Physics Exam > Physics Questions > There are two vessels; each of them contains ...
Start Learning for Free
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Then
- a)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 K
- b)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 K
- c)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pa
- d)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 Pa
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic i...
According to 1st law of thermodynamics,
ΔQ = ΔU+ΔW
So for the vessel for which internal energy (and hence, temperature) remains constant

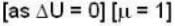
i.e.,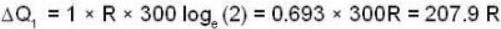
and for the vessel for which volume is kept constt.,
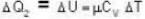
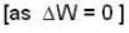
i.e.,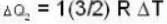
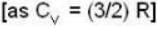
According to given problem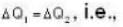
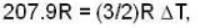
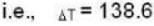
i.e.,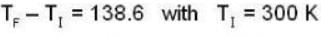
so
Now when the free mixing of gases is allowed
u1+u2 = u
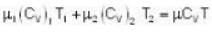 With
With 
Here and
and 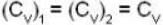
so 1 x 300 + 1 x 438.6 = 2T, i.e., T = 369.3 K
Further for the mixture from PV = μRT with V = V + 2V = 3V and μ = μ1 + μ2 = 2.
we have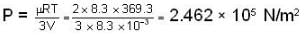
ΔQ = ΔU+ΔW
So for the vessel for which internal energy (and hence, temperature) remains constant

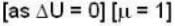
i.e.,
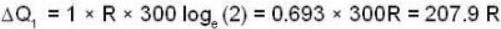
and for the vessel for which volume is kept constt.,
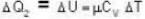
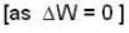
i.e.,
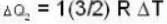
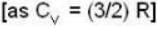
According to given problem
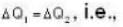
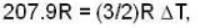
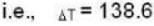
i.e.,
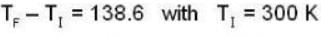
so

Now when the free mixing of gases is allowed
u1+u2 = u
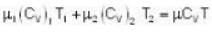 With
With 
Here
 and
and 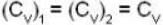
so 1 x 300 + 1 x 438.6 = 2T, i.e., T = 369.3 K
Further for the mixture from PV = μRT with V = V + 2V = 3V and μ = μ1 + μ2 = 2.
we have
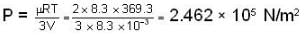
Most Upvoted Answer
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic i...
The Combined System
The problem states that we have two vessels, each containing one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. The initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10^-3 m^3 at a temperature of 27°C. The vessels are then connected to allow free mixing of the gas.
Equal Heat Supply
It is mentioned that an equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. This means that the change in internal energy of both vessels will be the same.
Expansion with Constant Internal Energy
In one of the vessels, the volume of the gas is doubled without any change in internal energy. This means that the heat supplied to this vessel is used only for expansion work, and not for increasing the internal energy of the gas.
Expansion at Constant Volume
In the second vessel, the volume of the gas is held constant. This means that the heat supplied to this vessel is used to increase the internal energy of the gas, as no expansion work is done.
Connecting the Vessels
After the expansion and heating processes in the two vessels, they are connected to allow free mixing of the gases. This means that the gases will reach a thermal equilibrium, where their temperatures and pressures will become equal.
Final Temperature of the Combined System
Since the amount of heat supplied to each vessel is the same, the change in internal energy of both vessels is the same. However, in one vessel, this change is used for expansion work, while in the other vessel, it is used to increase internal energy.
The vessel where the volume was doubled without change in internal energy will have a lower final temperature than the vessel where the volume was held constant. This is because the expansion work reduces the internal energy of the gas, resulting in a lower temperature.
When the vessels are connected, the gases will mix and reach a common final temperature. Since the gas from the vessel with constant volume has a higher initial temperature, it will transfer heat to the gas from the vessel with expansion. This will cause the temperature of the gas with expansion to increase and the temperature of the gas with constant volume to decrease.
Therefore, the final temperature of the combined system will be lower than the initial temperature of the constant volume vessel, but higher than the initial temperature of the expansion vessel.
Final Pressure of the Combined System
The problem does not provide any information about the pressure of the gases or any changes in pressure during the process. Therefore, it is not possible to determine the final pressure of the combined system based on the given information.
Conclusion
The correct answers are options A and C. The final temperature of the combined system is lower than the initial temperature of the vessel with constant volume, and the final pressure of the combined system cannot be determined with the given information.
The problem states that we have two vessels, each containing one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. The initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10^-3 m^3 at a temperature of 27°C. The vessels are then connected to allow free mixing of the gas.
Equal Heat Supply
It is mentioned that an equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. This means that the change in internal energy of both vessels will be the same.
Expansion with Constant Internal Energy
In one of the vessels, the volume of the gas is doubled without any change in internal energy. This means that the heat supplied to this vessel is used only for expansion work, and not for increasing the internal energy of the gas.
Expansion at Constant Volume
In the second vessel, the volume of the gas is held constant. This means that the heat supplied to this vessel is used to increase the internal energy of the gas, as no expansion work is done.
Connecting the Vessels
After the expansion and heating processes in the two vessels, they are connected to allow free mixing of the gases. This means that the gases will reach a thermal equilibrium, where their temperatures and pressures will become equal.
Final Temperature of the Combined System
Since the amount of heat supplied to each vessel is the same, the change in internal energy of both vessels is the same. However, in one vessel, this change is used for expansion work, while in the other vessel, it is used to increase internal energy.
The vessel where the volume was doubled without change in internal energy will have a lower final temperature than the vessel where the volume was held constant. This is because the expansion work reduces the internal energy of the gas, resulting in a lower temperature.
When the vessels are connected, the gases will mix and reach a common final temperature. Since the gas from the vessel with constant volume has a higher initial temperature, it will transfer heat to the gas from the vessel with expansion. This will cause the temperature of the gas with expansion to increase and the temperature of the gas with constant volume to decrease.
Therefore, the final temperature of the combined system will be lower than the initial temperature of the constant volume vessel, but higher than the initial temperature of the expansion vessel.
Final Pressure of the Combined System
The problem does not provide any information about the pressure of the gases or any changes in pressure during the process. Therefore, it is not possible to determine the final pressure of the combined system based on the given information.
Conclusion
The correct answers are options A and C. The final temperature of the combined system is lower than the initial temperature of the vessel with constant volume, and the final pressure of the combined system cannot be determined with the given information.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic i...
According to 1st law of thermodynamics,
ΔQ = ΔU+ΔW
So for the vessel for which internal energy (and hence, temperature) remains constant

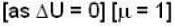
i.e.,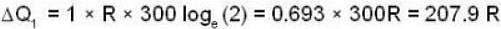
and for the vessel for which volume is kept constt.,
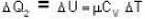
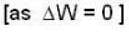
i.e.,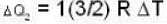
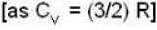
According to given problem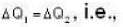
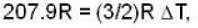
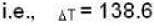
i.e.,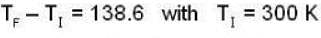
so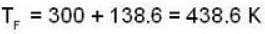
Now when the free mixing of gases is allowed
u1+u2 = u
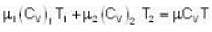 With
With 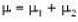
Here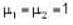 and
and 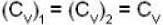
so 1 x 300 + 1 x 438.6 = 2T, i.e., T = 369.3 K
Further for the mixture from PV = μRT with V = V + 2V = 3V and μ = μ1 + μ2 = 2.
we have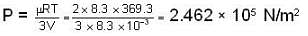
ΔQ = ΔU+ΔW
So for the vessel for which internal energy (and hence, temperature) remains constant

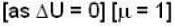
i.e.,
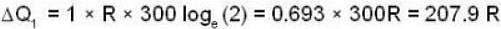
and for the vessel for which volume is kept constt.,
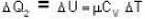
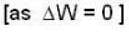
i.e.,
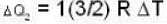
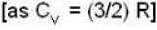
According to given problem
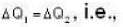
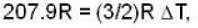
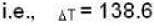
i.e.,
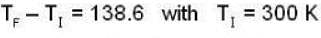
so
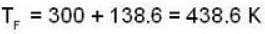
Now when the free mixing of gases is allowed
u1+u2 = u
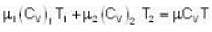 With
With 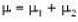
Here
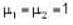 and
and 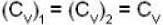
so 1 x 300 + 1 x 438.6 = 2T, i.e., T = 369.3 K
Further for the mixture from PV = μRT with V = V + 2V = 3V and μ = μ1 + μ2 = 2.
we have
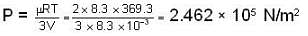

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Thena)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 Kb)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 Kc)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pad)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 PaCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















