Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS ...
Start Learning for Free
what is AC generator
?Verified Answer
what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | N...
An AC generator is an electric generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in form of alternative emf or alternating current. AC generator works on the principle of ”Electromagnetic Induction”
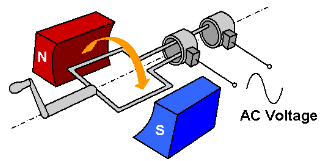
Parts of an AC Generator
An Ac generator consists of two poles i.e is the north pole and south pole of a magnet so that we can have a uniform magnetic field. There is also a coil which is rectangular in shape that is the armature. These coils are connected to the slip rings and attached to them are carbon brushes.
The slip rings are made of metal and are insulated from each other. The brushes are carbon brushes and one end of each brush connects to the ring and other connects to the circuit. The rectangular coils rotate about an axis which is perpendicular to the magnetic field. There is also a shaft which rotates rapidly. This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | N...
What is an AC Generator?
An AC generator, also known as an alternator, is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current (AC). It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a conductor moving through a magnetic field generates an electric current.
Key Components of an AC Generator:
- Rotor: The rotating part of the generator, usually consisting of coils of wire.
- Stator: The stationary part that contains the magnetic field, often created by either permanent magnets or electromagnets.
- Slip Rings: These are conductive rings that allow the rotor to maintain electrical contact with the external circuit while it spins.
Working Principle:
- When the rotor spins within the magnetic field, the motion induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the coils according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
- The generated current alternates direction because the rotor's position relative to the magnetic field changes continuously.
Types of AC Generators:
- Synchronous Generators: Operate at a constant speed, generating electricity in sync with the frequency of the power grid.
- Induction Generators: Generate electricity when driven above synchronous speed and are often used in wind turbines.
Applications of AC Generators:
- Power Plants: Used for generating electricity on a large scale.
- Backup Generators: Provide power during outages for homes and businesses.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Utilized in wind and hydroelectric power generation.
In summary, AC generators are crucial for modern electricity generation, providing a reliable and efficient means to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy for various applications.
An AC generator, also known as an alternator, is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current (AC). It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a conductor moving through a magnetic field generates an electric current.
Key Components of an AC Generator:
- Rotor: The rotating part of the generator, usually consisting of coils of wire.
- Stator: The stationary part that contains the magnetic field, often created by either permanent magnets or electromagnets.
- Slip Rings: These are conductive rings that allow the rotor to maintain electrical contact with the external circuit while it spins.
Working Principle:
- When the rotor spins within the magnetic field, the motion induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the coils according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
- The generated current alternates direction because the rotor's position relative to the magnetic field changes continuously.
Types of AC Generators:
- Synchronous Generators: Operate at a constant speed, generating electricity in sync with the frequency of the power grid.
- Induction Generators: Generate electricity when driven above synchronous speed and are often used in wind turbines.
Applications of AC Generators:
- Power Plants: Used for generating electricity on a large scale.
- Backup Generators: Provide power during outages for homes and businesses.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Utilized in wind and hydroelectric power generation.
In summary, AC generators are crucial for modern electricity generation, providing a reliable and efficient means to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy for various applications.
Attention Class 10 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 10 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 10.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |?
Question Description
what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |?.
what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |?.
Solutions for what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |?, a detailed solution for what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? has been provided alongside types of what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is AC generator Related: #10th PHYSICS | Reflection of Light | Numericals | PART- 13 | by Rajnish Kumar |? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























