Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity...
Start Learning for Free
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.
- a)510
- b)511
Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivi...
Electrical resistance of wire,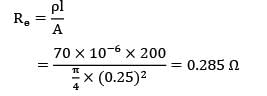
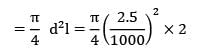
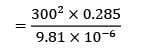
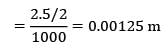
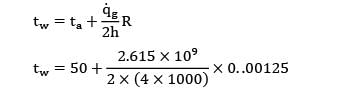
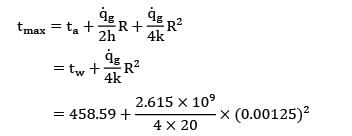
View all questions of this test
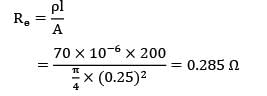
Here generated, 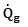
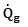
= I2Rs = 3002 X 0.285 Watt
Volume of wire, V
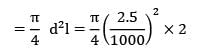
= 9.81 X 10-6m3
Heat generated per unit volume,qg
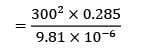
= 2.615 X 109 W/m3
Radius of wire, R
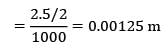
The wire surface temperature is given by,
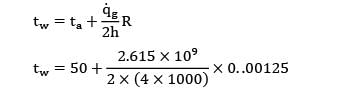
= 50 + 408.59 = 458.59°C
Maximum temperature in the wire occurs at its geometric center line, and can be computed from the relation,
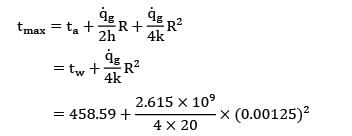
= 458.59 + 51.07 = 510.66°C
Most Upvoted Answer
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivi...
Is used to transfer heat from a hot gas to a cooler liquid. The wire has a diameter of 2 mm and a length of 1 m. The gas temperature is 200°C and the liquid temperature is 30°C. The heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the gas is 100 W/m2°C, and the heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the liquid is 500 W/m2°C. Assuming steady-state conditions and neglecting any heat losses from the wire to the surroundings, calculate:
a) The rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire
b) The rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid
c) The temperature of the wire along its length, assuming a uniform heat transfer coefficient between the wire and both the gas and the liquid.
a) The rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire can be calculated using the following formula:
Q_gas = h_gas * A * (T_gas - T_wire)
where Q_gas is the rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire, A is the cross-sectional area of the wire, T_gas is the gas temperature, T_wire is the temperature of the wire, and h_gas is the heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the gas.
The cross-sectional area of the wire can be calculated as:
A = π * (d/2)^2
where d is the diameter of the wire.
Substituting the given values, we get:
A = π * (2/2)^2 = 3.14 mm2
Q_gas = 100 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (200 - T_wire)
b) The rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid can be calculated using the following formula:
Q_liquid = h_liquid * A * (T_wire - T_liquid)
where Q_liquid is the rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid, T_liquid is the liquid temperature, and h_liquid is the heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the liquid.
Substituting the given values, we get:
Q_liquid = 500 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (T_wire - 30)
c) The temperature of the wire along its length can be calculated using the following formula:
T_wire = T_gas - Q_gas/(h_gas * A) = T_liquid + Q_liquid/(h_liquid * A)
Substituting the values of Q_gas and Q_liquid, we get:
T_gas - 100 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (200 - T_wire)/(20 * 3.14 * 10^-6) = T_liquid + 500 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (T_wire - 30)/(20 * 3.14 * 10^-6)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
T_gas - 10 * (200 - T_wire) = T_liquid + 25 * (T_wire - 30)
Solving for T_wire, we get:
T_wire = 59.5°C
Therefore, the rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire is 628.32 W, the rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid is 628.32 W, and the temperature of the wire is 59.5°C along its length.
a) The rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire
b) The rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid
c) The temperature of the wire along its length, assuming a uniform heat transfer coefficient between the wire and both the gas and the liquid.
a) The rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire can be calculated using the following formula:
Q_gas = h_gas * A * (T_gas - T_wire)
where Q_gas is the rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire, A is the cross-sectional area of the wire, T_gas is the gas temperature, T_wire is the temperature of the wire, and h_gas is the heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the gas.
The cross-sectional area of the wire can be calculated as:
A = π * (d/2)^2
where d is the diameter of the wire.
Substituting the given values, we get:
A = π * (2/2)^2 = 3.14 mm2
Q_gas = 100 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (200 - T_wire)
b) The rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid can be calculated using the following formula:
Q_liquid = h_liquid * A * (T_wire - T_liquid)
where Q_liquid is the rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid, T_liquid is the liquid temperature, and h_liquid is the heat transfer coefficient between the wire and the liquid.
Substituting the given values, we get:
Q_liquid = 500 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (T_wire - 30)
c) The temperature of the wire along its length can be calculated using the following formula:
T_wire = T_gas - Q_gas/(h_gas * A) = T_liquid + Q_liquid/(h_liquid * A)
Substituting the values of Q_gas and Q_liquid, we get:
T_gas - 100 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (200 - T_wire)/(20 * 3.14 * 10^-6) = T_liquid + 500 * 3.14 * 10^-6 * (T_wire - 30)/(20 * 3.14 * 10^-6)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
T_gas - 10 * (200 - T_wire) = T_liquid + 25 * (T_wire - 30)
Solving for T_wire, we get:
T_wire = 59.5°C
Therefore, the rate of heat transfer from the gas to the wire is 628.32 W, the rate of heat transfer from the wire to the liquid is 628.32 W, and the temperature of the wire is 59.5°C along its length.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Chemical Engineering Doubts
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer?.
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A stainless steel wire (thermal conductivity = 20 W/m2°C) & resistivity = 70 micro ohm-cm) of length 2 m and diameter 2.5 mm is submerged in a fluid 50°C at and an electric current of intensity 300 amps passes through it. If heat convection coefficient at the wire surface is 4 kW/m2°C, workout the steady state temperature at the center.a)510b)511Correct answer is between '510,511'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















