Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Define the difference between G and g ( capit...
Start Learning for Free
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?
Most Upvoted Answer
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?
Community Answer
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?
Definition:
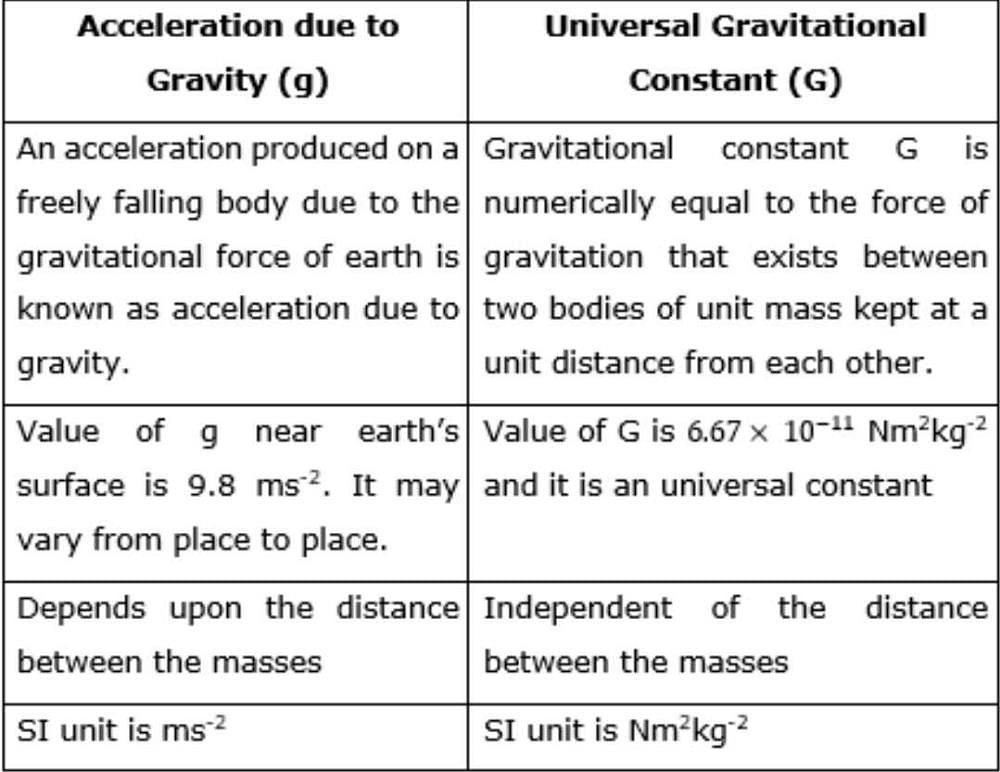
In mathematics and physics, G and g are used to represent different concepts. G (capital G) typically refers to the gravitational constant, while g (small g) usually represents the acceleration due to gravity.
G (Gravitational Constant):
The gravitational constant, denoted by G, is a fundamental constant in physics that appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation. It is the proportionality constant that determines the strength of the gravitational force between two objects. The value of G is approximately 6.67430 x 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2.
g (Acceleration due to Gravity):
The acceleration due to gravity, denoted by g, is the acceleration experienced by an object in a gravitational field. It is the rate at which the velocity of an object changes under the influence of gravity alone. Near the surface of the Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.8 m/s^2.
Difference between G and g:
1. Concept:
- G: Gravitational constant.
- g: Acceleration due to gravity.
2. Representation:
- G: Capital letter G is used to represent the gravitational constant.
- g: Small letter g is used to represent the acceleration due to gravity.
3. Units:
- G: The unit of G is N(m/kg)^2, which stands for newton multiplied by square meters divided by kilograms squared.
- g: The unit of g is m/s^2, which stands for meters per second squared.
4. Magnitude:
- G: The value of G is a very small constant, approximately equal to 6.67430 x 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2.
- g: The value of g is approximately 9.8 m/s^2, which is significantly larger than G.
5. Application:
- G: The gravitational constant is used in the calculation of gravitational forces between celestial bodies, such as planets, stars, and galaxies.
- g: The acceleration due to gravity is used in various calculations involving free fall, projectile motion, and weight.
6. Dependence:
- G: The value of G is a universal constant and does not depend on the mass or location of the objects involved.
- g: The value of g varies depending on the mass and radius of the celestial body. It is stronger on larger objects with greater mass and smaller radii.
Conclusion:
In summary, G represents the gravitational constant, which determines the strength of the gravitational force, while g represents the acceleration due to gravity, which is the acceleration experienced by an object in a gravitational field. G is a small constant used for celestial calculations, while g is the acceleration experienced near the surface of the Earth.
In mathematics and physics, G and g are used to represent different concepts. G (capital G) typically refers to the gravitational constant, while g (small g) usually represents the acceleration due to gravity.
G (Gravitational Constant):
The gravitational constant, denoted by G, is a fundamental constant in physics that appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation. It is the proportionality constant that determines the strength of the gravitational force between two objects. The value of G is approximately 6.67430 x 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2.
g (Acceleration due to Gravity):
The acceleration due to gravity, denoted by g, is the acceleration experienced by an object in a gravitational field. It is the rate at which the velocity of an object changes under the influence of gravity alone. Near the surface of the Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.8 m/s^2.
Difference between G and g:
1. Concept:
- G: Gravitational constant.
- g: Acceleration due to gravity.
2. Representation:
- G: Capital letter G is used to represent the gravitational constant.
- g: Small letter g is used to represent the acceleration due to gravity.
3. Units:
- G: The unit of G is N(m/kg)^2, which stands for newton multiplied by square meters divided by kilograms squared.
- g: The unit of g is m/s^2, which stands for meters per second squared.
4. Magnitude:
- G: The value of G is a very small constant, approximately equal to 6.67430 x 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2.
- g: The value of g is approximately 9.8 m/s^2, which is significantly larger than G.
5. Application:
- G: The gravitational constant is used in the calculation of gravitational forces between celestial bodies, such as planets, stars, and galaxies.
- g: The acceleration due to gravity is used in various calculations involving free fall, projectile motion, and weight.
6. Dependence:
- G: The value of G is a universal constant and does not depend on the mass or location of the objects involved.
- g: The value of g varies depending on the mass and radius of the celestial body. It is stronger on larger objects with greater mass and smaller radii.
Conclusion:
In summary, G represents the gravitational constant, which determines the strength of the gravitational force, while g represents the acceleration due to gravity, which is the acceleration experienced by an object in a gravitational field. G is a small constant used for celestial calculations, while g is the acceleration experienced near the surface of the Earth.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?
Question Description
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?.
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?.
Solutions for Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)?, a detailed solution for Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? has been provided alongside types of Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Define the difference between G and g ( capital and small g)? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























