Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Questions > A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is...
Start Learning for Free
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?
- a)15
- b)25
- c)35
- d)45
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data...

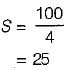
Most Upvoted Answer
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data...
Understanding Data Transfer Rates
- The device has a data transfer rate of 10 KB/sec, which translates to 10,000 bytes per second.
- This means that the time to transfer one byte is 1/10,000 seconds or 0.1 milliseconds (100 microseconds).
Interrupt Overhead Calculation
- The interrupt overhead is given as 4 microseconds. This is the time taken for the CPU to handle an interrupt.
- When operating in interrupt mode, the CPU can continue executing other tasks while waiting for data to arrive, minimizing wasted cycles.
Comparing Interrupt Mode vs. Program Controlled Mode
- Program Controlled Mode: The CPU continuously polls the device to check if data is ready, leading to wasted CPU cycles.
- Time spent polling: If we assume a simple polling mechanism takes a significant amount of time per byte, say 100 microseconds (for example), then the CPU is busy polling and not doing useful work during this time.
- Interrupt Mode: The CPU only reacts when the device signals that data is ready.
- Time spent on handling an interrupt: 4 microseconds.
- Effective data transfer time per byte (including the overhead): 4 microseconds (interrupt) + 100 microseconds (transfer time) = 104 microseconds.
Performance Gain Calculation
- Time per byte in Program Controlled Mode: 100 microseconds.
- Time per byte in Interrupt Mode: 104 microseconds.
- To find the performance gain, we calculate the ratio of the two modes:
Performance Gain = (Time in Program Controlled Mode) / (Time in Interrupt Mode)
= 100 / 104 = 0.9615 (approx. 1.04 times faster)
- This means that operating in interrupt mode offers significant efficiency as it frees the CPU to perform other tasks, effectively yielding a performance gain of about 25%.
Conclusion
- The minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over program-controlled mode is approximately 25%, confirming option 'B' as correct.
- The device has a data transfer rate of 10 KB/sec, which translates to 10,000 bytes per second.
- This means that the time to transfer one byte is 1/10,000 seconds or 0.1 milliseconds (100 microseconds).
Interrupt Overhead Calculation
- The interrupt overhead is given as 4 microseconds. This is the time taken for the CPU to handle an interrupt.
- When operating in interrupt mode, the CPU can continue executing other tasks while waiting for data to arrive, minimizing wasted cycles.
Comparing Interrupt Mode vs. Program Controlled Mode
- Program Controlled Mode: The CPU continuously polls the device to check if data is ready, leading to wasted CPU cycles.
- Time spent polling: If we assume a simple polling mechanism takes a significant amount of time per byte, say 100 microseconds (for example), then the CPU is busy polling and not doing useful work during this time.
- Interrupt Mode: The CPU only reacts when the device signals that data is ready.
- Time spent on handling an interrupt: 4 microseconds.
- Effective data transfer time per byte (including the overhead): 4 microseconds (interrupt) + 100 microseconds (transfer time) = 104 microseconds.
Performance Gain Calculation
- Time per byte in Program Controlled Mode: 100 microseconds.
- Time per byte in Interrupt Mode: 104 microseconds.
- To find the performance gain, we calculate the ratio of the two modes:
Performance Gain = (Time in Program Controlled Mode) / (Time in Interrupt Mode)
= 100 / 104 = 0.9615 (approx. 1.04 times faster)
- This means that operating in interrupt mode offers significant efficiency as it frees the CPU to perform other tasks, effectively yielding a performance gain of about 25%.
Conclusion
- The minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over program-controlled mode is approximately 25%, confirming option 'B' as correct.
Attention Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Computer Science Engineering (CSE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Computer Science Engineering (CSE).

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Similar Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Doubts
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A device with data transfer rate 10 KB/sec is connected to a CPU. Data is transferred byte- wise. Let the interrupt overhead be 4 μsec. The byte transfer time between the device interface register and CPU or memory is negligible. What is the minimum performance gain of operating the device under interrupt mode over operating it under program controlled mode?a)15b)25c)35d)45Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Computer Science Engineering (CSE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























