NEET Exam > NEET Questions > What kind of development takes place in zygot...
Start Learning for Free
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle?
Verified Answer
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplo...
Diplontic
In this type of life cycle, Diploid zygote, germinates by mitosis to form unicellular or multicellular diploid sporophyte.All seed- bearing plants i.e. gymnosperms and angiosperms, follow this pattern.
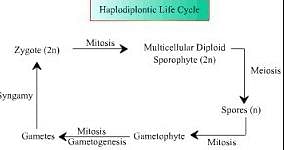
Haplontic life cycle:
In most of the plants, the zygote undergoes mitotic cell division and produces diploid sporophytes. The sporophyte divides meiotically to produce haploid spores. These spores again undergo mitotic cell division and produce haploid gametophytes. This gametophyte produces gametes by mitosis. This type of life cycle is known as Haplodiplontic Life Cycle.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplo...
In diplontic life cycle, the zygote undergoes mitosis and forms a diploid sporophytic stage which is dominant and independent. it includes all seed bearing plants i.e., angiosperms and gymnosperms
whereas, in haplo-diplontic life cycle it shows an intermediate condn. the zygote undergoes meiosis and forms a haploid gametophyte which is dominant and altered with sporophytic stage which is wholly or partially dependent on gametophyte.
whereas, in haplo-diplontic life cycle it shows an intermediate condn. the zygote undergoes meiosis and forms a haploid gametophyte which is dominant and altered with sporophytic stage which is wholly or partially dependent on gametophyte.
Community Answer
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplo...
Development in Zygote in Organisms with Diplontic Life Cycle:
In organisms with a diplontic life cycle, the zygote undergoes development to form a multicellular diploid organism. This type of life cycle is observed in most animals, including humans, where the zygote develops into an adult organism directly without any alternation of generations.
Fertilization:
- The diplontic life cycle begins with the fusion of gametes during fertilization.
- This fusion results in the formation of a zygote, which is a diploid cell with a complete set of chromosomes.
Cleavage:
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a process called cleavage.
- Cleavage involves a series of rapid cell divisions without any significant growth in size.
- These divisions lead to the formation of a multicellular embryo consisting of a cluster of cells called blastomeres.
Gastrulation:
- Gastrulation is the next crucial step in zygote development.
- During gastrulation, the blastomeres rearrange and differentiate to form three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- The ectoderm gives rise to the skin, nervous system, and sensory organs.
- The endoderm develops into the digestive system and internal organs.
- The mesoderm forms the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, and reproductive organs.
Organogenesis:
- Following gastrulation, organogenesis occurs, which involves the formation and differentiation of specific organs and tissues.
- Various signals and interactions between cells and tissues guide the development of specific structures.
- Organs such as the heart, brain, lungs, and liver begin to form during this stage.
Growth and Maturation:
- As the embryo continues to develop, it undergoes growth in size and complexity.
- The cells divide, differentiate, and organize into specific tissues and organs.
- This growth and maturation process continues until the organism reaches adulthood.
Development in Zygote in Organisms with Haplo-Diplontic Life Cycle:
In organisms with a haplo-diplontic life cycle, there are two distinct multicellular stages: the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte. The zygote plays a crucial role in the development of both stages.
Fertilization:
- Similar to the diplontic life cycle, the haplo-diplontic life cycle also begins with the fusion of gametes during fertilization.
- The fusion of a haploid egg and a haploid sperm results in the formation of a diploid zygote.
Embryo Development:
- The diploid zygote undergoes development to form a multicellular diploid embryo, which represents the sporophyte generation.
- The embryo develops through various stages, including cleavage, gastrulation, and organogenesis, similar to the diplontic life cycle.
Spore Formation:
- Once the diploid embryo has fully developed, it undergoes a process of spore formation.
- The sporophyte undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
- These spores are released into the environment and give rise to the haploid gametophyte generation.
Gametophyte Development:
- The haploid spores
In organisms with a diplontic life cycle, the zygote undergoes development to form a multicellular diploid organism. This type of life cycle is observed in most animals, including humans, where the zygote develops into an adult organism directly without any alternation of generations.
Fertilization:
- The diplontic life cycle begins with the fusion of gametes during fertilization.
- This fusion results in the formation of a zygote, which is a diploid cell with a complete set of chromosomes.
Cleavage:
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a process called cleavage.
- Cleavage involves a series of rapid cell divisions without any significant growth in size.
- These divisions lead to the formation of a multicellular embryo consisting of a cluster of cells called blastomeres.
Gastrulation:
- Gastrulation is the next crucial step in zygote development.
- During gastrulation, the blastomeres rearrange and differentiate to form three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- The ectoderm gives rise to the skin, nervous system, and sensory organs.
- The endoderm develops into the digestive system and internal organs.
- The mesoderm forms the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, and reproductive organs.
Organogenesis:
- Following gastrulation, organogenesis occurs, which involves the formation and differentiation of specific organs and tissues.
- Various signals and interactions between cells and tissues guide the development of specific structures.
- Organs such as the heart, brain, lungs, and liver begin to form during this stage.
Growth and Maturation:
- As the embryo continues to develop, it undergoes growth in size and complexity.
- The cells divide, differentiate, and organize into specific tissues and organs.
- This growth and maturation process continues until the organism reaches adulthood.
Development in Zygote in Organisms with Haplo-Diplontic Life Cycle:
In organisms with a haplo-diplontic life cycle, there are two distinct multicellular stages: the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte. The zygote plays a crucial role in the development of both stages.
Fertilization:
- Similar to the diplontic life cycle, the haplo-diplontic life cycle also begins with the fusion of gametes during fertilization.
- The fusion of a haploid egg and a haploid sperm results in the formation of a diploid zygote.
Embryo Development:
- The diploid zygote undergoes development to form a multicellular diploid embryo, which represents the sporophyte generation.
- The embryo develops through various stages, including cleavage, gastrulation, and organogenesis, similar to the diplontic life cycle.
Spore Formation:
- Once the diploid embryo has fully developed, it undergoes a process of spore formation.
- The sporophyte undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
- These spores are released into the environment and give rise to the haploid gametophyte generation.
Gametophyte Development:
- The haploid spores
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle?
Question Description
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle?.
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle?.
Solutions for What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle?, a detailed solution for What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? has been provided alongside types of What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What kind of development takes place in zygote in organisms with diplontic and haplo-diplontic life cycle? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























