Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > State 3 differences between linear motion and...
Start Learning for Free
State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.?
Most Upvoted Answer
State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.?
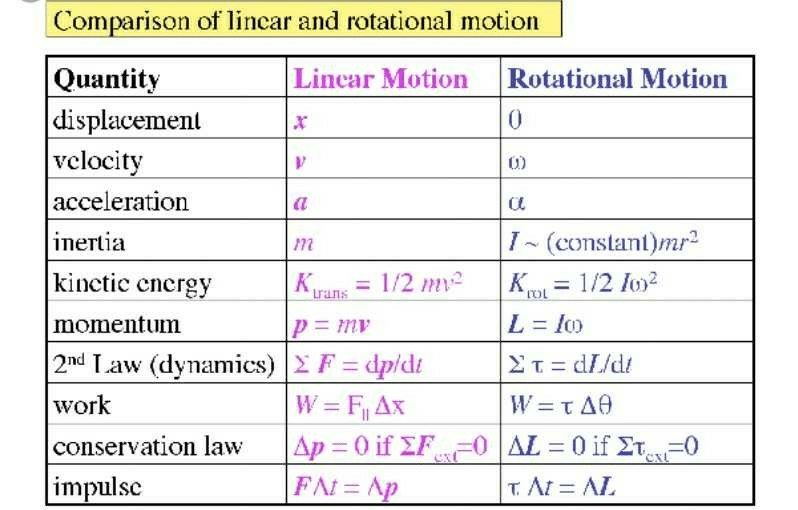
Community Answer
State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.?
**Differences Between Linear Motion and Circular Motion**
Linear motion and circular motion are two fundamental types of motion observed in physics. While linear motion occurs in a straight line, circular motion revolves around a fixed axis. Here are three key differences between linear motion and circular motion:
**1. Path and Direction:**
Linear Motion:
- In linear motion, an object moves along a straight line or path.
- The direction of linear motion remains constant throughout the movement.
- Examples of linear motion include a car moving in a straight line, a ball thrown vertically upwards, or a person walking in a straight line.
Circular Motion:
- In circular motion, an object moves in a circular path around a fixed axis.
- The direction of circular motion constantly changes as the object continuously rotates.
- Examples of circular motion include a satellite orbiting the Earth, a spinning top, or a cyclist moving along a curved path.
**2. Velocity and Acceleration:**
Linear Motion:
- In linear motion, velocity refers to the speed of an object in a particular direction.
- Acceleration in linear motion is the rate of change of velocity.
- The velocity and acceleration vectors in linear motion are parallel or anti-parallel to each other.
- The magnitude of velocity and acceleration can be easily determined using formulas and equations.
Circular Motion:
- In circular motion, velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position around the circular path.
- Acceleration in circular motion is the rate of change of velocity, but it also includes a change in direction.
- The velocity and acceleration vectors in circular motion are perpendicular to each other.
- Determining the magnitude of velocity and acceleration in circular motion requires the understanding of concepts such as centripetal acceleration and tangential velocity.
**3. Forces Involved:**
Linear Motion:
- In linear motion, forces acting on an object can be applied in any direction along the straight path.
- Forces like friction, gravity, and applied force can affect the motion of an object in linear motion.
- The net force acting on the object determines its acceleration and change in velocity.
Circular Motion:
- In circular motion, a centripetal force is required to keep an object moving along the circular path.
- Centripetal force is always directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for changing the direction of velocity.
- Without a centripetal force, an object in circular motion would move tangentially away from the circular path.
- The magnitude of the centripetal force can be calculated using the mass of the object, its velocity, and the radius of the circular path.
In conclusion, linear motion and circular motion differ in terms of their path and direction, velocity and acceleration vectors, and the forces involved. Understanding these differences is crucial for analyzing and solving problems related to motion in various physical scenarios.
Linear motion and circular motion are two fundamental types of motion observed in physics. While linear motion occurs in a straight line, circular motion revolves around a fixed axis. Here are three key differences between linear motion and circular motion:
**1. Path and Direction:**
Linear Motion:
- In linear motion, an object moves along a straight line or path.
- The direction of linear motion remains constant throughout the movement.
- Examples of linear motion include a car moving in a straight line, a ball thrown vertically upwards, or a person walking in a straight line.
Circular Motion:
- In circular motion, an object moves in a circular path around a fixed axis.
- The direction of circular motion constantly changes as the object continuously rotates.
- Examples of circular motion include a satellite orbiting the Earth, a spinning top, or a cyclist moving along a curved path.
**2. Velocity and Acceleration:**
Linear Motion:
- In linear motion, velocity refers to the speed of an object in a particular direction.
- Acceleration in linear motion is the rate of change of velocity.
- The velocity and acceleration vectors in linear motion are parallel or anti-parallel to each other.
- The magnitude of velocity and acceleration can be easily determined using formulas and equations.
Circular Motion:
- In circular motion, velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position around the circular path.
- Acceleration in circular motion is the rate of change of velocity, but it also includes a change in direction.
- The velocity and acceleration vectors in circular motion are perpendicular to each other.
- Determining the magnitude of velocity and acceleration in circular motion requires the understanding of concepts such as centripetal acceleration and tangential velocity.
**3. Forces Involved:**
Linear Motion:
- In linear motion, forces acting on an object can be applied in any direction along the straight path.
- Forces like friction, gravity, and applied force can affect the motion of an object in linear motion.
- The net force acting on the object determines its acceleration and change in velocity.
Circular Motion:
- In circular motion, a centripetal force is required to keep an object moving along the circular path.
- Centripetal force is always directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for changing the direction of velocity.
- Without a centripetal force, an object in circular motion would move tangentially away from the circular path.
- The magnitude of the centripetal force can be calculated using the mass of the object, its velocity, and the radius of the circular path.
In conclusion, linear motion and circular motion differ in terms of their path and direction, velocity and acceleration vectors, and the forces involved. Understanding these differences is crucial for analyzing and solving problems related to motion in various physical scenarios.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Question Description
State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.?.
State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.?.
Solutions for State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.?, a detailed solution for State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? has been provided alongside types of State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice State 3 differences between linear motion and circular motion.? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















