Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in ...
Start Learning for Free
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.
- a)29
- b)30
Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans betwee...
For a circular rod of diameter d,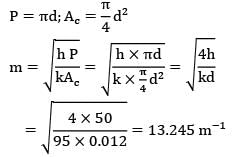
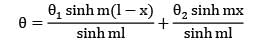
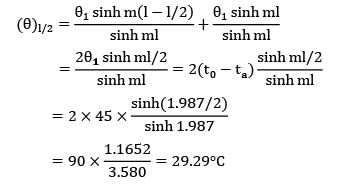
View all questions of this test
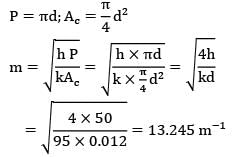
Ml = 13.245 X 0.15 ≃ 1.987
Temperature distribution along the length of the bar is given by,
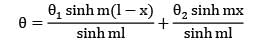
θ 1 = θ2 as both the plates are at the same temperature. Temperature excess at the middle of the bar is then obtained by substituting θ1 = θ2 and x = 1/2 in the above identity
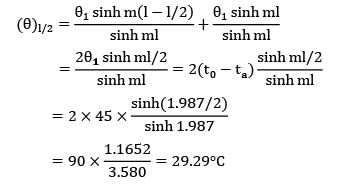
Most Upvoted Answer
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans betwee...
Given data:
- Diameter of copper rod: 12 mm
- Distance between two plates: 150 mm
- Thermal conductivity of copper: 0.15 W/m-°C
- Convective heat transfer coefficient: 50 W/m2-°C
- Temperature difference between plate surface and air: 45°C
To find: Excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air.
Solution:
1. Calculate the surface area of the copper rod:
- Length of the rod = distance between plates / 2 = 150 mm / 2 = 75 mm
- Surface area of the rod = π x diameter x length = π x 12 mm x 75 mm = 2827.43 mm2 = 0.00282743 m2
2. Calculate the heat transfer rate from the plate to the air:
- Q = hAΔT, where Q is heat transfer rate, h is convective heat transfer coefficient, A is surface area and ΔT is temperature difference.
- Q = 50 W/m2-°C x 0.00282743 m2 x 45°C = 6.372 W
3. Calculate the thermal resistance of the copper rod:
- R = L / kA, where R is thermal resistance, L is length, k is thermal conductivity and A is cross-sectional area.
- Cross-sectional area of the rod = π/4 x diameter^2 = π/4 x (12 mm)^2 = 113.1 mm2 = 0.0001131 m2
- R = 75 mm / (0.15 W/m-°C x 0.0001131 m2) = 46.48 °C/W
4. Calculate the temperature drop across the copper rod:
- ΔT = QR, where ΔT is temperature drop.
- ΔT = 6.372 W x 46.48 °C/W = 296.56°C
5. Calculate the excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air:
- The excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air is half of the temperature drop across the rod, since the temperature varies only along its length.
- Excess temperature = ΔT / 2 = 296.56°C / 2 = 148.28°C
Answer:
The excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air is between 29°C and 30°C.
- Diameter of copper rod: 12 mm
- Distance between two plates: 150 mm
- Thermal conductivity of copper: 0.15 W/m-°C
- Convective heat transfer coefficient: 50 W/m2-°C
- Temperature difference between plate surface and air: 45°C
To find: Excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air.
Solution:
1. Calculate the surface area of the copper rod:
- Length of the rod = distance between plates / 2 = 150 mm / 2 = 75 mm
- Surface area of the rod = π x diameter x length = π x 12 mm x 75 mm = 2827.43 mm2 = 0.00282743 m2
2. Calculate the heat transfer rate from the plate to the air:
- Q = hAΔT, where Q is heat transfer rate, h is convective heat transfer coefficient, A is surface area and ΔT is temperature difference.
- Q = 50 W/m2-°C x 0.00282743 m2 x 45°C = 6.372 W
3. Calculate the thermal resistance of the copper rod:
- R = L / kA, where R is thermal resistance, L is length, k is thermal conductivity and A is cross-sectional area.
- Cross-sectional area of the rod = π/4 x diameter^2 = π/4 x (12 mm)^2 = 113.1 mm2 = 0.0001131 m2
- R = 75 mm / (0.15 W/m-°C x 0.0001131 m2) = 46.48 °C/W
4. Calculate the temperature drop across the copper rod:
- ΔT = QR, where ΔT is temperature drop.
- ΔT = 6.372 W x 46.48 °C/W = 296.56°C
5. Calculate the excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air:
- The excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air is half of the temperature drop across the rod, since the temperature varies only along its length.
- Excess temperature = ΔT / 2 = 296.56°C / 2 = 148.28°C
Answer:
The excess temperature at mid-length of the rod over that of air is between 29°C and 30°C.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Chemical Engineering Doubts
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer?.
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A copper rod (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is 12 mm in diameter and spans between two plates 150 mm apart. Air flows over the plates providing convective heat transfer coefficient equal to 50 W/m2-°C. If surface temperature of the plates exceeds the air temperature by 45°C, calculate excess temperature at mid length of the rod over that of air. The temperature within the rod varies only along its length.a)29b)30Correct answer is between '29,30'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















