Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A charge q is placed at the centre of the lin...
Start Learning for Free
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal to
- a)- Q/3
- b)- Q/4
- c)Q/4
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charg...
Let two equal charges Q each, be held at A and B. where AB = 2x. C is the centre of AB. where charge q is held.
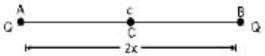
For the three charges to be in equilibrium, net force on each charge must be zero.
Now. total force on Q at B is


For the three charges to be in equilibrium, net force on each charge must be zero.
Now. total force on Q at B is

Most Upvoted Answer
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charg...
Understanding the System of Charges
When we consider the equilibrium of three charges, we need to analyze the forces acting on each charge. Here, we have two equal charges, say +Q, placed at points A and B, and a charge q placed at the center between them.
Determining Forces on Charge q
- The charge q experiences forces due to both +Q charges.
- The forces exerted by the two +Q charges on the charge q will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction if q is at the midpoint.
Condition for Equilibrium
For the system to be in equilibrium, the net force acting on charge q must be zero. This happens when the attractive and repulsive forces balance each other.
- The force exerted by charge +Q at distance d (the distance from +Q to q) is given by Coulomb's law.
Calculating the Required Charge q
- The force on charge q due to one +Q charge is proportional to Q and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d^2).
- Since both +Q charges exert forces on q, the total force on q will be the sum of these two forces.
To maintain equilibrium:
- The attractive force due to charge q (if q is negative) must equal the repulsive force from the two charges +Q.
After balancing the forces mathematically:
- The equilibrium condition leads to q being equal to -Q/4.
Thus, for the system to be in equilibrium, the charge q must be equal to -Q/4. This matches option B.
Conclusion
The charge q placed at the center must equal to -Q/4 for the system to maintain equilibrium, balancing the forces exerted by the equal charges at both ends.
When we consider the equilibrium of three charges, we need to analyze the forces acting on each charge. Here, we have two equal charges, say +Q, placed at points A and B, and a charge q placed at the center between them.
Determining Forces on Charge q
- The charge q experiences forces due to both +Q charges.
- The forces exerted by the two +Q charges on the charge q will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction if q is at the midpoint.
Condition for Equilibrium
For the system to be in equilibrium, the net force acting on charge q must be zero. This happens when the attractive and repulsive forces balance each other.
- The force exerted by charge +Q at distance d (the distance from +Q to q) is given by Coulomb's law.
Calculating the Required Charge q
- The force on charge q due to one +Q charge is proportional to Q and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d^2).
- Since both +Q charges exert forces on q, the total force on q will be the sum of these two forces.
To maintain equilibrium:
- The attractive force due to charge q (if q is negative) must equal the repulsive force from the two charges +Q.
After balancing the forces mathematically:
- The equilibrium condition leads to q being equal to -Q/4.
Thus, for the system to be in equilibrium, the charge q must be equal to -Q/4. This matches option B.
Conclusion
The charge q placed at the center must equal to -Q/4 for the system to maintain equilibrium, balancing the forces exerted by the equal charges at both ends.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charg...
Let two equal charges Q each, be held at A and B. where AB = 2x. C is the centre of AB. where charge q is held.
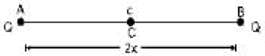
For the three charges to be in equilibrium, net force on each charge must be zero.
Now. total force on Q at B is
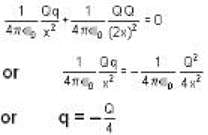

For the three charges to be in equilibrium, net force on each charge must be zero.
Now. total force on Q at B is
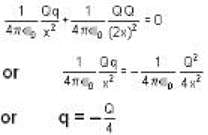

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges O. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if q equal toa)- Q/3b)- Q/4c)Q/4d)0Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















