All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
Structural Analysis >
All Questions
All questions of Force Method of Analysis for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
Which of the following primary structure is best for computational purposes?- a)symmetric
- b)non-symmetric
- c)anti-symmetric
- d)depends upon loads applied
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following primary structure is best for computational purposes?
a)
symmetric
b)
non-symmetric
c)
anti-symmetric
d)
depends upon loads applied

|
Garima Basak answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: It is easier to compute solutions for flexibility coefficient matrix in that case.
Explanation: It is easier to compute solutions for flexibility coefficient matrix in that case.
Flexibility matrix is always:-- a)symmetric
- b)non-symmetric
- c)anti-symmetric
- d)depends upon loads applied
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Flexibility matrix is always:-
a)
symmetric
b)
non-symmetric
c)
anti-symmetric
d)
depends upon loads applied

|
Poulomi Khanna answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Flexibility matrixes are always symmetric as a consequence of Betti’s law.
Explanation: Flexibility matrixes are always symmetric as a consequence of Betti’s law.
In capacitor start single phase induction motor, the current in the- a)Supply lines leads the voltage
- b)Starting winding lags the voltage
- c)Main winding leads the voltage
- d)Starting winding leads the voltage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In capacitor start single phase induction motor, the current in the
a)
Supply lines leads the voltage
b)
Starting winding lags the voltage
c)
Main winding leads the voltage
d)
Starting winding leads the voltage
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
A Capacitor Start Motors are a single phase Induction Motor that employs a capacitor in the auxiliary winding circuit to produce a greater phase difference between the current in the main and the auxiliary windings. The name capacitor starts itself shows that the motor uses a capacitor for the purpose of the starting.In phase induction motors, we are unable to get starting torque, So we mostly use permanent capacitor split phase starting method in ceiling fans. Its main aim is to split the single phase supply into phases, having time displacement of 90 degrees, also mechanically the windings are placed 90 degrees in space. It gives an rmf which produces a starting torque & makes it a self starting motor. So, the capacitor used in the other auxiliary winding mainly provides this 90 degrees time displacement. An inductor can also be used, but it has the following drawbacksBulky size of the inductor.Leakage reactance of it affects the value of the starting torque.Its delay in current affects the transients.
Indeterminate analysis of a symmetrical structure is difficult from that of a non symmetric one.
State whether the above statement is true or false.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Indeterminate analysis of a symmetrical structure is difficult from that of a non symmetric one.
State whether the above statement is true or false.
State whether the above statement is true or false.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Gitanjali Chauhan answered |
Detailed Answer:
The statement "Indeterminate analysis of a symmetrical structure is difficult from that of a non-symmetric one" is false. Indeterminate analysis refers to the calculation of unknown reactions, internal forces, and displacements in a structure. While the presence of symmetry simplifies the analysis, it does not necessarily make it more difficult.
Symmetry in Structures: A structure is considered symmetrical when it possesses a balanced arrangement of its elements or components. This can include symmetry about a central axis, as well as symmetry about a plane or multiple planes. Symmetry is a common feature in many structures, such as buildings, bridges, and machines.
Advantages of Symmetry: The presence of symmetry in a structure offers several advantages:
1. Simplification of Geometry: Symmetry allows for the simplification of the structure's geometry, as certain elements or sections can be mirrored or replicated. This simplification reduces the number of unknowns in the analysis.
2. Reduction of Unknown Forces: Symmetry ensures that certain forces or reactions are balanced, eliminating the need to calculate them separately. This reduces the complexity of the analysis.
3. Conservation of Energy: Symmetry often leads to the conservation of energy in a structure, as forces and displacements are evenly distributed. This can simplify the determination of internal forces and displacements.
Non-Symmetric Structures: Non-symmetrical structures do not possess a balanced arrangement of their elements or components. They can have irregular shapes, varied load distributions, or lack any form of symmetry.
Challenges of Non-Symmetrical Structures: The analysis of non-symmetrical structures can be more challenging due to the following reasons:
1. Complex Geometry: Non-symmetrical structures often have complex geometries, making it difficult to determine the internal forces and displacements accurately.
2. Varied Load Distribution: The load distribution in non-symmetrical structures is often uneven, leading to varying internal forces throughout the structure. Analyzing these variations requires more detailed calculations.
3. Increased Unknowns: Non-symmetrical structures typically have a higher number of unknown reactions and internal forces compared to symmetrical structures. This increases the complexity of the analysis.
In conclusion, the statement that indeterminate analysis of a symmetrical structure is difficult compared to a non-symmetrical one is false. Symmetry in a structure simplifies the analysis by reducing unknowns, simplifying geometry, and conserving energy. Non-symmetrical structures, on the other hand, present challenges such as complex geometry, varied load distribution, and increased unknowns. Therefore, while the analysis of non-symmetrical structures may be more complex, the presence of symmetry in a structure does not necessarily make the analysis more difficult.
Introduction
The statement "Indeterminate analysis of a symmetrical structure is difficult from that of a non-symmetric one" is false. Indeterminate analysis refers to the calculation of unknown reactions, internal forces, and displacements in a structure. While the presence of symmetry simplifies the analysis, it does not necessarily make it more difficult.
Analysis of Symmetrical Structures
Symmetry in Structures: A structure is considered symmetrical when it possesses a balanced arrangement of its elements or components. This can include symmetry about a central axis, as well as symmetry about a plane or multiple planes. Symmetry is a common feature in many structures, such as buildings, bridges, and machines.
Advantages of Symmetry: The presence of symmetry in a structure offers several advantages:
1. Simplification of Geometry: Symmetry allows for the simplification of the structure's geometry, as certain elements or sections can be mirrored or replicated. This simplification reduces the number of unknowns in the analysis.
2. Reduction of Unknown Forces: Symmetry ensures that certain forces or reactions are balanced, eliminating the need to calculate them separately. This reduces the complexity of the analysis.
3. Conservation of Energy: Symmetry often leads to the conservation of energy in a structure, as forces and displacements are evenly distributed. This can simplify the determination of internal forces and displacements.
Analysis of Non-Symmetrical Structures
Non-Symmetric Structures: Non-symmetrical structures do not possess a balanced arrangement of their elements or components. They can have irregular shapes, varied load distributions, or lack any form of symmetry.
Challenges of Non-Symmetrical Structures: The analysis of non-symmetrical structures can be more challenging due to the following reasons:
1. Complex Geometry: Non-symmetrical structures often have complex geometries, making it difficult to determine the internal forces and displacements accurately.
2. Varied Load Distribution: The load distribution in non-symmetrical structures is often uneven, leading to varying internal forces throughout the structure. Analyzing these variations requires more detailed calculations.
3. Increased Unknowns: Non-symmetrical structures typically have a higher number of unknown reactions and internal forces compared to symmetrical structures. This increases the complexity of the analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the statement that indeterminate analysis of a symmetrical structure is difficult compared to a non-symmetrical one is false. Symmetry in a structure simplifies the analysis by reducing unknowns, simplifying geometry, and conserving energy. Non-symmetrical structures, on the other hand, present challenges such as complex geometry, varied load distribution, and increased unknowns. Therefore, while the analysis of non-symmetrical structures may be more complex, the presence of symmetry in a structure does not necessarily make the analysis more difficult.
Flexibility coefficients depend upon loading of the primary structure.
State whether the above statement is true or false - a)true
- b)false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Flexibility coefficients depend upon loading of the primary structure.
State whether the above statement is true or false
State whether the above statement is true or false
a)
true
b)
false

|
Garima Basak answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: It does not depend upon loading of the primary structure.
Explanation: It does not depend upon loading of the primary structure.
Consider the following components Out of these components, which component(s)can be common for primary & back up protection- a)CB's
- b)CTs
- c)Battery room
- d)Equipment to be protected
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following components Out of these components, which component(s)can be common for primary & back up protection
a)
CB's
b)
CTs
c)
Battery room
d)
Equipment to be protected

|
Rashi Shah answered |
Primary backup protection is the first line of defense in a power system to protect the equipment from faults and abnormal conditions. It is designed to provide fast and reliable protection in case of any abnormalities.
In the given components, the option 'D' - Equipment to be protected, can be common for primary backup protection. Here's why:
Equipment Protection:
- The primary objective of backup protection is to ensure the safety and integrity of the equipment in the power system.
- Equipment such as transformers, generators, motors, and other electrical devices are susceptible to faults and abnormal conditions that can lead to damage or failure.
- Primary backup protection is designed to detect these faults and disconnect the faulty equipment from the power supply to prevent further damage.
Importance of Equipment Protection:
- Equipment in a power system is expensive and vital for the operation of the system.
- Faults or abnormalities in equipment can lead to power outages, damage to other equipment, and even safety hazards.
- Protection systems are installed to minimize the impact of faults and ensure the reliability and longevity of the equipment.
Primary Backup Protection:
- Primary backup protection operates quickly and independently to detect faults and isolate the faulty equipment.
- It is designed to provide a reliable and fast response to faults, ensuring the safety and integrity of the equipment.
- The primary backup protection system typically includes protective relays, which are devices that monitor electrical parameters and can trip circuit breakers to isolate the faulty equipment.
Role of Other Components:
- Circuit breakers (option 'A') are essential components of the primary backup protection system as they are responsible for disconnecting the faulty equipment from the power supply.
- Current transformers (option 'B') are used to measure the current flowing through the equipment and provide input to the protective relays for fault detection.
- The battery room (option 'C') is not directly related to primary backup protection. However, it may provide backup power for the protection system in case of a power failure.
Conclusion:
While circuit breakers and current transformers are crucial components of the primary backup protection system, the equipment to be protected (option 'D') is common to all protection schemes. The primary backup protection is designed to ensure the safety and integrity of the equipment in the power system by detecting faults and isolating the faulty equipment.
In the given components, the option 'D' - Equipment to be protected, can be common for primary backup protection. Here's why:
Equipment Protection:
- The primary objective of backup protection is to ensure the safety and integrity of the equipment in the power system.
- Equipment such as transformers, generators, motors, and other electrical devices are susceptible to faults and abnormal conditions that can lead to damage or failure.
- Primary backup protection is designed to detect these faults and disconnect the faulty equipment from the power supply to prevent further damage.
Importance of Equipment Protection:
- Equipment in a power system is expensive and vital for the operation of the system.
- Faults or abnormalities in equipment can lead to power outages, damage to other equipment, and even safety hazards.
- Protection systems are installed to minimize the impact of faults and ensure the reliability and longevity of the equipment.
Primary Backup Protection:
- Primary backup protection operates quickly and independently to detect faults and isolate the faulty equipment.
- It is designed to provide a reliable and fast response to faults, ensuring the safety and integrity of the equipment.
- The primary backup protection system typically includes protective relays, which are devices that monitor electrical parameters and can trip circuit breakers to isolate the faulty equipment.
Role of Other Components:
- Circuit breakers (option 'A') are essential components of the primary backup protection system as they are responsible for disconnecting the faulty equipment from the power supply.
- Current transformers (option 'B') are used to measure the current flowing through the equipment and provide input to the protective relays for fault detection.
- The battery room (option 'C') is not directly related to primary backup protection. However, it may provide backup power for the protection system in case of a power failure.
Conclusion:
While circuit breakers and current transformers are crucial components of the primary backup protection system, the equipment to be protected (option 'D') is common to all protection schemes. The primary backup protection is designed to ensure the safety and integrity of the equipment in the power system by detecting faults and isolating the faulty equipment.
Bimetallic strip is- a)active transducer
- b)passive transducer
- c)linear transducer
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bimetallic strip is
a)
active transducer
b)
passive transducer
c)
linear transducer
d)
none of these
|
|
Jithendri Accha answered |
Bimetallic strip is used to convert temperature change into mechanical displacement. As it requires additional electrical energy for stimulation. So it is known as passive transducer
Numerical accuracy of solution increases if flexibility coefficients with larger values are located:-- a)near main diagonal
- b)near edges
- c)in between
- d)near side middles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Numerical accuracy of solution increases if flexibility coefficients with larger values are located:-
a)
near main diagonal
b)
near edges
c)
in between
d)
near side middles

|
Gowri Singh answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Numerical accuracy increases if larger coefficients are located near the main diagonal of matrix.
Explanation: Numerical accuracy increases if larger coefficients are located near the main diagonal of matrix.
In general, any structure can be classified as a symmetric one :-- a)when its structure is symmetric
- b)when its loading is symmetric
- c)when its supports are symmetric
- d)when it develops symmetric internal loading and deflections
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In general, any structure can be classified as a symmetric one :-
a)
when its structure is symmetric
b)
when its loading is symmetric
c)
when its supports are symmetric
d)
when it develops symmetric internal loading and deflections

|
Gowri Singh answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: It is deemed as symmetric when when it develops symmetric internal loading and deflections about central axis.
Explanation: It is deemed as symmetric when when it develops symmetric internal loading and deflections about central axis.
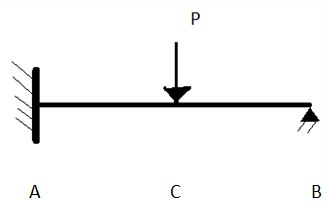 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q.How many unknowns are there in the above figure?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q.How many unknowns are there in the above figure?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q.How many unknowns are there in the above figure?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Yashvi Choudhury answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: 4 unknown forces are there, 3 forces and one moment.
Explanation: 4 unknown forces are there, 3 forces and one moment.
The B-H curve for.......will be straight line passing through the origin.- a)air
- b)soft iron
- c)hardened steel
- d)silicon steel
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The B-H curve for.......will be straight line passing through the origin.
a)
air
b)
soft iron
c)
hardened steel
d)
silicon steel

|
Sravya Rane answered |
B-H curve is a graph that represents the relationship between the magnetic field strength (H) and the magnetic flux density (B) of a material. It is commonly used to characterize the magnetic properties of different materials. In this case, we are asked to determine the shape of the B-H curve for a specific material.
The correct answer is option 'A', which is air. The B-H curve for air will be a straight line passing through the origin.
Here is the explanation:
1. B-H Curve:
The B-H curve is used to describe the magnetic behavior of a material. It illustrates how the magnetic flux density (B) changes with respect to the magnetic field strength (H). The curve is obtained by measuring the magnetic properties of the material under varying magnetic field strengths.
2. Shape of B-H Curve:
The shape of the B-H curve depends on the material being tested. Different materials exhibit different magnetic properties, and therefore, have different B-H curves. The shape can be classified into different types, such as linear, non-linear, or hysteresis loop.
3. B-H Curve for Air:
Air is a non-magnetic material, which means it does not possess any inherent magnetic properties. It does not exhibit any significant magnetic behavior when subjected to a magnetic field. Therefore, the B-H curve for air is a straight line passing through the origin.
4. Explanation of a Straight Line Curve:
A straight line passing through the origin indicates that there is a linear relationship between the magnetic field strength (H) and the magnetic flux density (B). This means that the magnetic flux density is directly proportional to the magnetic field strength for air.
5. Why is the B-H Curve for Air a Straight Line?
Air is a paramagnetic material, which means it only exhibits a weak magnetic response when exposed to a magnetic field. The magnetic susceptibility of air is very close to zero, thus resulting in a linear relationship between H and B. This linear relationship indicates that the magnetic flux density in air increases proportionally with the magnetic field strength.
In conclusion, the B-H curve for air is a straight line passing through the origin because air is a non-magnetic material with a magnetic susceptibility close to zero. This indicates a linear relationship between the magnetic field strength and the magnetic flux density for air.
The correct answer is option 'A', which is air. The B-H curve for air will be a straight line passing through the origin.
Here is the explanation:
1. B-H Curve:
The B-H curve is used to describe the magnetic behavior of a material. It illustrates how the magnetic flux density (B) changes with respect to the magnetic field strength (H). The curve is obtained by measuring the magnetic properties of the material under varying magnetic field strengths.
2. Shape of B-H Curve:
The shape of the B-H curve depends on the material being tested. Different materials exhibit different magnetic properties, and therefore, have different B-H curves. The shape can be classified into different types, such as linear, non-linear, or hysteresis loop.
3. B-H Curve for Air:
Air is a non-magnetic material, which means it does not possess any inherent magnetic properties. It does not exhibit any significant magnetic behavior when subjected to a magnetic field. Therefore, the B-H curve for air is a straight line passing through the origin.
4. Explanation of a Straight Line Curve:
A straight line passing through the origin indicates that there is a linear relationship between the magnetic field strength (H) and the magnetic flux density (B). This means that the magnetic flux density is directly proportional to the magnetic field strength for air.
5. Why is the B-H Curve for Air a Straight Line?
Air is a paramagnetic material, which means it only exhibits a weak magnetic response when exposed to a magnetic field. The magnetic susceptibility of air is very close to zero, thus resulting in a linear relationship between H and B. This linear relationship indicates that the magnetic flux density in air increases proportionally with the magnetic field strength.
In conclusion, the B-H curve for air is a straight line passing through the origin because air is a non-magnetic material with a magnetic susceptibility close to zero. This indicates a linear relationship between the magnetic field strength and the magnetic flux density for air.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Which of the following forces can’t be chosen to be redundant?- a)Vertical support at point A
- b)P
- c)Vertical support at B
- d)Moment at A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Which of the following forces can’t be chosen to be redundant?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Which of the following forces can’t be chosen to be redundant?
a)
Vertical support at point A
b)
P
c)
Vertical support at B
d)
Moment at A

|
Ankit Joshi answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Load P can’t be chosen as this is the load causing deflection. Rest all support forces can be chosen to be redundant.
Explanation: Load P can’t be chosen as this is the load causing deflection. Rest all support forces can be chosen to be redundant.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. How much load acts and in which direction at point B for the displacement to be fbb?- a)Unit, opposite to By
- b)Unit, same as by
- c)Small, opposite to By
- d)Large, same as By
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. How much load acts and in which direction at point B for the displacement to be fbb?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. How much load acts and in which direction at point B for the displacement to be fbb?
a)
Unit, opposite to By
b)
Unit, same as by
c)
Small, opposite to By
d)
Large, same as By

|
Sahana Choudhary answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Displacement caused by unit load acting in the direction of By is termed as fbb.
Explanation: Displacement caused by unit load acting in the direction of By is termed as fbb.
How many compatibility equations should be written if we have n no. of redundant reactions?- a)n – 1
- b)n
- c)n + 1
- d)n + 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many compatibility equations should be written if we have n no. of redundant reactions?
a)
n – 1
b)
n
c)
n + 1
d)
n + 2

|
Siddharth Bajaj answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: No. of redundant reactions and compatibility equations are equal.
Explanation: No. of redundant reactions and compatibility equations are equal.
Normally, which of the following things may/may not be symmetric to develop symmetricity?- a)material
- b)geometry
- c)loading
- d)dki
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Normally, which of the following things may/may not be symmetric to develop symmetricity?
a)
material
b)
geometry
c)
loading
d)
dki

|
Pranavi Choudhury answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Composition, geometry and loading are generally require to be symmetric.
Explanation: Composition, geometry and loading are generally require to be symmetric.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. What is the compatibility equation for the above mentioned condition?- a)Δ/ bb – Δb = 0
- b)Δ/ bb + Δb = 0
- c)Δ/ bb – Δb > 0
- d)Δ/ bb – Δb < 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. What is the compatibility equation for the above mentioned condition?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. What is the compatibility equation for the above mentioned condition?
a)
Δ/ bb – Δb = 0
b)
Δ/ bb + Δb = 0
c)
Δ/ bb – Δb > 0
d)
Δ/ bb – Δb < 0

|
Rohan Singh answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Both the displacement will be opposite in direction and equal in magnitude.
Explanation: Both the displacement will be opposite in direction and equal in magnitude.
The Req for the circuit shown in figure is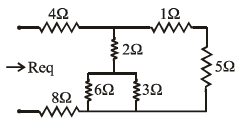
- a)
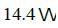
- b)
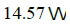
- c)
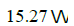
- d)
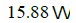
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Req for the circuit shown in figure is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Kalyan Pandu answered |
Step 1:5 and 1 ohm resistors are in series which gives 6 ohms
step 2: 6 and 3 are in parallel which gives 2 ohms and this 2 ohm is in series with 2ohms which gives 4 ohms
step 3: 6ohms and 4 ohms are in parallel the resultant resistance is 2.4 ohms
step 4:2.4 is in series with 8 and 4 which gives 2.4+4+8=14.4ohms
step 2: 6 and 3 are in parallel which gives 2 ohms and this 2 ohm is in series with 2ohms which gives 4 ohms
step 3: 6ohms and 4 ohms are in parallel the resultant resistance is 2.4 ohms
step 4:2.4 is in series with 8 and 4 which gives 2.4+4+8=14.4ohms
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. According to maxwell’s theorem:-- a)fab = faa
- b)fbb = faa
- c)fba = fab
- d)fba = fbb
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. According to maxwell’s theorem:-
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. According to maxwell’s theorem:-
a)
fab = faa
b)
fbb = faa
c)
fba = fab
d)
fba = fbb

|
Prasad Desai answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The displacement of a point B on a structure due to a unit load acting at point A is equal to the displacement of point A when the unit load is acting at point B
Explanation: The displacement of a point B on a structure due to a unit load acting at point A is equal to the displacement of point A when the unit load is acting at point B
A monopole consists of- a)a single charge
- b)two positive and two negative charges
- c)two positive and one negative charges
- d)two negative and one positive charges
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A monopole consists of
a)
a single charge
b)
two positive and two negative charges
c)
two positive and one negative charges
d)
two negative and one positive charges

|
Subhankar Ghoshal answered |
Monopole:
Monopole consists of a single charge, which means it has only one type of charge present, either positive or negative.
Explanation:
Monopole is a theoretical concept in physics that describes a single isolated charge. In a monopole, there is no accompanying opposite charge to balance it out, unlike in a dipole where positive and negative charges are present.
Characteristics of a Monopole:
- It has a single charge, either positive or negative.
- Monopoles are theoretical as no isolated magnetic monopoles have been discovered yet.
- In theory, monopoles would have quantized magnetic charge similar to electric charge.
Relevance:
Monopoles are important in the study of electromagnetism and theoretical physics. The existence of magnetic monopoles could have significant implications for our understanding of the universe and fundamental forces.
In conclusion, a monopole consists of a single charge, making it distinct from dipoles which have both positive and negative charges.
Monopole consists of a single charge, which means it has only one type of charge present, either positive or negative.
Explanation:
Monopole is a theoretical concept in physics that describes a single isolated charge. In a monopole, there is no accompanying opposite charge to balance it out, unlike in a dipole where positive and negative charges are present.
Characteristics of a Monopole:
- It has a single charge, either positive or negative.
- Monopoles are theoretical as no isolated magnetic monopoles have been discovered yet.
- In theory, monopoles would have quantized magnetic charge similar to electric charge.
Relevance:
Monopoles are important in the study of electromagnetism and theoretical physics. The existence of magnetic monopoles could have significant implications for our understanding of the universe and fundamental forces.
In conclusion, a monopole consists of a single charge, making it distinct from dipoles which have both positive and negative charges.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. This structure is made redundant by temporarily removing how many support reactions?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. This structure is made redundant by temporarily removing how many support reactions?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. This structure is made redundant by temporarily removing how many support reactions?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Sahana Choudhary answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: As the degree of indeterminacy is one, one of the support reactions is chosen to be redundant.
Explanation: As the degree of indeterminacy is one, one of the support reactions is chosen to be redundant.
Indeterminate analysis of a anti-symmetrically loaded structure is difficult from that of non symmetric one.
State whether the above statement is true or false.- a)True
- b)false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Indeterminate analysis of a anti-symmetrically loaded structure is difficult from that of non symmetric one.
State whether the above statement is true or false.
State whether the above statement is true or false.
a)
True
b)
false

|
Pranavi Choudhury answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Solving one side would give modulus of deflections of other side as well.
Explanation: Solving one side would give modulus of deflections of other side as well.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Which one of the following describes fbb?- a)Δ/ bb / By
- b)By/ Δ / bb
- c)Δ/ bb – By
- d)Δ/ bb + By
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Which one of the following describes fbb?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Which one of the following describes fbb?
a)
Δ/ bb / By
b)
By/ Δ / bb
c)
Δ/ bb – By
d)
Δ/ bb + By

|
Ankit Joshi answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Δ/ bb is actual displacement caused by By, and fbb is caused by unit load. So, its fbb times By Δ/ bb/By.
Explanation: Δ/ bb is actual displacement caused by By, and fbb is caused by unit load. So, its fbb times By Δ/ bb/By.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q.The above structure is statically indeterminate.
State whether the above sentence is true or false.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q.The above structure is statically indeterminate.
State whether the above sentence is true or false.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q.The above structure is statically indeterminate.
State whether the above sentence is true or false.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Bhaskar Mukherjee answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: 4 unknown forces and 3 reactions are there. So, it is statically indeterminate.
Explanation: 4 unknown forces and 3 reactions are there. So, it is statically indeterminate.
The resistance of the field regulator of a dc shunt motor is of the order of- a)100
- b)10
- c)2
- d)0.5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The resistance of the field regulator of a dc shunt motor is of the order of
a)
100
b)
10
c)
2
d)
0.5

|
Anmol Choudhary answered |
Resistance of Field Regulator in DC Shunt Motor
Field regulator is an important component in a DC shunt motor which is responsible for controlling the field current. The resistance of the field regulator determines the amount of current flowing through the field winding, thereby influencing the motor's speed and torque characteristics.
The resistance of the field regulator is typically specified in ohms and is denoted by the symbol 'Rf'. It is important to choose the appropriate resistance value for the field regulator to ensure optimal motor performance.
The resistance of the field regulator is determined based on various factors such as motor design, voltage rating, and desired operating characteristics. In the case of a DC shunt motor, the resistance of the field regulator is typically in the range of 100 ohms.
Explanation:
1. DC Shunt Motor:
- A DC shunt motor is a type of DC motor where the field winding is connected in parallel (shunt) with the armature winding.
- It is widely used in various applications due to its simple construction, good speed regulation, and ability to provide high starting torque.
2. Field Regulator:
- The field regulator is a device that controls the field current in a DC shunt motor.
- It consists of a variable resistance connected in series with the field winding.
- By adjusting the resistance, the field current can be varied, thereby controlling the motor's speed and torque characteristics.
3. Importance of Field Regulator Resistance:
- The resistance of the field regulator determines the amount of current flowing through the field winding.
- A higher resistance value reduces the field current, resulting in a slower motor speed.
- Conversely, a lower resistance value increases the field current, leading to a higher motor speed.
4. Order of Resistance:
- The given question states that the resistance of the field regulator in a DC shunt motor is of the order of 100 ohms.
- The term "order" refers to the magnitude of the resistance value.
- In this case, the resistance value is approximately 100 ohms, which is the correct answer (option 'A').
In conclusion, the resistance of the field regulator in a DC shunt motor is typically in the range of 100 ohms. This resistance value plays a crucial role in controlling the field current and, subsequently, the speed and torque characteristics of the motor.
Field regulator is an important component in a DC shunt motor which is responsible for controlling the field current. The resistance of the field regulator determines the amount of current flowing through the field winding, thereby influencing the motor's speed and torque characteristics.
The resistance of the field regulator is typically specified in ohms and is denoted by the symbol 'Rf'. It is important to choose the appropriate resistance value for the field regulator to ensure optimal motor performance.
The resistance of the field regulator is determined based on various factors such as motor design, voltage rating, and desired operating characteristics. In the case of a DC shunt motor, the resistance of the field regulator is typically in the range of 100 ohms.
Explanation:
1. DC Shunt Motor:
- A DC shunt motor is a type of DC motor where the field winding is connected in parallel (shunt) with the armature winding.
- It is widely used in various applications due to its simple construction, good speed regulation, and ability to provide high starting torque.
2. Field Regulator:
- The field regulator is a device that controls the field current in a DC shunt motor.
- It consists of a variable resistance connected in series with the field winding.
- By adjusting the resistance, the field current can be varied, thereby controlling the motor's speed and torque characteristics.
3. Importance of Field Regulator Resistance:
- The resistance of the field regulator determines the amount of current flowing through the field winding.
- A higher resistance value reduces the field current, resulting in a slower motor speed.
- Conversely, a lower resistance value increases the field current, leading to a higher motor speed.
4. Order of Resistance:
- The given question states that the resistance of the field regulator in a DC shunt motor is of the order of 100 ohms.
- The term "order" refers to the magnitude of the resistance value.
- In this case, the resistance value is approximately 100 ohms, which is the correct answer (option 'A').
In conclusion, the resistance of the field regulator in a DC shunt motor is typically in the range of 100 ohms. This resistance value plays a crucial role in controlling the field current and, subsequently, the speed and torque characteristics of the motor.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Maxwell’s theorem doesn’t apply when external moments are placed on the beam.
State whether the above statement is true or false.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Maxwell’s theorem doesn’t apply when external moments are placed on the beam.
State whether the above statement is true or false.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Maxwell’s theorem doesn’t apply when external moments are placed on the beam.
State whether the above statement is true or false.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Rohan Singh answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: It is also applicable when external moments are acting on the structure instead of forces.
Explanation: It is also applicable when external moments are acting on the structure instead of forces.
 In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Δ/ bb refers to displacement cause by By.
What does first b in Δ/ bb stands for?- a)Where unknown reaction acts
- b)Point whose deflection is considered
- c)Can be anything
- d)Depends upon load applied
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In above figure, joint A is fixed and joint B is pinned. C lies in between A and B and a load of P are applied there.
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Δ/ bb refers to displacement cause by By.
What does first b in Δ/ bb stands for?
Δb = Displacement caused when vertical support at point B is chosen to be neglected.
By = redundant force
Q. Δ/ bb refers to displacement cause by By.
What does first b in Δ/ bb stands for?
a)
Where unknown reaction acts
b)
Point whose deflection is considered
c)
Can be anything
d)
Depends upon load applied

|
Yashvi Choudhury answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: First b refers to the point where load is specified, second B refers to the point where load is applied.
Explanation: First b refers to the point where load is specified, second B refers to the point where load is applied.
Chapter doubts & questions for Force Method of Analysis - Structural Analysis 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Force Method of Analysis - Structural Analysis in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Structural Analysis
34 videos|164 docs|31 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











