All Exams >
BMAT >
Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2) >
All Questions
All questions of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids for BMAT Exam
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is:- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Ethanal
- c)Formaldehyde
- d)Methanal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is:
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Ethanal
c)
Formaldehyde
d)
Methanal

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- The functional group is an aldehyde; −CHO and the given compound has two carbon atoms.
- Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is ethanal.
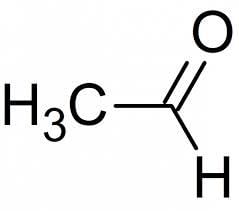
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO?- a)2,2-Dimethylpropanal
- b)3-Hydroxypropanal
- c)But-3-en-2-one
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO?
a)
2,2-Dimethylpropanal
b)
3-Hydroxypropanal
c)
But-3-en-2-one
d)
None of these
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO is 2-methylpropanal and its chemical name is Isobutyraldehyde.
Which of the following statements are correct in case of the carbonyl bond between carbon and oxygen?- a)Carbon is the nucleophilic centre and Oxygen is the electrophilic centre.
- b)Oxygen is the nucleophilic centre and Carbon is the electrophilic centre.
- c)Carbon and Oxygen double bond is polarised.
- d)Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ are correct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct in case of the carbonyl bond between carbon and oxygen?
a)
Carbon is the nucleophilic centre and Oxygen is the electrophilic centre.
b)
Oxygen is the nucleophilic centre and Carbon is the electrophilic centre.
c)
Carbon and Oxygen double bond is polarised.
d)
Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ are correct
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The double bonds in alkenes and double bonds in carbonyl groups are VERY different in terms of reactivity. The C=C is less reactive due to C=O electronegativity attributed to the oxygen and its two lone pairs of electrons. One pair of the oxygen lone pairs are located in 2s while the other pair are in 2p orbital where its axis is directed perpendicular to the direction of the pi orbitals. The Carbonyl groups properties are directly tied to its electronic structure as well as geometric positioning. For example, the electronegativity of oxygen also polarizes the pi bond allowing the single bonded substituent connected to become electron withdrawing.
Which of the following statement about C=O and C=C is correct?- a)Both consist of a sigma and pi bond
- b)C=O is polar but C=C is non-polar
- c)Both a and b are correct
- d)Both C=O and C=C undergo nucleophilic addition reactions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement about C=O and C=C is correct?
a)
Both consist of a sigma and pi bond
b)
C=O is polar but C=C is non-polar
c)
Both a and b are correct
d)
Both C=O and C=C undergo nucleophilic addition reactions

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- The first bond formed is a sigma bind and the second one is a pi bond.
- O has a higher electronegativity than C and hence the electron cloud will be shifted towards the O atom, making the compound polar.
- This is not possible in C=C.
Among the following functional groups, which of these is not a carbonyl compound?- a)alcohols
- b)aldehydes
- c)Carboxylic acid
- d)ketones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following functional groups, which of these is not a carbonyl compound?
a)
alcohols
b)
aldehydes
c)
Carboxylic acid
d)
ketones
|
|
Pari answered |
In carbonyl compound C=O is present bt in alchol OH is present. So alchol is not a carbonyl compound
Propanone and prop-2-en-1-ol are examples of which type of isomerism?
- a)Functional isomers
- b)Chain isomers
- c)Tautomers
- d)Position isomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Propanone and prop-2-en-1-ol are examples of which type of isomerism?
a)
Functional isomers
b)
Chain isomers
c)
Tautomers
d)
Position isomers
|
|
Gayatri Banerjee answered |
Functional isomers
Explanation: Propanone (CH3COCH3) and prop-2-en-1-ol (CH2=CHCH2OH) are examples of functional isomers because they have the same molecular formula (C3H6O) but different functional groups. Propanone has a carbonyl group (C=O) while prop-2-en-1-ol has an alcohol group (OH) and a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Explanation: Propanone (CH3COCH3) and prop-2-en-1-ol (CH2=CHCH2OH) are examples of functional isomers because they have the same molecular formula (C3H6O) but different functional groups. Propanone has a carbonyl group (C=O) while prop-2-en-1-ol has an alcohol group (OH) and a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Correct IUPAC name of the following compound is :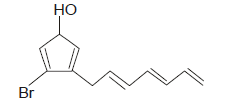
- a)3-(Hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)-4 bromo cyclopenta-2, 4, -dien-1-ol
- b)7-(2-Bromo-4-hydroxy cyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
- c)7-(5-Bromo-3-hydroxycyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
- d)3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct IUPAC name of the following compound is :
a)
3-(Hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)-4 bromo cyclopenta-2, 4, -dien-1-ol
b)
7-(2-Bromo-4-hydroxy cyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
c)
7-(5-Bromo-3-hydroxycyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
d)
3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option D
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
according to the rule of nearly attached halogen count first.so we count the the chain where bromo is near
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
according to the rule of nearly attached halogen count first.so we count the the chain where bromo is near
The correct IUPAC name of the folllowing compound is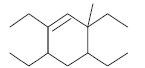
- a)5,6-Diethyl-8-methyl dec-6-ene
- b)5,7-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
- c)5,6-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
- d)2,4,5-Triethylnon-3-ene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of the folllowing compound is
a)
5,6-Diethyl-8-methyl dec-6-ene
b)
5,7-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
c)
5,6-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
d)
2,4,5-Triethylnon-3-ene

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
The IUPAC name of the given compound is 5, 6 - diethyl -2- methyldec - 4 - ene.
The parent hydrocarbon contains 10 carbon atoms and a double bond.
It is called dec-4-ene.
One methyl group is present on second carbon atom and two ethyl groups are present on fifth and sixth carbon atoms.
The parent hydrocarbon contains 10 carbon atoms and a double bond.
It is called dec-4-ene.
One methyl group is present on second carbon atom and two ethyl groups are present on fifth and sixth carbon atoms.
Acetone is isomeric to:- a)n-propyl alcohol
- b)propanal
- c)ethyl methyl ether
- d)isopropyl alcohol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acetone is isomeric to:
a)
n-propyl alcohol
b)
propanal
c)
ethyl methyl ether
d)
isopropyl alcohol
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Acetone (CH3COCH3) and Propanal (CH3CH2CHO) are functional isomers.
- Acetone:
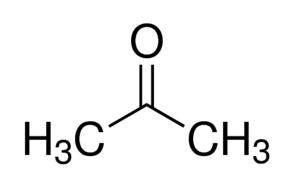
- Propanal:

How many structural isomers can compound with molecular formula ‘C3H6O’ have?- a)6
- b)4
- c)5
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many structural isomers can compound with molecular formula ‘C3H6O’ have?
a)
6
b)
4
c)
5
d)
11
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The Isomers of C3H6O include:
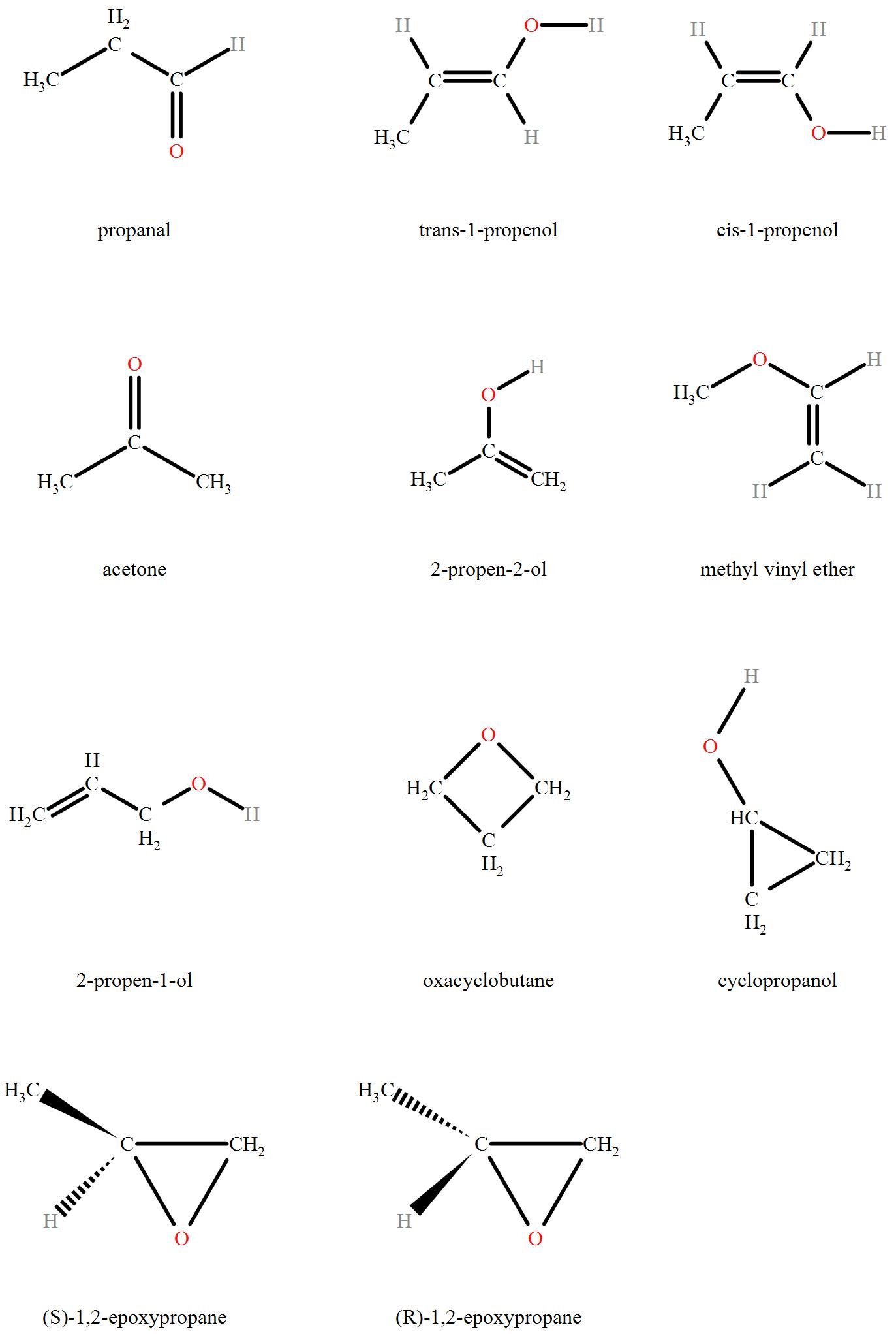
Hence we can see that a total of 11 isomers of C3H6O are possible.
What is the common name of 2-methyl-propanal?- a)formaldehyde
- b)Isobutyraldehyde
- c)carbaldehyde
- d)acetaldehyde
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the common name of 2-methyl-propanal?
a)
formaldehyde
b)
Isobutyraldehyde
c)
carbaldehyde
d)
acetaldehyde
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- Isobutyraldehyde is the chemical compound with the formula (CH₃)₂CHCHO.

- It is an aldehyde, isomeric with n-butyraldehyde.
- Isobutyraldehyde is manufactured, often as a side-product, by the hydroformylation of propene. Its odour is described as that of wet cereal or straw.
Identify the pair of enantiomers amongst the given pairs:- a)
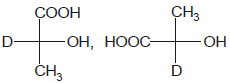
- b)
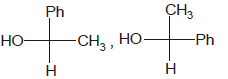
- c)
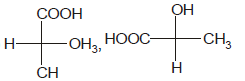
- d)
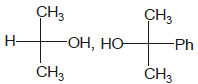
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the pair of enantiomers amongst the given pairs:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
The 1st option has R configuration and 2nd has S configuration hence they are non super imposable mirror images of each other and are enantiomers.
The 1st option has R configuration and 2nd has S configuration hence they are non super imposable mirror images of each other and are enantiomers.
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by:- a)Benedict test
- b)Iodoform test
- c)Tollen's reagent test
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by:
a)
Benedict test
b)
Iodoform test
c)
Tollen's reagent test
d)
None of these

|
Samridhi Bajaj answered |
CH3CHO will give iodoform test and C6H5CH2CHO will not give iodoform test.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following form(s) yellow precipitate with NaOH/I2 solution?- a)CH3CHO
- b)
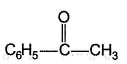
- c)
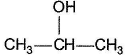
- d)CH3CH2OH
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following form(s) yellow precipitate with NaOH/I2 solution?
a)
CH3CHO
b)
c)
d)
CH3CH2OH

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Carbonyls with 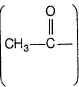 group or an alcohol with a methyl group and a “H” at α-carbon gives iodoform test.
group or an alcohol with a methyl group and a “H” at α-carbon gives iodoform test.
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Tollen’s reagent used for the distinction of aldehydes with ketones is- a)Pb(NO3),-NH3(aq)
- b)Cu(NO3)2-NH3(aq)
- c)AgNO3-NH3(aq)
- d)Cu(ll) citrate-NH3(aq)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Tollen’s reagent used for the distinction of aldehydes with ketones is
a)
Pb(NO3),-NH3(aq)
b)
Cu(NO3)2-NH3(aq)
c)
AgNO3-NH3(aq)
d)
Cu(ll) citrate-NH3(aq)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Tollen’s reagent is ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate in which silver remains as [Ag(NH3)2]+.
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,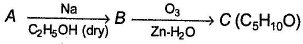 C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.
C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.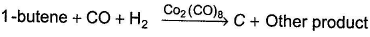 Consider the reaction given below,
Consider the reaction given below,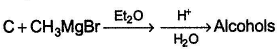 Q. How many different alcohols are expected?
Q. How many different alcohols are expected?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
How many different alcohols are expected?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Learners Habitat answered |
Compound A has a triple bond and it is symmetrical because its partially reduced product B gives single ozonolysis product C, Also, A shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism, it must be
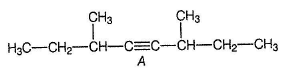
As shown above, A has two chiral carbons but simultaneously, it is symmetrical. Hence, it has both meso and a pair of enantiomers as stereoisomers.
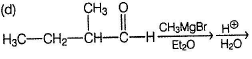
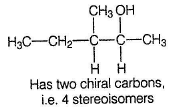
As shown above, A has two chiral carbons but simultaneously, it is symmetrical. Hence, it has both meso and a pair of enantiomers as stereoisomers.
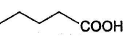
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q, Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following will give a racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4 followed by acid work-up?- a)
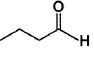
- b)
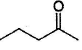
- c)
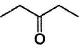
- d)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q, Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following will give a racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4 followed by acid work-up?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Amisha answered |
The ans is B . coz after the action of NaBH4 ,chiral carbon is present only in the product of B.And hence it can give both R and S configuration.
Which of the following could result as a product in the aldol condensation reaction?- a)4-methyl-3-penten-2-on
- b)4-methyl-4-penten-2-one
- c)4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one
- d)3-methyl-4-hexen-2-one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following could result as a product in the aldol condensation reaction?
a)
4-methyl-3-penten-2-on
b)
4-methyl-4-penten-2-one
c)
4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one
d)
3-methyl-4-hexen-2-one

|
Maulik Verma answered |
It is an α, β-unsaturated ketone which can be formed in an aldol condensation followed by dehydration.
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage. The reaction is called?- a)Etard reaction
- b)Stephen reaction
- c)Friedel – crafts reaction
- d)Gatterman – Koch reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage. The reaction is called?
a)
Etard reaction
b)
Stephen reaction
c)
Friedel – crafts reaction
d)
Gatterman – Koch reaction

|
Indu Indu answered |
Red algae .it is also responsible for red colour water in mediterreian sea
In the propanoate ion- a)both the carbon – oxygen bonds are the same length.
- b)the carbon atom bears a – 1 charge.
- c)one of the oxygen atoms bears a – 1 charge
- d)the carbon – oxygen double bond is shorter.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the propanoate ion
a)
both the carbon – oxygen bonds are the same length.
b)
the carbon atom bears a – 1 charge.
c)
one of the oxygen atoms bears a – 1 charge
d)
the carbon – oxygen double bond is shorter.
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
This is because of Resonance.
The incorrect statement regarding oxo process for synthesis of an aldehyde is- a)Mixture of CO and H2 is allowed to react with an alkene
- b)Co2(CO)8 may be used as a catalyst
- c)[Co(CO)4H] may act as a catalyst
- d)This process can also be used in the same manner for the synthesis of ketone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The incorrect statement regarding oxo process for synthesis of an aldehyde is
a)
Mixture of CO and H2 is allowed to react with an alkene
b)
Co2(CO)8 may be used as a catalyst
c)
[Co(CO)4H] may act as a catalyst
d)
This process can also be used in the same manner for the synthesis of ketone

|
Yoganand Pendem answered |
Oxo process involves formulation of alkene to form aldehyde only not ketone
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?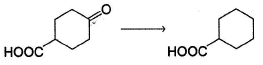
- a)Zn(Hg)-HCI
- b)N2H4/NaOH/Heat
- c)LiAIH4
- d)NaBH4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?
a)
Zn(Hg)-HCI
b)
N2H4/NaOH/Heat
c)
LiAIH4
d)
NaBH4
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Clemmensen reduction is suitable for reductio n of carbonyls containing additional acidic functional group.
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of their acid strength: i) trichloroacetic acid ii) trifluoroacetic acid iii) acetic acid and iv) formic acid- a)trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, formic acid and acetic acid
- b)formic acid., trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, and acetic acid
- c)trichloroacetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, acetic acid and formic acid.
- d)trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid acetic acid and Propan – 1 – ol, 4 – methylphenol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of their acid strength: i) trichloroacetic acid ii) trifluoroacetic acid iii) acetic acid and iv) formic acid
a)
trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, formic acid and acetic acid
b)
formic acid., trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, and acetic acid
c)
trichloroacetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, acetic acid and formic acid.
d)
trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid acetic acid and Propan – 1 – ol, 4 – methylphenol
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Acidic strength of carboxylic acid -
– More acidic than phenols or alcohols.
– Acidity increase with the presence of a group with -I effect in the alkyl group.Whereas it decreases with the presence of +I group.
– Acidity increases with increase in the number of halogen atoms on  - position.
- position.
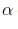 - position.
- position.– It decreases with increasing distance of halogen from 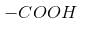
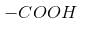
– It increases with increase in the electronegativity of halogen.
- CF3COOH > CCl3COOH > HCOOH > CH3 COOH
One mole of a symmetrical alkane on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde having molecular mass of 44u. The alkene is: - a)Ethene
- b)Propene
- c)1-butene
- d)2-butene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of a symmetrical alkane on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde having molecular mass of 44u. The alkene is:
a)
Ethene
b)
Propene
c)
1-butene
d)
2-butene
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
One mole of a symmetrical alkene on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde having a molecular weight of mass of 44 u. The alkene is
CH3CH=CHCH3 +O3 ------2CH3CHO
molecular mass of CH3CHO is 12*2+4*1+16 =44
Thus the alkene is 2 butene and the aldehyde formed is ethanal(acetaldehyde)
Consider the following reaction,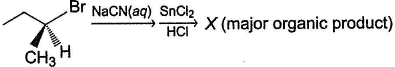
(A pure enantiomer)Q. The incorrect statement regarding X is- a)It is an aldehyde
- b)Product has inverted configuration at the α-carbon
- c)X is a racemic mixture
- d)Product can be either laevorotatory or dextrorotatory isomer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction,
(A pure enantiomer)
Q.
The incorrect statement regarding X is
a)
It is an aldehyde
b)
Product has inverted configuration at the α-carbon
c)
X is a racemic mixture
d)
Product can be either laevorotatory or dextrorotatory isomer
|
|
Om Desai answered |
X will be a pure enantiomer of aldehyde.
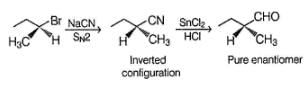

An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q. If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will give- a)a pure enantiomer
- b)a racemic mixture
- c)a pair of diastereomers
- d)an achiral alcohol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.
Q.
If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will give
a)
a pure enantiomer
b)
a racemic mixture
c)
a pair of diastereomers
d)
an achiral alcohol
|
|
Kashish Garg answered |
Since, A is completely saturated, it must contain more than one chiral carbon atoms in order to show both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Also, C on ozonolysis gives D (C5H10O) as one product, other product must be CH3SHO. Hence, C must be 
B is enantiomeric. If a pure enantiomer of B is reduced with LiAIH4, pair of diastereomers would be formed.
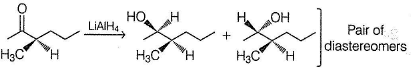
B is enantiomeric. If a pure enantiomer of B is reduced with LiAIH4, pair of diastereomers would be formed.
A strong base can abstract an α – hydrogen from- a)Alkane.
- b)Amine
- c)Ketone
- d)Alkene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A strong base can abstract an α – hydrogen from
a)
Alkane.
b)
Amine
c)
Ketone
d)
Alkene
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
After deprotonation the negative charge will be in conjugation with the pi orbital of carbonyl..so base will prefer to abstract alpha hydrogen from ketone.
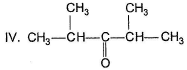
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Arrange the following in the increasing order of reactivity with NH3.I. CH2O
II. CH3CHO
III. CH3—CO—CH3
- a)I < II < III < IV
- b)IV < III < II < I
- c)III < IV < I < II
- d)II < I < IV < III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of reactivity with NH3.
I. CH2O
II. CH3CHO
III. CH3—CO—CH3

II. CH3CHO
III. CH3—CO—CH3
a)
I < II < III < IV
b)
IV < III < II < I
c)
III < IV < I < II
d)
II < I < IV < III

|
Harsharma answered |
I think this is because of steric hindrance.... because NH3 attack carbonyl carbon as nucleophile (Sn2)...and then steric hindrance is main factor
In which of the following reactions, ketone is formed as the major organic product?- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions, ketone is formed as the major organic product?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
If acid derivatives like nitrile, acid chlorid e or ester is taken in excess in Grignard synthesis, second addition of Grignard’s reagent on carbonyl product does not succeed and carbonyls are obtained as major products.
In option (b), carboxylic acids and in option (d), an aldehyde is formed.
In option (b), carboxylic acids and in option (d), an aldehyde is formed.
IUPAC name of compound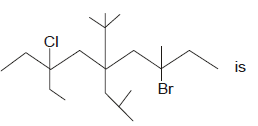
- a)3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-3-methylnonane
- b)3-Bromo7-chloro-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-7-ethyl-3methyl-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
- c)3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-3-,methyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
- d)3-Bromo-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-7-chloro-7ethyl-5--3-methylnonane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of compound
a)
3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-3-methylnonane
b)
3-Bromo7-chloro-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-7-ethyl-3methyl-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
c)
3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-3-,methyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
d)
3-Bromo-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-7-chloro-7ethyl-5--3-methylnonane

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The correct answer is option B
First of all, we should number the carbon atoms from right to left for the above molecule. According to IUPAC rule, we have to name the functional groups alphabetically. Hence, bromine which is attached to 3rd carbon is named as 3-bromo, chlorine which is attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-chloro and ethyl group which is also attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-ethyl. 5-(1,1-dimethyethyl) indicates that, 2 methyl groups are attached to the 1st carbon of ethyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. 5-(2-methylpropyl) indicates that, a methyl group is attached to the 2nd carbon of propyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. Finally, since the molecule has nine atoms and it is an alkane, the word nonane is added to the IUPAC name.
First of all, we should number the carbon atoms from right to left for the above molecule. According to IUPAC rule, we have to name the functional groups alphabetically. Hence, bromine which is attached to 3rd carbon is named as 3-bromo, chlorine which is attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-chloro and ethyl group which is also attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-ethyl. 5-(1,1-dimethyethyl) indicates that, 2 methyl groups are attached to the 1st carbon of ethyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. 5-(2-methylpropyl) indicates that, a methyl group is attached to the 2nd carbon of propyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. Finally, since the molecule has nine atoms and it is an alkane, the word nonane is added to the IUPAC name.
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a)A compound whose molecule has D configuration will always be dextrorotatory
- b)A compound whose molecule has D configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory
- c)A compound whose molecule has R configuration may be dexrotatory or levorotatory
- d)A compound whose molecule has L configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
A compound whose molecule has D configuration will always be dextrorotatory
b)
A compound whose molecule has D configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory
c)
A compound whose molecule has R configuration may be dexrotatory or levorotatory
d)
A compound whose molecule has L configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory

|
Avantika Saha answered |
The configuration in a compound is independent of its physical properties (optical activity)
How manyh assymmetric carbon atoms are present in
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene- a)2,1,1
- b)1,1,1
- c)2,0.2
- d)2,0,1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How manyh assymmetric carbon atoms are present in
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene
a)
2,1,1
b)
1,1,1
c)
2,0.2
d)
2,0,1
|
|
Aarya Khanna answered |
Asymmetric carbon atoms are those carbon atoms which are attached to four different groups or atoms. These carbon atoms are also known as chiral centers.
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane:
- Cyclohexane has no asymmetric carbon atoms.
- When two methyl groups are attached to cyclohexane, it becomes 2,3-dimethyl cyclohexane.
- The carbon at position 2 is attached to two methyl groups and two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, it is not an asymmetric carbon atom.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one methyl group, and one cyclohexane ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane.
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene:
- Cyclopentene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclopentene at position 3, it becomes 3-methyl cyclopentene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclopentene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methyl cyclopentene.
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene:
- Cyclohexene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclohexene at position 3, it becomes 3-methylcyclohexene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclohexene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methylcyclohexene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (2,1,1) as there are 2 asymmetric carbon atoms in total, with 1 in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane, 1 in 3-methyl cyclopentene, and 1 in 3-methylcyclohexene.
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane:
- Cyclohexane has no asymmetric carbon atoms.
- When two methyl groups are attached to cyclohexane, it becomes 2,3-dimethyl cyclohexane.
- The carbon at position 2 is attached to two methyl groups and two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, it is not an asymmetric carbon atom.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one methyl group, and one cyclohexane ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane.
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene:
- Cyclopentene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclopentene at position 3, it becomes 3-methyl cyclopentene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclopentene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methyl cyclopentene.
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene:
- Cyclohexene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclohexene at position 3, it becomes 3-methylcyclohexene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclohexene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methylcyclohexene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (2,1,1) as there are 2 asymmetric carbon atoms in total, with 1 in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane, 1 in 3-methyl cyclopentene, and 1 in 3-methylcyclohexene.
All of the following reaction gives atleast one ketone as a significant organic product except- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following reaction gives atleast one ketone as a significant organic product except
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
It gives aldehydes as major product.
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?- a)adipic acid
- b)succinic acid
- c)hexanoic acid
- d)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?
a)
adipic acid
b)
succinic acid
c)
hexanoic acid
d)
cyclohexanecarboxylic acid

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
Conc KMnO4 will cause oxidation and ring opening forming adipic acid.
 A is optically active and C is one of the several aldol possible in the above reaction.Q. The product B is stereomeric. If a mixture containing all stereoisomers of B is treated with excess of LiAIH4 followed by the acidification will give how many different isomeric diols ?
A is optically active and C is one of the several aldol possible in the above reaction.Q. The product B is stereomeric. If a mixture containing all stereoisomers of B is treated with excess of LiAIH4 followed by the acidification will give how many different isomeric diols ?- a)2
- b)4
- c)6
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

A is optically active and C is one of the several aldol possible in the above reaction.
Q.
The product B is stereomeric. If a mixture containing all stereoisomers of B is treated with excess of LiAIH4 followed by the acidification will give how many different isomeric diols ?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
6
d)
8

|
Niti Saha answered |
The common name for pentanedioic acid is:- a)succinic acid
- b)oxalic acid
- c)glutaric acid
- d)pimelic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The common name for pentanedioic acid is:
a)
succinic acid
b)
oxalic acid
c)
glutaric acid
d)
pimelic acid

|
Aryan Sen answered |
Pentanedioic acid is glutaric acid.
The compound obtained when acetaldehyde reacts with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide exhibits:- a)geometrical isomerism
- b)both optical and geometrical isomerism
- c)optical isomerism.
- d)neither optical nor geometrical isomerism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound obtained when acetaldehyde reacts with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide exhibits:
a)
geometrical isomerism
b)
both optical and geometrical isomerism
c)
optical isomerism.
d)
neither optical nor geometrical isomerism

|
Amrutha Pillai answered |
CH3CH=CHCHO is the product which is suitably substituted so will show geometrical isomer.
If glyoxal glycol is treated with a mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr in diethyl ether followed by acid hydrolysis, how many different diols would be formed, which are simultaneously optically active?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
If glyoxal glycol is treated with a mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr in diethyl ether followed by acid hydrolysis, how many different diols would be formed, which are simultaneously optically active?

|
Ishani Yadav answered |
One pair of enantiomers for each (I) and (II) while two pairs of enantiomers for (III).
In which of the following compounds, enol form exist? - a)C6H5COCH3
- b)C6H5CHO
- c)
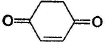
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following compounds, enol form exist?
a)
C6H5COCH3
b)
C6H5CHO
c)
d)
Both (a) and (c)
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Both option (a) and option (c) forms enol but option (b) does not form enol.
Which of the following is correct?
- a)On reduction any aldehyde gives secondary alcohol
- b)Reaction of vegetable oil with H2SO4 gives glycerine
- c)Alcoholic iodine with NaOH gives iodoform
- d)Sucrose on reaction with NaCl gives invert sugar
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct?
a)
On reduction any aldehyde gives secondary alcohol
b)
Reaction of vegetable oil with H2SO4 gives glycerine
c)
Alcoholic iodine with NaOH gives iodoform
d)
Sucrose on reaction with NaCl gives invert sugar

|
Pooja Pillai answered |
Many naturally occurring aldehydes and ketones are used in the blending of perfumes and flavouring agents. But the preferred ones are- a)higher ketones
- b)lower aldehydes
- c)lower ketones
- d)higher aldehydes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Many naturally occurring aldehydes and ketones are used in the blending of perfumes and flavouring agents. But the preferred ones are
a)
higher ketones
b)
lower aldehydes
c)
lower ketones
d)
higher aldehydes

|
Pritam Malik answered |
Higher aldehydes are preferred.
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageA neutral organic compound A(C10H20O2) neither reduces Tollen’s reagent nor forms precipitate with 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine, but can be resolved into enantiomers. A on acid hydrolysis forms two compounds B and C, both are enantiomeric. C neither reduces Fehling’s solution nor forms iodoform with alkaline iodine solution. C on oxidation with CrO3/HCI /pyridineforms D which is still resolvable into enantiomers. D on further treatment with aqueous (C2H5O)3 Al solution gives back A.Q. How many different stereoisomers exist for A ?- a)2
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
A neutral organic compound A(C10H20O2) neither reduces Tollen’s reagent nor forms precipitate with 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine, but can be resolved into enantiomers. A on acid hydrolysis forms two compounds B and C, both are enantiomeric. C neither reduces Fehling’s solution nor forms iodoform with alkaline iodine solution. C on oxidation with CrO3/HCI /pyridineforms D which is still resolvable into enantiomers. D on further treatment with aqueous (C2H5O)3 Al solution gives back A.
Q.
How many different stereoisomers exist for A ?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
From the given information, it appears that A is an ester. Since, D on Tischenko reaction gives back A indicates that in ester, both acid and alcohol fragments (B and C respectively) has five carbon atoms each. Also, C is an alcohol which has a chiral carbon and no CH3CH(OH)— grouping (not giving iodoform). Controlled oxidation of C gives D, a carbonyl which is still chiral. Hence, D must be an aldehyde with a chiral carbon.
The above ester has two chiral carbons and no symmetry hence, four stereoisomers.
Chapter doubts & questions for Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2) 2025 is part of BMAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BMAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BMAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2) in English & Hindi are available as part of BMAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BMAT Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2)
146 videos|126 docs|121 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily
















