JEE Exam > JEE Questions > An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-p...
Start Learning for Free
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produc...
C8H10O2 → Gives FeCl3 test means Phenol derivative
↓
Rotate plane polarized light means optically active
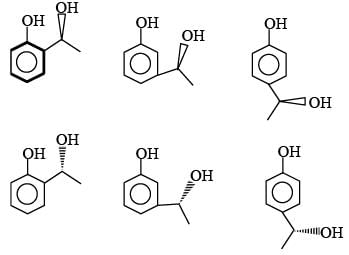
↓
Rotate plane polarized light means optically active

Most Upvoted Answer
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produc...
Possible isomers for an organic compound (C8H10O2)
Introduction:
Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. In other words, they have the same number and types of atoms, but arranged differently. The total number of possible isomers for a given molecular formula can be determined by analyzing the different possible arrangements of atoms.
Given:
Molecular formula: C8H10O2
Properties: Rotates plane-polarized light, Produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution.
Solution:
To determine the possible isomers for this compound, we need to consider the different possible arrangements of atoms. There are several ways to do this, but one common method is to use the concept of functional groups.
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms that give a molecule its characteristic chemical properties. For example, the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) in a molecule can make it more reactive towards nucleophiles, while the presence of a hydroxyl group (OH) can make it more acidic.
Based on the given properties of the compound, we can infer that it contains a carbonyl group and/or a hydroxyl group. We can also assume that it is a chiral molecule, since it rotates plane-polarized light.
Using this information, we can generate the following possible isomers:
1. Two enantiomers with a carbonyl group:
- 3-phenylpropanal (also known as benzylacetaldehyde)
- 2-phenylpropanal (also known as phenylacetaldehyde)
These two compounds have the same molecular formula (C8H10O2) and contain a carbonyl group. They are also chiral molecules that rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Therefore, they are enantiomers of each other.
2. Two enantiomers with a hydroxyl group:
- 1-phenylethanol
- 2-phenylethanol
These two compounds have the same molecular formula (C8H10O2) and contain a hydroxyl group. They are also chiral molecules that rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Therefore, they are enantiomers of each other.
3. Two diastereomers with both carbonyl and hydroxyl groups:
- 3-phenylpropan-1,2-diol
- 2-phenylpropan-1,3-diol
These two compounds have the same molecular formula (C8H10O2) and contain both a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group. They are also diastereomers of each other, meaning they are not mirror images and have different physical properties.
Therefore, the total number of possible isomers for this compound is 6, consisting of 2 enantiomers and 2 diastereomers.
Introduction:
Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. In other words, they have the same number and types of atoms, but arranged differently. The total number of possible isomers for a given molecular formula can be determined by analyzing the different possible arrangements of atoms.
Given:
Molecular formula: C8H10O2
Properties: Rotates plane-polarized light, Produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution.
Solution:
To determine the possible isomers for this compound, we need to consider the different possible arrangements of atoms. There are several ways to do this, but one common method is to use the concept of functional groups.
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms that give a molecule its characteristic chemical properties. For example, the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) in a molecule can make it more reactive towards nucleophiles, while the presence of a hydroxyl group (OH) can make it more acidic.
Based on the given properties of the compound, we can infer that it contains a carbonyl group and/or a hydroxyl group. We can also assume that it is a chiral molecule, since it rotates plane-polarized light.
Using this information, we can generate the following possible isomers:
1. Two enantiomers with a carbonyl group:
- 3-phenylpropanal (also known as benzylacetaldehyde)
- 2-phenylpropanal (also known as phenylacetaldehyde)
These two compounds have the same molecular formula (C8H10O2) and contain a carbonyl group. They are also chiral molecules that rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Therefore, they are enantiomers of each other.
2. Two enantiomers with a hydroxyl group:
- 1-phenylethanol
- 2-phenylethanol
These two compounds have the same molecular formula (C8H10O2) and contain a hydroxyl group. They are also chiral molecules that rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Therefore, they are enantiomers of each other.
3. Two diastereomers with both carbonyl and hydroxyl groups:
- 3-phenylpropan-1,2-diol
- 2-phenylpropan-1,3-diol
These two compounds have the same molecular formula (C8H10O2) and contain both a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group. They are also diastereomers of each other, meaning they are not mirror images and have different physical properties.
Therefore, the total number of possible isomers for this compound is 6, consisting of 2 enantiomers and 2 diastereomers.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?.
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























