NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?
Start Learning for Free
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?
Most Upvoted Answer
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?
Community Answer
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?
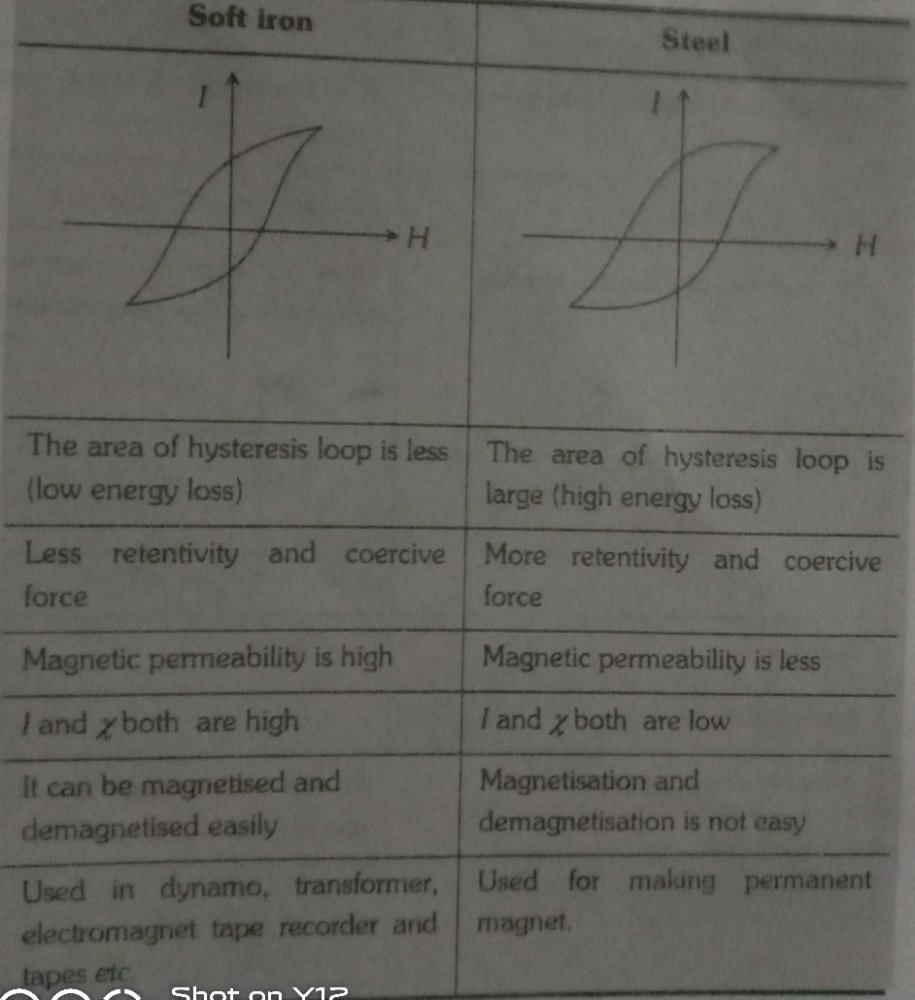
Comparison between Soft Iron and Steel:
Soft iron and steel are both widely used metals in various industries due to their unique properties and characteristics. While they share some similarities, there are also significant differences between the two. Let's explore and compare these two materials in detail:
Magnetic Properties:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is known for its excellent magnetic properties. It is highly permeable to magnetic fields and can be easily magnetized and demagnetized. Due to its low coercivity, soft iron is commonly used in the construction of magnetic cores for transformers, electromagnets, and relays.
- Steel: Steel, on the other hand, has a lower permeability compared to soft iron. It exhibits ferromagnetic properties but is not as easily magnetized or demagnetized as soft iron. However, certain types of steel, such as electrical steel or silicon steel, are specifically designed to have high magnetic permeability for use in electrical applications.
Mechanical Strength:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is relatively ductile and has low mechanical strength. It can be easily bent, shaped, and formed into various structures. However, it lacks hardness and is susceptible to deformation and wear.
- Steel: Steel is much stronger and harder than soft iron. It has excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, hardness, and toughness. Steel is widely used in the construction industry, automotive manufacturing, and other applications that require sturdy and durable materials.
Corrosion Resistance:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is highly prone to corrosion and rusting when exposed to moisture and oxygen. It requires proper coating or plating to protect it from corrosion.
- Steel: Depending on the composition and treatment, steel can have varying degrees of corrosion resistance. Stainless steel, for example, is highly resistant to corrosion due to the presence of chromium. It forms a passive oxide layer that protects it from rusting.
Electrical Conductivity:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron has relatively low electrical conductivity. It is often used as a magnetic core material where electrical conductivity is not a primary concern.
- Steel: Steel has moderate to high electrical conductivity, depending on its composition. It is commonly used in electrical wiring, power transmission lines, and other electrical applications.
Applications:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is primarily used in applications where magnetic properties are crucial, such as transformers, motors, and generators.
- Steel: Steel has a wide range of applications due to its strength, versatility, and durability. It is used in construction, automotive manufacturing, appliances, tools, and many other industries.
In summary, soft iron and steel have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Soft iron's superior magnetic properties make it ideal for magnet cores, while steel's strength and versatility make it a popular choice for various industries. Understanding their properties can help in selecting the appropriate material for specific requirements.
Soft iron and steel are both widely used metals in various industries due to their unique properties and characteristics. While they share some similarities, there are also significant differences between the two. Let's explore and compare these two materials in detail:
Magnetic Properties:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is known for its excellent magnetic properties. It is highly permeable to magnetic fields and can be easily magnetized and demagnetized. Due to its low coercivity, soft iron is commonly used in the construction of magnetic cores for transformers, electromagnets, and relays.
- Steel: Steel, on the other hand, has a lower permeability compared to soft iron. It exhibits ferromagnetic properties but is not as easily magnetized or demagnetized as soft iron. However, certain types of steel, such as electrical steel or silicon steel, are specifically designed to have high magnetic permeability for use in electrical applications.
Mechanical Strength:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is relatively ductile and has low mechanical strength. It can be easily bent, shaped, and formed into various structures. However, it lacks hardness and is susceptible to deformation and wear.
- Steel: Steel is much stronger and harder than soft iron. It has excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, hardness, and toughness. Steel is widely used in the construction industry, automotive manufacturing, and other applications that require sturdy and durable materials.
Corrosion Resistance:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is highly prone to corrosion and rusting when exposed to moisture and oxygen. It requires proper coating or plating to protect it from corrosion.
- Steel: Depending on the composition and treatment, steel can have varying degrees of corrosion resistance. Stainless steel, for example, is highly resistant to corrosion due to the presence of chromium. It forms a passive oxide layer that protects it from rusting.
Electrical Conductivity:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron has relatively low electrical conductivity. It is often used as a magnetic core material where electrical conductivity is not a primary concern.
- Steel: Steel has moderate to high electrical conductivity, depending on its composition. It is commonly used in electrical wiring, power transmission lines, and other electrical applications.
Applications:
- Soft Iron: Soft iron is primarily used in applications where magnetic properties are crucial, such as transformers, motors, and generators.
- Steel: Steel has a wide range of applications due to its strength, versatility, and durability. It is used in construction, automotive manufacturing, appliances, tools, and many other industries.
In summary, soft iron and steel have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Soft iron's superior magnetic properties make it ideal for magnet cores, while steel's strength and versatility make it a popular choice for various industries. Understanding their properties can help in selecting the appropriate material for specific requirements.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?
Question Description
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?.
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?.
Solutions for Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Give comparison between soft iron and steel ?, a detailed solution for Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? has been provided alongside types of Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Give comparison between soft iron and steel ? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























