Physics Exam > Physics Questions > When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4&Omega...
Start Learning for Free
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).
- a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω only
- b)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω only
- c)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω only
- d)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflect...
Case I
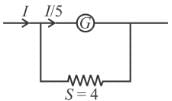
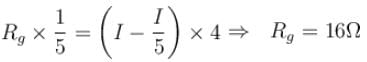
Case II
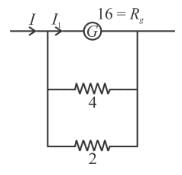
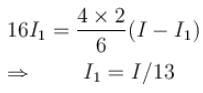
so decrease in current to previous current

The correct answer is: (8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω only
Most Upvoted Answer
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflect...
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4, it means that a shunt resistor with a resistance of 4 times the internal resistance of the galvanometer is connected in parallel with the galvanometer. This is done to increase the range of currents that can be measured by the galvanometer.
By connecting the shunt resistor in parallel with the galvanometer, a portion of the current bypasses the galvanometer and flows through the shunt resistor. This reduces the overall current passing through the galvanometer and prevents it from being damaged by excessive current.
The shunt resistor is designed to have a known resistance value that is much lower than the internal resistance of the galvanometer. This allows a larger current to flow through the shunt resistor, while only a small fraction of the current passes through the galvanometer. The galvanometer then measures this small fraction of the current and displays it as the reading.
For example, if the internal resistance of the galvanometer is 10 ohms and a shunt resistor with a resistance of 40 ohms is connected in parallel, the total resistance in the circuit becomes 40/50 ohms. This means that only 1/5th of the total current flows through the galvanometer, and the galvanometer reading is multiplied by 5 to get the actual current.
By connecting the shunt resistor in parallel with the galvanometer, a portion of the current bypasses the galvanometer and flows through the shunt resistor. This reduces the overall current passing through the galvanometer and prevents it from being damaged by excessive current.
The shunt resistor is designed to have a known resistance value that is much lower than the internal resistance of the galvanometer. This allows a larger current to flow through the shunt resistor, while only a small fraction of the current passes through the galvanometer. The galvanometer then measures this small fraction of the current and displays it as the reading.
For example, if the internal resistance of the galvanometer is 10 ohms and a shunt resistor with a resistance of 40 ohms is connected in parallel, the total resistance in the circuit becomes 40/50 ohms. This means that only 1/5th of the total current flows through the galvanometer, and the galvanometer reading is multiplied by 5 to get the actual current.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2Ω wire, the further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same).a)(3/4) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyb)(8/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyc)(3/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyd)(5/13) of the deflection when shunted with 4Ω onlyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















