Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Questions > classical political theory Related: NCERT So...
Start Learning for Free
classical political theory
?Most Upvoted Answer
classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theor...
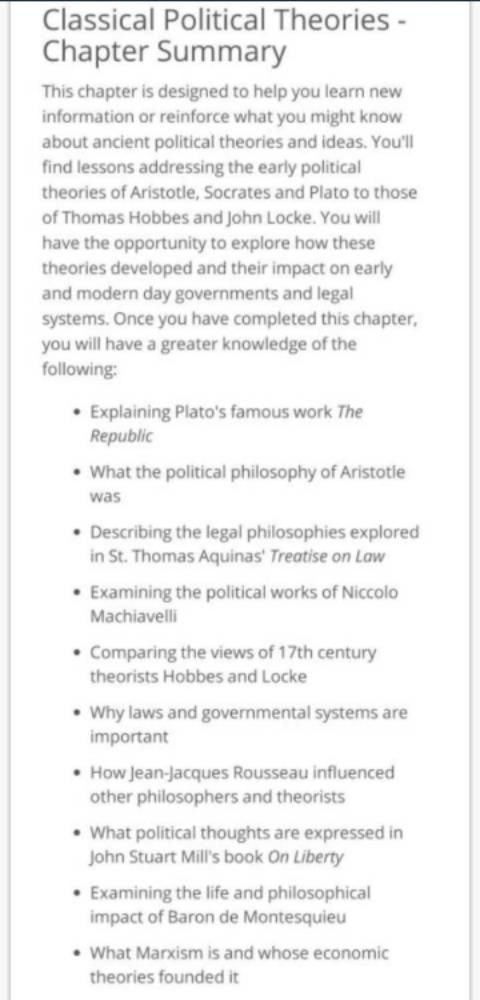
Community Answer
classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theor...
Classical Political Theory Overview
Classical political theory primarily refers to the philosophical ideas and works that have shaped political thought from ancient times to the early modern period. This body of work includes influential figures such as Plato, Aristotle, Machiavelli, and others, whose ideas continue to resonate in contemporary political discourse.
Key Concepts in Classical Political Theory
- Justice and the Ideal State: Many classical theorists focused on the concept of justice and how it relates to the structure of the state. Plato’s "Republic" explores the idea of an ideal state governed by philosopher-kings, advocating for a society based on rationality and virtue.
- Human Nature and Politics: Aristotle emphasized the importance of understanding human nature in the development of political systems. He viewed humans as "political animals" and believed that the state exists to promote the good life.
- Power and Authority: Machiavelli's "The Prince" provides a pragmatic view of power, suggesting that rulers should focus on effectiveness rather than morality. This marked a shift towards realism in political theory.
- Citizenship and Civic Virtue: Classical theorists often stressed the significance of active citizenship and civic responsibility. Aristotle’s concept of the "good citizen" reflects the idea that individuals should contribute to the common good.
Relevance Today
The discussions initiated by classical political theorists remain relevant as they provide foundational insights into democracy, governance, and ethics in politics. Modern political debates often revisit these themes, reflecting the enduring nature of classical ideas.
In summary, classical political theory offers crucial insights into the nature of justice, power, and the role of individuals within society, laying the groundwork for contemporary political thought.
Classical political theory primarily refers to the philosophical ideas and works that have shaped political thought from ancient times to the early modern period. This body of work includes influential figures such as Plato, Aristotle, Machiavelli, and others, whose ideas continue to resonate in contemporary political discourse.
Key Concepts in Classical Political Theory
- Justice and the Ideal State: Many classical theorists focused on the concept of justice and how it relates to the structure of the state. Plato’s "Republic" explores the idea of an ideal state governed by philosopher-kings, advocating for a society based on rationality and virtue.
- Human Nature and Politics: Aristotle emphasized the importance of understanding human nature in the development of political systems. He viewed humans as "political animals" and believed that the state exists to promote the good life.
- Power and Authority: Machiavelli's "The Prince" provides a pragmatic view of power, suggesting that rulers should focus on effectiveness rather than morality. This marked a shift towards realism in political theory.
- Citizenship and Civic Virtue: Classical theorists often stressed the significance of active citizenship and civic responsibility. Aristotle’s concept of the "good citizen" reflects the idea that individuals should contribute to the common good.
Relevance Today
The discussions initiated by classical political theorists remain relevant as they provide foundational insights into democracy, governance, and ethics in politics. Modern political debates often revisit these themes, reflecting the enduring nature of classical ideas.
In summary, classical political theory offers crucial insights into the nature of justice, power, and the role of individuals within society, laying the groundwork for contemporary political thought.

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|
Question Description
classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? for Humanities/Arts 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. Information about classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? covers all topics & solutions for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction?.
classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? for Humanities/Arts 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. Information about classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? covers all topics & solutions for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction?.
Solutions for classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Humanities/Arts.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Humanities/Arts Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction?, a detailed solution for classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? has been provided alongside types of classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice classical political theory Related: NCERT Solutions - Political Theory: An Introduction? tests, examples and also practice Humanities/Arts tests.

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















