Physics Exam > Physics Questions > At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root m...
Start Learning for Free
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?
Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal...
K.E. of a molecule of mass m and mean square speed 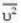
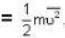
But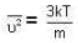
∴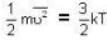
Escape velocity.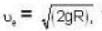 where R is the radius of the earth.
where R is the radius of the earth.
Given
∴ K.E. of a molecule =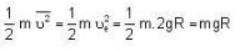
∴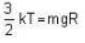
Or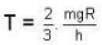
Temperature for hydrogen
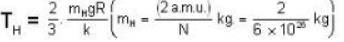
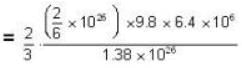
Temperature for oxvaen.
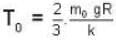
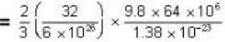
= 16 x 104K.
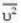
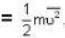
But
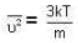
∴
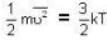
Escape velocity.
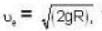 where R is the radius of the earth.
where R is the radius of the earth. Given
∴ K.E. of a molecule =
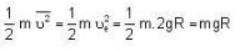
∴
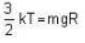
Or
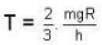
Temperature for hydrogen
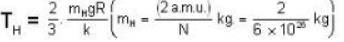
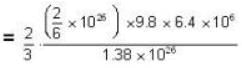
Temperature for oxvaen.
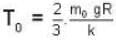
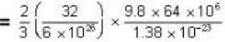
= 16 x 104K.
Most Upvoted Answer
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal...
Introduction:
In order to understand why the root mean square velocity is equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and oxygen at a certain temperature, we need to consider the kinetic theory of gases and the concept of escape velocity.
Kinetic Theory of Gases:
The kinetic theory of gases states that the average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. This means that as the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy and hence the velocity of the gas molecules also increase.
Escape Velocity:
Escape velocity is the minimum velocity an object must have in order to escape the gravitational pull of a planet or other celestial body. It is given by the formula:
Escape velocity = sqrt(2 * gravitational constant * mass of the planet / radius of the planet)
Root Mean Square Velocity:
The root mean square velocity is a measure of the average velocity of gas molecules in a sample. It is given by the formula:
Root mean square velocity = sqrt(3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature / molar mass)
Equating the Root Mean Square Velocity and Escape Velocity:
To find the temperature at which the root mean square velocity is equal to the escape velocity, we need to equate the two formulas:
sqrt(3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_H2 / molar mass_H2) = sqrt(2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth)
sqrt(3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_O2 / molar mass_O2) = sqrt(2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth)
Simplifying these equations, we get:
3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_H2 / molar mass_H2 = 2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth
3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_O2 / molar mass_O2 = 2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth
Since the molar mass of hydrogen (H2) is smaller than the molar mass of oxygen (O2), it takes a higher temperature for hydrogen molecules to have the same root mean square velocity as oxygen molecules.
Calculating the Temperature:
To calculate the temperature at which the root mean square velocity is equal to the escape velocity, we need to rearrange the equations and solve for temperature:
temperature_H2 = (2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth * molar mass_H2) / (3 * Boltzmann constant * radius_earth)
temperature_O2 = (2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth * molar mass_O2) / (3 * Boltzmann constant * radius_earth)
Substituting the known values for the gravitational constant, mass of the earth, molar masses of hydrogen and oxygen, and the radius of the earth, we can calculate the temperatures:
temperature_H2 = (2 * 6.67430 × 10^-11 m^3 kg^-1 s^-2 * 5.972 × 10^24 kg * 2.016 g/mol) / (3 * 1.38064852 × 10^-23 J/K * 6.371 × 10^6 m)
temperature_O2 = (2 * 6.67430 × 10^-11 m^3 kg^-1 s^-2 * 5.972 ×
In order to understand why the root mean square velocity is equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and oxygen at a certain temperature, we need to consider the kinetic theory of gases and the concept of escape velocity.
Kinetic Theory of Gases:
The kinetic theory of gases states that the average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. This means that as the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy and hence the velocity of the gas molecules also increase.
Escape Velocity:
Escape velocity is the minimum velocity an object must have in order to escape the gravitational pull of a planet or other celestial body. It is given by the formula:
Escape velocity = sqrt(2 * gravitational constant * mass of the planet / radius of the planet)
Root Mean Square Velocity:
The root mean square velocity is a measure of the average velocity of gas molecules in a sample. It is given by the formula:
Root mean square velocity = sqrt(3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature / molar mass)
Equating the Root Mean Square Velocity and Escape Velocity:
To find the temperature at which the root mean square velocity is equal to the escape velocity, we need to equate the two formulas:
sqrt(3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_H2 / molar mass_H2) = sqrt(2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth)
sqrt(3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_O2 / molar mass_O2) = sqrt(2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth)
Simplifying these equations, we get:
3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_H2 / molar mass_H2 = 2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth
3 * Boltzmann constant * temperature_O2 / molar mass_O2 = 2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth / radius_earth
Since the molar mass of hydrogen (H2) is smaller than the molar mass of oxygen (O2), it takes a higher temperature for hydrogen molecules to have the same root mean square velocity as oxygen molecules.
Calculating the Temperature:
To calculate the temperature at which the root mean square velocity is equal to the escape velocity, we need to rearrange the equations and solve for temperature:
temperature_H2 = (2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth * molar mass_H2) / (3 * Boltzmann constant * radius_earth)
temperature_O2 = (2 * gravitational constant * mass_earth * molar mass_O2) / (3 * Boltzmann constant * radius_earth)
Substituting the known values for the gravitational constant, mass of the earth, molar masses of hydrogen and oxygen, and the radius of the earth, we can calculate the temperatures:
temperature_H2 = (2 * 6.67430 × 10^-11 m^3 kg^-1 s^-2 * 5.972 × 10^24 kg * 2.016 g/mol) / (3 * 1.38064852 × 10^-23 J/K * 6.371 × 10^6 m)
temperature_O2 = (2 * 6.67430 × 10^-11 m^3 kg^-1 s^-2 * 5.972 ×
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal...
K.E. of a molecule of mass m and mean square speed 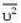
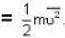
But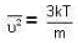
∴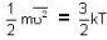
Escape velocity.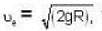 where R is the radius of the earth.
where R is the radius of the earth.
Given
∴ K.E. of a molecule =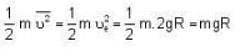
∴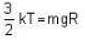
Or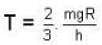
Temperature for hydrogen
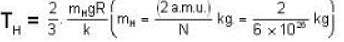
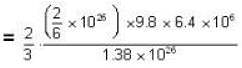
Temperature for oxvaen.
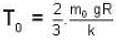
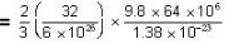
= 16 x 104K.
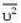
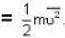
But
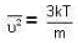
∴
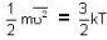
Escape velocity.
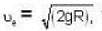 where R is the radius of the earth.
where R is the radius of the earth. Given
∴ K.E. of a molecule =
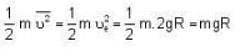
∴
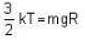
Or
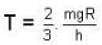
Temperature for hydrogen
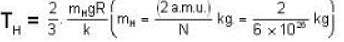
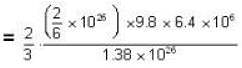
Temperature for oxvaen.
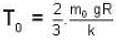
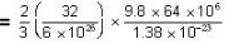
= 16 x 104K.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer?.
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?Correct answer is '160000'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















