JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the p...
Start Learning for Free
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :
- a)Phenolphthalein
- b)Alizarin
- c)Coumarin
- d)Fluorescein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H...
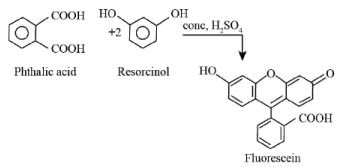
The formation of fluorescein takes place due to the reaction of phthalic acid with resorcinol as shown below.

Most Upvoted Answer
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H...
Phthalic acid, when reacted with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4, undergoes a condensation reaction to produce fluorescein.
Here is a detailed explanation of the reaction:
1. Condensation reaction:
The reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol is a condensation reaction. In this type of reaction, two molecules combine to form a larger molecule while eliminating a smaller molecule, such as water. In this case, the smaller molecule being eliminated is water.
2. Formation of fluorescein:
The reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol leads to the formation of fluorescein. Fluorescein is a fluorescent dye that is commonly used in biological and chemical applications. It is known for its bright green fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
3. Role of concentrated H2SO4:
Concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) acts as a catalyst in this reaction. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change itself. In this case, the concentrated sulfuric acid facilitates the reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol, leading to the formation of fluorescein.
4. Mechanism of the reaction:
The exact mechanism of the reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol is complex and involves multiple steps. However, the general mechanism can be summarized as follows:
- The acidic conditions provided by concentrated H2SO4 protonate the carbonyl group in phthalic acid, making it more reactive.
- The protonated carbonyl group then undergoes a nucleophilic attack by the hydroxyl group in resorcinol.
- This leads to the formation of an intermediate compound.
- The intermediate compound further undergoes dehydration, eliminating a water molecule and forming the final product, fluorescein.
In conclusion, the reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 results in the formation of fluorescein. This reaction is a condensation reaction and involves the elimination of water. The concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to facilitate the reaction.
Here is a detailed explanation of the reaction:
1. Condensation reaction:
The reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol is a condensation reaction. In this type of reaction, two molecules combine to form a larger molecule while eliminating a smaller molecule, such as water. In this case, the smaller molecule being eliminated is water.
2. Formation of fluorescein:
The reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol leads to the formation of fluorescein. Fluorescein is a fluorescent dye that is commonly used in biological and chemical applications. It is known for its bright green fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
3. Role of concentrated H2SO4:
Concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) acts as a catalyst in this reaction. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change itself. In this case, the concentrated sulfuric acid facilitates the reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol, leading to the formation of fluorescein.
4. Mechanism of the reaction:
The exact mechanism of the reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol is complex and involves multiple steps. However, the general mechanism can be summarized as follows:
- The acidic conditions provided by concentrated H2SO4 protonate the carbonyl group in phthalic acid, making it more reactive.
- The protonated carbonyl group then undergoes a nucleophilic attack by the hydroxyl group in resorcinol.
- This leads to the formation of an intermediate compound.
- The intermediate compound further undergoes dehydration, eliminating a water molecule and forming the final product, fluorescein.
In conclusion, the reaction between phthalic acid and resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 results in the formation of fluorescein. This reaction is a condensation reaction and involves the elimination of water. The concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to facilitate the reaction.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H...
Phthalic acid gets dehydrated on treatment with concentrated H2SO4 to form phthalic anhydride. Phthalic anhydride further reacts with resorsinol to form fluorescin
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Phthalic acid reacts with resorcinol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give :a)Phenolphthaleinb)Alizarinc)Coumarind)FluoresceinCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.