Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > Directions: In the following questions, a st...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.
Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.
- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
- e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) ...
In the given cross, geneticists found 50% tall and 50% dwarf plants. The dwarf phenomenon is the recessive character which can only be expressed in homozygous condition. Here the cross shows that 50% of the population of the plant are dwarfs. Thus it can be concluded that one of the parent plants of this plant must be heterozygous.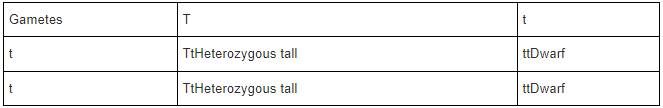
View all questions of this test
Let, the genotype of the heterozygous tall plant it Tt. Here T stands for tall and t expresses the dwarf phenomenon. As T is dominant over t it appears phenotypically.
The genotype of dwarf plant tt
Possible gametes come from the heterozygous tall plant and the homozygous dwarf are T, t and t, t respectively.
The cross is shown in the checkerboard:

The cross shows a 50% tall plant and 50% dwarf plant.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”, both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) ...
A. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Assertion: A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.
Reason: One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.
The given assertion states that a geneticist crossed two pea plants and obtained 50% tall and 50% dwarf plants in the progeny. The reason provided is that one plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.
Explanation:
Understanding Genetics:
Before we explain the given assertion and reason, let's understand some basic concepts of genetics.
1. Genes: Genes are segments of DNA that determine specific traits in an organism. They are responsible for the inheritance of characteristics from one generation to the next.
2. Alleles: Alleles are different forms or variants of a gene. For example, the gene for plant height can have two alleles: one for tallness (T) and one for dwarfness (t).
3. Dominant and Recessive Alleles: In a pair of alleles, one allele may be dominant over another. The dominant allele is represented by a capital letter (T) and expresses its trait, while the recessive allele is represented by a lowercase letter (t) and is only expressed when both alleles are recessive.
4. Homozygous and Heterozygous: If an individual has two identical alleles for a particular gene, they are said to be homozygous (TT or tt). If an individual has two different alleles for a particular gene, they are said to be heterozygous (Tt).
Explanation of the Assertion and Reason:
In the given scenario, the geneticist crossed two pea plants. Let's assume that one plant had the genotype Tt (heterozygous) for the gene controlling plant height, and the other plant had the genotype tt (dwarf).
When these plants are crossed, the possible combinations of alleles in the offspring are:
1. Tt x tt:
- The T allele from the heterozygous plant can combine with the t allele from the dwarf plant.
- The resulting genotype would be Tt for the plant height gene.
- This genotype will express the dominant tall trait.
2. Tt x tt:
- The t allele from the dwarf plant can also combine with the T allele from the heterozygous plant.
- The resulting genotype would be Tt for the plant height gene.
- This genotype will express the dominant tall trait.
Therefore, in both cases, the offspring will have a genotype of Tt, which expresses the tall trait. This explains why the progeny obtained from the cross of these two plants shows 50% tall plants.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion.
Assertion: A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.
Reason: One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.
The given assertion states that a geneticist crossed two pea plants and obtained 50% tall and 50% dwarf plants in the progeny. The reason provided is that one plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.
Explanation:
Understanding Genetics:
Before we explain the given assertion and reason, let's understand some basic concepts of genetics.
1. Genes: Genes are segments of DNA that determine specific traits in an organism. They are responsible for the inheritance of characteristics from one generation to the next.
2. Alleles: Alleles are different forms or variants of a gene. For example, the gene for plant height can have two alleles: one for tallness (T) and one for dwarfness (t).
3. Dominant and Recessive Alleles: In a pair of alleles, one allele may be dominant over another. The dominant allele is represented by a capital letter (T) and expresses its trait, while the recessive allele is represented by a lowercase letter (t) and is only expressed when both alleles are recessive.
4. Homozygous and Heterozygous: If an individual has two identical alleles for a particular gene, they are said to be homozygous (TT or tt). If an individual has two different alleles for a particular gene, they are said to be heterozygous (Tt).
Explanation of the Assertion and Reason:
In the given scenario, the geneticist crossed two pea plants. Let's assume that one plant had the genotype Tt (heterozygous) for the gene controlling plant height, and the other plant had the genotype tt (dwarf).
When these plants are crossed, the possible combinations of alleles in the offspring are:
1. Tt x tt:
- The T allele from the heterozygous plant can combine with the t allele from the dwarf plant.
- The resulting genotype would be Tt for the plant height gene.
- This genotype will express the dominant tall trait.
2. Tt x tt:
- The t allele from the dwarf plant can also combine with the T allele from the heterozygous plant.
- The resulting genotype would be Tt for the plant height gene.
- This genotype will express the dominant tall trait.
Therefore, in both cases, the offspring will have a genotype of Tt, which expresses the tall trait. This explains why the progeny obtained from the cross of these two plants shows 50% tall plants.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
Question Description
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion : A geneticist crossed two pea plants and got 50% tall and 50% dwarf in the progeny.Reason : One plant was heterozygous and the other was dwarf.a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.e)Both Assertion and Reason are false.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















