Physics Exam > Physics Questions > Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons con...
Start Learning for Free
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B is
Select one:
Select one:
- a)42 K
- b)50 K
- c)30 K
- d)18 K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ...
A is free to move, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant pressure
∴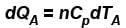 ...(i)
...(i)
B is held fixed, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant volume.
∴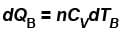 ...(ii)
...(ii)
But dQA = dQB (given)
∴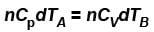
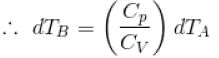
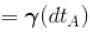 [
[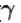 = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= (1.4) (30 K)
dTB = 42 K
The correct answer is: 42 K
∴
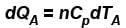 ...(i)
...(i)B is held fixed, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant volume.
∴
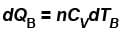 ...(ii)
...(ii)But dQA = dQB (given)
∴
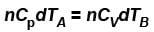
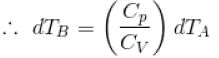
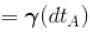 [
[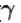 = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)= (1.4) (30 K)
dTB = 42 K
The correct answer is: 42 K
Most Upvoted Answer
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ...
A is free to move, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant pressure
∴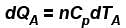 ...(i)
...(i)
B is held fixed, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant volume.
∴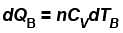 ...(ii)
...(ii)
But dQA = dQB (given)
∴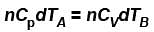
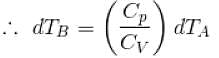
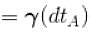 [
[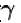 = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= (1.4) (30 K)
dTB = 42 K
The correct answer is: 42 K
∴
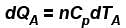 ...(i)
...(i)B is held fixed, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant volume.
∴
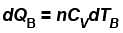 ...(ii)
...(ii)But dQA = dQB (given)
∴
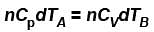
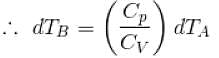
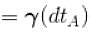 [
[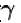 = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)= (1.4) (30 K)
dTB = 42 K
The correct answer is: 42 K
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ...
Understanding the Scenario
In this problem, we have two cylinders, A and B, containing an ideal diatomic gas at the same initial temperature (300 K). The key difference is that cylinder A has a movable piston, while cylinder B has a fixed piston.
Heat Transfer and Temperature Change
When heat is added to the gas in both cylinders:
- Cylinder A (Movable Piston): The gas expands, allowing the piston to move. This means that the system can do work on the piston. For an ideal diatomic gas, the specific heat at constant volume (Cv) is 5/2 R, and the specific heat at constant pressure (Cp) is 7/2 R. The temperature rise (ΔT) in cylinder A is given as 30 K.
- Cylinder B (Fixed Piston): Since the piston is fixed, the gas cannot expand freely and therefore cannot do work on the surroundings. In this case, all the heat added to the system contributes to increasing the internal energy of the gas, resulting in a temperature rise.
Comparative Analysis
The essential relationship between the heat added (Q), the change in internal energy (ΔU), and the temperature change (ΔT) can be summarized:
- For Cylinder A: Q = n * Cv * ΔT_A
- For Cylinder B: Q = n * Cp * ΔT_B
Given that the same amount of heat is added to both cylinders, the temperature change in the fixed piston cylinder (B) will be greater as it is not losing energy to do work.
Calculating the Temperature Rise in Cylinder B
Since the gas is diatomic and behaves ideally, the relationship of the heat capacities allows us to conclude:
- The ratio of temperature rises can be established: ΔT_B = (Cp/Cv) * ΔT_A
Using the values for diatomic gases, where Cp/Cv = 7/5:
- ΔT_B = (7/5) * 30 K = 42 K
Conclusion
Thus, the rise in temperature of the gas in cylinder B is 42 K. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
In this problem, we have two cylinders, A and B, containing an ideal diatomic gas at the same initial temperature (300 K). The key difference is that cylinder A has a movable piston, while cylinder B has a fixed piston.
Heat Transfer and Temperature Change
When heat is added to the gas in both cylinders:
- Cylinder A (Movable Piston): The gas expands, allowing the piston to move. This means that the system can do work on the piston. For an ideal diatomic gas, the specific heat at constant volume (Cv) is 5/2 R, and the specific heat at constant pressure (Cp) is 7/2 R. The temperature rise (ΔT) in cylinder A is given as 30 K.
- Cylinder B (Fixed Piston): Since the piston is fixed, the gas cannot expand freely and therefore cannot do work on the surroundings. In this case, all the heat added to the system contributes to increasing the internal energy of the gas, resulting in a temperature rise.
Comparative Analysis
The essential relationship between the heat added (Q), the change in internal energy (ΔU), and the temperature change (ΔT) can be summarized:
- For Cylinder A: Q = n * Cv * ΔT_A
- For Cylinder B: Q = n * Cp * ΔT_B
Given that the same amount of heat is added to both cylinders, the temperature change in the fixed piston cylinder (B) will be greater as it is not losing energy to do work.
Calculating the Temperature Rise in Cylinder B
Since the gas is diatomic and behaves ideally, the relationship of the heat capacities allows us to conclude:
- The ratio of temperature rises can be established: ΔT_B = (Cp/Cv) * ΔT_A
Using the values for diatomic gases, where Cp/Cv = 7/5:
- ΔT_B = (7/5) * 30 K = 42 K
Conclusion
Thus, the rise in temperature of the gas in cylinder B is 42 K. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B isSelect one:a)42 Kb)50 Kc)30 Kd)18 KCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















