Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Which one of the following is correct?The eff...
Start Learning for Free
Which one of the following is correct?
The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment with
The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment with
- a)Free convection
- b)Forced convection
- c)Radiation
- d)Convection and radiation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will ...
Ans. (a) The effectiveness of a fin can also be characterized as
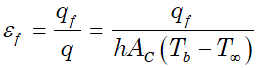

It is a ratio of the thermal resistance due to convection to the thermal resistance
of a fin. In order to enhance heat transfer, the fin's resistance should be lower
than that of the resistance due only to convection.
of a fin. In order to enhance heat transfer, the fin's resistance should be lower
than that of the resistance due only to convection.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will ...
The effectiveness of a fin refers to its ability to transfer heat from a solid surface to a surrounding fluid. Fins are commonly used in many engineering applications to enhance heat transfer in systems such as heat exchangers, air conditioning units, and electronic cooling devices. The effectiveness of a fin is influenced by various factors, including the type of heat transfer mechanism present in the environment.
In this case, the question asks about the effectiveness of a fin in different heat transfer environments: free convection, forced convection, radiation, and convection combined with radiation. Let's analyze each option to understand which one would result in the maximum effectiveness of a fin.
1. Free convection:
- Free convection occurs when heat is transferred through a fluid medium (such as air or liquid) due to natural buoyancy forces.
- In free convection, the fluid motion is driven solely by density differences caused by temperature variations.
- The effectiveness of a fin in free convection is generally higher compared to other mechanisms because the natural fluid motion enhances heat transfer.
- This is because the convective fluid motion helps to remove the boundary layer of stagnant fluid near the fin surface, allowing fresh fluid to come in contact with the fin and carry away heat more efficiently.
2. Forced convection:
- Forced convection occurs when heat is transferred through a fluid medium by external means such as a fan or pump.
- In forced convection, the fluid motion is artificially induced, leading to higher heat transfer rates compared to free convection.
- However, the effectiveness of a fin in forced convection is generally lower than in free convection.
- This is because the forced fluid motion tends to create a thinner boundary layer near the fin surface, reducing the contact area between the fin and the fluid and limiting heat transfer.
3. Radiation:
- Radiation is a heat transfer mechanism that does not require a medium for heat transfer.
- Instead, heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves (i.e., thermal radiation) from a hotter surface to a cooler surface.
- The effectiveness of a fin in radiation depends on the emissivity of the fin material and its surroundings.
- Generally, radiation heat transfer is less effective than convection heat transfer, especially when the temperature difference between the fin and the fluid is large.
4. Convection and radiation:
- When both convection and radiation are present, the effectiveness of a fin depends on the relative contributions of each mechanism.
- In most cases, convection dominates over radiation, especially at lower temperature differences.
- Therefore, the effectiveness of a fin in this case would be lower compared to free convection alone.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'A' - the effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment with free convection. This is because free convection enhances heat transfer by promoting fluid motion and reducing the boundary layer thickness, resulting in improved contact between the fin and the fluid.
In this case, the question asks about the effectiveness of a fin in different heat transfer environments: free convection, forced convection, radiation, and convection combined with radiation. Let's analyze each option to understand which one would result in the maximum effectiveness of a fin.
1. Free convection:
- Free convection occurs when heat is transferred through a fluid medium (such as air or liquid) due to natural buoyancy forces.
- In free convection, the fluid motion is driven solely by density differences caused by temperature variations.
- The effectiveness of a fin in free convection is generally higher compared to other mechanisms because the natural fluid motion enhances heat transfer.
- This is because the convective fluid motion helps to remove the boundary layer of stagnant fluid near the fin surface, allowing fresh fluid to come in contact with the fin and carry away heat more efficiently.
2. Forced convection:
- Forced convection occurs when heat is transferred through a fluid medium by external means such as a fan or pump.
- In forced convection, the fluid motion is artificially induced, leading to higher heat transfer rates compared to free convection.
- However, the effectiveness of a fin in forced convection is generally lower than in free convection.
- This is because the forced fluid motion tends to create a thinner boundary layer near the fin surface, reducing the contact area between the fin and the fluid and limiting heat transfer.
3. Radiation:
- Radiation is a heat transfer mechanism that does not require a medium for heat transfer.
- Instead, heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves (i.e., thermal radiation) from a hotter surface to a cooler surface.
- The effectiveness of a fin in radiation depends on the emissivity of the fin material and its surroundings.
- Generally, radiation heat transfer is less effective than convection heat transfer, especially when the temperature difference between the fin and the fluid is large.
4. Convection and radiation:
- When both convection and radiation are present, the effectiveness of a fin depends on the relative contributions of each mechanism.
- In most cases, convection dominates over radiation, especially at lower temperature differences.
- Therefore, the effectiveness of a fin in this case would be lower compared to free convection alone.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'A' - the effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment with free convection. This is because free convection enhances heat transfer by promoting fluid motion and reducing the boundary layer thickness, resulting in improved contact between the fin and the fluid.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which one of the following is correct?The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment witha)Free convectionb)Forced convectionc)Radiationd)Convection and radiationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















