Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of b...
Start Learning for Free
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many...
Most Upvoted Answer
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many...
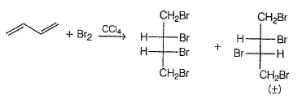
The reaction between 1,3-butadiene and excess bromine in CCI4 can lead to the formation of multiple tetrabromides. Let's break down the reaction and identify the different products that can be formed.
1. Reaction overview:
1,3-butadiene (C4H6) is a conjugated diene, which means it has alternating double bonds. When it reacts with bromine (Br2) in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), addition reactions occur at the double bonds.
2. Addition reactions:
In the presence of excess bromine, two types of addition reactions can occur at the double bonds of 1,3-butadiene:
a. Electrophilic addition: Bromine acts as an electrophile, attacking the electron-rich double bonds of the butadiene molecule. This leads to the formation of bromonium ions, which can then react with bromine or other nucleophiles.
b. Radical addition: Bromine can also undergo radical addition, where one of the bromine atoms is split into a bromine radical. This radical can then react with the double bonds of butadiene, resulting in the formation of a tetrabromide.
3. Possible tetrabromides:
Based on the addition reactions described above, three different tetrabromides can be formed:
a. 1,2,3,4-tetrabromobutane: This tetrabromide is formed when two bromine molecules add to the double bonds of 1,3-butadiene, resulting in the addition of four bromine atoms.
b. 1,2,4,5-tetrabromobutane: This tetrabromide is formed when one bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 1 and 4 of 1,3-butadiene, while the other bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 2 and 3.
c. 1,4-dibromo-2,3-dibromobutane: This tetrabromide is formed when one bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 1 and 4 of 1,3-butadiene, while the other bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 2 and 3. In this case, the bromine atoms are added in a different arrangement compared to the previous tetrabromide.
4. Conclusion:
In summary, the reaction between 1,3-butadiene and excess bromine in CCl4 can result in the formation of three different tetrabromides: 1,2,3,4-tetrabromobutane, 1,2,4,5-tetrabromobutane, and 1,4-dibromo-2,3-dibromobutane. These tetrabromides are formed due to the different addition reactions that can occur at the double bonds of 1,3-butadiene.
1. Reaction overview:
1,3-butadiene (C4H6) is a conjugated diene, which means it has alternating double bonds. When it reacts with bromine (Br2) in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), addition reactions occur at the double bonds.
2. Addition reactions:
In the presence of excess bromine, two types of addition reactions can occur at the double bonds of 1,3-butadiene:
a. Electrophilic addition: Bromine acts as an electrophile, attacking the electron-rich double bonds of the butadiene molecule. This leads to the formation of bromonium ions, which can then react with bromine or other nucleophiles.
b. Radical addition: Bromine can also undergo radical addition, where one of the bromine atoms is split into a bromine radical. This radical can then react with the double bonds of butadiene, resulting in the formation of a tetrabromide.
3. Possible tetrabromides:
Based on the addition reactions described above, three different tetrabromides can be formed:
a. 1,2,3,4-tetrabromobutane: This tetrabromide is formed when two bromine molecules add to the double bonds of 1,3-butadiene, resulting in the addition of four bromine atoms.
b. 1,2,4,5-tetrabromobutane: This tetrabromide is formed when one bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 1 and 4 of 1,3-butadiene, while the other bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 2 and 3.
c. 1,4-dibromo-2,3-dibromobutane: This tetrabromide is formed when one bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 1 and 4 of 1,3-butadiene, while the other bromine molecule adds to the double bond at positions 2 and 3. In this case, the bromine atoms are added in a different arrangement compared to the previous tetrabromide.
4. Conclusion:
In summary, the reaction between 1,3-butadiene and excess bromine in CCl4 can result in the formation of three different tetrabromides: 1,2,3,4-tetrabromobutane, 1,2,4,5-tetrabromobutane, and 1,4-dibromo-2,3-dibromobutane. These tetrabromides are formed due to the different addition reactions that can occur at the double bonds of 1,3-butadiene.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?.
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If 1, 3-butadiene is treated with excess of bromine in CCI4 , how many different tetrabromides would be formed?Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















