Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > With the help of ray diagram illustrate the c...
Start Learning for Free
With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length?
Most Upvoted Answer
With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature ...
Community Answer
With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature ...
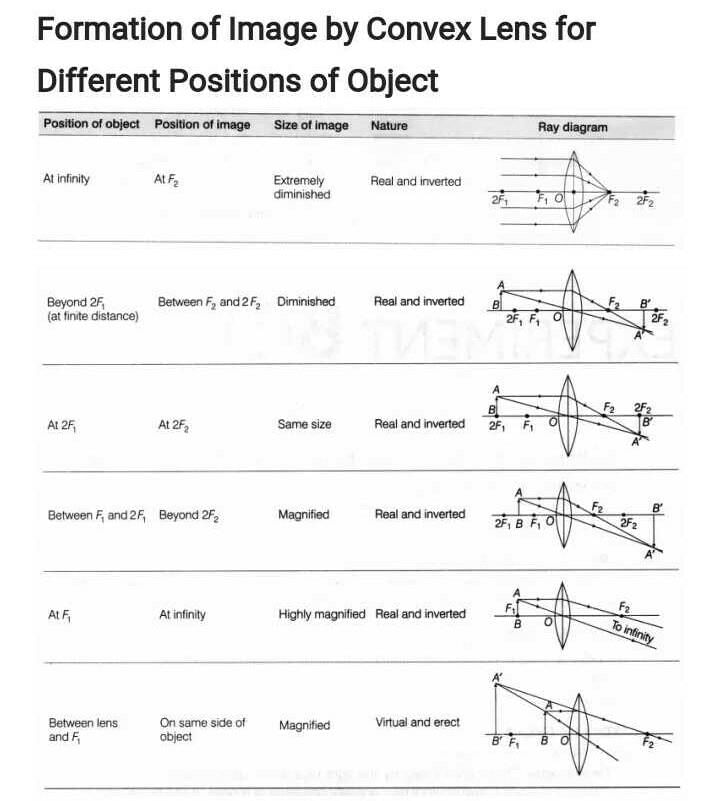
Change in Position, Nature and Size of Image Formed by Replacing Convex Lens with Concave Lens of Same Focal Length
Ray Diagram for Convex Lens
A convex lens is a converging lens which forms a real and inverted image when the object is placed beyond its focal length and a virtual and erect image when the object is placed within its focal length. The ray diagram for a convex lens is as follows:
Ray Diagram for Concave Lens
A concave lens is a diverging lens which always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image. The ray diagram for a concave lens is as follows:
Difference in Image Formation
When a convex lens is replaced by a concave lens of the same focal length, there is a significant difference in the formation of the image. The image formed by the concave lens is always virtual, erect, and diminished, whereas the image formed by the convex lens can be real or virtual, inverted or erect, and magnified or diminished depending on the position of the object.
Effect on Position of Image
When a convex lens is replaced by a concave lens of the same focal length, the position of the image also changes. In the case of a convex lens, the position of the image depends on the position of the object, whereas in the case of a concave lens, the image is always formed on the same side as the object and closer to the lens.
Effect on Size of Image
The size of the image formed by a concave lens is always smaller than the size of the object, whereas the size of the image formed by a convex lens can be either larger or smaller than the size of the object depending on the position of the object.
Conclusion
To sum up, when a convex lens is replaced by a concave lens of the same focal length, the nature of the image formed changes from real/inverted or virtual/erect to always virtual/erect. The position of the image changes from being position-dependent to always being on the same side as the object and closer to the lens. The size of the image formed by the concave lens is always smaller than the size of the object, whereas the size of the image formed by the convex lens can be either larger or smaller than the size of the object depending on the position of the object.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Question Description
With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length?.
With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length?.
Solutions for With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length?, a detailed solution for With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? has been provided alongside types of With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice With the help of ray diagram illustrate the change in position nature and size of the image formed if the convex lens in replaced by concave lens of same focal length? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























