Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction d...
Start Learning for Free
The barrier voltage (V0 or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect of
- a)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.
- b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.
- c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.
- d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)th...
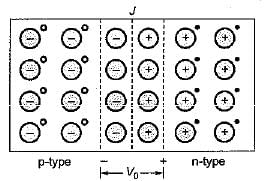
Due to the density gradient across the junction, holes will initially diffuse to the right across the junction, and electrons to the left. The positive holes which neutralizes the acceptor ions near the junction in the p-type silicon disappears as a result of combination with electrons which have diffused across the junction. Similarly, electrons in n-type semiconductor combines with holes.
Most Upvoted Answer
The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)th...
The barrier voltage (V0 or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect of:
The correct answer is option 'D': the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.
Explanation:
A junction diode is formed by bringing together a p-type semiconductor material and an n-type semiconductor material. The p-side is doped with acceptor impurities, creating positively charged holes, while the n-side is doped with donor impurities, creating negatively charged electrons. When these two materials are brought together to form a junction, a depletion region is formed at the interface.
Depletion Region:
The depletion region is a region near the junction where there are no free charge carriers. This region is created due to the diffusion of charge carriers from the p-side to the n-side and vice versa. As a result, positive ions are left behind on the n-side and negative ions are left behind on the p-side, creating an electric field that opposes further diffusion.
Barrier Voltage:
The barrier voltage, also known as the built-in potential (V0 or Vr), is the voltage difference across the junction that arises due to the presence of the depletion region. This voltage is necessary to maintain the equilibrium of charge carriers in the diode.
Recombination of Charge Carriers:
The barrier voltage is primarily the result of the recombination of charge carriers across the junction. When a positive hole from the p-side and a negative electron from the n-side come close to each other within the depletion region, they can recombine. This recombination process leaves behind positively charged ions on the n-side and negatively charged ions on the p-side.
Effect of Recombination:
The recombination of charge carriers creates a region near the junction with a net positive charge on the n-side and a net negative charge on the p-side. This results in the formation of a potential difference, known as the barrier voltage, which opposes the further flow of charge carriers across the junction.
Conclusion:
In summary, the barrier voltage in a junction diode is primarily the result of the recombination of charge carriers across the junction. This recombination process leaves behind oppositely charged ions, creating a potential difference that acts as a barrier to the flow of current in the reverse biased condition of the diode.
The correct answer is option 'D': the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.
Explanation:
A junction diode is formed by bringing together a p-type semiconductor material and an n-type semiconductor material. The p-side is doped with acceptor impurities, creating positively charged holes, while the n-side is doped with donor impurities, creating negatively charged electrons. When these two materials are brought together to form a junction, a depletion region is formed at the interface.
Depletion Region:
The depletion region is a region near the junction where there are no free charge carriers. This region is created due to the diffusion of charge carriers from the p-side to the n-side and vice versa. As a result, positive ions are left behind on the n-side and negative ions are left behind on the p-side, creating an electric field that opposes further diffusion.
Barrier Voltage:
The barrier voltage, also known as the built-in potential (V0 or Vr), is the voltage difference across the junction that arises due to the presence of the depletion region. This voltage is necessary to maintain the equilibrium of charge carriers in the diode.
Recombination of Charge Carriers:
The barrier voltage is primarily the result of the recombination of charge carriers across the junction. When a positive hole from the p-side and a negative electron from the n-side come close to each other within the depletion region, they can recombine. This recombination process leaves behind positively charged ions on the n-side and negatively charged ions on the p-side.
Effect of Recombination:
The recombination of charge carriers creates a region near the junction with a net positive charge on the n-side and a net negative charge on the p-side. This results in the formation of a potential difference, known as the barrier voltage, which opposes the further flow of charge carriers across the junction.
Conclusion:
In summary, the barrier voltage in a junction diode is primarily the result of the recombination of charge carriers across the junction. This recombination process leaves behind oppositely charged ions, creating a potential difference that acts as a barrier to the flow of current in the reverse biased condition of the diode.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The barrier voltage (V0or Vr) in a junction diode is the effect ofa)the voltage needed to make the semiconductor material behave as a conductor.b)the emf required to move the holes fast enough to have the mobility equal to that of the electrons.c)the p-side and n-side of the junction forming a battery.d)the recombination of charge carriers across the junction leaving behind the opposite charged ions.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























