NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Differentiate between litter and detritus.?
Start Learning for Free
Differentiate between litter and detritus.?
Most Upvoted Answer
Differentiate between litter and detritus.?
Community Answer
Differentiate between litter and detritus.?
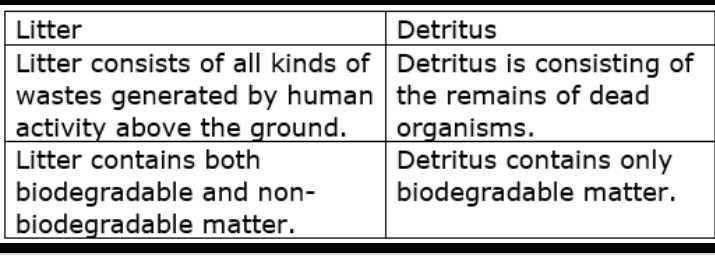
Litter:
Litter refers to the waste material that is improperly disposed of and is scattered or abandoned in public places such as streets, parks, or beaches. It includes various items such as plastic bags, bottles, food wrappers, cigarette butts, and other discarded objects that are not biodegradable. Litter is often a result of human activities and negligence, and it poses serious environmental and health hazards.
Detritus:
Detritus, on the other hand, is the organic matter that results from the decomposition or breakdown of dead plants, animals, or other organic materials. It primarily consists of decaying leaves, fallen branches, dead organisms, and other natural debris found in ecosystems. Detritus is an essential component of the ecosystem as it serves as a source of nutrients and energy for decomposers and detritivores, which play a crucial role in the nutrient cycling process.
Differences between Litter and Detritus:
1. Origin: Litter is mainly a result of human activities and is often intentionally or unintentionally discarded in public places. On the other hand, detritus is a natural byproduct of the decomposition process in ecosystems.
2. Composition: Litter primarily consists of non-biodegradable materials such as plastics, glass, and metals, while detritus consists of organic matter derived from dead plants, animals, and organic debris.
3. Effects on the Environment: Litter poses significant environmental hazards as it can pollute water bodies, harm wildlife, and disrupt ecosystems. It can also release harmful chemicals and contribute to air pollution. In contrast, detritus plays a vital role in nutrient cycling and supports the growth of plants and other organisms in the ecosystem.
4. Decomposition: Litter takes a long time to decompose, especially in the case of materials like plastics that can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. Detritus, however, undergoes the natural process of decomposition relatively quickly due to the action of organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and detritivores.
5. Management: Litter requires proper waste management practices such as recycling, waste reduction, and responsible disposal to minimize its negative impacts. Detritus, being a natural component of ecosystems, does not require specific management practices as it is broken down and recycled within the ecosystem itself.
In conclusion, while litter is the result of human activities and poses environmental hazards, detritus is a natural component of ecosystems that plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling. Managing litter and promoting responsible waste disposal practices is essential for maintaining a clean and healthy environment.
Litter refers to the waste material that is improperly disposed of and is scattered or abandoned in public places such as streets, parks, or beaches. It includes various items such as plastic bags, bottles, food wrappers, cigarette butts, and other discarded objects that are not biodegradable. Litter is often a result of human activities and negligence, and it poses serious environmental and health hazards.
Detritus:
Detritus, on the other hand, is the organic matter that results from the decomposition or breakdown of dead plants, animals, or other organic materials. It primarily consists of decaying leaves, fallen branches, dead organisms, and other natural debris found in ecosystems. Detritus is an essential component of the ecosystem as it serves as a source of nutrients and energy for decomposers and detritivores, which play a crucial role in the nutrient cycling process.
Differences between Litter and Detritus:
1. Origin: Litter is mainly a result of human activities and is often intentionally or unintentionally discarded in public places. On the other hand, detritus is a natural byproduct of the decomposition process in ecosystems.
2. Composition: Litter primarily consists of non-biodegradable materials such as plastics, glass, and metals, while detritus consists of organic matter derived from dead plants, animals, and organic debris.
3. Effects on the Environment: Litter poses significant environmental hazards as it can pollute water bodies, harm wildlife, and disrupt ecosystems. It can also release harmful chemicals and contribute to air pollution. In contrast, detritus plays a vital role in nutrient cycling and supports the growth of plants and other organisms in the ecosystem.
4. Decomposition: Litter takes a long time to decompose, especially in the case of materials like plastics that can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. Detritus, however, undergoes the natural process of decomposition relatively quickly due to the action of organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and detritivores.
5. Management: Litter requires proper waste management practices such as recycling, waste reduction, and responsible disposal to minimize its negative impacts. Detritus, being a natural component of ecosystems, does not require specific management practices as it is broken down and recycled within the ecosystem itself.
In conclusion, while litter is the result of human activities and poses environmental hazards, detritus is a natural component of ecosystems that plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling. Managing litter and promoting responsible waste disposal practices is essential for maintaining a clean and healthy environment.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Differentiate between litter and detritus.?
Question Description
Differentiate between litter and detritus.? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Differentiate between litter and detritus.? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Differentiate between litter and detritus.?.
Differentiate between litter and detritus.? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Differentiate between litter and detritus.? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Differentiate between litter and detritus.?.
Solutions for Differentiate between litter and detritus.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Differentiate between litter and detritus.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Differentiate between litter and detritus.?, a detailed solution for Differentiate between litter and detritus.? has been provided alongside types of Differentiate between litter and detritus.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Differentiate between litter and detritus.? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























