
b)
Transport saturation
c)
High selectivity
d)
Requirement of special membrane
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Downhill movement
Net transport of molecules is from high conc. To low conc.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Root hairs absorb water from soil with the help of
a) Root pressure
b) Osmatic pressure
c) Suction pressure
d) Turger pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Osmotic Pressure is the right option. As because roots need water for transportation. They dont have water at first but the surrounding soil does have. So, due to hypertonic state, roots absorb water by osmosis.
Consider the following statements about facilitated transport:(I) Requires ATP energy(II) Transport saturates(III) Highly selective(IV) Requires special membrane, properties(V) Uphill transportOf the above statements,A) (II), (III) and (V) are relevant, but (I) and (IV) are irrelevant.B) (I), (II) and (III) are relevant, but (IV) and (V) are irrelevant.C) (I), (IV) and (V) are relevant, but (II) and (III) are irrelevant.D) (III), (IV) and (V) are relevant, but (I) and (II) are irrelevant.E) (II), (III) and (IV) are relevant, but (I) and (V) are irrelevant.The correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Transport systems that use carrier molecules but which do not require energy to proceed are called facilitated diffusion. A chemical first binds to the carrier protein in the cell membrane and then diffuses through the membrane. Because no energy is used, facilitated transport into the cell cannot proceed if the concentration of that chemical is greater inside the cell membrane than outside. The involvement of carriers means that the process is also subject to competitive inhibition and saturation.
The main significance of facilitated diffusion is- a)Excretion of urea and hydrogen ions by mammalian kidneys
- b)Absorption of amino acids from the gut
- c)Absorption of mineral ions by plant roots
- d)Absorption of fructose and nucleotides in the small intestine
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main significance of facilitated diffusion is
a)
Excretion of urea and hydrogen ions by mammalian kidneys
b)
Absorption of amino acids from the gut
c)
Absorption of mineral ions by plant roots
d)
Absorption of fructose and nucleotides in the small intestine
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Facilitated diffusion in Glucose. Glucose is a six-carbon sugar that provides energy needed by cells. Since glucose is a large molecule, it is difficult to be transported across the membrane through passive diffusion Hence, it diffuses across membranes through facilitated diffusion, down the concentration gradient.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following statements are true/false?(I) The positive hydrostatic pressure is called turgor pressure.(II) Wall pressure is exerted to prevent the increase of protoplasm size.(III) Diffusion is more rapid in liquids than in gases.(IV) Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane is called imbibition.(V) Osmosis is the movement of substances that occurs along a diffusion gradient.A: (I) and (III) are true, and (II), (IV) and (V) are false.B: (III), (IV) and (V) are true, and (I) and (II) are false.C: (I) and (V) are true, and (II), (III) and (IV) are false.D: (I) and (II) are true, and (III), (IV) and (V) are false.E: (I) and (IV) are true, and (II), (III) and (V) are false.The answer is D.
(I) The positive hydrostatic pressure is called turgor pressure.
(II) Wall pressure is exerted to prevent the increase of protoplasm size.
(III) Diffusion is more rapid in liquids than in gases.
(IV) Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane is called imbibition.
(V) Osmosis is the movement of substances that occurs along a diffusion gradient.
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Turgor pressure is the positive hydrostatic pressure applied by protoplasm on the cell wall when protoplasm swells due to an increase in volume caused due to endosmosis.
When protoplasm applies turgor pressure on the wall, the wall applies an equal and opposite wall pressure on to the protoplasm.
Diffusion is a slow physical process, which describes the movement of substances along the concentration gradient. It occurs in all three states of matter and its rate does not changes with the physical state of substance.
Imbibition is a physical surface adsorption of solvent onto the matrix or adsorbing surface.
The statement 'e' is wrong, because osmosis is the movement of water not substances.
Main function of lenticels is- a)Transpiration
- b)Guttation
- c)Gaseous exchange
- d)Bleeding
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Main function of lenticels is
a)
Transpiration
b)
Guttation
c)
Gaseous exchange
d)
Bleeding
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
A lenticel is a porous tissue which possesses cells with large intercellular spaces in the periderm of the secondary organs and the bark of woody stems. It functions as a pore and participates in the direct exchange of gasses between the internal tissues and atmosphere through the bark, which is otherwise impermeable to gasses. Thus, the correct answer is option 'C'.
Absorption of diffusible ions by cells against the concentration gradient is called- a)Donnan equilibrium
- b)Passive absorption
- c)Active absorption
- d)Osmosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Absorption of diffusible ions by cells against the concentration gradient is called
a)
Donnan equilibrium
b)
Passive absorption
c)
Active absorption
d)
Osmosis
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Active absorption , this is the only absorption method that can move species against their concentration gradient (from low to high concentration). Facilitated diffusion only moves species down their concentration gradient from high to low concentration.
Veins in the leaves are useful for- a)Transport of water and minerals
- b)Mechanical support
- c)Transport of organic food material
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Veins in the leaves are useful for
a)
Transport of water and minerals
b)
Mechanical support
c)
Transport of organic food material
d)
All of the above
|
|
Megha Sengar answered |
Leaf is the main source of food so organic food is transport by leaf to all other part of plant but vein act as the carrier to collect all the food stuff and pass it on ,the transport of water and mineral are also got to the leaf as it is the last portion for water transport as water don't move backward, veins provide a mechanical support to the leaf cells thus act as a piece which had clustered all the leaf cell.hope you understand.
The molecules which move from higher to lower regions are called as- a)Imbibition
- b)Diffusion
- c)Osmosis
- d)Guttation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecules which move from higher to lower regions are called as
a)
Imbibition
b)
Diffusion
c)
Osmosis
d)
Guttation
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
In diffusion, molecules move in a random fashion, the net result being substances moving from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration.
Which one of the following will not directly affect transpiration?- a)Temperature
- b)Chlorophyll content of leaves
- c)Wind speed
- d)Light
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
a)
Temperature
b)
Chlorophyll content of leaves
c)
Wind speed
d)
Light

|
Anchal Maurya answered |
Transpiration is process in which water relies from leaves.Temprature,wind speed, light speed directly effect the transpiration as its increase the transpiration
but chlorphyll contents from leaves does not effect directly in transpiration.
but chlorphyll contents from leaves does not effect directly in transpiration.
The hydathode helps in- a)Respiration
- b)Guttation
- c)Transpiration
- d)Photosynthesis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The hydathode helps in
a)
Respiration
b)
Guttation
c)
Transpiration
d)
Photosynthesis

|
Ramesh Chand answered |
The hydathodes are made of a group of living cell with numerous intercellular spaces filled with water, but few or no chloroplast and represent modified bundle ends . Therefore , hydathodes are involved in the process of guttation, in which positive xylem pressure (due to root pressure ) causes liquid to excude from the pores.
Which of the following statements does not apply to reverse osmosis?- a)It is a passive process.
- b)It is an active process.
- c)It is used for water purification.
- d)In this technique, pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied to the system.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements does not apply to reverse osmosis?
a)
It is a passive process.
b)
It is an active process.
c)
It is used for water purification.
d)
In this technique, pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied to the system.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Osmosis is passive transport where water follows down the gradient across a semi-permeable membrane from a higher concentration to a lower concentration. Reverse osmosis simply means that the cumulative pressure gradients cause the flow of water molecules to go against the osmotic pressure gradient from a lower concentration to the higher concentration.
As the process of reverse osmosis requires energy for transporting molecules against the concentration gradient, it is an active process.
Hence, Option A is the correct one.
The ingredient not used for preserving food stuff is
a) Vinegar
b) Salt and sugar
c) Sugar and vinegar
d) Ethanol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Pooja Saha answered |
For preserving food stuff vinegar, salt and sugar is used. Ethanol is antiseptic in nature but not used for preserving food stuff.
Which one is not show by plasmolysis- a)Cell membrane is semipermeable
- b)Cell is elastic as well as permeable
- c)Cell wall is semipermeable
- d)It is shown by living cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not show by plasmolysis
a)
Cell membrane is semipermeable
b)
Cell is elastic as well as permeable
c)
Cell wall is semipermeable
d)
It is shown by living cells
|
|
Amita Verma answered |
The cell wall is only found in plants, and both nucleated and non-nucleated bacteria. A cell wall provides structure for plant and bacterial cells, is most definitely semi-permeable in plants, allowing small molecules and proteins to pass through based on size, anything under about 30 Kilodaltons.
Select the correct statement:- a)The translocation in phloem is unidirectional, whereas it is bidirectional in the xylem
- b)Pinus seeds cannot germinate and establish without the presence of mycorrhizae.
- c)Absorption of water by seeds and dry wood is an example of facilitated diffusion.
- d)The apoplast is a system of interconnected protoplasts.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement:
a)
The translocation in phloem is unidirectional, whereas it is bidirectional in the xylem
b)
Pinus seeds cannot germinate and establish without the presence of mycorrhizae.
c)
Absorption of water by seeds and dry wood is an example of facilitated diffusion.
d)
The apoplast is a system of interconnected protoplasts.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without mycorrhizae due to lack of water as because the mycorrhizal symbiotic association
helps the plant in formation of root.
helps the plant in formation of root.
Water is lost in a liquid state in some plants through hydathodes. These hydathodes- a)Remain closed at night
- b)Remain closed during the day
- c)Do not show any specificity in opening and closing
- d)Always remain open
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is lost in a liquid state in some plants through hydathodes. These hydathodes
a)
Remain closed at night
b)
Remain closed during the day
c)
Do not show any specificity in opening and closing
d)
Always remain open
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Hydathodes are specialized pores (openings) particularly present on the leaf margins, which exudes or secretes drops of water. The exudation of water as drops from the tip or margin of the leaves is called guttation. The process of guttation is facilitated by the hydathodes. They are also called as Water Stomata because they structurally resemble stomata and they facilitate guttation. Hydathodes are commonly found in Angiosperms, especially in grasses. The water stomata always stay opened since, they do not have opening and closing mechanism.
Rate of transpiration is highest when- a)Soil is dry and air is humid
- b)Soil is wet and air is dry
- c)Both soil and air are dry
- d)Soil is wet and air is humid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of transpiration is highest when
a)
Soil is dry and air is humid
b)
Soil is wet and air is dry
c)
Both soil and air are dry
d)
Soil is wet and air is humid

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Rate of transpiration is influenced by wind speed, availability of water and temperature. Rate of transpiration is highest when soil is wet and air is dry.
A sudden increase in CO2 concentration around a leaf will cause- a)Closure of stomata
- b)Wider opening of stomata
- c)Increase in transpiration
- d)Decrease in transpiration due to closure of stomata
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A sudden increase in CO2 concentration around a leaf will cause
a)
Closure of stomata
b)
Wider opening of stomata
c)
Increase in transpiration
d)
Decrease in transpiration due to closure of stomata

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
A sudden increase in carbon dioxide gas concentration around a leaf will cause decrease in transpiration due to closure of stomata.
A and B are contiguous cells. A has OP = 10 atm and TP = 7atm, B has OP = 8atm, TP = 3 atm, DPD = 5 atm. The result would be- a)No movement of water
- b)Equilibrium between the two
- c)Movement of water from B to A
- d)Movement of water from A to B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A and B are contiguous cells. A has OP = 10 atm and TP = 7atm, B has OP = 8atm, TP = 3 atm, DPD = 5 atm. The result would be
a)
No movement of water
b)
Equilibrium between the two
c)
Movement of water from B to A
d)
Movement of water from A to B

|
Swara Desai answered |
Two cells close to each other are called contiguous cells. Movement of water from one cell to other depends upon Diffusiion pressure deficit (DPD). DPD depends upon osmotic pressure and water pressure. So, movement of water from A to B will take place.
A cell when kept in a sugar solution gets dehydrated. Then the solution is
- a)Hypotonic
- b)Hypertonic
- c)Isotonic
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell when kept in a sugar solution gets dehydrated. Then the solution is
a)
Hypotonic
b)
Hypertonic
c)
Isotonic
d)
None of the above
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
When a cell is placed in a solution, the movement of water molecules across the cell membrane depends on the concentration of solutes inside and outside the cell. If the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell, the solution is hypertonic. In such a solution, water molecules move from the area of higher concentration (inside the cell) to the area of lower concentration (outside the cell) by a process called osmosis. As a result, the cell loses water and gets dehydrated.
In the given scenario, the sugar solution outside the cell is hypertonic as the concentration of solutes (sugar molecules) is higher than inside the cell. Therefore, water molecules move out of the cell, causing it to shrink or get dehydrated.
Organic and mineral nutrients transported by- a)Multidirectional
- b)Unidirectional
- c)Symport
- d)Antiport
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic and mineral nutrients transported by
a)
Multidirectional
b)
Unidirectional
c)
Symport
d)
Antiport

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
An important aspect that needs to be considered is the direction of transport organic and mineral nutrients however, undergo multidirectional transport.
Main function of lenticel is- a)Bleeding
- b)Transpiration
- c)Gaseous exchange
- d)Guttation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Main function of lenticel is
a)
Bleeding
b)
Transpiration
c)
Gaseous exchange
d)
Guttation

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Lenticels are minute pore in stems through which exchangeof gases takes place between plant and atmosphere.
Water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase- a)Adhesion
- b)Surface tension
- c)cohesion
- d)capillarity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase
a)
Adhesion
b)
Surface tension
c)
cohesion
d)
capillarity

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase due to surface tension.
The movement of diffusion is- a)active
- b)Passive
- c)facilitated
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The movement of diffusion is
a)
active
b)
Passive
c)
facilitated
d)
none of the above
|
|
Aashna Khanna answered |
Passive movement of diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Explanation
Diffusion is a form of passive transport, which means it does not require any energy input from the cell or organism. This is in contrast to active transport, which requires energy input to move particles against their concentration gradient.
In diffusion, particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is due to the random motion of particles, which causes them to spread out over time. The rate of diffusion is influenced by several factors, including the concentration gradient, temperature, and the size and shape of the particles.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins. This process also does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the movement of diffusion is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism. It involves the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, due to the random motion of particles. Facilitated diffusion is another type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Explanation
Diffusion is a form of passive transport, which means it does not require any energy input from the cell or organism. This is in contrast to active transport, which requires energy input to move particles against their concentration gradient.
In diffusion, particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is due to the random motion of particles, which causes them to spread out over time. The rate of diffusion is influenced by several factors, including the concentration gradient, temperature, and the size and shape of the particles.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins. This process also does not require energy input from the cell or organism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the movement of diffusion is a passive process that does not require energy input from the cell or organism. It involves the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, due to the random motion of particles. Facilitated diffusion is another type of passive transport that involves the movement of particles across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
Stomata close down if relative humidity of atmosphere falls below- a)50%
- b)70%
- c)80%
- d)60%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stomata close down if relative humidity of atmosphere falls below
a)
50%
b)
70%
c)
80%
d)
60%

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
Relative humidity of atmosphere also influencetheopening and closing of stomata. If relative humidity of atmosphere comes below 50% stomata close down.
Stomata of CAM plants- a)Open during the night and close during the day
- b)Never open
- c)Open during the day and close at night
- d)Are always open
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stomata of CAM plants
a)
Open during the night and close during the day
b)
Never open
c)
Open during the day and close at night
d)
Are always open

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
Many cacti and other succulent plants with CAM metabolism open their stomata at night and close them during the day. ... In contrast to C3 and C4 plants, CAM plants open their stomata and fix CO2 at night. The basic role of stomata is to regulate transpiration and photosynthesis.
The process by which water is absorbed by solids such as colloids causing them to increase in volume is called- a)Diffusion
- b)Osmosis
- c)Plasmolysis
- d)Imbibition
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The process by which water is absorbed by solids such as colloids causing them to increase in volume is called
a)
Diffusion
b)
Osmosis
c)
Plasmolysis
d)
Imbibition
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Imbibition
The process of adsorption of water by solid particles of a substance without forming a solution is called 'imbibition'.
It is a type of diffusion by which movement of water take place along a diffusion gradient.
The solid particles which adsorb water or any other liquid are called imbibants. The liquid which is imbibed is known as imbibate.Cellulose, pectic substances, protoplasmic protein and other organic compound in plant cells show great power of imbibition.
Water in the soil available to plants is- a)Gravitational water
- b)Capillary water
- c)Hygroscopic water
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water in the soil available to plants is
a)
Gravitational water
b)
Capillary water
c)
Hygroscopic water
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ruchi Singh answered |
Explanation:
Water in the soil available to plants is referred to as capillary water. This water is held in the soil pores by capillary forces and is accessible to plant roots for absorption.
Types of Soil Water:
There are three types of soil water, namely:
1. Gravitational Water
2. Capillary Water
3. Hygroscopic Water
Gravitational Water:
Gravitational water is the water that drains rapidly through the soil due to the force of gravity. It is not available to plants as it moves down beyond the root zone. This water is usually lost as runoff or percolates deeper into the ground.
Capillary Water:
Capillary water is the water that is held in the soil pores against the force of gravity. It is available to plants as it is held in the root zone. Capillary water is crucial for plant growth as it provides the necessary moisture and nutrients for absorption by the roots. This water moves upward through the soil by capillary action, ensuring that the root zone remains adequately moist.
Hygroscopic Water:
Hygroscopic water is the water that is tightly bound to the soil particles and is unavailable to plants. This water is held so tightly that it cannot be removed by plant roots. It is considered as soil moisture at hygroscopic equilibrium and is not accessible for plant uptake.
Conclusion:
Water in the soil available to plants is capillary water, as it is held against the force of gravity in the root zone and is accessible for absorption by plant roots. Gravitational water drains rapidly, while hygroscopic water is tightly bound to the soil particles and not available for plant uptake.
Water in the soil available to plants is referred to as capillary water. This water is held in the soil pores by capillary forces and is accessible to plant roots for absorption.
Types of Soil Water:
There are three types of soil water, namely:
1. Gravitational Water
2. Capillary Water
3. Hygroscopic Water
Gravitational Water:
Gravitational water is the water that drains rapidly through the soil due to the force of gravity. It is not available to plants as it moves down beyond the root zone. This water is usually lost as runoff or percolates deeper into the ground.
Capillary Water:
Capillary water is the water that is held in the soil pores against the force of gravity. It is available to plants as it is held in the root zone. Capillary water is crucial for plant growth as it provides the necessary moisture and nutrients for absorption by the roots. This water moves upward through the soil by capillary action, ensuring that the root zone remains adequately moist.
Hygroscopic Water:
Hygroscopic water is the water that is tightly bound to the soil particles and is unavailable to plants. This water is held so tightly that it cannot be removed by plant roots. It is considered as soil moisture at hygroscopic equilibrium and is not accessible for plant uptake.
Conclusion:
Water in the soil available to plants is capillary water, as it is held against the force of gravity in the root zone and is accessible for absorption by plant roots. Gravitational water drains rapidly, while hygroscopic water is tightly bound to the soil particles and not available for plant uptake.
Passive water absorption by root system is due to- a)Force created in root
- b)High respiratory activity of root
- c)Osmotic pressure in shoot
- d)Tension in sap due to transpiration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passive water absorption by root system is due to
a)
Force created in root
b)
High respiratory activity of root
c)
Osmotic pressure in shoot
d)
Tension in sap due to transpiration

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Absorption of water by root system is passive due to tension in sap created by transpiration. No energy molecule is required in this process, so it is passive in nature.
When a plant undergoes senescence, the nutrients may be- a)Exported
- b)Absorbed
- c)Translocated
- d)Withdrawn
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a plant undergoes senescence, the nutrients may be
a)
Exported
b)
Absorbed
c)
Translocated
d)
Withdrawn
|
|
Sunil Jakhar answered |
Obviously translocated.. why the plant get loss . bcz when he absorb them with energy.. now the plant release them freely .. no no brother . the plant use them in the senseable direction ... ok
Which one of the following theories for ascent of sap was proposed by the eminent Indian scientist J. C. Bose?- a)Relay pump theory
- b)Transpiration pull theory
- c)Root pressure theory
- d)Pulsation theory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following theories for ascent of sap was proposed by the eminent Indian scientist J. C. Bose?
a)
Relay pump theory
b)
Transpiration pull theory
c)
Root pressure theory
d)
Pulsation theory
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A common vital force theory about the ascent of sap was put forward by J.C. Bose (1923). It is called the pulsation theory. The theory believes that the innermost cortical cells of the root absorb water from the outer side and pump the same into xylem channels. So the correct option is 'Pulsation theory'.
Munch hypothesis is based on- a)Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient and imbibition force
- b)Translocation of organic solutes
- c)Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient
- d)Translocation of food due to imbibition force
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Munch hypothesis is based on
a)
Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient and imbibition force
b)
Translocation of organic solutes
c)
Translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient
d)
Translocation of food due to imbibition force
|
|
Nishtha Joshi answered |
Munch hypothesis is one of the two hypotheses that explain the translocation of food in plants, the other being the pressure flow hypothesis. The hypothesis was proposed by Ernst Munch in 1930 and is based on the idea of translocation of food due to turgor pressure gradient.
Explanation:
Translocation of Food:
Translocation is the process of transporting food from the leaves, where it is synthesized, to the other parts of the plant. The food is transported in the form of sucrose and other organic solutes.
Turgor Pressure Gradient:
Turgor pressure is the pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall. The pressure is created by the entry of water into the cell through osmosis. The turgor pressure gradient is the difference in the pressure between the source and the sink regions of the plant.
Mechanism of Translocation:
According to the Munch hypothesis, the movement of food is driven by the turgor pressure gradient. The process involves the following steps:
1. Synthesis of sucrose in the source region (leaves) through photosynthesis.
2. The sucrose is loaded into the phloem sieve tubes of the source region by active transport.
3. The loading of sucrose reduces the water potential in the phloem sieve tubes, creating a high turgor pressure.
4. The high turgor pressure in the source region creates a pressure gradient, which drives the movement of sucrose towards the sink region.
5. The sucrose unloads in the sink region (roots, stem, fruits, etc.) by diffusion.
6. The unloading of sucrose increases the water potential in the sink region, reducing the turgor pressure.
7. The reduction in turgor pressure creates a pressure gradient, which draws the water back to the source region.
Conclusion:
Thus, the Munch hypothesis explains the translocation of food in plants by the movement of sucrose due to the turgor pressure gradient. It is an important theory that helps in understanding the mechanism of nutrient transport in plants.
Explanation:
Translocation of Food:
Translocation is the process of transporting food from the leaves, where it is synthesized, to the other parts of the plant. The food is transported in the form of sucrose and other organic solutes.
Turgor Pressure Gradient:
Turgor pressure is the pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall. The pressure is created by the entry of water into the cell through osmosis. The turgor pressure gradient is the difference in the pressure between the source and the sink regions of the plant.
Mechanism of Translocation:
According to the Munch hypothesis, the movement of food is driven by the turgor pressure gradient. The process involves the following steps:
1. Synthesis of sucrose in the source region (leaves) through photosynthesis.
2. The sucrose is loaded into the phloem sieve tubes of the source region by active transport.
3. The loading of sucrose reduces the water potential in the phloem sieve tubes, creating a high turgor pressure.
4. The high turgor pressure in the source region creates a pressure gradient, which drives the movement of sucrose towards the sink region.
5. The sucrose unloads in the sink region (roots, stem, fruits, etc.) by diffusion.
6. The unloading of sucrose increases the water potential in the sink region, reducing the turgor pressure.
7. The reduction in turgor pressure creates a pressure gradient, which draws the water back to the source region.
Conclusion:
Thus, the Munch hypothesis explains the translocation of food in plants by the movement of sucrose due to the turgor pressure gradient. It is an important theory that helps in understanding the mechanism of nutrient transport in plants.
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without- a)pressure
- b)mycorrhiza
- c)water
- d)soil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without
a)
pressure
b)
mycorrhiza
c)
water
d)
soil

|
Kajal Bose answered |
The fungus provides minerals and water to the roots, inturn the roots provide sugars and N-containing compounds to themycorrhizae. Some plants have an obligate association with themycorrhizae.
The ratio of number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells and stomata per unit leaf area is called- a)Stomatal count
- b)Epidermal index
- c)Stomatal index
- d)Stomatal ratio
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells and stomata per unit leaf area is called
a)
Stomatal count
b)
Epidermal index
c)
Stomatal index
d)
Stomatal ratio

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
Stomatal index is the ratio of number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells and stomata per unit area of leaf.
When separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. What would you call the sugar solution- a)Osmotic inactive
- b)Osmotically reactive
- c)Osmotically active
- d)Less osmotic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. What would you call the sugar solution
a)
Osmotic inactive
b)
Osmotically reactive
c)
Osmotically active
d)
Less osmotic

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
When two solution are separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. Themovement of water always occurs from higher concentration to lower concentration. Such solution are called osmotically active.
Solute potential of a solution is always- a)Less than 0
- b)Between 0.1 and 1
- c)Equal to 0
- d)More than 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Solute potential of a solution is always
a)
Less than 0
b)
Between 0.1 and 1
c)
Equal to 0
d)
More than 0

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
Solute potential of a solution is always less than 0 as solute potential of distilled water is 0 and addition of solute decrease the solute potential.
A cell dipped in 0.5 M sucrose has no effect. It is dipped in 0.5 M NaCl, the cell will
a) Get plasmolysed
b) Became turgid
c) Increase in size
d) Same in size
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
A cell dipped in 0.5M sucrose solution do decrease in size but this takes time. The process of shrinking of the protoplasm of cell due to movement of water from its higher concentration (inside cell) to the region where its concentration is low (in sucrose or salt solution) is known as plasmolysis. Plasmolysis takes more time when the cell is placed in the solutions of low molarity. When the same cell is placed in 0.5M NaCl solution, the decrease in cell size is seen immediately because though the molarity is same but the solution contains salt as a solute and is an electrolye solute. Thus, it causes the rate of plasmolysis to increase.
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without- a)soil
- b)pressure
- c)mycorrhiza
- d)water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pinus seeds cannot germinate without
a)
soil
b)
pressure
c)
mycorrhiza
d)
water

|
Arya Khanna answered |
The fungus provides minerals and water to the roots, inturn the roots provide sugars and N-containing compounds to themycorrhizae. Some plants have an obligate association with themycorrhizae
The concentration of minerals in the soil is usually- a)Higher than the concentration of minerals in root
- b)Diluted in than in root
- c)Lower than the concentration of minerals in root
- d)Equilibrium in both soil and root
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The concentration of minerals in the soil is usually
a)
Higher than the concentration of minerals in root
b)
Diluted in than in root
c)
Lower than the concentration of minerals in root
d)
Equilibrium in both soil and root

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
The concentration of minerals in the soil is usually lower than the concentration of minerals in the root.
Select the correct equation from the following- a)DPD = WP – OP
- b)DPD = WP + OP
- c)DPD = OP + WP
- d)DPD = OP – WP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct equation from the following
a)
DPD = WP – OP
b)
DPD = WP + OP
c)
DPD = OP + WP
d)
DPD = OP – WP

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Diffusion pressure deficit is equal to osmotic pressure minus water potential. Higher the DPD more faster osmosis will occur.(DPD = OP – WP).
The instrument used for measuring rate of transpiration is- a)Potometer
- b)Porometer
- c)Osmometer
- d)Manometer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The instrument used for measuring rate of transpiration is
a)
Potometer
b)
Porometer
c)
Osmometer
d)
Manometer
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
A potometer sometimes known as a transpirometer, is a device used for measuring the rate of water uptake of a leafy shoot. The causes of water uptake are photosynthesis and transpiration.
What is the effect of turgor pressure in Munch hypothesis?- a)Increase of turgor pressure
- b)Decrease of turgor pressure
- c)No change in turgor pressure
- d)Independent to water potential gradient
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the effect of turgor pressure in Munch hypothesis?
a)
Increase of turgor pressure
b)
Decrease of turgor pressure
c)
No change in turgor pressure
d)
Independent to water potential gradient

|
Jyoti Mukherjee answered |
Munch Hypothesis was about the theory on the translocation of organic solutes. In protoplasm of a sieve tube is connected through plasmodesmata and forms a continuous system which is called symplast. The translocation of solutes occurs in a mass along with cell sap through the sieve tubes form a region of higher turgor pressure (turgor pressure gradient).
The external solution having less concentration than the cell sap is called- a)Hypertonic solution
- b)Isotonic solution
- c)Hypotonic solution
- d)Ultratonic solution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The external solution having less concentration than the cell sap is called
a)
Hypertonic solution
b)
Isotonic solution
c)
Hypotonic solution
d)
Ultratonic solution
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
A hypotonic solution is any solution that has a lower osmotic pressure than another solution. In the biological fields, this generally refers to a solution that has less solute and more water than another solution.
In a hypotonic solution the total molar concentration of all dissolved solute particles is less than that of another solution or less than that of a cell.
Diffusion rate is affected by- a)Pressure and soil
- b)Water and pressure
- c)Gradient concentration and pressure
- d)Soil and water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diffusion rate is affected by
a)
Pressure and soil
b)
Water and pressure
c)
Gradient concentration and pressure
d)
Soil and water

|
Bhavya Yadav answered |
Diffusion rates are affected by the gradient of concentration, the permeability of the membrane separating them, temperature and pressure.
In plants, capillarity is aided by the small diameter of- a)Trachery elements
- b)Cortical cells
- c)Parenchyma cells
- d)Phloem tissue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, capillarity is aided by the small diameter of
a)
Trachery elements
b)
Cortical cells
c)
Parenchyma cells
d)
Phloem tissue

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
In plants capillarity is aided by the small diameter of the tracheary elements – the tracheids and vessel elements.
Which part of the plant under goes transpiration?- a)Stem
- b)Flowers
- c)Leaves
- d)Roots
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the plant under goes transpiration?
a)
Stem
b)
Flowers
c)
Leaves
d)
Roots

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Terrestrial plants take up huge amount water daily but most of it is lost to the air through evaporation from the leaves, i.e., transpiration.
Mutual attraction between water molecules- a)Cohesion
- b)Capillarity
- c)Surface tension
- d)Adhesion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mutual attraction between water molecules
a)
Cohesion
b)
Capillarity
c)
Surface tension
d)
Adhesion

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
The transpiration driven ascent of xylem sap depends mainly on the physical properties of water. Cohesion– mutual attraction between water molecules.
Guttation is the result of- a)Transpiration
- b)Osmosis
- c)Diffusion
- d)Root pressure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Guttation is the result of
a)
Transpiration
b)
Osmosis
c)
Diffusion
d)
Root pressure
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Loss of water in the liquid state from uninjured parts of plants is known as Guttation.It is due to root pressure .
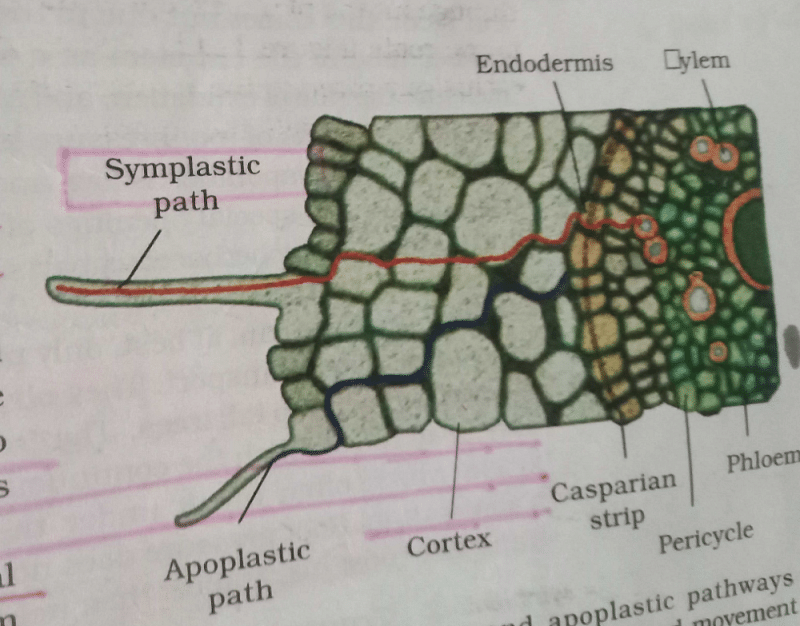
Which of the following statements are true?
(A) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any membranes.
(B) Solutes present in a cell (or in any solution) increase the free energy of water or water potential.
(C) The symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(D) Membrane permeability depends on membrane composition and the chemical nature of the solute.- a)A, B and D only
- b)B and D only
- c)A and B only
- d)A, C and D only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are true?
(A) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any membranes.
(B) Solutes present in a cell (or in any solution) increase the free energy of water or water potential.
(C) The symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(D) Membrane permeability depends on membrane composition and the chemical nature of the solute.
(A) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any membranes.
(B) Solutes present in a cell (or in any solution) increase the free energy of water or water potential.
(C) The symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(D) Membrane permeability depends on membrane composition and the chemical nature of the solute.
a)
A, B and D only
b)
B and D only
c)
A and B only
d)
A, C and D only
|
|
Anwesha Pati answered |
Ya D is right because only Opt. B is wrong.As solute decreases the water potential.
Chapter doubts & questions for Transport in Plants - Biology A-Level 2024 is part of A Level exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the A Level exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for A Level 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Transport in Plants - Biology A-Level in English & Hindi are available as part of A Level exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for A Level Exam by signing up for free.
Biology A-Level
280 videos|166 docs|147 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup