JEE Exam > JEE Questions > An organic compound (A) having molecular for...
Start Learning for Free
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.
- a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.
- b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.
- c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.
- d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily dec...
Answer:
To understand the given question, let's break it down into different parts and analyze each part individually.
Part A:
The given compound (A) has a molecular formula of C5H9Br. It readily decolorizes bromine water and KMnO4 solution. From this information, we can conclude that compound (A) is an unsaturated organic compound, capable of undergoing addition reactions with bromine and KMnO4.
The IUPAC name of compound (A) can be determined by analyzing its structure. The molecular formula C5H9Br suggests that compound (A) is a 5-carbon chain with a bromine atom attached. The presence of a bromine atom indicates that the compound is a halogenated organic compound. The double bond in the compound is indicated by the decolorization of bromine water and KMnO4 solution. The position of the double bond can be determined by numbering the carbon atoms in the chain. Thus, the IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.
Part B:
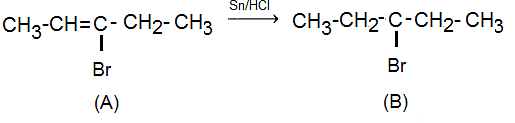
Compound (A), on treatment with Sn/HCl, gives compound (B). This reaction suggests that compound (B) is the product of a reduction reaction. The reaction with Sn/HCl indicates that compound (B) contains a functional group that can be reduced by tin and hydrochloric acid to form a different compound.
Part C:
Compound (A), on treatment with NaNH2, produces compound (C) with the evolution of ammonia. This reaction suggests that compound (C) is the product of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The presence of NaNH2, a strong base, indicates that compound (C) contains a functional group that can be replaced by the nucleophile (NH2-) to form a different compound. The evolution of ammonia indicates the presence of an amino group in compound (C).
Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia. This information suggests that compound (C) is an alkyne. Lindlar's catalyst is used to selectively hydrogenate alkynes to form cis-alkenes. Therefore, compound (C) reacts with Lindlar's catalyst to give cis-pent-2-ene. On the other hand, the reaction with Na/liquid ammonia suggests that compound (C) can form a metal acetylide, which is a characteristic reaction of alkynes.
Part D:
Compound (B) has only two structural isomers. This information suggests that compound (B) is a symmetrical compound. The two structural isomers could be the result of different arrangements of substituents on a symmetrical backbone.
In conclusion, the correct answers are options 'A' and 'B'. Compound (A) is named 2-Bromo pent-2-ene, and compound (C) reacts with Lindlar's catalyst to give cis-pent-2-ene. Compound (B) has only two structural isomers, indicating its symmetrical nature.
To understand the given question, let's break it down into different parts and analyze each part individually.
Part A:
The given compound (A) has a molecular formula of C5H9Br. It readily decolorizes bromine water and KMnO4 solution. From this information, we can conclude that compound (A) is an unsaturated organic compound, capable of undergoing addition reactions with bromine and KMnO4.
The IUPAC name of compound (A) can be determined by analyzing its structure. The molecular formula C5H9Br suggests that compound (A) is a 5-carbon chain with a bromine atom attached. The presence of a bromine atom indicates that the compound is a halogenated organic compound. The double bond in the compound is indicated by the decolorization of bromine water and KMnO4 solution. The position of the double bond can be determined by numbering the carbon atoms in the chain. Thus, the IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.
Part B:
Compound (A), on treatment with Sn/HCl, gives compound (B). This reaction suggests that compound (B) is the product of a reduction reaction. The reaction with Sn/HCl indicates that compound (B) contains a functional group that can be reduced by tin and hydrochloric acid to form a different compound.
Part C:
Compound (A), on treatment with NaNH2, produces compound (C) with the evolution of ammonia. This reaction suggests that compound (C) is the product of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The presence of NaNH2, a strong base, indicates that compound (C) contains a functional group that can be replaced by the nucleophile (NH2-) to form a different compound. The evolution of ammonia indicates the presence of an amino group in compound (C).
Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia. This information suggests that compound (C) is an alkyne. Lindlar's catalyst is used to selectively hydrogenate alkynes to form cis-alkenes. Therefore, compound (C) reacts with Lindlar's catalyst to give cis-pent-2-ene. On the other hand, the reaction with Na/liquid ammonia suggests that compound (C) can form a metal acetylide, which is a characteristic reaction of alkynes.
Part D:
Compound (B) has only two structural isomers. This information suggests that compound (B) is a symmetrical compound. The two structural isomers could be the result of different arrangements of substituents on a symmetrical backbone.
In conclusion, the correct answers are options 'A' and 'B'. Compound (A) is named 2-Bromo pent-2-ene, and compound (C) reacts with Lindlar's catalyst to give cis-pent-2-ene. Compound (B) has only two structural isomers, indicating its symmetrical nature.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily dec...
As (A) decolourises bromine water and KMnO4 solution, it has unsaturation (double bond). Thus, structure of (A) could be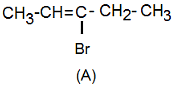
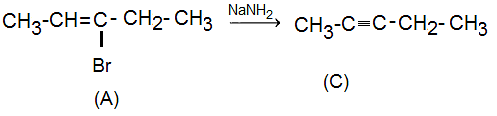
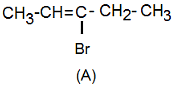
Thus, option (1) is correct.
(A) on reaction with NaNH2 gives Pent-2-yne (C). Since, compound (C) is not a terminal alkyne and it does not react with sodium metal nor forms metal acetylide and on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst, it will form cis-pent-2-ene.
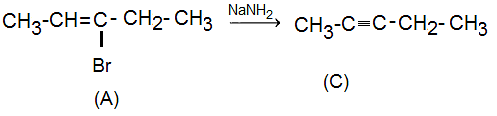
Therefore, option (2) is correct while option (3) is incorrect.
Compound (B) has four structural isomers.

Thus, option (4) is incorrect.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?.
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An organic compound (A) having molecular formula (C5H9Br) readily decolorises bromine water and KMnO4 solution. (A) On treatment with Sn/HCl gives compound (B) and with NaNH2 produces compound (C) with evolution of ammonia. Compound (C) reacts with both Lindlar's catalyst and Na/liquid ammonia.a)The IUPAC name of compound (A) is 2-Bromo pent-2-ene.b)Compound(C) on reaction with Lindlar's catalyst gives cis-pent-2-ene.c)Compound (C) reacts with sodium metal and forms metal acetylide.d)Compound (B) has only two structural isomers.Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























