All Exams >
Electrical Engineering (EE) >
Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT) >
All Questions
All questions of Time Varying Electromagnetic Fields for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam
Find the time constant of a capacitor with capacitance of 2 microfarad having an internal resistance of 4 megaohm.- a)2
- b)0.5
- c)8
- d)0.25
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the time constant of a capacitor with capacitance of 2 microfarad having an internal resistance of 4 megaohm.
a)
2
b)
0.5
c)
8
d)
0.25
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The time constant of capacitor is given by T = RC, where R = 4×106 and C = 2×10-6. Thus T = 4×106 x2x10-6 = 8 seconds.
Explanation: The time constant of capacitor is given by T = RC, where R = 4×106 and C = 2×10-6. Thus T = 4×106 x2x10-6 = 8 seconds.
For a perfect dielectric, which parameter will be zero?- a)Conductivity
- b)Frequency
- c)Permittivity
- d)Permeability
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For a perfect dielectric, which parameter will be zero?
a)
Conductivity
b)
Frequency
c)
Permittivity
d)
Permeability
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The conductivity will be minimum for a dielectric. For a perfect dielectric, the conductivity will be zero.
Explanation: The conductivity will be minimum for a dielectric. For a perfect dielectric, the conductivity will be zero.
The conductivity in free space medium is- a)Infinity
- b)Unity
- c)Zero
- d)Negative
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The conductivity in free space medium is
a)
Infinity
b)
Unity
c)
Zero
d)
Negative
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: As the charge carriers are not available in free space, the conductivity will be very low. For ideal cases, the conductivity can be taken as zero.
Explanation: As the charge carriers are not available in free space, the conductivity will be very low. For ideal cases, the conductivity can be taken as zero.
In free space, which parameter will be unity?- a)Permittivity
- b)Absolute permittivity
- c)Relative permittivity
- d)Permeability
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In free space, which parameter will be unity?
a)
Permittivity
b)
Absolute permittivity
c)
Relative permittivity
d)
Permeability
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The relative permittivity is a constant for a particular material. It is unity for free space or air. The absolute permittivity is a constant given by 8.854 x 10-12 C/m2.
Explanation: The relative permittivity is a constant for a particular material. It is unity for free space or air. The absolute permittivity is a constant given by 8.854 x 10-12 C/m2.
The Gauss law for magnetic field is valid in- a)Air
- b)Conductor
- c)Dielectric
- d)All cases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Gauss law for magnetic field is valid in
a)
Air
b)
Conductor
c)
Dielectric
d)
All cases
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The Gauss law for magnetic field states that the divergence of B is always zero. This is valid for all cases like free space, dielectric medium etc.
Explanation: The Gauss law for magnetic field states that the divergence of B is always zero. This is valid for all cases like free space, dielectric medium etc.
Which components exist in an electromagnetic wave?- a)Only E
- b)Only H
- c)Both E and H
- d)Neither E or H
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which components exist in an electromagnetic wave?
a)
Only E
b)
Only H
c)
Both E and H
d)
Neither E or H
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic components coexist. They propagate perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation in space.
Explanation: In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic components coexist. They propagate perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation in space.
Identify the polarisation of the wave given, Ex = Exo cos wt and Ey = Eyo sin wt. The phase difference is +900.- a)Left hand circularly polarised
- b)Right hand circularly polarised
- c)Left hand elliptically polarised
- d)Right hand elliptically polarised
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the polarisation of the wave given, Ex = Exo cos wt and Ey = Eyo sin wt. The phase difference is +900.
a)
Left hand circularly polarised
b)
Right hand circularly polarised
c)
Left hand elliptically polarised
d)
Right hand elliptically polarised
|
|
Uday Saini answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The magnitude of the Ex and Ey components are not same. Thus it is elliptical polarisation. For +90 phase difference, the polarisation is left handed. In other words, the rotation is in clockwise direction. Thus the polarisation is left hand elliptical.
Explanation: The magnitude of the Ex and Ey components are not same. Thus it is elliptical polarisation. For +90 phase difference, the polarisation is left handed. In other words, the rotation is in clockwise direction. Thus the polarisation is left hand elliptical.
In waveguides, which of the following conditions will be true?- a)V > c
- b)V < c
- c)V = c
- d)V >> c
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In waveguides, which of the following conditions will be true?
a)
V > c
b)
V < c
c)
V = c
d)
V >> c
|
|
Mansi Choudhury answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: In waveguides, the phase velocity will always be greater than the speed of light. This enables the wave to propagate through the waveguide. Thus V > c is the required condition.
Explanation: In waveguides, the phase velocity will always be greater than the speed of light. This enables the wave to propagate through the waveguide. Thus V > c is the required condition.
Calculate the emf of a material having flux density 5sin t in an area of 0.5 units.- a)2.5 sin t
- b)-2.5 cos t
- c)-5 sin t
- d)5 cos t
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the emf of a material having flux density 5sin t in an area of 0.5 units.
a)
2.5 sin t
b)
-2.5 cos t
c)
-5 sin t
d)
5 cos t
|
|
Harsh Kulkarni answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The emf can be written as Vemf = -d(∫B.ds)/dt. It can be written as Vemf = -B= -5sin t, since the integration and differentiation gets cancelled.
Explanation: The emf can be written as Vemf = -d(∫B.ds)/dt. It can be written as Vemf = -B= -5sin t, since the integration and differentiation gets cancelled.
The Brewster angle is expressed as - a)Tan-1(n)
- b)Tan-1(n1/n2)
- c)Tan-1(n2/n1)
- d)Tan (n)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Brewster angle is expressed as
a)
Tan-1(n)
b)
Tan-1(n1/n2)
c)
Tan-1(n2/n1)
d)
Tan (n)
|
|
Sushant Mehta answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The tangent of the Brewster angle is the ratio of the refractive indices of the second medium to that of the first medium. It is given by tan θb= n2/n1. Thus the Brewster angle will be θb = tan-1(n2/n1).
Explanation: The tangent of the Brewster angle is the ratio of the refractive indices of the second medium to that of the first medium. It is given by tan θb= n2/n1. Thus the Brewster angle will be θb = tan-1(n2/n1).
Brewster angle is valid for which type of polarisation?- a)Perpendicular
- b)Parallel
- c)S polarised
- d)P polarised
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Brewster angle is valid for which type of polarisation?
a)
Perpendicular
b)
Parallel
c)
S polarised
d)
P polarised
|
|
Ritika Mukherjee answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The parallel polarisation of the electromagnetic waves is possible only when the transmission occurs at the Brewster angle.
Explanation: The parallel polarisation of the electromagnetic waves is possible only when the transmission occurs at the Brewster angle.
Calculate the phase constant of a wave with skin depth of 2.5 units.- a)5/2
- b)5
- c)2
- d)2/5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the phase constant of a wave with skin depth of 2.5 units.
a)
5/2
b)
5
c)
2
d)
2/5
|
|
Malavika Nair answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The skin depth is the reciprocal of the phase constant and the attenuation constant too. Thus δ = 1/β. On substituting for δ = 2.5, we get β = 1/δ = 1/2.5 = 2/5 units.
Explanation: The skin depth is the reciprocal of the phase constant and the attenuation constant too. Thus δ = 1/β. On substituting for δ = 2.5, we get β = 1/δ = 1/2.5 = 2/5 units.
The line integral of which parameter is zero for static fields?- a)E
- b)H
- c)D
- d)B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The line integral of which parameter is zero for static fields?
a)
E
b)
H
c)
D
d)
B
|
|
Charvi Reddy answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The field is irrotational for static fields. Thus curl of E is zero. From Stokes theorem, the line integral of E is same as the surface integral of the curl of E. Since it is zero, the line integral of E will also be zero.
Explanation: The field is irrotational for static fields. Thus curl of E is zero. From Stokes theorem, the line integral of E is same as the surface integral of the curl of E. Since it is zero, the line integral of E will also be zero.
In free space, the charge carriers will be- a)0
- b)1
- c)100
- d)Infinity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In free space, the charge carriers will be
a)
0
b)
1
c)
100
d)
Infinity
|
|
Rounak Rane answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Free space is not a conductor. Thus the charge carrier in free space is assumed to be zero. But the free space consists of particles or ions that get ionized during conduction.
Explanation: Free space is not a conductor. Thus the charge carrier in free space is assumed to be zero. But the free space consists of particles or ions that get ionized during conduction.
The electric field intensity of a field with velocity 10m/s and flux density of 2.8 units is- a)0.28
- b)28
- c)280
- d)10/2.8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The electric field intensity of a field with velocity 10m/s and flux density of 2.8 units is
a)
0.28
b)
28
c)
280
d)
10/2.8
|
|
Sanchita Choudhary answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The electric field is the product of the velocity and the magnetic flux density given by E = v x B. On substituting v = 10 and B = 2.8, we get E = 10 x 2.8 = 28 units.
Explanation: The electric field is the product of the velocity and the magnetic flux density given by E = v x B. On substituting v = 10 and B = 2.8, we get E = 10 x 2.8 = 28 units.
In conductors, which two parameters are same?- a)Wavelength and phase constant
- b)Phase and attenuation constant
- c)Attenuation constant and skin depth
- d)Skin depth and wavelength
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In conductors, which two parameters are same?
a)
Wavelength and phase constant
b)
Phase and attenuation constant
c)
Attenuation constant and skin depth
d)
Skin depth and wavelength
|
|
Sushant Mehta answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: In conductors, which are considered to be lossy, the attenuation and the phase constant are the same. It is given by α=β= √(ωμσ/2).
Explanation: In conductors, which are considered to be lossy, the attenuation and the phase constant are the same. It is given by α=β= √(ωμσ/2).
When the length of the solenoid is doubled without any change in the number of turns and the area of the coil.Then its self-inductance will - a)Nine times
- b)Half times
- c)Doubled
- d)Unchanged
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the length of the solenoid is doubled without any change in the number of turns and the area of the coil.Then its self-inductance will
a)
Nine times
b)
Half times
c)
Doubled
d)
Unchanged
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Concept:
- Whenever the electric current passing through a coil changes, the magnetic flux linked with it will also change.
- As a result of this, in accordance with Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction, an emf is induced in the coil which opposes the change that causes it.
- This phenomenon is called ‘self-induction’ and the emf induced is called back emf, current so produced in the coil is called induced current.
- Self-inductance of a solenoid is given by –
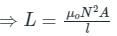 Where μo = Absolute permeability, N = Number of turns, l = length of the solenoid, and A = Area of the solenoid.
Where μo = Absolute permeability, N = Number of turns, l = length of the solenoid, and A = Area of the solenoid.
Explanation
Given - l2 = 2l1
- Self-inductance of a solenoid is given by:
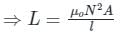
- According to the question, the length of the solenoid is doubled without any change in the number of turns and the area of the coil
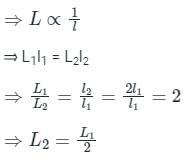
The non existence of the magnetic monopole is due to which operation?- a)Gradient
- b)Divergence
- c)Curl
- d)Laplacian
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The non existence of the magnetic monopole is due to which operation?
a)
Gradient
b)
Divergence
c)
Curl
d)
Laplacian
|
|
Devansh Das answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The Maxwell fourth law or the Gauss law for magnetic field states that the divergence of B is zero, implies the non existence of magnetic monopoles. Thus the operation involved is divergence.
Explanation: The Maxwell fourth law or the Gauss law for magnetic field states that the divergence of B is zero, implies the non existence of magnetic monopoles. Thus the operation involved is divergence.
When the polarisation of the receiving antenna is unknown, to ensure that it receives atleast half the power, the transmitted wave should be- a)Linearly polarised
- b)Elliptically polarised
- c)Circularly polarised
- d)Normally polarised
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When the polarisation of the receiving antenna is unknown, to ensure that it receives atleast half the power, the transmitted wave should be
a)
Linearly polarised
b)
Elliptically polarised
c)
Circularly polarised
d)
Normally polarised
|
|
Samarth Khanna answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The polarisation of the transmitting and receiving antenna has to be the same. This is the condition for maximum power transfer to occur. This is possible only when the polarisation is circular.
Explanation: The polarisation of the transmitting and receiving antenna has to be the same. This is the condition for maximum power transfer to occur. This is possible only when the polarisation is circular.
The Snell law is applicable for perpendicular polarisation and the Brewster law is applicable for parallel polarisation. State True/False.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Snell law is applicable for perpendicular polarisation and the Brewster law is applicable for parallel polarisation. State True/False.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Kritika Gupta answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The Snell law is calculated from the oblique incidence media. Thus it is applicable for perpendicular polarisation. The Brewster law is applicable for perpendicular polarisation.
Explanation: The Snell law is calculated from the oblique incidence media. Thus it is applicable for perpendicular polarisation. The Brewster law is applicable for perpendicular polarisation.
The benefit of Maxwell equation is that- a)Any parameter can be calculated
- b)Antenna can be designed
- c)Polarisation of the wave can be calculated
- d)Transmission line constants can be found
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The benefit of Maxwell equation is that
a)
Any parameter can be calculated
b)
Antenna can be designed
c)
Polarisation of the wave can be calculated
d)
Transmission line constants can be found
|
|
Uday Saini answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The Maxwell equation relates the parameters E, D, H, B. When one parameter is known the other parameters can be easily calculated. In other words, it is used to relate an electric field parameter with its equivalent magnetic field.
Explanation: The Maxwell equation relates the parameters E, D, H, B. When one parameter is known the other parameters can be easily calculated. In other words, it is used to relate an electric field parameter with its equivalent magnetic field.
Which one of the following laws will not contribute to the Maxwell’s equations?- a)Gauss law
- b)Faraday law
- c)Ampere law
- d)Curie Weiss law
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following laws will not contribute to the Maxwell’s equations?
a)
Gauss law
b)
Faraday law
c)
Ampere law
d)
Curie Weiss law
|
|
Siddharth Khanna answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The Gauss law, Faraday law and the Ampere law are directly used to find the parameters E, H, D, B. Thus it contributes to the Maxwell equations. The Curie Weiss law pertains to the property of any magnetic material. Thus it is not related to the Maxwell equation.
Explanation: The Gauss law, Faraday law and the Ampere law are directly used to find the parameters E, H, D, B. Thus it contributes to the Maxwell equations. The Curie Weiss law pertains to the property of any magnetic material. Thus it is not related to the Maxwell equation.
An implication of the continuity equation of conductors is given by- a)J = σ E
- b)J = E/σ
- c)J = σ/E
- d)J = jwEσ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An implication of the continuity equation of conductors is given by
a)
J = σ E
b)
J = E/σ
c)
J = σ/E
d)
J = jwEσ
|
|
Mansi Datta answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The continuity equation indicates the current density in conductors. This is the product of the conductivity of the conductor and the electric field subjected to it. Thus J = σE is the implication of the continuity equation for conductors.
Explanation: The continuity equation indicates the current density in conductors. This is the product of the conductivity of the conductor and the electric field subjected to it. Thus J = σE is the implication of the continuity equation for conductors.
Which quantity is solenoidal in the electromagnetic theory?- a)Electric field intensity
- b)Electric flux density
- c)Magnetic field intensity
- d)Magnetic flux density
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which quantity is solenoidal in the electromagnetic theory?
a)
Electric field intensity
b)
Electric flux density
c)
Magnetic field intensity
d)
Magnetic flux density
|
|
Tarun Chawla answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The divergence of the magnetic flux density is zero. This is the Maxwell fourth equation. As the divergence is zero, the quantity will be solenoidal or divergent less.
Explanation: The divergence of the magnetic flux density is zero. This is the Maxwell fourth equation. As the divergence is zero, the quantity will be solenoidal or divergent less.
In dielectric medium, the Maxwell second equation becomes- a)Curl(H) = Jd
- b)Curl(H) = Jc
- c)Curl(E) = Jd
- d)Curl(E) = Jd
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In dielectric medium, the Maxwell second equation becomes
a)
Curl(H) = Jd
b)
Curl(H) = Jc
c)
Curl(E) = Jd
d)
Curl(E) = Jd
|
|
Sakshi Roy answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: In dielectric medium conductivity σ will be zero. So the current density has only the displacement current density. Thus the Maxwell equation will be Curl(H) = Jd.
Explanation: In dielectric medium conductivity σ will be zero. So the current density has only the displacement current density. Thus the Maxwell equation will be Curl(H) = Jd.
Find the electric field applied on a system with electrons having a velocity 5m/s subjected to a magnetic flux of 3.6 units.- a)15
- b)18
- c)1.38
- d)0.72
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the electric field applied on a system with electrons having a velocity 5m/s subjected to a magnetic flux of 3.6 units.
a)
15
b)
18
c)
1.38
d)
0.72
|
|
Vaibhav Mukherjee answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The electric field intensity is the product of the velocity and the magnetic flux density. Thus E = v x B, on substituting v = 5 and B = 3.6, we get E = 5 x 3.6 = 18 units.
Explanation: The electric field intensity is the product of the velocity and the magnetic flux density. Thus E = v x B, on substituting v = 5 and B = 3.6, we get E = 5 x 3.6 = 18 units.
In a dipole, the Gauss theorem value will be- a)1
- b)0
- c)-1
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a dipole, the Gauss theorem value will be
a)
1
b)
0
c)
-1
d)
2
|
|
Upasana Joshi answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The Gauss theorem for an electric field is given by Div(D)= ρ. In a dipole only static charge exists and the divergence will be zero. Thus the Gauss theorem value for the dipole will be zero.
Explanation: The Gauss theorem for an electric field is given by Div(D)= ρ. In a dipole only static charge exists and the divergence will be zero. Thus the Gauss theorem value for the dipole will be zero.
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance:- a)0.138 H
- b)138.88 H
- c)1.389 H
- d)13.89 H
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance:
a)
0.138 H
b)
138.88 H
c)
1.389 H
d)
13.89 H
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
Concept:
- The coil which stores magnetic energy in a magnetic field is called an inductor.
- The property of an inductor which causes the emf to generate by a change in electric current is called as inductance of the inductor.
- The SI unit of inductance is Henry (H).
- The magnetic potential energy stored in an inductor is given by,
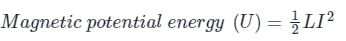
Where L is inductance of the inductor and I is current flowing.
Explanation:
Given that:
Magnetic potential energy (U) = 25 mJ = 25 x 10-3 J
Current (I) = 60 mA = 60 x 10-3A
Use the formula:
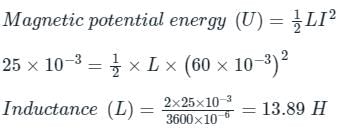
Given that:
Magnetic potential energy (U) = 25 mJ = 25 x 10-3 J
Current (I) = 60 mA = 60 x 10-3A
Use the formula:
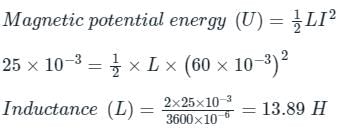
The intrinsic impedance is the ratio of square root of- a)Permittivity to permeability
- b)Permeability to permittivity
- c)Phase constant to wavelength
- d)Wavelength to phase constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The intrinsic impedance is the ratio of square root of
a)
Permittivity to permeability
b)
Permeability to permittivity
c)
Phase constant to wavelength
d)
Wavelength to phase constant
|
|
Sanchita Sharma answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The intrinsic impedance is the impedance of a particular material. It is the ratio of square root of the permeability to permittivity. For air, the intrinsic impedance is 377 ohm or 120π.
Explanation: The intrinsic impedance is the impedance of a particular material. It is the ratio of square root of the permeability to permittivity. For air, the intrinsic impedance is 377 ohm or 120π.
Zero permeability/permittivity implies which state?- a)No ions are allowed in the medium
- b)No current is generated in the medium
- c)No magnetic or electric energy is permitted in the medium
- d)No resistivity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Zero permeability/permittivity implies which state?
a)
No ions are allowed in the medium
b)
No current is generated in the medium
c)
No magnetic or electric energy is permitted in the medium
d)
No resistivity
|
|
Poulomi Chopra answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The zero permittivity in an electric field refers to the ability of the field/medium to permit electric charges in it. Similarly, zero permeability in a magnetic field refers to the ability of the field/medium to permit the magnetic energy into the field.
Explanation: The zero permittivity in an electric field refers to the ability of the field/medium to permit electric charges in it. Similarly, zero permeability in a magnetic field refers to the ability of the field/medium to permit the magnetic energy into the field.
Calculate the velocity of a wave with frequency 2 x109 rad/s and phase constant of 4 x 108units.- a)0.5
- b)5
- c)0.2
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the velocity of a wave with frequency 2 x109 rad/s and phase constant of 4 x 108units.
a)
0.5
b)
5
c)
0.2
d)
2
|
|
Megha Datta answered |
The velocity of a wave is the ratio of the frequency to the phase constant. Thus V = ω/β. On substituting the given values, we get V = 2 x109/ 4 x 108 = 5 units.
The correct sequence to find H, when D is given is- a)D-E-B-H
- b)D-B-E-H
- c)It cannot be computed from the data given
- d)D-H
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence to find H, when D is given is
a)
D-E-B-H
b)
D-B-E-H
c)
It cannot be computed from the data given
d)
D-H
|
|
Rajat Kumar answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: There is no direct relation between D and H, so the option D-H is not possible. Using the formula D = εE, the parameter E can be computed from D. By Maxwell equation, Curl(E) = -dB/dt, the parameter B can be calculated. Using the formula B = μH, the parameter H can be calculated. Thus the sequence is D-E-B-H.
Explanation: There is no direct relation between D and H, so the option D-H is not possible. Using the formula D = εE, the parameter E can be computed from D. By Maxwell equation, Curl(E) = -dB/dt, the parameter B can be calculated. Using the formula B = μH, the parameter H can be calculated. Thus the sequence is D-E-B-H.
The total current density is given as 0.5i + j – 1.5k units. Find the curl of the magnetic field intensity.- a)0.5i – 0.5j + 0.5k
- b)0.5i + j -1.5k
- c)i – j + k
- d)i + j – k
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The total current density is given as 0.5i + j – 1.5k units. Find the curl of the magnetic field intensity.
a)
0.5i – 0.5j + 0.5k
b)
0.5i + j -1.5k
c)
i – j + k
d)
i + j – k
|
|
Gargi Mishra answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: By Maxwell second equation, the curl of H is same as the sum of conduction current density and displacement current density. Thus Curl(H) = J = 0.5i + j – 1.5k units.
Explanation: By Maxwell second equation, the curl of H is same as the sum of conduction current density and displacement current density. Thus Curl(H) = J = 0.5i + j – 1.5k units.
Calculate the wavelength of the wave with phase constant of 3.14 units.- a)1
- b)2
- c)0.5
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the wavelength of the wave with phase constant of 3.14 units.
a)
1
b)
2
c)
0.5
d)
4
|
|
Prasad Verma answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The wavelength is the ratio of 2π to the phase constant β. On substituting for β = 3.14, we get λ = 2π/β = 2π/3.14 = 2 units.
Explanation: The wavelength is the ratio of 2π to the phase constant β. On substituting for β = 3.14, we get λ = 2π/β = 2π/3.14 = 2 units.
The Maxwell second equation that is valid in any conductor is- a)Curl(H) = Jc
- b)Curl(E) = Jc
- c)Curl(E) = Jd
- d)Curl(H) = Jd
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Maxwell second equation that is valid in any conductor is
a)
Curl(H) = Jc
b)
Curl(E) = Jc
c)
Curl(E) = Jd
d)
Curl(H) = Jd
|
|
Ankita Das answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: For conductors, the conductivity parameter σ is significant and only the conduction current density exists. Thus the component J = Jc and Curl(H) = Jc.
Explanation: For conductors, the conductivity parameter σ is significant and only the conduction current density exists. Thus the component J = Jc and Curl(H) = Jc.
Calculate the conduction density of a material with resistivity of 0.02 units and electric intensity of 12 units.- a)300
- b)600
- c)50
- d)120
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the conduction density of a material with resistivity of 0.02 units and electric intensity of 12 units.
a)
300
b)
600
c)
50
d)
120
|
|
Nayanika Singh answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The conduction density is given by Jc = σE, where σ is the inverse of resistivity and it is 1/0.02 = 50. Thus we get, Jc = 50 x 12 = 600 units.
Explanation: The conduction density is given by Jc = σE, where σ is the inverse of resistivity and it is 1/0.02 = 50. Thus we get, Jc = 50 x 12 = 600 units.
Calculate the emf of a material having a flux linkage of 2t2 at time t = 1second.- a)2
- b)4
- c)8
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the emf of a material having a flux linkage of 2t2 at time t = 1second.
a)
2
b)
4
c)
8
d)
16
|
|
Ishani Iyer answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The emf of a material is given by Vemf = -dλ/dt. On substituting λ = 2t2, the emf is 4t. At t = 1 sec, the emf will be 4 units.
Explanation: The emf of a material is given by Vemf = -dλ/dt. On substituting λ = 2t2, the emf is 4t. At t = 1 sec, the emf will be 4 units.
The curl of the electric field intensity is- a)Conservative
- b)Rotational
- c)Divergent
- d)Static
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The curl of the electric field intensity is
a)
Conservative
b)
Rotational
c)
Divergent
d)
Static
|
|
Prasad Saini answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The curl of electric field intensity is Curl(E). From Maxwell law, the curl of E is a non-zero value. Thus E will be rotational.
Explanation: The curl of electric field intensity is Curl(E). From Maxwell law, the curl of E is a non-zero value. Thus E will be rotational.
Calculate the velocity of wave propagation in a conductor with frequency 5 x 108 rad/s and phase constant of 3 x 108 units. - a)3/5
- b)15
- c)5/3
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the velocity of wave propagation in a conductor with frequency 5 x 108 rad/s and phase constant of 3 x 108 units.
a)
3/5
b)
15
c)
5/3
d)
8
|
|
Mainak Pillai answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The velocity of wave propagation is the ratio of the frequency to the phase constant. It is given by V = ω/β. On substituting the given values, we get V = 5/3 units.
Explanation: The velocity of wave propagation is the ratio of the frequency to the phase constant. It is given by V = ω/β. On substituting the given values, we get V = 5/3 units.
The gradient of the magnetic vector potential can be expressed as- a)–με dV/dt
- b)+με dE/dt
- c)–με dA/dt
- d)+με dB/dt
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The gradient of the magnetic vector potential can be expressed as
a)
–με dV/dt
b)
+με dE/dt
c)
–με dA/dt
d)
+με dB/dt
|
|
Arya Mukherjee answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The gradient of A is the ratio of the negative gradient of electric potential to the speed of light c. We can write c = 1/√(με). Thus grad(A) = -με dV/dt is the required expression.
Explanation: The gradient of A is the ratio of the negative gradient of electric potential to the speed of light c. We can write c = 1/√(με). Thus grad(A) = -με dV/dt is the required expression.
When the Maxwell equation is expressed in frequency domain, then which substitution is possible?- a)d/dt = w/j
- b)d/dt = j/w
- c)d/dt = jw
- d)Expression in frequency domain is not possible
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When the Maxwell equation is expressed in frequency domain, then which substitution is possible?
a)
d/dt = w/j
b)
d/dt = j/w
c)
d/dt = jw
d)
Expression in frequency domain is not possible
|
|
Arshiya Basu answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The conversion of time to frequency domain in Maxwell equation is given by the Fourier Transform. Differentiation in time gives jw in frequency domain. Thus d/dt = jw in frequency domain.
Explanation: The conversion of time to frequency domain in Maxwell equation is given by the Fourier Transform. Differentiation in time gives jw in frequency domain. Thus d/dt = jw in frequency domain.
The surface integral of which parameter is zero?- a)E
- b)D
- c)B
- d)H
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The surface integral of which parameter is zero?
a)
E
b)
D
c)
B
d)
H
|
|
Bibek Saha answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The divergence of the magnetic flux density is always zero. By Stokes theorem, the surface integral of B is same as the volume integral of the divergence of B. Thus the surface integral of B is also zero.
Explanation: The divergence of the magnetic flux density is always zero. By Stokes theorem, the surface integral of B is same as the volume integral of the divergence of B. Thus the surface integral of B is also zero.
The magnitude of the conduction current density for a magnetic field intensity of a vector yi + zj + xk will be- a)1.414
- b)1.732
- c)-1.414
- d)-1.732
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnitude of the conduction current density for a magnetic field intensity of a vector yi + zj + xk will be
a)
1.414
b)
1.732
c)
-1.414
d)
-1.732
|
|
Poulomi Ahuja answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: From the Ampere circuital law, the curl of H is the conduction current density. The curl of H = yi + zj + xk is –i – j – k. Thus conduction current density is –i – j – k. The magnitude will be √(1 + 1 + 1) = √3 = 1.732 units.
Explanation: From the Ampere circuital law, the curl of H is the conduction current density. The curl of H = yi + zj + xk is –i – j – k. Thus conduction current density is –i – j – k. The magnitude will be √(1 + 1 + 1) = √3 = 1.732 units.
The transmission coefficient of a wave propagating in the Brewster angle is- a)0
- b)1
- c)-1
- d)Infinity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The transmission coefficient of a wave propagating in the Brewster angle is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
-1
d)
Infinity
|
|
Bijoy Nair answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The transmission coefficient is the reverse of the reflection coefficient. At Brewster angle, the reflection will be zero. Thus the transmission is T = 1-R. Since R = 0, T = 1. It is to be noted that T and R lies in the range of 0 to 1.
Explanation: The transmission coefficient is the reverse of the reflection coefficient. At Brewster angle, the reflection will be zero. Thus the transmission is T = 1-R. Since R = 0, T = 1. It is to be noted that T and R lies in the range of 0 to 1.
The loss tangent is also referred to as- a)Attenuation
- b)Propagation
- c)Dissipation factor
- d)Polarization
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The loss tangent is also referred to as
a)
Attenuation
b)
Propagation
c)
Dissipation factor
d)
Polarization
|
|
Ankita Das answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The loss tangent is the measure of the loss of power due to propagation in a dielectric, when compared to that in a conductor. Hence it is also referred to as dissipation factor.
Explanation: The loss tangent is the measure of the loss of power due to propagation in a dielectric, when compared to that in a conductor. Hence it is also referred to as dissipation factor.
In free space, the condition that holds good is- a)Minimum attenuation and propagation
- b)Minimum attenuation and maximum propagation
- c)Maximum attenuation and minimum propagation
- d)Maximum attenuation and propagation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In free space, the condition that holds good is
a)
Minimum attenuation and propagation
b)
Minimum attenuation and maximum propagation
c)
Maximum attenuation and minimum propagation
d)
Maximum attenuation and propagation
|
|
Megha Datta answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The free space does not have any barrier for attenuation. Thus it enables minimum attenuation and maximum propagation. This technique is employed in line of sight communication
Explanation: The free space does not have any barrier for attenuation. Thus it enables minimum attenuation and maximum propagation. This technique is employed in line of sight communication
Find the Brewster angle of a wave transmitted from a medium of permittivity 4 to a medium of permittivity 2.- a)35.26
- b)53.62
- c)26.35
- d)62.53
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the Brewster angle of a wave transmitted from a medium of permittivity 4 to a medium of permittivity 2.
a)
35.26
b)
53.62
c)
26.35
d)
62.53
|
|
Vaibhav Mukherjee answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The Brewster angle is given by θb = tan-1(n2/n1), where n = √ε. Thus we can express the formula in terms of permittivity as θb = tan-1√ (ε 2/ε 1). Here ε1 = 4 and ε2 = 2. Thus we get θb = tan-1√ (2/4) =
tan-1(0.707) = 35.26 degree.
Explanation: The Brewster angle is given by θb = tan-1(n2/n1), where n = √ε. Thus we can express the formula in terms of permittivity as θb = tan-1√ (ε 2/ε 1). Here ε1 = 4 and ε2 = 2. Thus we get θb = tan-1√ (2/4) =
tan-1(0.707) = 35.26 degree.
Identify the polarisation of the wave given, Ex = 2 cos wt and Ey = sin wt. The phase difference is -900. - a)Left hand circularly polarised
- b)Right hand circularly polarised
- c)Left hand elliptically polarised
- d)Right hand elliptically polarised
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the polarisation of the wave given, Ex = 2 cos wt and Ey = sin wt. The phase difference is -900.
a)
Left hand circularly polarised
b)
Right hand circularly polarised
c)
Left hand elliptically polarised
d)
Right hand elliptically polarised
|
|
Mira Mukherjee answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The magnitude of the Ex and Ey components are not same. Thus it is elliptical polarisation. For -90 phase difference, the polarisation is right handed. In other words, the rotation is in anti-clockwise direction. Thus the polarisation is right hand elliptical.
Explanation: The magnitude of the Ex and Ey components are not same. Thus it is elliptical polarisation. For -90 phase difference, the polarisation is right handed. In other words, the rotation is in anti-clockwise direction. Thus the polarisation is right hand elliptical.
Calculate the reluctance when the magnetomotive force is 10A turns and the flux is 5Wb.- a)0.5A/Wb
- b)5A/Wb
- c)10A/Wb
- d)2A/Wb
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the reluctance when the magnetomotive force is 10A turns and the flux is 5Wb.
a)
0.5A/Wb
b)
5A/Wb
c)
10A/Wb
d)
2A/Wb
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
We know that:
F = ϕ*S
Substituting the given values from the question:
S = 2A/Wb.
F = ϕ*S
Substituting the given values from the question:
S = 2A/Wb.
In free space, the ratio of frequency to the velocity of light gives the phase constant. State True/False. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In free space, the ratio of frequency to the velocity of light gives the phase constant. State True/False.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Aman Datta answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: The phase constant is given by the ratio of the frequency in radian/sec to the velocity of the wave propagating. In free space, the velocity is considered to be the velocity of light. Thus the statement is true.
Explanation: The phase constant is given by the ratio of the frequency in radian/sec to the velocity of the wave propagating. In free space, the velocity is considered to be the velocity of light. Thus the statement is true.
Chapter doubts & questions for Time Varying Electromagnetic Fields - Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Time Varying Electromagnetic Fields - Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT) in English & Hindi are available as part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT)
11 videos|50 docs|56 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









