Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > differences between plant cell and animal ce...
Start Learning for Free
differences between plant cell and animal cell
Verified Answer
differences between plant cell and animal cell
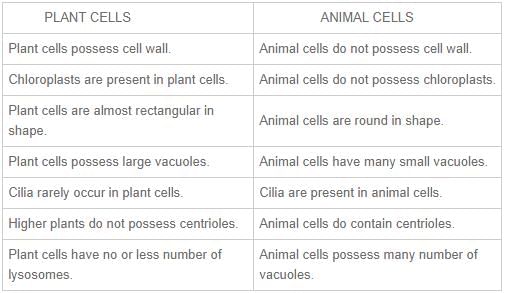
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
differences between plant cell and animal cell
Plant Cell vs Animal Cell
Introduction:
Plant cells and animal cells are the basic units of life. Both types of cells have similarities as well as differences in their structure and function. Understanding these differences is crucial to comprehend the characteristics and functions of plants and animals.
Cell Wall:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made up of cellulose. The cell wall provides shape, support, and protection to the plant cell.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells lack a cell wall. Instead, they have a flexible cell membrane that helps maintain cell shape and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Shape:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells are typically rectangular or square-shaped. The presence of a cell wall helps maintain their shape.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells have a more irregular shape, often rounded or irregularly shaped. They lack a cell wall, so their shape can change more easily.
Plastids:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells contain specialized organelles called plastids, including chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, and chromoplasts, which give color to plant tissues.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells do not contain plastids, so they cannot perform photosynthesis or store pigments like chlorophyll.
Vacuoles:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells typically have one large central vacuole that occupies a significant portion of the cell's volume. The vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells usually have multiple small vacuoles, which are relatively insignificant in size compared to the central vacuole of plant cells.
Lysosomes:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells have fewer lysosomes, which are responsible for cellular waste management and digestion of macromolecules.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells contain numerous lysosomes that aid in the breakdown of various substances and cellular processes such as apoptosis (cell death).
Conclusion:
In summary, plant cells and animal cells have distinct differences in their structure and function. Plant cells possess a cell wall, plastids, a large central vacuole, and fewer lysosomes, while animal cells lack a cell wall, plastids, have multiple small vacuoles, and have numerous lysosomes. Understanding these differences is essential to comprehend the unique characteristics and functions of plants and animals.
Introduction:
Plant cells and animal cells are the basic units of life. Both types of cells have similarities as well as differences in their structure and function. Understanding these differences is crucial to comprehend the characteristics and functions of plants and animals.
Cell Wall:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made up of cellulose. The cell wall provides shape, support, and protection to the plant cell.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells lack a cell wall. Instead, they have a flexible cell membrane that helps maintain cell shape and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Shape:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells are typically rectangular or square-shaped. The presence of a cell wall helps maintain their shape.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells have a more irregular shape, often rounded or irregularly shaped. They lack a cell wall, so their shape can change more easily.
Plastids:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells contain specialized organelles called plastids, including chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, and chromoplasts, which give color to plant tissues.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells do not contain plastids, so they cannot perform photosynthesis or store pigments like chlorophyll.
Vacuoles:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells typically have one large central vacuole that occupies a significant portion of the cell's volume. The vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells usually have multiple small vacuoles, which are relatively insignificant in size compared to the central vacuole of plant cells.
Lysosomes:
- Plant Cell: Plant cells have fewer lysosomes, which are responsible for cellular waste management and digestion of macromolecules.
- Animal Cell: Animal cells contain numerous lysosomes that aid in the breakdown of various substances and cellular processes such as apoptosis (cell death).
Conclusion:
In summary, plant cells and animal cells have distinct differences in their structure and function. Plant cells possess a cell wall, plastids, a large central vacuole, and fewer lysosomes, while animal cells lack a cell wall, plastids, have multiple small vacuoles, and have numerous lysosomes. Understanding these differences is essential to comprehend the unique characteristics and functions of plants and animals.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
differences between plant cell and animal cell
Question Description
differences between plant cell and animal cell for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about differences between plant cell and animal cell covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for differences between plant cell and animal cell.
differences between plant cell and animal cell for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about differences between plant cell and animal cell covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for differences between plant cell and animal cell.
Solutions for differences between plant cell and animal cell in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of differences between plant cell and animal cell defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
differences between plant cell and animal cell, a detailed solution for differences between plant cell and animal cell has been provided alongside types of differences between plant cell and animal cell theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice differences between plant cell and animal cell tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























