JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Passage IA and B are two structural isomers w...
Start Learning for Free
Passage I
A and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14O and both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or B with hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2O gives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.
Q.
Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and B is true?
- a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominat
- b)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, B predominat
- c)Isomerisation of A to B or B to A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final step
- d)Both (b) and (c) are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formu...
Explanation:
Isomerisation of A and B:
- When A is treated with dilute H2SO4, it isomerises to form B.
- At equilibrium, B predominates over A.
Reasoning:
- Acid-catalysed isomerisation involves the formation of a more stable carbocation.
- In this case, the isomerisation of A to B results in the formation of a more stable product, B.
- Therefore, A is converted to B in the presence of the acid catalyst, and at equilibrium, B predominates.
Conclusion:
- The correct statement regarding the acid-catalysed isomerisation of A and B is that A, when treated with dilute H2SO4, isomerises to form B, and at equilibrium, B predominates.
Isomerisation of A and B:
- When A is treated with dilute H2SO4, it isomerises to form B.
- At equilibrium, B predominates over A.
Reasoning:
- Acid-catalysed isomerisation involves the formation of a more stable carbocation.
- In this case, the isomerisation of A to B results in the formation of a more stable product, B.
- Therefore, A is converted to B in the presence of the acid catalyst, and at equilibrium, B predominates.
Conclusion:
- The correct statement regarding the acid-catalysed isomerisation of A and B is that A, when treated with dilute H2SO4, isomerises to form B, and at equilibrium, B predominates.
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formu...
Both A and B are alcohols with one degree of unsaturation but none of them decolourise Br2 - H2O solution,hence they are cyclic.
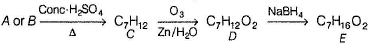
E has only one methyl group and gives iodoform test hence, E may be :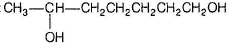
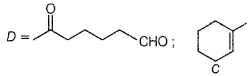
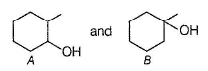
A has a chiral carbon but B does not.
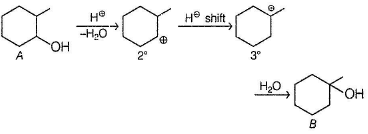
E has only one methyl group and gives iodoform test hence, E may be :
A has a chiral carbon but B does not.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Passage IA and B are two structural isomers with their molecular formula C7H14Oand both gives-off effervescence on heating with Na-metal. However, neither A nor B decolourise brown colour of Br2-H2O. Treating either A or Bwith hot conc, sulphuric acid solution results in the form ation of the same compound C (C7H12). C on treatment with O3 followed by Zn-H2Ogives D (C7H12O2). D gives E (C7H16O2) on treatm ent with NaBH4. E has only one methyl group and forms yellow ppt with I2/KOH. Also, A gives delayed turbidity on treatment with conc. HCI/ZnCI2 while B gives immediate turbidity on similar treatment.Q.Which of the following statement regarding acid catalysed isomerisation of A and Bis true?a)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to B and at equilibrium, A predominatb)A on treatment with dil. H2SO4 isomerises to Band at equilibrium, Bpredominatc)Isomerisation of A to Bor Bto A in the presence of acid catalyst involve the same carbocation in the last final stepd)Both (b) and (c) are correctCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























