Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > What is enzymes?
Start Learning for Free
What is enzymes?
Community Answer
What is enzymes?
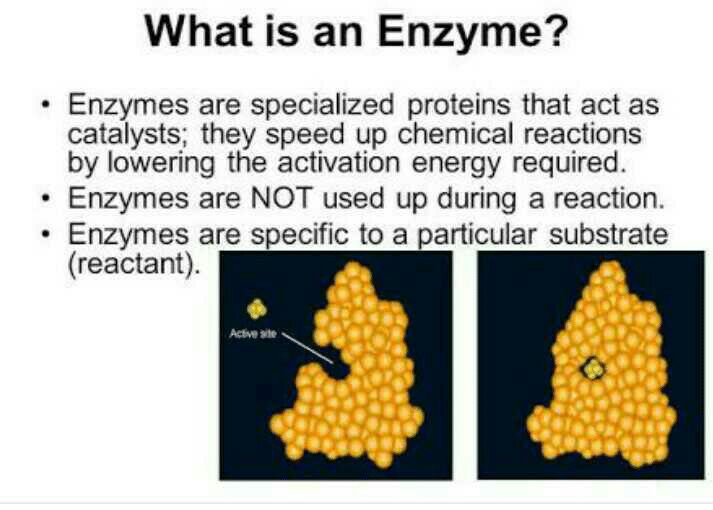
Enzymes are biological molecules that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms. They are important in maintaining the metabolic processes of cells and are involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions.
Structure and Function
Enzymes are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also possess catalytic activity. The three-dimensional structure of enzymes is critical to their function, as they must be able to bind to specific substrates and catalyze chemical reactions.
Types of Enzymes
There are several different types of enzymes, including:
1. Hydrolases - catalyze the hydrolysis of various substrates
2. Oxidoreductases - catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
3. Transferases - transfer functional groups from one molecule to another
4. Isomerases - catalyze the rearrangement of molecules
5. Ligases - join two molecules together
Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme activity is often measured in terms of its kinetics, which involves measuring the rate of a reaction as a function of substrate concentration. Enzymes typically exhibit a saturation effect, where the rate of a reaction increases with substrate concentration until a maximum rate is achieved.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Enzyme activity can be affected by several factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors or activators. Enzymes typically have an optimal temperature and pH range, outside of which their activity can be decreased or even completely inhibited.
Applications of Enzymes
Enzymes are used in a wide range of applications, including:
1. Industrial processes, such as the production of biofuels and food processing
2. Medical diagnostics and therapeutics
3. Bioremediation and environmental cleanup
4. Scientific research, such as in molecular biology and biochemistry.
Overall, enzymes are essential biological molecules that play a critical role in maintaining the metabolic processes of cells and are involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions.
Structure and Function
Enzymes are typically proteins, although some RNA molecules also possess catalytic activity. The three-dimensional structure of enzymes is critical to their function, as they must be able to bind to specific substrates and catalyze chemical reactions.
Types of Enzymes
There are several different types of enzymes, including:
1. Hydrolases - catalyze the hydrolysis of various substrates
2. Oxidoreductases - catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
3. Transferases - transfer functional groups from one molecule to another
4. Isomerases - catalyze the rearrangement of molecules
5. Ligases - join two molecules together
Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme activity is often measured in terms of its kinetics, which involves measuring the rate of a reaction as a function of substrate concentration. Enzymes typically exhibit a saturation effect, where the rate of a reaction increases with substrate concentration until a maximum rate is achieved.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Enzyme activity can be affected by several factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors or activators. Enzymes typically have an optimal temperature and pH range, outside of which their activity can be decreased or even completely inhibited.
Applications of Enzymes
Enzymes are used in a wide range of applications, including:
1. Industrial processes, such as the production of biofuels and food processing
2. Medical diagnostics and therapeutics
3. Bioremediation and environmental cleanup
4. Scientific research, such as in molecular biology and biochemistry.
Overall, enzymes are essential biological molecules that play a critical role in maintaining the metabolic processes of cells and are involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
What is enzymes?
Question Description
What is enzymes? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What is enzymes? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is enzymes?.
What is enzymes? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What is enzymes? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is enzymes?.
Solutions for What is enzymes? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is enzymes? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is enzymes?, a detailed solution for What is enzymes? has been provided alongside types of What is enzymes? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is enzymes? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.