All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series >
All Questions
All questions of Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
The correction to be applied to each 30 metre chain length along θ° slope, is
- a)30 (cosθ - 1)m
- b)30 (sinθ - 1)m
- c)30 (secθ - 1)m,
- d)30 (tanθ - 1)m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correction to be applied to each 30 metre chain length along θ° slope, is
a)
30 (cosθ - 1)m
b)
30 (sinθ - 1)m
c)
30 (secθ - 1)m,
d)
30 (tanθ - 1)m

|
Aniket Pillai answered |
The survey line is called the chaining correction. This correction takes into account any errors or variations in the length of the chain due to temperature, tension, or wear and tear. The chaining correction is usually calculated by measuring the true length of the chain against a standard reference length and then applying a correction factor to each chain length along the survey line. This ensures that the survey measurements are accurate and reliable.
The RL, of the point A which is on the floor is 100 m and back sight reading on A is 2.455 m. If the foresight reading on the point B which is one the ceiling is 2.745 m, the RL of point B will be- a)94.80 m
- b)99.71 m
- c)100.29 m
- d)105.20
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The RL, of the point A which is on the floor is 100 m and back sight reading on A is 2.455 m. If the foresight reading on the point B which is one the ceiling is 2.745 m, the RL of point B will be
a)
94.80 m
b)
99.71 m
c)
100.29 m
d)
105.20

|
Srestha Khanna answered |
Since the staff at the elevated point B on the ceiling is held vertically inverted
RL of B = RL of A + B.S.on A + FS on B
= 100 + 2.455 + 2.745 = 105.20 m
RL of B = RL of A + B.S.on A + FS on B
= 100 + 2.455 + 2.745 = 105.20 m
An observer standing on the deck of a ship just sees the top of a lighthouse which is 30 m above the sea level. If the height of the observer’s eye is 10 m above the sea level, then the distance of the observer from the lighthouse will be nearly- a)22.5 km
- b)24.3 km
- c)33.3 km
- d)59.7 km
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An observer standing on the deck of a ship just sees the top of a lighthouse which is 30 m above the sea level. If the height of the observer’s eye is 10 m above the sea level, then the distance of the observer from the lighthouse will be nearly
a)
22.5 km
b)
24.3 km
c)
33.3 km
d)
59.7 km

|
Sneha Roy answered |
Above the sea level is 10 m, then what is the distance between the ship and the lighthouse?
We can use trigonometry to solve the problem. Let's draw a diagram:
```
A (lighthouse)
|\
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
|θ \
| \
| \
| \
O (observer)
|
|
|
|
S (ship)
```
We want to find the distance OS. We know that the height of the lighthouse is 30 m, the height of the observer is 10 m, and we can assume that the angle θ is small enough that we can use the approximation tan(θ) ≈ θ. Then we have:
tan(θ) = OA / OA'
tan(θ) = 30 / OS
θ = tan^-1(30 / OS)
tan(θ) = OB / OA'
tan(θ) = 10 / OS
θ = tan^-1(10 / OS)
Setting these two expressions for θ equal to each other, we get:
tan^-1(30 / OS) = tan^-1(10 / OS)
30 / OS = 10 / OS
OS = 20
Therefore, the distance between the ship and the lighthouse is 20 meters.
We can use trigonometry to solve the problem. Let's draw a diagram:
```
A (lighthouse)
|\
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
| \
|θ \
| \
| \
| \
O (observer)
|
|
|
|
S (ship)
```
We want to find the distance OS. We know that the height of the lighthouse is 30 m, the height of the observer is 10 m, and we can assume that the angle θ is small enough that we can use the approximation tan(θ) ≈ θ. Then we have:
tan(θ) = OA / OA'
tan(θ) = 30 / OS
θ = tan^-1(30 / OS)
tan(θ) = OB / OA'
tan(θ) = 10 / OS
θ = tan^-1(10 / OS)
Setting these two expressions for θ equal to each other, we get:
tan^-1(30 / OS) = tan^-1(10 / OS)
30 / OS = 10 / OS
OS = 20
Therefore, the distance between the ship and the lighthouse is 20 meters.
Which one of the following surveys is employed for collecting sufficient data in connection with sewage disposal and water supply works?- a)Topographic survey
- b)Cadastral survey
- c)Geodetic survey
- d)Cross-sectioning and profile levelling
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following surveys is employed for collecting sufficient data in connection with sewage disposal and water supply works?
a)
Topographic survey
b)
Cadastral survey
c)
Geodetic survey
d)
Cross-sectioning and profile levelling

|
Ankit Joshi answered |
Cadastral Survey: to establish a boundary of properties for legal use
Topographical Survey: Surveys which are carried out to depict mountains, rivers, water bodies, wooded areas and other cultural details
Geodetic Survey: Considering earth’s curvature. Usually used when area to be surveyed is greater than 260 sq.km
Cross-Sectioning and Profile Levelling- Collecting sufficient data in connection with sewage disposal and water supply works
City Survey: survey of city
Guide Map Survey: For showing relief by contours and spot heights.
Topographical Survey: Surveys which are carried out to depict mountains, rivers, water bodies, wooded areas and other cultural details
Geodetic Survey: Considering earth’s curvature. Usually used when area to be surveyed is greater than 260 sq.km
Cross-Sectioning and Profile Levelling- Collecting sufficient data in connection with sewage disposal and water supply works
City Survey: survey of city
Guide Map Survey: For showing relief by contours and spot heights.
The representative fraction 1/2500 means that the scale 1 cm is equal to- a)0.25 m
- b)2,5 m
- c)25 m
- d)2.5 km
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The representative fraction 1/2500 means that the scale 1 cm is equal to
a)
0.25 m
b)
2,5 m
c)
25 m
d)
2.5 km

|
Priyanka Shah answered |
1/2500 means
1 cm = 2500 cm
∴ 1 cm = 25 m
What is the magnetic declination at a place if the magnetic bearing of the sun at noon is 184°- a)4°W
- b)4°E
- c)176°W
- d)176°E
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the magnetic declination at a place if the magnetic bearing of the sun at noon is 184°
a)
4°W
b)
4°E
c)
176°W
d)
176°E
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
True bearing
= Magnetic bearing + Declination
∴ 180° = 184° + Declination
or Declination = -4° = 4°W
= Magnetic bearing + Declination
∴ 180° = 184° + Declination
or Declination = -4° = 4°W
In a closed traverse, the sum of south latitudes exceeds the sum of north latitudes and the sum of east departures exceeds the sum of west departures. The closing line will lie in the- a)N-W quadrant
- b)N-E quadrant
- c)S-E quadrant
- d)S-W quadrant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a closed traverse, the sum of south latitudes exceeds the sum of north latitudes and the sum of east departures exceeds the sum of west departures. The closing line will lie in the
a)
N-W quadrant
b)
N-E quadrant
c)
S-E quadrant
d)
S-W quadrant

|
Juhi Choudhary answered |
The closing line will have south latitude and east departure. Therefore it will lie in S-E quadrant.
The difference between a level line and a horizontal line is that- a)level line is a curved line while horizontal line is a straight line
- b)level line is normal to plumb line while horizontal line may not be normal to plump line at the tangent point to level line
- c)horizontal line is normal to plumb line while level line may not be normal to the plumb line
- d)both are same
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between a level line and a horizontal line is that
a)
level line is a curved line while horizontal line is a straight line
b)
level line is normal to plumb line while horizontal line may not be normal to plump line at the tangent point to level line
c)
horizontal line is normal to plumb line while level line may not be normal to the plumb line
d)
both are same

|
Maulik Joshi answered |
Level Line vs Horizontal Line
Definition of Level Line and Horizontal Line:
- Level Line: A level line is a curved line on the Earth's surface that is perpendicular to the plumb line at all points. It represents a line of constant elevation or altitude.
- Horizontal Line: A horizontal line is a straight line on a plane that is perpendicular to the vertical or plumb line. It represents a line of constant height or depth.
Difference between Level Line and Horizontal Line:
- Shape: A level line is a curved line, while a horizontal line is a straight line.
- Orientation: A level line is perpendicular to the plumb line at all points, while a horizontal line is perpendicular to the vertical or plumb line only at its tangent point.
- Meaning: A level line represents a line of constant elevation or altitude, while a horizontal line represents a line of constant height or depth.
Examples:
- A contour line on a topographic map is a level line because it connects points of equal elevation.
- The horizon is a horizontal line because it represents the line where the sky meets the earth.
Conclusion:
Level lines and horizontal lines are different in terms of shape, orientation, and meaning. A level line is a curved line on the Earth's surface that is always perpendicular to the plumb line, while a horizontal line is a straight line on a plane that is perpendicular to the vertical or plumb line only at its tangent point.
Definition of Level Line and Horizontal Line:
- Level Line: A level line is a curved line on the Earth's surface that is perpendicular to the plumb line at all points. It represents a line of constant elevation or altitude.
- Horizontal Line: A horizontal line is a straight line on a plane that is perpendicular to the vertical or plumb line. It represents a line of constant height or depth.
Difference between Level Line and Horizontal Line:
- Shape: A level line is a curved line, while a horizontal line is a straight line.
- Orientation: A level line is perpendicular to the plumb line at all points, while a horizontal line is perpendicular to the vertical or plumb line only at its tangent point.
- Meaning: A level line represents a line of constant elevation or altitude, while a horizontal line represents a line of constant height or depth.
Examples:
- A contour line on a topographic map is a level line because it connects points of equal elevation.
- The horizon is a horizontal line because it represents the line where the sky meets the earth.
Conclusion:
Level lines and horizontal lines are different in terms of shape, orientation, and meaning. A level line is a curved line on the Earth's surface that is always perpendicular to the plumb line, while a horizontal line is a straight line on a plane that is perpendicular to the vertical or plumb line only at its tangent point.
Geodetic surveying is different from plane surveying because of- a)the curvature of earth
- b)the large difference of elevations between various points
- c)coverage of very large area
- d)undulations of very large area
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Geodetic surveying is different from plane surveying because of
a)
the curvature of earth
b)
the large difference of elevations between various points
c)
coverage of very large area
d)
undulations of very large area

|
Ameya Roy answered |
Geodetic Surveying:
Geodetic surveying is a type of surveying that takes into account the curvature of the earth. It is used to accurately measure large distances and areas, such as the size and shape of the earth, the location of continents, and the distances between them.
Difference from Plane Surveying:
Plane surveying, on the other hand, assumes that the earth is flat and is used to measure smaller distances and areas. The main difference between geodetic and plane surveying is the curvature of the earth.
Importance of the Curvature of the Earth:
The curvature of the earth is an important factor in geodetic surveying because it affects the accuracy of measurements over large distances. When measuring over a long distance, the curvature of the earth must be taken into account to ensure that the measurements are accurate. Failure to take the curvature of the earth into account can result in significant errors in measurements.
Applications of Geodetic Surveying:
Geodetic surveying is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Mapping of large areas such as continents, countries, and regions
- Navigation and positioning of ships, airplanes, and other vehicles
- Determination of the size and shape of the earth
- Monitoring of changes in the earth's surface, such as tectonic movements, sea level changes, and the melting of ice caps
- Planning and construction of large-scale engineering projects such as bridges, tunnels, and dams
Conclusion:
In conclusion, geodetic surveying is different from plane surveying because it takes into account the curvature of the earth, which is an important factor in accurately measuring large distances and areas. It is used in a wide range of applications, from mapping large areas to the planning and construction of large-scale engineering projects.
Geodetic surveying is a type of surveying that takes into account the curvature of the earth. It is used to accurately measure large distances and areas, such as the size and shape of the earth, the location of continents, and the distances between them.
Difference from Plane Surveying:
Plane surveying, on the other hand, assumes that the earth is flat and is used to measure smaller distances and areas. The main difference between geodetic and plane surveying is the curvature of the earth.
Importance of the Curvature of the Earth:
The curvature of the earth is an important factor in geodetic surveying because it affects the accuracy of measurements over large distances. When measuring over a long distance, the curvature of the earth must be taken into account to ensure that the measurements are accurate. Failure to take the curvature of the earth into account can result in significant errors in measurements.
Applications of Geodetic Surveying:
Geodetic surveying is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Mapping of large areas such as continents, countries, and regions
- Navigation and positioning of ships, airplanes, and other vehicles
- Determination of the size and shape of the earth
- Monitoring of changes in the earth's surface, such as tectonic movements, sea level changes, and the melting of ice caps
- Planning and construction of large-scale engineering projects such as bridges, tunnels, and dams
Conclusion:
In conclusion, geodetic surveying is different from plane surveying because it takes into account the curvature of the earth, which is an important factor in accurately measuring large distances and areas. It is used in a wide range of applications, from mapping large areas to the planning and construction of large-scale engineering projects.
The instrument which is used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distances directly without resorting fo chaining, is known as- a)Plane alidade
- b)telescopic alidade
- c)clinometer
- d)tacheometer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The instrument which is used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distances directly without resorting fo chaining, is known as
a)
Plane alidade
b)
telescopic alidade
c)
clinometer
d)
tacheometer

|
Nitya Nambiar answered |
Telescopic Alidade: The Instrument for Obtaining Horizontal and Vertical Distances in Plane Tabling
Introduction:
In plane tabling, a surveying method used to obtain accurate topographic maps, various instruments are used to measure horizontal and vertical distances. One such instrument is the telescopic alidade. The telescopic alidade is an essential tool in plane tabling as it allows surveyors to obtain horizontal and vertical distances directly without the need for chaining.
Explanation:
The telescopic alidade consists of a telescope mounted on a tripod. It is equipped with various features that enable accurate measurements in plane tabling surveys.
Horizontal Distance:
To measure horizontal distances, the telescopic alidade is fitted with a stadia diaphragm. This diaphragm has horizontal crosshairs and stadia hairs. The horizontal crosshairs help align the telescope with the target, while the stadia hairs allow the surveyor to measure the distance between the instrument and the target. By measuring the subtended stadia interval on the stadia hairs, the horizontal distance can be directly obtained.
Vertical Distance:
For measuring vertical distances, the telescopic alidade is equipped with a vertical arc or clinometer. The vertical arc is graduated in degrees, allowing the surveyor to measure the vertical angles of inclination or depression. By measuring the vertical angle, along with the known horizontal distance, the vertical distance can be calculated using trigonometric principles.
Advantages of Telescopic Alidade:
1. Efficiency: The telescopic alidade allows surveyors to obtain horizontal and vertical distances directly, eliminating the need for time-consuming chaining.
2. Accuracy: The instrument provides precise measurements due to the use of stadia hairs and the ability to read vertical angles.
3. Portability: The telescopic alidade is lightweight and can be easily transported, making it suitable for fieldwork and plane table surveys.
4. Versatility: It can be used in various surveying applications, including topographic mapping, contouring, and construction layout.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the telescopic alidade is a crucial instrument used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distances directly. Its features, such as the stadia diaphragm and vertical arc, enable surveyors to measure distances accurately and efficiently.
Introduction:
In plane tabling, a surveying method used to obtain accurate topographic maps, various instruments are used to measure horizontal and vertical distances. One such instrument is the telescopic alidade. The telescopic alidade is an essential tool in plane tabling as it allows surveyors to obtain horizontal and vertical distances directly without the need for chaining.
Explanation:
The telescopic alidade consists of a telescope mounted on a tripod. It is equipped with various features that enable accurate measurements in plane tabling surveys.
Horizontal Distance:
To measure horizontal distances, the telescopic alidade is fitted with a stadia diaphragm. This diaphragm has horizontal crosshairs and stadia hairs. The horizontal crosshairs help align the telescope with the target, while the stadia hairs allow the surveyor to measure the distance between the instrument and the target. By measuring the subtended stadia interval on the stadia hairs, the horizontal distance can be directly obtained.
Vertical Distance:
For measuring vertical distances, the telescopic alidade is equipped with a vertical arc or clinometer. The vertical arc is graduated in degrees, allowing the surveyor to measure the vertical angles of inclination or depression. By measuring the vertical angle, along with the known horizontal distance, the vertical distance can be calculated using trigonometric principles.
Advantages of Telescopic Alidade:
1. Efficiency: The telescopic alidade allows surveyors to obtain horizontal and vertical distances directly, eliminating the need for time-consuming chaining.
2. Accuracy: The instrument provides precise measurements due to the use of stadia hairs and the ability to read vertical angles.
3. Portability: The telescopic alidade is lightweight and can be easily transported, making it suitable for fieldwork and plane table surveys.
4. Versatility: It can be used in various surveying applications, including topographic mapping, contouring, and construction layout.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the telescopic alidade is a crucial instrument used in plane tabling for obtaining horizontal and vertical distances directly. Its features, such as the stadia diaphragm and vertical arc, enable surveyors to measure distances accurately and efficiently.
In reciprocal levelling, the error which is not completely eliminated, is due to
- a)earth’s curvature
- b)non-adjustment of line of collimation
- c)refraction
- d)non-adjustment of the bubble tube
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In reciprocal levelling, the error which is not completely eliminated, is due to
a)
earth’s curvature
b)
non-adjustment of line of collimation
c)
refraction
d)
non-adjustment of the bubble tube
|
|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Reciprocal Leveling:
- This technique of leveling work is used to find the exact height difference or to find the exact RL(Reduce level) of the point by equalizing the distance when there is a large obstruction like a river, ponds, lakes, etc. in direction of the survey.
-
It eliminates the following errors:i) error in instrument adjustments i.e error due to collimationii) the combined effect of Earth's curvature and the refraction of the atmosphereiii) variation in the average refraction.
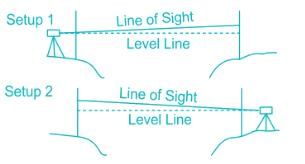
Which of the following is an obstacle to chaining but not to ranging?
- a)river
- b)hillock
- c)building
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an obstacle to chaining but not to ranging?
a)
river
b)
hillock
c)
building
d)
none of the above

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
Obstacles to chaining:
- Cases often occur in the field where the distance between two points is required, but direct chaining from one point to the other is impossible because of some sort of obstacle.
- A river and pond is an obstacle to chaining but not ranging.
The relationship between tropical year TY and sidereal year SY is- a)TY > SY
- b)TY < SY
- c)TY = SY
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The relationship between tropical year TY and sidereal year SY is
a)
TY > SY
b)
TY < SY
c)
TY = SY
d)
Any of the above
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Tropical year = 365.2422 mean solar days.
Sidereal year = 365.2564 mean solar days.
Sidereal year = 365.2564 mean solar days.
Theory of probability is applied to
- a)both accidental and cumulative errors
- b)cumulative errors only
- c)accidental errors only
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Theory of probability is applied to
a)
both accidental and cumulative errors
b)
cumulative errors only
c)
accidental errors only
d)
none of the above
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Laws of accidental errors follow the probability law, which is having a definite law for accidental error occurrence. It defines the errors and helps in expressing them in the form of equations.
Which one of the following is carried out by two theodolite method?- a)Circular curve ranging
- b)Tacheometric survey
- c)Geodetic survey
- d)Astronomical survey
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is carried out by two theodolite method?
a)
Circular curve ranging
b)
Tacheometric survey
c)
Geodetic survey
d)
Astronomical survey

|
Simran Saha answered |
Circular Curve Ranging using Two Theodolite Method
Circular curve ranging is a process of determining the position of points on a curve with respect to a given reference line. Two theodolite method is a common technique used to carry out circular curve ranging. This method involves the use of two theodolites placed at two stations on the reference line.
Steps involved in circular curve ranging using two theodolite method:
1. Setting up the theodolites: Two theodolites are set up at two stations on the reference line. The distance between the two stations should be at least equal to the radius of the curve.
2. Taking readings: The theodolites are used to take readings of the angles between the reference line and the tangent at each point on the curve. The readings are taken from both the stations.
3. Calculating the position of points on the curve: The angles measured at each point on the curve are used to calculate the position of the point with respect to the reference line. This calculation involves trigonometry and geometry.
4. Plotting the curve: The points calculated in the previous step are plotted on a graph to obtain the curve.
Advantages of two theodolite method:
1. It is a simple and accurate method of circular curve ranging.
2. It can be used in areas with difficult terrain.
3. It is relatively inexpensive compared to other methods.
Disadvantages of two theodolite method:
1. It requires skilled personnel to operate the instruments.
2. It is time-consuming and may take longer to complete compared to other methods.
Conclusion:
Circular curve ranging using two theodolite method is a useful technique in civil engineering for determining the position of points on a curve with respect to a reference line. It is a simple and accurate method that can be used in a variety of situations. However, it does require skilled personnel to operate the instruments and can be time-consuming.
Circular curve ranging is a process of determining the position of points on a curve with respect to a given reference line. Two theodolite method is a common technique used to carry out circular curve ranging. This method involves the use of two theodolites placed at two stations on the reference line.
Steps involved in circular curve ranging using two theodolite method:
1. Setting up the theodolites: Two theodolites are set up at two stations on the reference line. The distance between the two stations should be at least equal to the radius of the curve.
2. Taking readings: The theodolites are used to take readings of the angles between the reference line and the tangent at each point on the curve. The readings are taken from both the stations.
3. Calculating the position of points on the curve: The angles measured at each point on the curve are used to calculate the position of the point with respect to the reference line. This calculation involves trigonometry and geometry.
4. Plotting the curve: The points calculated in the previous step are plotted on a graph to obtain the curve.
Advantages of two theodolite method:
1. It is a simple and accurate method of circular curve ranging.
2. It can be used in areas with difficult terrain.
3. It is relatively inexpensive compared to other methods.
Disadvantages of two theodolite method:
1. It requires skilled personnel to operate the instruments.
2. It is time-consuming and may take longer to complete compared to other methods.
Conclusion:
Circular curve ranging using two theodolite method is a useful technique in civil engineering for determining the position of points on a curve with respect to a reference line. It is a simple and accurate method that can be used in a variety of situations. However, it does require skilled personnel to operate the instruments and can be time-consuming.
Transit rule of balancing a traverse is applied when- a)the linear and angular measurements are of same precision.
- b)the linear measurements are more precise than angular measurements.
- c)the angular measurements are more precise than linear measurements.
- d)the linear measurements are proportional to l and angular measurements are proportional to (1/l) where l is the length of the line.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Transit rule of balancing a traverse is applied when
a)
the linear and angular measurements are of same precision.
b)
the linear measurements are more precise than angular measurements.
c)
the angular measurements are more precise than linear measurements.
d)
the linear measurements are proportional to l and angular measurements are proportional to (1/l) where l is the length of the line.
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
The Transit Rule of Balancing a Traverse, also known as the Compass Rule, states that when the angular measurements are more precise than the linear measurements, the angular measurements should be used to balance the traverse.
When the linear measurements are more precise than the angular measurements, it is more appropriate to use the Distance Rule, also known as the Chain Rule. In this case, the linear measurements are used to balance the traverse.
It's crucial to have in mind that the Transit Rule and the Distance Rule are applied in different conditions, as they are used to balance the traverse differently depending on the precision of the measurements.
The option "d" is not correct because the Transit rule depends on the precision of the measurements and the proportionality of measurements with respect to length is not affecting the decision of choosing the rule.
Offsets are
- a)parallel lines erected from chain lines
- b)lateral measurements made with respect to main survey lines
- c)taken to avoid unnecessary walking between stations
- d)measurements which are not made at right angles to the chain line
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Offsets are
a)
parallel lines erected from chain lines
b)
lateral measurements made with respect to main survey lines
c)
taken to avoid unnecessary walking between stations
d)
measurements which are not made at right angles to the chain line

|
Sankar Dasgupta answered |
In surveying, offsets are lateral measurements taken from the main survey line (baseline) to plot the position of different points or objects. These measurements are generally taken at a right angle to the main survey lines, helping to create an accurate representation of the area being surveyed.
For example, if a surveyor is measuring a piece of land with a building on it, they would first establish the main survey line (baseline) and then measure the distance from the line to the corners of the building. These lateral measurements are called offsets.
Offsets allow surveyors to accurately map the location of various features on a piece of land, such as buildings, fences, or natural features like streams or trees. This information is then used to create maps, plan construction projects, or establish property boundaries.
For example, if a surveyor is measuring a piece of land with a building on it, they would first establish the main survey line (baseline) and then measure the distance from the line to the corners of the building. These lateral measurements are called offsets.
Offsets allow surveyors to accurately map the location of various features on a piece of land, such as buildings, fences, or natural features like streams or trees. This information is then used to create maps, plan construction projects, or establish property boundaries.
The error due to eccentricity of inner and outer axes can be eliminated by - a) reading both verniers and taking the mean of the two
- b)taking both face observations and taking the mean of the two
- c)double sighting
- d)taking mean of several readings distributed over different'portions of the graduated circle.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The error due to eccentricity of inner and outer axes can be eliminated by
a)
reading both verniers and taking the mean of the two
b)
taking both face observations and taking the mean of the two
c)
double sighting
d)
taking mean of several readings distributed over different'portions of the graduated circle.

|
Juhi Choudhary answered |
Error due to eccentricity of inner and outer axes means that the centre of graduated horizontal circle does not coincide with the centre of vernier plate.
As applied to staff readings, the corrections for curvature and refraction are respectively
- a)+ and -
- b)- and +
- c)+ and +
- d)- and -
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As applied to staff readings, the corrections for curvature and refraction are respectively
a)
+ and -
b)
- and +
c)
+ and +
d)
- and -

|
Gate Gurus answered |
The curvature increases the staff reading, hence its correction is negative. The rays of light when passing through the atmosphere bend down and follows a curved path, hence correction is positive.
Correction due to curvature = -0.0785D2
Correction due to refraction = 0.0112D2
Combined correction = -0.0673D2
The correction for refraction as applied to staff reading is
where R is radius of earth- a)
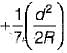
- b)
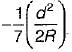
- c)
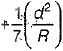
- d)
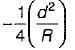
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correction for refraction as applied to staff reading is
where R is radius of earth
where R is radius of earth
a)
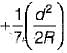
b)
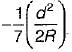
c)
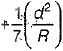
d)
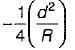
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Correction due to refraction is approximately about 1/7th of correction due to earth curvature.
CR = 1/7 Cc
= 1/7[d2/2R]
CR = 1/7 Cc
= 1/7[d2/2R]
Which one of the following instruments is used in plane table surveying for the measurement of horizontal and vertical distances directly?
- a)Telescopic alidade
- b)Plain alidade
- c)Tacheometer
- d)Clinometer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following instruments is used in plane table surveying for the measurement of horizontal and vertical distances directly?
a)
Telescopic alidade
b)
Plain alidade
c)
Tacheometer
d)
Clinometer
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Telescopic alidade
Explanation:
Plane table surveying is a graphical method of surveying in which the fieldwork and plotting are done simultaneously. It is used to map the details of the topography of the land. The main instrument used in plane table surveying is the alidade. There are different types of alidades, such as plain alidade and telescopic alidade.
1. Telescopic alidade: This is an alidade with a small telescope mounted on it. The telescope helps in sighting more accurately and can measure horizontal and vertical distances directly. It has a stadia diaphragm with horizontal stadia hairs, which allows for the direct measurement of distances by multiplying the staff intercept by the stadia multiplying constant. Thus, telescopic alidade is the correct answer.
Explanation:
Plane table surveying is a graphical method of surveying in which the fieldwork and plotting are done simultaneously. It is used to map the details of the topography of the land. The main instrument used in plane table surveying is the alidade. There are different types of alidades, such as plain alidade and telescopic alidade.
1. Telescopic alidade: This is an alidade with a small telescope mounted on it. The telescope helps in sighting more accurately and can measure horizontal and vertical distances directly. It has a stadia diaphragm with horizontal stadia hairs, which allows for the direct measurement of distances by multiplying the staff intercept by the stadia multiplying constant. Thus, telescopic alidade is the correct answer.
2. Plain alidade: This is a simple, straight-edged ruler with a vertical sight vane at each end. It is used for sighting and drawing lines on the plane table sheet. However, it does not provide direct measurement of distances.
3. Tacheometer: This is a type of theodolite with a stadia diaphragm, specially designed for rapid measurements of horizontal and vertical distances. It is not used in plane table surveying.
4. Clinometer: This is an instrument used to measure the angles of slope or elevation of an object with respect to gravity. It is not used in plane table surveying for the direct measurement of horizontal and vertical distances.
3. Tacheometer: This is a type of theodolite with a stadia diaphragm, specially designed for rapid measurements of horizontal and vertical distances. It is not used in plane table surveying.
4. Clinometer: This is an instrument used to measure the angles of slope or elevation of an object with respect to gravity. It is not used in plane table surveying for the direct measurement of horizontal and vertical distances.
Closed contours, with higher value inwards, represent a- a)depression
- b)hillock
- c)plain surface
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Closed contours, with higher value inwards, represent a
a)
depression
b)
hillock
c)
plain surface
d)
None of the above

|
Gate Funda answered |
Closed contours with higher values inwards represent a depression.
Explanation:
- Depression: In topographic maps, a depression is shown by closed contours with the highest elevation in the center. These contours are typically marked with hachure lines (short lines) pointing towards the center of the depression to indicate that the terrain dips downward.
- Hillock: A hillock would have the highest elevation at the center, with contours arranged around it in concentric circles, representing a rise in elevation, not a depression.
- Plain Surface: A plain would be represented by evenly spaced, straight, or gently curved contours, showing a flat or nearly level surface.
Answer:
If the declination is 5°40'W, which one of the following magnetic bearing would represent the true bearing of S25°20'E?- a)S19°20'E
- b)S31°0'E
- c)S20°0'E
- d)S19°20'W
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the declination is 5°40'W, which one of the following magnetic bearing would represent the true bearing of S25°20'E?
a)
S19°20'E
b)
S31°0'E
c)
S20°0'E
d)
S19°20'W

|
Sreemoyee Deshpande answered |
Note that negative (W) declination should be added to quadrantal bearing in second and fourth quadrant i.e. NθW or SθE and it should be subtracted from quadrantal bearing in first and third quadrant i.e., NθE and SθW. Reverse should be done for positive (E) declination.
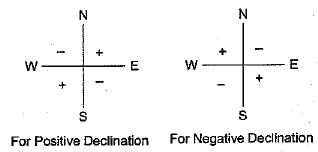
True bearing = S25°20'E+5°40'
= S31°0'E
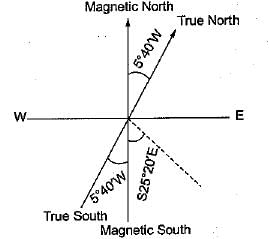

True bearing = S25°20'E+5°40'
= S31°0'E

For a well-conditional triangle, no angle should be less than- a)2CP
- b)30°
- c)45°
- d)6CF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a well-conditional triangle, no angle should be less than
a)
2CP
b)
30°
c)
45°
d)
6CF

|
Raghavendra Goyal answered |
For a well-conditioned triangle all the angles must lie in the range of 300-1200.
If the coordinates bf A are 100 N and 200 E and those of Care 100 S end 200 E, then the length AC is- a)400.00
- b)282.84
- c)244.94
- d)200.00
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the coordinates bf A are 100 N and 200 E and those of Care 100 S end 200 E, then the length AC is
a)
400.00
b)
282.84
c)
244.94
d)
200.00

|
Naina Das answered |
Given information:
Coordinates of A: 100 N and 200 E
Coordinates of C: 100 S and 200 E
To find: Length of AC
Approach:
1. Draw a rough diagram with the given coordinates.
2. Calculate the difference in latitude and longitude between A and C.
3. Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the distance between A and C.
Calculation:
1. The given coordinates can be plotted on a map as shown below.
```
A (100 N, 200 E)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C (100 S, 200 E)
```
2. The difference in latitude between A and C is 100 N - 100 S = 200 units (since one degree of latitude is equal to 60 nautical miles or 111.12 km).
The difference in longitude between A and C is 200 E - 200 E = 0 units (since the two points are on the same longitude).
3. The distance between A and C can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem as follows:
```
AC² = (latitude difference)² + (longitude difference)²
AC² = 200² + 0²
AC² = 40,000
AC = √40,000
AC = 200 units
```
Therefore, the length of AC is 200.00 units.
Answer: option D.
Coordinates of A: 100 N and 200 E
Coordinates of C: 100 S and 200 E
To find: Length of AC
Approach:
1. Draw a rough diagram with the given coordinates.
2. Calculate the difference in latitude and longitude between A and C.
3. Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the distance between A and C.
Calculation:
1. The given coordinates can be plotted on a map as shown below.
```
A (100 N, 200 E)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C (100 S, 200 E)
```
2. The difference in latitude between A and C is 100 N - 100 S = 200 units (since one degree of latitude is equal to 60 nautical miles or 111.12 km).
The difference in longitude between A and C is 200 E - 200 E = 0 units (since the two points are on the same longitude).
3. The distance between A and C can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem as follows:
```
AC² = (latitude difference)² + (longitude difference)²
AC² = 200² + 0²
AC² = 40,000
AC = √40,000
AC = 200 units
```
Therefore, the length of AC is 200.00 units.
Answer: option D.
Spring tides are caused when- a)sun and moon are in line with earth
- b)solar tidal force acts opposite to lunar tidal force
- c)solar tidal force and lunar tidal force both coincide
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Spring tides are caused when
a)
sun and moon are in line with earth
b)
solar tidal force acts opposite to lunar tidal force
c)
solar tidal force and lunar tidal force both coincide
d)
none of these

|
Sanchita Pillai answered |
Spring tides are caused when solar tidal force and lunar tidal force both coincide.
Spring tides occur when the gravitational forces of the Sun and the Moon align with each other. These tides are characterized by higher high tides and lower low tides compared to normal tides. To understand why spring tides occur when solar tidal force and lunar tidal force coincide, let's break down the process:
- The Moon exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, causing tides. This force is known as the lunar tidal force.
- Similarly, the Sun also exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, causing solar tides. This force is known as the solar tidal force.
- The gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun create tidal bulges on the Earth's surface.
- The lunar tidal force creates two tidal bulges, one facing the Moon and the other on the opposite side of the Earth.
- Similarly, the solar tidal force creates two tidal bulges, one facing the Sun and the other on the opposite side of the Earth.
- Spring tides occur when the lunar tidal bulges and the solar tidal bulges coincide.
- This happens when the Moon, Earth, and Sun are aligned in a straight line.
- During a new moon or a full moon, the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in alignment, and their gravitational forces combine.
- The combined gravitational force of the Sun and the Moon results in higher high tides and lower low tides, creating spring tides.
- Neap tides, on the other hand, occur when the solar tidal force and lunar tidal force act in opposition to each other.
- Neap tides happen during the first and third quarter phases of the moon when the Sun, Earth, and Moon form a right angle.
- During neap tides, the gravitational forces partially cancel each other out, resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides compared to spring tides.
Therefore, spring tides occur when solar tidal force and lunar tidal force both coincide, creating higher high tides and lower low tides on Earth.
Explanation:
Spring tides occur when the gravitational forces of the Sun and the Moon align with each other. These tides are characterized by higher high tides and lower low tides compared to normal tides. To understand why spring tides occur when solar tidal force and lunar tidal force coincide, let's break down the process:
Gravitational Forces:
- The Moon exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, causing tides. This force is known as the lunar tidal force.
- Similarly, the Sun also exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, causing solar tides. This force is known as the solar tidal force.
Tidal Bulges:
- The gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun create tidal bulges on the Earth's surface.
- The lunar tidal force creates two tidal bulges, one facing the Moon and the other on the opposite side of the Earth.
- Similarly, the solar tidal force creates two tidal bulges, one facing the Sun and the other on the opposite side of the Earth.
Spring Tides:
- Spring tides occur when the lunar tidal bulges and the solar tidal bulges coincide.
- This happens when the Moon, Earth, and Sun are aligned in a straight line.
- During a new moon or a full moon, the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in alignment, and their gravitational forces combine.
- The combined gravitational force of the Sun and the Moon results in higher high tides and lower low tides, creating spring tides.
Other Tidal Patterns:
- Neap tides, on the other hand, occur when the solar tidal force and lunar tidal force act in opposition to each other.
- Neap tides happen during the first and third quarter phases of the moon when the Sun, Earth, and Moon form a right angle.
- During neap tides, the gravitational forces partially cancel each other out, resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides compared to spring tides.
Therefore, spring tides occur when solar tidal force and lunar tidal force both coincide, creating higher high tides and lower low tides on Earth.
The maximum tolerance in a 20 m chain is- a)± 2 mm
- b)± 3 mm
- c)± 5 mm
- d)± 8 mm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum tolerance in a 20 m chain is
a)
± 2 mm
b)
± 3 mm
c)
± 5 mm
d)
± 8 mm

|
Simran Saha answered |
The maximum tolerance in 20 m chain is ±5 mm in 30 m chain is ±8 mm
For a simple circular curve, which one of the following gives the correct relation between the radius, R and degree of curve D, for 20 m arc length?- a)R = 5729.6/D
- b)R = 1718.9/D
- c)R = 1145.9/D
- d)R = 572.9/D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a simple circular curve, which one of the following gives the correct relation between the radius, R and degree of curve D, for 20 m arc length?
a)
R = 5729.6/D
b)
R = 1718.9/D
c)
R = 1145.9/D
d)
R = 572.9/D

|
Subhankar Khanna answered |
For 20 m arc R = 1145.9/D
for 30 m arc R = 1718.9/D
for 30 m arc R = 1718.9/D
The methods used for locating the plane table stations are
1. radiation
2. traversing
3. intersection
4. resectionThe correct answer is- a)1 and 2
- b)3 and 4
- c)2 and 4
- d)1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The methods used for locating the plane table stations are
1. radiation
2. traversing
3. intersection
4. resection
1. radiation
2. traversing
3. intersection
4. resection
The correct answer is
a)
1 and 2
b)
3 and 4
c)
2 and 4
d)
1 and 3

|
Nilesh Verma answered |
Radiation- All the measurements are taken from a single section

Intersection- Plotting same point from two stations

Traversing -Traversing by the plane table is similar to compass or theodolite traversing. The method, therefore, can be used for laying down the survey lines of a closed or unclosed traverse.It can be used to locate the plane table stations.

Resection: Resection is a method of plane table surveying in which location of plane table is unknown and it is determined by sighting it to known points or plotted points. It is also called method of orientation.

Intersection- Plotting same point from two stations

Traversing -Traversing by the plane table is similar to compass or theodolite traversing. The method, therefore, can be used for laying down the survey lines of a closed or unclosed traverse.It can be used to locate the plane table stations.

Resection: Resection is a method of plane table surveying in which location of plane table is unknown and it is determined by sighting it to known points or plotted points. It is also called method of orientation.

A series of closely spaced contour lines represents a- a)steep slope
- b)gentle slope
- c)uniform slope
- d)plane surface
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A series of closely spaced contour lines represents a
a)
steep slope
b)
gentle slope
c)
uniform slope
d)
plane surface
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Closed contours ⇒ Steep slope
Apart contour lines ⇒ Gentle slope
Equally spaced ⇒ Uniform slope Straight parallel and equally speed contours ⇒ plane surface
Apart contour lines ⇒ Gentle slope
Equally spaced ⇒ Uniform slope Straight parallel and equally speed contours ⇒ plane surface
The difference between the most probable value of a quantity and its observer value is- a)true error
- b)weighted observations
- c)conditional error
- d)residual error
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between the most probable value of a quantity and its observer value is
a)
true error
b)
weighted observations
c)
conditional error
d)
residual error

|
Madhurima Banerjee answered |
True Error = Actual Value-Observed Value
Weighted Observations=Observations taken with proportion to any quantity like an area
Conditional Error= Error occurring due to certain conditions prevailing. Like temperature error.
Residual Error = Most Probable Value- Observed Value
Weighted Observations=Observations taken with proportion to any quantity like an area
Conditional Error= Error occurring due to certain conditions prevailing. Like temperature error.
Residual Error = Most Probable Value- Observed Value
During the measurement of a line by chain or tape in slopes, if the length of line is ‘l’ and height difference between the ends of the line is ‘h’ then the correction to the measured length is more than h2/2l by
- a)Zero
- b)
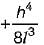
- c)
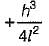
- d)
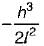
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During the measurement of a line by chain or tape in slopes, if the length of line is ‘l’ and height difference between the ends of the line is ‘h’ then the correction to the measured length is more than h2/2l by
a)
Zero
b)
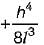
c)
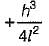
d)
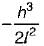

|
Priyanka Shah answered |



A 30 m steel tape was standardized at 20°C and measurements of distances were taken at 15°C. if the coefficient of linear expansion α of the material of the tape were 0.000112 per °C, then error due to temperature per tape length would be
- a)-0.00,00560 m
- b)+0.00,00560 m
- c)+0.00,16800 m
- d)-0.00,16800 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A 30 m steel tape was standardized at 20°C and measurements of distances were taken at 15°C. if the coefficient of linear expansion α of the material of the tape were 0.000112 per °C, then error due to temperature per tape length would be
a)
-0.00,00560 m
b)
+0.00,00560 m
c)
+0.00,16800 m
d)
-0.00,16800 m

|
Gitanjali Menon answered |
αΔT= 0.0000112(15-20)
= -0.0000560 m
= -0.0000560 m
For a star at its upper transit, the local sidereal time is equal to- a)H. A. of the star
- b)Declination of the star
- c)R.A. of the star
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a star at its upper transit, the local sidereal time is equal to
a)
H. A. of the star
b)
Declination of the star
c)
R.A. of the star
d)
None of the above

|
Gitanjali Chauhan answered |
When star is at its upper transit, Hour angle (H) is equal to zero.
If fore bearing of a line is S49°52'E (assuming there is no local attraction), the back bearing of the line will be- a)S52°49'E
- b)S49°52'E
- c)N49°08'E
- d)N49°52'W
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If fore bearing of a line is S49°52'E (assuming there is no local attraction), the back bearing of the line will be
a)
S52°49'E
b)
S49°52'E
c)
N49°08'E
d)
N49°52'W

|
Anisha Chakraborty answered |
if the fore bearing of a line is given as the quadrantal bearing, then back bearing is numerically equal to the fore bearing. However N changes to S and Exchanges to W and vice versa.
The downhill end of a 30 m tape is held 90 cm too low. What is the horizontal distance measured- a)29.8265 m
- b)29.9865 m
- c)30.0125 m
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The downhill end of a 30 m tape is held 90 cm too low. What is the horizontal distance measured
a)
29.8265 m
b)
29.9865 m
c)
30.0125 m
d)
None of these

|
Sreemoyee Deshpande answered |
Correction for slope
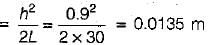
∴ Horizontal distance
= 30 - 0.0135 = 29.9865 m
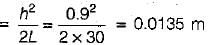
∴ Horizontal distance
= 30 - 0.0135 = 29.9865 m
The length of a chain is measured from- a)centre of one handle to centre of other handle
- b)outside of one handle to outside of other handle
- c)outside of one handle to inside of other handle
- d)inside of one handle to inside of other handle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of a chain is measured from
a)
centre of one handle to centre of other handle
b)
outside of one handle to outside of other handle
c)
outside of one handle to inside of other handle
d)
inside of one handle to inside of other handle

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Becoz the measurements on chain are marked from the outside to outside of handle while designing
A surveyor measured the distance between two points on the plan drawn to a scale of 1 cm = 40 m and the result was 468 m. Later he discovered that he used a scale of 1 cm - 20 m. What is the true distance between the two points?- a)936 m
- b)234 m
- c)117 m
- d)702 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A surveyor measured the distance between two points on the plan drawn to a scale of 1 cm = 40 m and the result was 468 m. Later he discovered that he used a scale of 1 cm - 20 m. What is the true distance between the two points?
a)
936 m
b)
234 m
c)
117 m
d)
702 m

|
Rounak Mehta answered |
Distance between two points measured with scale of 1 cm to 20 cm
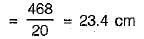
Actual scale of the plan is 1 cm = 40 m
∴ True distance between points
= 23.4 x 40 = 936 m
With the rise of temperature, the sensitivity of a bubble tube- a)decreases
- b)increases
- c)remains unaffected
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
With the rise of temperature, the sensitivity of a bubble tube
a)
decreases
b)
increases
c)
remains unaffected
d)
None of the above

|
Tanishq Menon answered |
With a rise in temperature the liquid expands. Hence the bubble shortens and consequently its sensitivity decreases.
While doing levelling in undulating terrain, it is preferable to set the level on- a)the top of summit
- b)the bottom of a valley
- c)only side of the slope
- d)anywhere
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
While doing levelling in undulating terrain, it is preferable to set the level on
a)
the top of summit
b)
the bottom of a valley
c)
only side of the slope
d)
anywhere
|
|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option "c) only side of the slope."
When doing levelling in undulating terrain, it is important to set the level at a location that is stable and not prone to movement. The best location for setting the level in undulating terrain is usually the side of the slope, rather than the top of a summit or the bottom of a valley.
Setting the level on the side of the slope allows the operator to take readings that are more representative of the overall slope of the terrain. It also allows the operator to take readings that are more accurate, as the level is less likely to be affected by small movements or vibrations that may occur at the top of a summit or the bottom of a valley.
Setting the level anywhere else (option "d") may not provide accurate or representative readings, and may result in incorrect levelling measurements.
The resected position of plane-table station from three known position is unreliable if the station lies- a)in the great triangle
- b)on circumference of circumscribing circle
- c)outside the great triangle
- d)in the centre of the circumscribing circle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The resected position of plane-table station from three known position is unreliable if the station lies
a)
in the great triangle
b)
on circumference of circumscribing circle
c)
outside the great triangle
d)
in the centre of the circumscribing circle

|
Rhea Dasgupta answered |
The reliability of the resected position of a plane-table station depends on the configuration of the known positions used for resection. In this case, the question asks about the reliability of the resected position if the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle.
To understand why this is the case, let's first define what a circumscribing circle is. In plane-table surveying, a circumscribing circle is formed by drawing a circle around the three known positions or control points. This circle is used as a reference for locating the unknown position or station.
Now, let's examine each option to understand why the resected position is unreliable if the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle.
**A) In the great triangle:**
If the station lies within the great triangle formed by the three known positions, the resected position can be determined with a high degree of accuracy. This is because the station is well within the region defined by the known positions, allowing for precise triangulation.
**B) On the circumference of the circumscribing circle:**
If the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle, the resected position becomes unreliable. This is because the station is located at an equal distance from each of the known positions, making it difficult to accurately determine its exact location. The intersecting lines used for resection will pass through the station but may not converge at a single point due to the station being equidistant from the known positions.
**C) Outside the great triangle:**
If the station lies outside the great triangle, the resected position can still be determined with reasonable accuracy. However, the further the station is from the known positions, the higher the chance of error in the resected position.
**D) In the center of the circumscribing circle:**
If the station lies in the center of the circumscribing circle, the resected position can be accurately determined. This is because the station is equidistant from the known positions, allowing for precise triangulation.
In conclusion, the resected position of a plane-table station is unreliable if the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle. This is because the station is equidistant from the known positions, making it difficult to accurately determine its exact location through resection.
To understand why this is the case, let's first define what a circumscribing circle is. In plane-table surveying, a circumscribing circle is formed by drawing a circle around the three known positions or control points. This circle is used as a reference for locating the unknown position or station.
Now, let's examine each option to understand why the resected position is unreliable if the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle.
**A) In the great triangle:**
If the station lies within the great triangle formed by the three known positions, the resected position can be determined with a high degree of accuracy. This is because the station is well within the region defined by the known positions, allowing for precise triangulation.
**B) On the circumference of the circumscribing circle:**
If the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle, the resected position becomes unreliable. This is because the station is located at an equal distance from each of the known positions, making it difficult to accurately determine its exact location. The intersecting lines used for resection will pass through the station but may not converge at a single point due to the station being equidistant from the known positions.
**C) Outside the great triangle:**
If the station lies outside the great triangle, the resected position can still be determined with reasonable accuracy. However, the further the station is from the known positions, the higher the chance of error in the resected position.
**D) In the center of the circumscribing circle:**
If the station lies in the center of the circumscribing circle, the resected position can be accurately determined. This is because the station is equidistant from the known positions, allowing for precise triangulation.
In conclusion, the resected position of a plane-table station is unreliable if the station lies on the circumference of the circumscribing circle. This is because the station is equidistant from the known positions, making it difficult to accurately determine its exact location through resection.
A transition curve is required for a circular curve of 200 m radius, the gauge being 1.5 m and maximum superelevation restricted to 15 cm. The transition is to be designed for a velocity such that no lateral pressure is imposed on the rails and rate of gain of radial acceleration is 30 cm/s2. The required length of transition curve will be- a)460 m
- b)46 m
- c)4.6
- d)0.46 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A transition curve is required for a circular curve of 200 m radius, the gauge being 1.5 m and maximum superelevation restricted to 15 cm. The transition is to be designed for a velocity such that no lateral pressure is imposed on the rails and rate of gain of radial acceleration is 30 cm/s2. The required length of transition curve will be
a)
460 m
b)
46 m
c)
4.6
d)
0.46 m

|
Arshiya Roy answered |
Given data:
Radius of circular curve, R = 200 m
Gauge, G = 1.5 m
Maximum superelevation, e = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Rate of gain of radial acceleration, G = 30 cm/s²
Formula used:
Length of transition curve, L = V²/127R
Calculation:
1. Calculation of velocity (V) at which no lateral pressure is imposed on the rails:
V = √RGe
= √(200 x 1.5 x 0.15)
= 3.087 m/s
2. Calculation of length of transition curve:
L = V²/127R
= (3.087)²/(127 x 200)
= 0.04599 m
≈ 46 m
Therefore, the required length of the transition curve is 46 m (approximately).
Radius of circular curve, R = 200 m
Gauge, G = 1.5 m
Maximum superelevation, e = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Rate of gain of radial acceleration, G = 30 cm/s²
Formula used:
Length of transition curve, L = V²/127R
Calculation:
1. Calculation of velocity (V) at which no lateral pressure is imposed on the rails:
V = √RGe
= √(200 x 1.5 x 0.15)
= 3.087 m/s
2. Calculation of length of transition curve:
L = V²/127R
= (3.087)²/(127 x 200)
= 0.04599 m
≈ 46 m
Therefore, the required length of the transition curve is 46 m (approximately).
Which of the following instruments is generally used for base line measurements?- a)chain
- b)metallic tape.
- c)steel tape
- d)invar tape
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following instruments is generally used for base line measurements?
a)
chain
b)
metallic tape.
c)
steel tape
d)
invar tape

|
Ameya Sen answered |
Invar tapes are used for linear measurement of very high degree precision such as base line measurements cloth or lines tap for rough and subsidiary measurements such as offset.
The distance between the points measured along a slope is 428 m. If the angle of slope between the points is 8° than the horizontal distance between them is- a)59.56 m
- b)70.26 m
- c)400 m
- d)423.83 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance between the points measured along a slope is 428 m. If the angle of slope between the points is 8° than the horizontal distance between them is
a)
59.56 m
b)
70.26 m
c)
400 m
d)
423.83 m

|
Maulik Das answered |
Horizontal distance = l cosθ
= 428 cos8° = 423.83 m
= 428 cos8° = 423.83 m
In the given formula formats, L is the length of a base line split into ‘n’ equal segments each of length ‘d’. O1, O2 .......On+1 are the ordinates at the sequential ends of the segments and M1, M2....Mn are the mid-ordinates of successive segments. Which of the following pairs of rules and the formulae for computation of the area standing on the base line are correctly matched?
1. Mid - ordinate Rule ...............
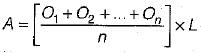
2. Average - ordinate Rule ......
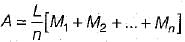
3. Trapezoidal Rule........
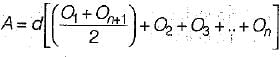
4. Simpsons’ rule
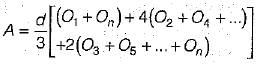 Select the correct answer using the codes given below
Select the correct answer using the codes given below- a)1 and 2
- b)1 and 3
- c)3 and 4
- d)2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given formula formats, L is the length of a base line split into ‘n’ equal segments each of length ‘d’. O1, O2 .......On+1 are the ordinates at the sequential ends of the segments and M1, M2....Mn are the mid-ordinates of successive segments. Which of the following pairs of rules and the formulae for computation of the area standing on the base line are correctly matched?
1. Mid - ordinate Rule ...............
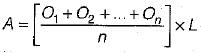
2. Average - ordinate Rule ......
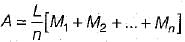
3. Trapezoidal Rule........
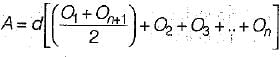
4. Simpsons’ rule
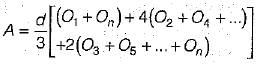
1. Mid - ordinate Rule ...............
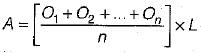
2. Average - ordinate Rule ......
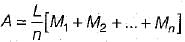
3. Trapezoidal Rule........
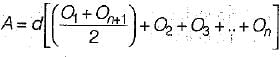
4. Simpsons’ rule
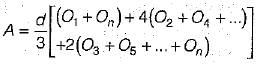
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
a)
1 and 2
b)
1 and 3
c)
3 and 4
d)
2 and 4

|
Diya Sarkar answered |

If the forebearing of a line AB is 35° and that of line BC 15° then the included angle between the lines is- a)20°
- b)50°
- c)160°
- d)230°
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the forebearing of a line AB is 35° and that of line BC 15° then the included angle between the lines is
a)
20°
b)
50°
c)
160°
d)
230°
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
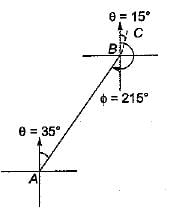
BB of AB = FB + 180°
= 35° + 180° = 215°
∴ included angle between line,
AB and BC = 360° - 215° + 15° = 160°
Chapter doubts & questions for Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) - GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Geomatics Engineering (Surveying) - GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series
33 docs|280 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup