Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4...
Start Learning for Free
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency of
ፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.
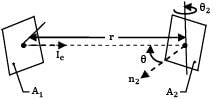
What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?
Option~
(A) 2 x 10-6j
(B) 4 x 10-6j
(C) 8.0 x 10-6j
(D) 16 x 10-6j
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a...
At time instant t the normal to surface of plate 2 which faces plate 1 makes an angle of ፀ2 with the direction of view ®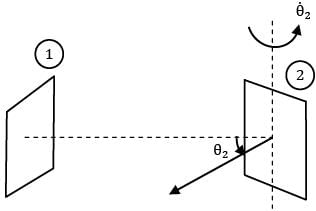
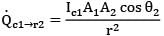
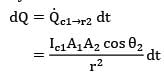
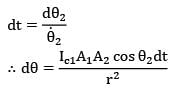
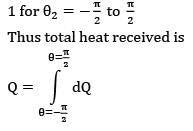
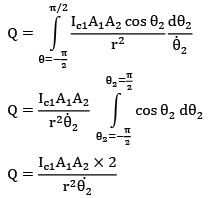
View all questions of this test

Thus for the given time instant the rate at which energy emitted by 1 strikes at 2 is
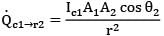
Thus for the given time instant the rate at which energy emitted by 1 strikes at 2 is
dQ = Qc1➝r2 dt
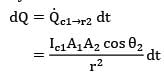
Where,
dt = dፀ2/θ2
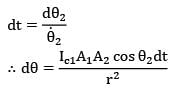
This face of the surface 2 is in front of surface
1 for θ2 = π/2 to π/2
Thus total heat received is
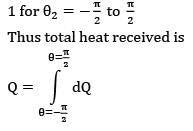
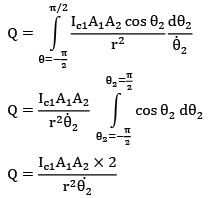
Similarly second face of surface 2 will also come in front of surface 1 during remaining half of revolution Thus total energy received by surface 2 during one complete revolution is
4Ic1A1A2 / r2ፀ2
= 4 x 100 x 10-4 x 10-4/(0.5)2 x 2
= 8 x 10-6 j
Most Upvoted Answer
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a...
At time instant t the normal to surface of plate 2 which faces plate 1 makes an angle of ፀ2 with the direction of view ®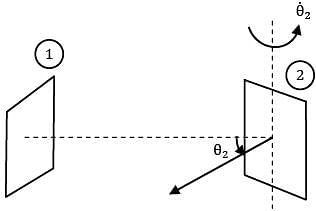
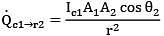
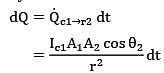
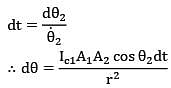
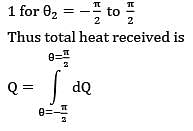
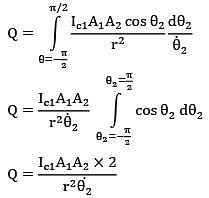

Thus for the given time instant the rate at which energy emitted by 1 strikes at 2 is
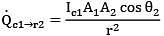
Thus for the given time instant the rate at which energy emitted by 1 strikes at 2 is
dQ = Qc1➝r2 dt
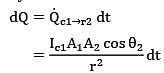
Where,
dt = dፀ2/θ2
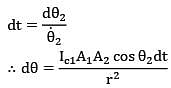
This face of the surface 2 is in front of surface
1 for θ2 = π/2 to π/2
Thus total heat received is
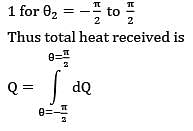
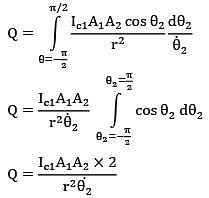
Similarly second face of surface 2 will also come in front of surface 1 during remaining half of revolution Thus total energy received by surface 2 during one complete revolution is
4Ic1A1A2 / r2ፀ2
= 4 x 100 x 10-4 x 10-4/(0.5)2 x 2
= 8 x 10-6 j
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a...
At time instant t the normal to surface of plate 2 which faces plate 1 makes an angle of ፀ2 with the direction of view ®
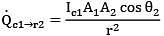
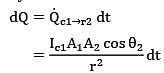
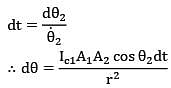
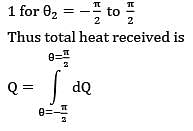
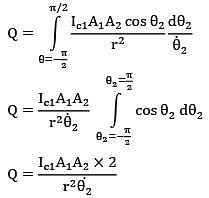

Thus for the given time instant the rate at which energy emitted by 1 strikes at 2 is
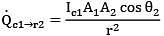
Thus for the given time instant the rate at which energy emitted by 1 strikes at 2 is
dQ = Qc1➝r2 dt
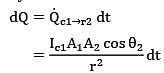
Where,
dt = dፀ2/θ2
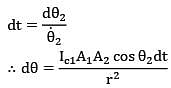
This face of the surface 2 is in front of surface
1 for θ2 = π/2 to π/2
Thus total heat received is
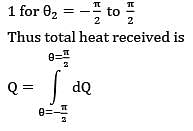
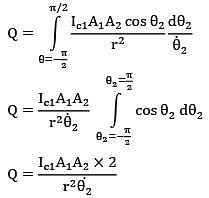
Similarly second face of surface 2 will also come in front of surface 1 during remaining half of revolution Thus total energy received by surface 2 during one complete revolution is
4Ic1A1A2 / r2ፀ2
= 4 x 100 x 10-4 x 10-4/(0.5)2 x 2
= 8 x 10-6 j

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A small stationary surface of area A1 = 10-4m2 emits diffusely with a total intensity of . A second surface of equivalent area is located at a fixed distance from . The connecting line between the two surfaces remains perpendicular to while rotates at an angular frequency ofፀ2 = dፀ2/dt = 2 rad/s about the axis as shown in the figure.What is the amount of energy intercepted by the two sides of , during one complete revolution?Option~(A) 2 x 10-6j(B) 4 x 10-6j(C) 8.0 x 10-6j(D) 16 x 10-6jCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















