All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 2: Conductors, Capacitors, Dielectrics for Grade 9 Exam
The electric field inside a dielectric decreases, when it is placed in an external electric field. This happens due to- a)Electrostatic shielding
- b)Polarization
- c)Electrostatic repulsion between atoms
- d)Electrostatic attraction between atoms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The electric field inside a dielectric decreases, when it is placed in an external electric field. This happens due to
a)
Electrostatic shielding
b)
Polarization
c)
Electrostatic repulsion between atoms
d)
Electrostatic attraction between atoms

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The external electric field polarizes the dielectric and an electric field is produced.
The net electric field inside the dielectric decreases due to polarization.
The net electric field inside the dielectric decreases due to polarization.
Three different capacitors are connected in series, then:- a)they will have equal charges
- b)they will have same potential
- c)both 1 & 2
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three different capacitors are connected in series, then:
a)
they will have equal charges
b)
they will have same potential
c)
both 1 & 2
d)
none of these
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
C = Q/V
series connection splits the battery potential, hence....
V = V1 + V2
V1 = Q/C1 & V2 = Q/C2
Therefore, both have equal charge
series connection splits the battery potential, hence....
V = V1 + V2
V1 = Q/C1 & V2 = Q/C2
Therefore, both have equal charge
What should be the radius of an isolated spherical conductor so that it has a capacity of 2μF?- a)1.8X105 m
- b)1.8X104 m
- c)2.5X104 m
- d)2.5X105 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What should be the radius of an isolated spherical conductor so that it has a capacity of 2μF?
a)
1.8X105 m
b)
1.8X104 m
c)
2.5X104 m
d)
2.5X105 m

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
Capacitance of an isolated spherical conductor =4π€R , where €=permittivity of vacuum
C=2×10-6F
C=4π€R
4×3.14×8.85×10-12×R=2×10-6
R=2×10-6/4×3.14×8.85×10-12
=1.8×104 m
C=2×10-6F
C=4π€R
4×3.14×8.85×10-12×R=2×10-6
R=2×10-6/4×3.14×8.85×10-12
=1.8×104 m
Which of the following is a non polar dielectric?- a)Water
- b)Alcohol
- c)HCl
- d)Benzene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a non polar dielectric?
a)
Water
b)
Alcohol
c)
HCl
d)
Benzene
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Alcohol and HCl are polar molecules since they have a net dipole moment towards a particular direction. Both water and benzene are non-polar molecules. But water is a conductor of electricity, whereas benzene is a dielectric (insulator).
What will be the effect on capacitance, if the distance between the parallel plates reduced to one-third of its original value?- a)decrease by a factor 3
- b)increase by a factor 3
- c)increase by a factor 3/2
- d)increase by a factor ½
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the effect on capacitance, if the distance between the parallel plates reduced to one-third of its original value?
a)
decrease by a factor 3
b)
increase by a factor 3
c)
increase by a factor 3/2
d)
increase by a factor ½
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
C=(Kε0A/d)∝K/d
Hence,C1/C2=d2/d1=(d/3)d=3
C2=3C1
Hence,C1/C2=d2/d1=(d/3)d=3
C2=3C1
1 microfarad is equal to- a)10-6F
- b)10-12F
- c)10-15F
- d)10-9F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 microfarad is equal to
a)
10-6F
b)
10-12F
c)
10-15F
d)
10-9F
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The microfarad (symbolized µF) is a unit of capacitance, equivalent to 0.000001 (10 to the -6th power) farad.
The polarized dielectric is equivalent to- a)non-zero volume charge density
- b)one charged surface with induced surface charge density
- c)two charged surfaces with induced surface charge densities
- d)zero surface charge density
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The polarized dielectric is equivalent to
a)
non-zero volume charge density
b)
one charged surface with induced surface charge density
c)
two charged surfaces with induced surface charge densities
d)
zero surface charge density

|
Learners Habitat answered |
A polarized dielectric is equivalent to two charged surfaces with induced charges (polarization charges).
Two capacitors of 20 μƒ and 30 μƒ are connected in series to a battery of 40V. Calculate charge on each capacitor.- a)480 C
- b)478 C
- c)450 C
- d)500 C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two capacitors of 20 μƒ and 30 μƒ are connected in series to a battery of 40V. Calculate charge on each capacitor.
a)
480 C
b)
478 C
c)
450 C
d)
500 C
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
C1= 20×10µf
and C2= 30×10µf
in series Ceq = C1C2/(C1+C2)
Ceq = 20×10^(-6)×30×10^(-6)/20×10^(-6)+30^×10(-6)
Ceq= 12×10^(-6)f
As we know that Q = CV
Putting the values of C and V= 40V, we get
Q = (12 * 10^-6) * 40
= 480µC
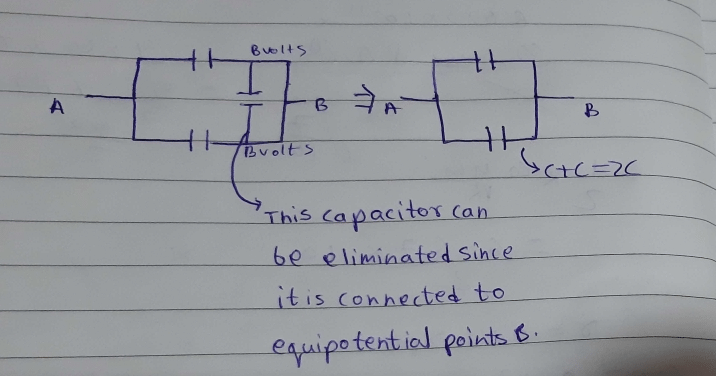
Here is a combination of three identical capacitors. If resultant capacitance is 1 μƒ, calculate capacitance of each capacitor.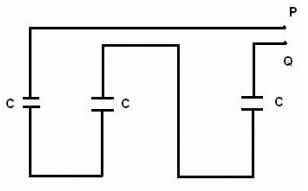
- a)6 μƒ
- b)3 μƒ
- c)4 μƒ
- d)2 μƒ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Here is a combination of three identical capacitors. If resultant capacitance is 1 μƒ, calculate capacitance of each capacitor.
a)
6 μƒ
b)
3 μƒ
c)
4 μƒ
d)
2 μƒ
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Combination of Capacitors in Series
C(effective) = C/3 = 1
C(effective) = C/3 = 1
When two capacitors C1 and C2 are connected in series and parallel, their equivalent capacitances comes out to be 3 μƒ and 16 μƒ respectively. Calculate values of C1 and C2.- a)4μƒ and 12μƒ
- b)6μƒ and 10μƒ
- c)4μƒ and 10μƒ
- d)6μƒ and 12μƒ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When two capacitors C1 and C2 are connected in series and parallel, their equivalent capacitances comes out to be 3 μƒ and 16 μƒ respectively. Calculate values of C1 and C2.
a)
4μƒ and 12μƒ
b)
6μƒ and 10μƒ
c)
4μƒ and 10μƒ
d)
6μƒ and 12μƒ

|
Anonymous answered |

Can you explain the answer of this question below:In a parallel plate capacitor the potential difference of 150 V is maintained between the plates. If distance between the plates is 6 mm, what will be the electric field at points A and B?
- A:
2.5×103
- B:
2.5×104
- C:
2.5×105
- D:
3.5×104
The answer is b.
In a parallel plate capacitor the potential difference of 150 V is maintained between the plates. If distance between the plates is 6 mm, what will be the electric field at points A and B?
2.5×103
2.5×104
2.5×105
3.5×104
|
|
Om Desai answered |
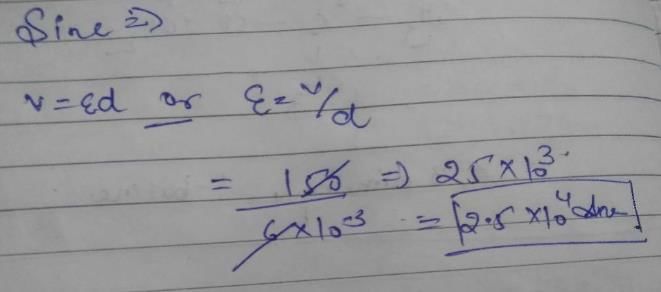
μμf is also called?- a)nanofarad
- b)microfarad
- c)picofarad
- d)fermifarad
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
μμf is also called?
a)
nanofarad
b)
microfarad
c)
picofarad
d)
fermifarad
|
|
Arghya answered |
10^(-6)=microfarad.... so ,10^(-6)*10^(-6)=10^(-12)=PICOFARAD
The distance between the plates of a capacitor is d. What will be the new capacitance if a metal plate of thickness d/2 is introduced between the plates without touching them- a)it will be thrice of its initial value
- b)it will be double of its initial value
- c)remains the same
- d)it will be half of its initial value
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance between the plates of a capacitor is d. What will be the new capacitance if a metal plate of thickness d/2 is introduced between the plates without touching them
a)
it will be thrice of its initial value
b)
it will be double of its initial value
c)
remains the same
d)
it will be half of its initial value
|
|
Nisha Patel answered |
Explanation:
Capacitance of a capacitor:
The capacitance of a capacitor is given by the equation:
C = εA/d
where C is the capacitance, ε is the permittivity of the medium between the plates, A is the area of the plates, and d is the distance between the plates.
Effect of introducing a metal plate:
When a metal plate of thickness d/2 is introduced between the plates without touching them, the distance between the plates decreases by d/2. This means that the new distance between the plates is d/2.
New capacitance:
Using the equation for capacitance, we can calculate the new capacitance as:
C' = εA/(d/2)
C' = 2εA/d
The new capacitance is double the initial capacitance. Therefore, the correct answer is option B, "it will be double of its initial value."
Capacitance of a capacitor:
The capacitance of a capacitor is given by the equation:
C = εA/d
where C is the capacitance, ε is the permittivity of the medium between the plates, A is the area of the plates, and d is the distance between the plates.
Effect of introducing a metal plate:
When a metal plate of thickness d/2 is introduced between the plates without touching them, the distance between the plates decreases by d/2. This means that the new distance between the plates is d/2.
New capacitance:
Using the equation for capacitance, we can calculate the new capacitance as:
C' = εA/(d/2)
C' = 2εA/d
The new capacitance is double the initial capacitance. Therefore, the correct answer is option B, "it will be double of its initial value."
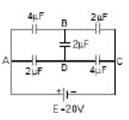
Find the equivalent capacitance of the combination.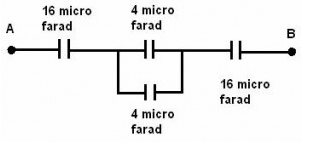
- a)16/3 μƒ
- b)16 μƒ
- c)19.0 μƒ
- d)8 μƒ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the equivalent capacitance of the combination.
a)
16/3 μƒ
b)
16 μƒ
c)
19.0 μƒ
d)
8 μƒ

|
Kumari Sakshi answered |
none of the optaion match answer should be 4
The dipole moment per unit volume is called- a)Polarization
- b)Surface charge density
- c)Linear charge density
- d)Volume charge density
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dipole moment per unit volume is called
a)
Polarization
b)
Surface charge density
c)
Linear charge density
d)
Volume charge density
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The electric dipole moment per unit volume is called polarization or polarization density (vector p).
It is always directed from negative charge to positive charge.
If there are N atoms per unit volume than
vector p = N (vector p)
where p is the electric dipole moment of individual atom.
When a conductor is placed in an electric field; its free charge carriers adjust itself in order to oppose the electric field. This happen until- a)Both the fields cancel out each other
- b)Induced field become more than external field
- c)External field reach the maximum value
- d)Induced field reach the maximum value
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a conductor is placed in an electric field; its free charge carriers adjust itself in order to oppose the electric field. This happen until
a)
Both the fields cancel out each other
b)
Induced field become more than external field
c)
External field reach the maximum value
d)
Induced field reach the maximum value
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
- When an external electric field is applied to the conductor, the free electrons in the conductor move in an opposite direction to that of the applied electric field.
- This movement of electrons induces another electric field inside the conductor which opposes the original external electric field.
- This continues until the induced electric field cancels out the external field.
Work done in placing a charge of 8 x 10-18 C on a condenser of capacity 100 microfarad is- a)4 x 10-10 J
- b)32 x 10-32 J
- c)16 x 10-32 J
- d)3.1 x 10-26 J
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done in placing a charge of 8 x 10-18 C on a condenser of capacity 100 microfarad is
a)
4 x 10-10 J
b)
32 x 10-32 J
c)
16 x 10-32 J
d)
3.1 x 10-26 J
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The work done is stored as the potential energy . The potential energy stored in a capacitor is given by
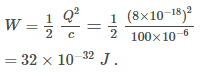
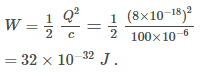
Which of the following statements is not true for polar molecules?- a)permanent dipole moment
- b)examples are oxygen and hydrogen molecules
- c)the centres of positive and negative charges are separated
- d)examples are HCl or water molecules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true for polar molecules?
a)
permanent dipole moment
b)
examples are oxygen and hydrogen molecules
c)
the centres of positive and negative charges are separated
d)
examples are HCl or water molecules
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond.
- The oxygen side of the molecule has a slight negative charge, while the side with the hydrogen atoms has a slight positive charge.
- Ethanol is polar because the oxygen atoms attract electrons because of their higher electronegativity than other atoms in the molecule.
The dielectric Constant of a metal is- a)infinite
- b)zero
- c)equal to one
- d)less than one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dielectric Constant of a metal is
a)
infinite
b)
zero
c)
equal to one
d)
less than one
|
|
Nabanita Sen answered |
An electric field (E) is generated both inside the metal and outer (plates) which are equal in magnitude but opposite, making the net resultant field (Er) in the metal to be zero. Hence, the derived dielectric constant (K) of the metal is (E/Er = E/0) which is infinity. This is why the dielectric constant is infinity.
If two spheres of different radii have equal charge, then the potential will be- a)dependent on nature of material of the spheres.
- b)more on smaller sphere
- c)more on bigger sphere
- d)equal on both spheres
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If two spheres of different radii have equal charge, then the potential will be
a)
dependent on nature of material of the spheres.
b)
more on smaller sphere
c)
more on bigger sphere
d)
equal on both spheres

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
When equal charges are given to two spheres of different radii, the potential will be more or the smaller sphere as per the equation, Potential = Charge / Radius.
Since potential is inversely proportional to radius, the smaller radius will have higher potential and vice versa.
Since potential is inversely proportional to radius, the smaller radius will have higher potential and vice versa.
The capacitor preferred for high-frequency circuit is - a)Air capacitor
- b)Mica capacitor
- c)Electrolytic capacitor
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The capacitor preferred for high-frequency circuit is
a)
Air capacitor
b)
Mica capacitor
c)
Electrolytic capacitor
d)
None of the above

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Mica capacitor. Mica capacitors have low resistive and inductive components associated with it. Hence, they have high Q factor and because of high Q factor their characteristics are mostly frequency independent, which allows this capacitor to work at high frequency.
The extent of polarization depends on- a)Kinetic energy of bound charges
- b)Dipole potential energy
- c)Dipole potential energy and thermal energy
- d)Thermal energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The extent of polarization depends on
a)
Kinetic energy of bound charges
b)
Dipole potential energy
c)
Dipole potential energy and thermal energy
d)
Thermal energy
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Two factors on which the extent of polarization depends are:
The potential energy of dipoles in the external field which tends to align the dipole with in the field.
Thermal energy of the agitation which tends to randomize the alignment of the dipole.
Increasing the charge on the plates of a capacitor means- a)increasing the capacitance
- b)increasing the potential difference between the plates
- c)both
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Increasing the charge on the plates of a capacitor means
a)
increasing the capacitance
b)
increasing the potential difference between the plates
c)
both
d)
none
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Q = CV, where C is decided only by the geometrical factors
The dielectric Constant of a metal is- a)infinite
- b)zero
- c)equal to one
- d)less than one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dielectric Constant of a metal is
a)
infinite
b)
zero
c)
equal to one
d)
less than one
|
|
Saanvi Bose answered |
**Dielectric Constant of a Metal**
The dielectric constant, also known as the relative permittivity, is a property that characterizes the ability of a material to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is defined as the ratio of the electric field in vacuum to the electric field in the material. The dielectric constant of a material is always greater than or equal to one.
**Explanation:**
1. **Definition of Dielectric Constant:** The dielectric constant, denoted by the symbol ε (epsilon), is a dimensionless quantity that represents the electrical permittivity of a material compared to the permittivity of a vacuum. It is given by the equation ε = εr/ε0, where εr is the relative permittivity of the material and ε0 is the permittivity of vacuum.
2. **Dielectric Constant of a Metal:** Metals are characterized by having a very low dielectric constant. In fact, the dielectric constant of a metal is considered to be infinite.
3. **Conductivity of Metals:** Metals are good conductors of electricity due to the presence of free electrons that can move easily through the material. In a metal, the free electrons are not bound to individual atoms and are delocalized, forming what is known as an electron sea. This electron sea allows for the efficient conduction of electric current.
4. **Effect on Electric Field:** When an electric field is applied to a metal, the free electrons in the metal quickly respond to the field and redistribute themselves. As a result, the electric field inside the metal becomes zero. This means that the electric field in a metal is completely shielded by the movement of the free electrons.
5. **No Energy Storage:** Due to the efficient conduction of electric current in metals and the shielding of the electric field, there is no energy storage in the form of electric fields within a metal. Therefore, the dielectric constant of a metal is considered to be infinite.
6. **Practical Implications:** The infinite dielectric constant of metals has practical implications in various fields. For example, in the design and construction of capacitors, metals are often used as the conducting plates since they have a negligible effect on the overall capacitance value.
In conclusion, the dielectric constant of a metal is infinite due to the efficient conduction of electric current and the shielding of the electric field by the movement of free electrons. This property of metals has practical implications in various applications involving capacitors and electric fields.
The dielectric constant, also known as the relative permittivity, is a property that characterizes the ability of a material to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is defined as the ratio of the electric field in vacuum to the electric field in the material. The dielectric constant of a material is always greater than or equal to one.
**Explanation:**
1. **Definition of Dielectric Constant:** The dielectric constant, denoted by the symbol ε (epsilon), is a dimensionless quantity that represents the electrical permittivity of a material compared to the permittivity of a vacuum. It is given by the equation ε = εr/ε0, where εr is the relative permittivity of the material and ε0 is the permittivity of vacuum.
2. **Dielectric Constant of a Metal:** Metals are characterized by having a very low dielectric constant. In fact, the dielectric constant of a metal is considered to be infinite.
3. **Conductivity of Metals:** Metals are good conductors of electricity due to the presence of free electrons that can move easily through the material. In a metal, the free electrons are not bound to individual atoms and are delocalized, forming what is known as an electron sea. This electron sea allows for the efficient conduction of electric current.
4. **Effect on Electric Field:** When an electric field is applied to a metal, the free electrons in the metal quickly respond to the field and redistribute themselves. As a result, the electric field inside the metal becomes zero. This means that the electric field in a metal is completely shielded by the movement of the free electrons.
5. **No Energy Storage:** Due to the efficient conduction of electric current in metals and the shielding of the electric field, there is no energy storage in the form of electric fields within a metal. Therefore, the dielectric constant of a metal is considered to be infinite.
6. **Practical Implications:** The infinite dielectric constant of metals has practical implications in various fields. For example, in the design and construction of capacitors, metals are often used as the conducting plates since they have a negligible effect on the overall capacitance value.
In conclusion, the dielectric constant of a metal is infinite due to the efficient conduction of electric current and the shielding of the electric field by the movement of free electrons. This property of metals has practical implications in various applications involving capacitors and electric fields.
The displacement of charges inside the dielectric stops when- a)the external field becomes maximum
- b)the external force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the force due to internal fields
- c)the internal force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the forces due to the internal fields
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The displacement of charges inside the dielectric stops when
a)
the external field becomes maximum
b)
the external force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the force due to internal fields
c)
the internal force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the forces due to the internal fields
d)
none of the above
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The displacement of charges inside the dielectric stops when the external force on the charges of the molecules is balanced by the force due to internal fields.
A uniformly polarized dielectric amounts to induced ______ charge density but no ______charge density.- a)volume, surface
- b)surface, volume
- c)volume, line
- d)line, volume
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniformly polarized dielectric amounts to induced ______ charge density but no ______charge density.
a)
volume, surface
b)
surface, volume
c)
volume, line
d)
line, volume
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
As charges are separated on the surface of the dielectric but not in its interior volume.
A Van de graph generator is used- a)to accelerate both charged and uncharged particles.
- b)to produce charged particle
- c)to accelerate uncharged particles.
- d)to accelerate charged particles.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A Van de graph generator is used
a)
to accelerate both charged and uncharged particles.
b)
to produce charged particle
c)
to accelerate uncharged particles.
d)
to accelerate charged particles.
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
The Van De Graaff Generator is basically an electrostatic machine that can generate high voltages. A typical Van De Graaff Generator consists of an insulating belt that transports electrical charge to a terminal. ... Generally used for scientific experiments, the generated charges are used to speed particles such as ions. It also used to accelerate charged particles.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Work done in charging a capacitor is stored in it in the form of electrostatic energy, given by
- A:
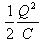
- B:
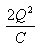
- C:
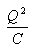
- D:
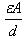
The answer is a.
Work done in charging a capacitor is stored in it in the form of electrostatic energy, given by

|
Divya Sara answered |
Energy stored in a capacitor is electrical potential energy, and it is thus related to the charge Q and voltage V on the capacitor. We must be careful when applying the equation for electrical potential energy ΔPE = qΔV to a capacitor. Remember that ΔPE is the potential energy of a charge q going through a voltage ΔV. But the capacitor starts with zero voltage and gradually comes up to its full voltage as it is charged. The first charge placed on a capacitor experiences a change in voltage ΔV = 0, since the capacitor has zero voltage when uncharged. The final charge placed on a capacitor experiences ΔV = V, since the capacitor now has its full voltage V on it. The average voltage on the capacitor during the charging process is V/2, and so the average voltage experienced by the full charge q is V/2. Thus the energy stored in a capacitor, Ecap, is E( cap)=QV/2 where Q is the charge on a capacitor with a voltage V applied. (Note that the energy is not QV, but QV/2 Charge and voltage are related to the capacitance C of a capacitor by Q = CV, and so the expression for Ecap can be algebraically manipulated into three equivalent expressions:E(cap)=QV/2=C(V.V)/2 =Q.Q/2Cwhere Q is the charge and V the voltage on a capacitor C. The energy is in joules for a charge in coulombs, voltage in volts, and capacitance in farads.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 2: Conductors, Capacitors, Dielectrics - AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 2: Conductors, Capacitors, Dielectrics - AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism
15 videos|46 docs|12 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily