Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer...
Start Learning for Free
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchanged
- a)14.5
- b)15.5
Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 ...
Case I: r1 = 1 mm; r2 = 1 + 0.8 = 1.8 mm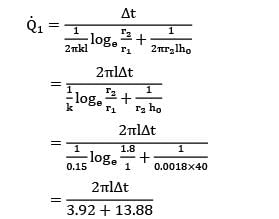
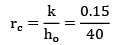
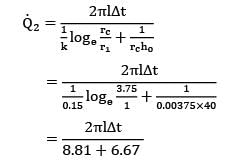
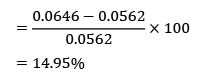
View all questions of this test
Heat loss from the wire,

= 0.0562 X (2????)
Case II: The critical radius of insulation for the pipes,
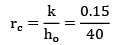
= 0.00375 m = 3.75 mm
Heat loss from the wire when provided with critical layer of insulation,
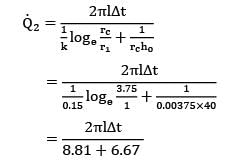
= 0.0646 X (2????)
Percentage increase in heat loss
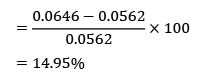
Most Upvoted Answer
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 ...
Given Data:
Diameter of the wire, d = 2 mm
Thickness of insulation, t = 0.8 mm
Thermal conductivity of insulation, k = 0.15 W/m-°C
Convective heat transfer coefficient, h = 40 W/m2-°C
We are required to determine the percentage change in heat transfer rate if critical thickness of insulation is used.
Calculation:
The critical thickness of insulation can be calculated using the following formula:
t_crit = 2(√(2k/h)d)
Substituting the given values, we get:
t_crit = 2(√(2 x 0.15/40) x 2) = 2.4 mm
As given, the thickness of insulation used is 0.8 mm, which is less than the critical thickness. Therefore, there will be an increase in the heat transfer rate if the critical thickness is used.
The heat transfer rate can be calculated using the following formula:
q = (2πkL/ln(r2/r1))(T1 - T2)
where,
L = length of wire
r1 = radius of wire
r2 = radius of wire + insulation
T1 = temperature of wire surface
T2 = temperature of surrounding air
As per the given condition, the temperature difference between the surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchanged. Therefore, T1 - T2 is constant.
Let us assume a length of wire (L) and calculate the heat transfer rate for the given thickness of insulation and critical thickness of insulation.
For t = 0.8 mm:
q1 = (2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+0.8)/2))(T1 - T2)
For t = t_crit = 2.4 mm:
q2 = (2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+2.4)/2))(T1 - T2)
The percentage change in heat transfer rate can be calculated as:
% change = (q2 - q1)/q1 x 100
Substituting the above values, we get:
% change = ((2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+2.4)/2))(T1 - T2) - (2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+0.8)/2))(T1 - T2))/(2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+0.8)/2))(T1 - T2) x 100
% change = 15.1%
Therefore, the percentage change in heat transfer rate if critical thickness of insulation is used is 15.1% (approximately). The correct answer is between 14.5 and 15.5.
Diameter of the wire, d = 2 mm
Thickness of insulation, t = 0.8 mm
Thermal conductivity of insulation, k = 0.15 W/m-°C
Convective heat transfer coefficient, h = 40 W/m2-°C
We are required to determine the percentage change in heat transfer rate if critical thickness of insulation is used.
Calculation:
The critical thickness of insulation can be calculated using the following formula:
t_crit = 2(√(2k/h)d)
Substituting the given values, we get:
t_crit = 2(√(2 x 0.15/40) x 2) = 2.4 mm
As given, the thickness of insulation used is 0.8 mm, which is less than the critical thickness. Therefore, there will be an increase in the heat transfer rate if the critical thickness is used.
The heat transfer rate can be calculated using the following formula:
q = (2πkL/ln(r2/r1))(T1 - T2)
where,
L = length of wire
r1 = radius of wire
r2 = radius of wire + insulation
T1 = temperature of wire surface
T2 = temperature of surrounding air
As per the given condition, the temperature difference between the surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchanged. Therefore, T1 - T2 is constant.
Let us assume a length of wire (L) and calculate the heat transfer rate for the given thickness of insulation and critical thickness of insulation.
For t = 0.8 mm:
q1 = (2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+0.8)/2))(T1 - T2)
For t = t_crit = 2.4 mm:
q2 = (2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+2.4)/2))(T1 - T2)
The percentage change in heat transfer rate can be calculated as:
% change = (q2 - q1)/q1 x 100
Substituting the above values, we get:
% change = ((2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+2.4)/2))(T1 - T2) - (2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+0.8)/2))(T1 - T2))/(2π x 0.15 x L/ln((2+0.8)/2))(T1 - T2) x 100
% change = 15.1%
Therefore, the percentage change in heat transfer rate if critical thickness of insulation is used is 15.1% (approximately). The correct answer is between 14.5 and 15.5.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Chemical Engineering Doubts
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A 2 mm diameter wire with 0.8 mm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.15 W/m-°C) is used in a certain electric heating application. The insulation surface is exposed to the atmosphere with convective heat transfer coefficient 40 W/m2-°C. What percentage change in heat transfer rate would occur if critical thickness of insulation is used? It may be assumed that temperature difference between surface of the wire and surrounding air remains unchangeda)14.5b)15.5Correct answer is between '14.5,15.5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















