Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > Explain me the spore formation.?
Start Learning for Free
Explain me the spore formation.?
Verified Answer
Explain me the spore formation.?
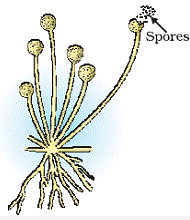
Spore formation is a method of asexual reproduction.
Plants like ferns, moss, fungi reproduce by this method.
Spores are unicellular reproductive bodies present in sac called sporangia.
When spores mature sporangia burst and spores are carried to different location by air, wind, water.
When spores fall on a suitable ground, they germinate and develop new individuals.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain me the spore formation.?
In this process organism store their re-generation cell or SPORE in a knob like structure called sprongia, when the condition are favourable that sprongia brust and spread spore into air these SPORE grow to produce new life. ✌️✋Examples Rhizopus, monera, algae etc 😊😋😆😊😆
Community Answer
Explain me the spore formation.?
Spore Formation
Spore formation is a method of reproduction that is utilized by certain organisms, including bacteria, fungi, algae, and some protozoans. It is a process by which these organisms produce specialized cells called spores, which are capable of developing into new individuals under favorable conditions. Spore formation plays a crucial role in the survival and dispersal of these organisms.
Process of Spore Formation
Spore formation typically involves several stages, which are as follows:
1. Initiation: The process of spore formation begins when the parent organism, also known as the sporophyte, produces specialized structures called sporangia or sporocytes. These structures serve as the site for spore development.
2. Meiosis: Within the sporangia, meiosis takes place. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the formation of haploid cells. These haploid cells are the precursor cells for spores.
3. Spore Development: The haploid cells undergo further development within the sporangia, eventually transforming into mature spores. This process involves the accumulation of reserve food materials and the formation of a protective outer layer.
4. Spore Release: Once the spores are mature, they are released from the sporangia. This can occur through various mechanisms depending on the organism. For example, in fungi, spores are often released into the air, while in bacteria, they may be released through cell lysis or specialized structures called sporangia.
5. Dispersal and Germination: The released spores are dispersed by external factors such as wind, water, or animals. They can survive harsh environmental conditions and remain dormant until they encounter suitable conditions for germination. When favorable conditions are present, spores germinate and develop into new individuals.
Significance of Spore Formation
Spore formation offers several advantages to organisms that utilize this reproductive strategy:
1. Survival: Spores are highly resistant to adverse environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, desiccation, and high radiation levels. This allows organisms to survive in harsh habitats where other forms of reproduction may not be feasible.
2. Dispersal: Spores are lightweight and easily dispersed by wind, water, or animals. This enables organisms to colonize new habitats and expand their range.
3. Genetic Variation: Meiosis during spore formation leads to genetic recombination, resulting in the production of genetically diverse spores. This promotes adaptation and evolution within populations.
4. Efficient Reproduction: Spore formation allows organisms to produce a large number of offspring in a relatively short period. This increases the chances of survival and successful reproduction.
In conclusion, spore formation is an essential reproductive strategy employed by various organisms. It involves the production of specialized cells called spores, which can withstand adverse conditions and disperse to new locations. Spore formation ensures the survival, dispersal, and genetic variation of these organisms, contributing to their evolutionary success.
Spore formation is a method of reproduction that is utilized by certain organisms, including bacteria, fungi, algae, and some protozoans. It is a process by which these organisms produce specialized cells called spores, which are capable of developing into new individuals under favorable conditions. Spore formation plays a crucial role in the survival and dispersal of these organisms.
Process of Spore Formation
Spore formation typically involves several stages, which are as follows:
1. Initiation: The process of spore formation begins when the parent organism, also known as the sporophyte, produces specialized structures called sporangia or sporocytes. These structures serve as the site for spore development.
2. Meiosis: Within the sporangia, meiosis takes place. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the formation of haploid cells. These haploid cells are the precursor cells for spores.
3. Spore Development: The haploid cells undergo further development within the sporangia, eventually transforming into mature spores. This process involves the accumulation of reserve food materials and the formation of a protective outer layer.
4. Spore Release: Once the spores are mature, they are released from the sporangia. This can occur through various mechanisms depending on the organism. For example, in fungi, spores are often released into the air, while in bacteria, they may be released through cell lysis or specialized structures called sporangia.
5. Dispersal and Germination: The released spores are dispersed by external factors such as wind, water, or animals. They can survive harsh environmental conditions and remain dormant until they encounter suitable conditions for germination. When favorable conditions are present, spores germinate and develop into new individuals.
Significance of Spore Formation
Spore formation offers several advantages to organisms that utilize this reproductive strategy:
1. Survival: Spores are highly resistant to adverse environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, desiccation, and high radiation levels. This allows organisms to survive in harsh habitats where other forms of reproduction may not be feasible.
2. Dispersal: Spores are lightweight and easily dispersed by wind, water, or animals. This enables organisms to colonize new habitats and expand their range.
3. Genetic Variation: Meiosis during spore formation leads to genetic recombination, resulting in the production of genetically diverse spores. This promotes adaptation and evolution within populations.
4. Efficient Reproduction: Spore formation allows organisms to produce a large number of offspring in a relatively short period. This increases the chances of survival and successful reproduction.
In conclusion, spore formation is an essential reproductive strategy employed by various organisms. It involves the production of specialized cells called spores, which can withstand adverse conditions and disperse to new locations. Spore formation ensures the survival, dispersal, and genetic variation of these organisms, contributing to their evolutionary success.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
Explain me the spore formation.?
Question Description
Explain me the spore formation.? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Explain me the spore formation.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain me the spore formation.?.
Explain me the spore formation.? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Explain me the spore formation.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain me the spore formation.?.
Solutions for Explain me the spore formation.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain me the spore formation.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain me the spore formation.?, a detailed solution for Explain me the spore formation.? has been provided alongside types of Explain me the spore formation.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain me the spore formation.? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























