NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles ...
Start Learning for Free
Raphe is
- a)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.
- b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.
- c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.
- d)Area between hilum and chalaza.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovul...
Ovule is an integumented megasporangium. The ovule consists of two parts: the body and a stalk. The stalk of the ovule is called the funiculus by which it is adhered to the placenta. The body of the ovule is attached to funiculus by a structure called Hilum.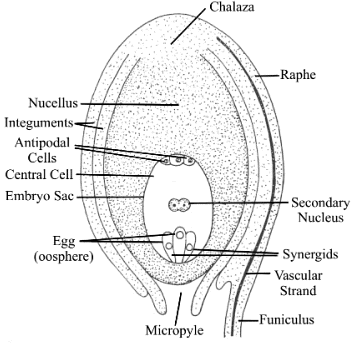
Sometimes there occurs fusion between the funiculus and the body of the ovule which results in the formation of a ridge which is called the Raphe.

So, the correct answer is A.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovul...
Raphe
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that the raphe is formed by the union of funicles with the body of the ovule. Let's understand this in detail.
What is an Ovule?
An ovule is a structure found in the ovaries of flowering plants. It is the part of the plant that develops into a seed after fertilization.
Structure of an Ovule
An ovule is typically composed of three main parts:
1. Integuments: These are the protective coverings of the ovule. They enclose the nucellus, which is the central part of the ovule.
2. Funicle: The funicle is a stalk-like structure that connects the ovule to the placenta (the tissue inside the ovary that nourishes the ovule).
3. Hilum: The hilum is the point of attachment of the funicle to the ovule. It is the scar left behind after the ovule is detached from the placenta.
The Raphe
The raphe is a ridge-like structure that is formed by the union of the funicles with the body of the ovule. It runs along the length of the ovule, connecting the hilum to the chalaza.
Function of the Raphe
The raphe plays an important role in seed development and germination. It acts as a pathway for the transfer of nutrients and water between the parent plant and the developing seed. It also helps in anchoring the seed within the fruit.
Other Options
Let's briefly discuss the other options mentioned in the question:
- Distance between chalaza and micropyle: The chalaza is the basal part of the ovule, while the micropyle is the opening through which the pollen tube enters during fertilization. The distance between these two structures can vary depending on the species of plant.
- Distance between hilum and micropyle: The hilum is the point of attachment of the funicle to the ovule, while the micropyle is the opening through which the pollen tube enters. Again, the distance between these two structures can vary.
- Area between hilum and chalaza: This refers to the region between the point of attachment (hilum) and the basal part of the ovule (chalaza). The size and shape of this area can vary among different plant species.
In conclusion, the raphe is formed by the union of funicles with the body of the ovule. It plays a crucial role in seed development and germination by facilitating the transfer of nutrients and water.
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that the raphe is formed by the union of funicles with the body of the ovule. Let's understand this in detail.
What is an Ovule?
An ovule is a structure found in the ovaries of flowering plants. It is the part of the plant that develops into a seed after fertilization.
Structure of an Ovule
An ovule is typically composed of three main parts:
1. Integuments: These are the protective coverings of the ovule. They enclose the nucellus, which is the central part of the ovule.
2. Funicle: The funicle is a stalk-like structure that connects the ovule to the placenta (the tissue inside the ovary that nourishes the ovule).
3. Hilum: The hilum is the point of attachment of the funicle to the ovule. It is the scar left behind after the ovule is detached from the placenta.
The Raphe
The raphe is a ridge-like structure that is formed by the union of the funicles with the body of the ovule. It runs along the length of the ovule, connecting the hilum to the chalaza.
Function of the Raphe
The raphe plays an important role in seed development and germination. It acts as a pathway for the transfer of nutrients and water between the parent plant and the developing seed. It also helps in anchoring the seed within the fruit.
Other Options
Let's briefly discuss the other options mentioned in the question:
- Distance between chalaza and micropyle: The chalaza is the basal part of the ovule, while the micropyle is the opening through which the pollen tube enters during fertilization. The distance between these two structures can vary depending on the species of plant.
- Distance between hilum and micropyle: The hilum is the point of attachment of the funicle to the ovule, while the micropyle is the opening through which the pollen tube enters. Again, the distance between these two structures can vary.
- Area between hilum and chalaza: This refers to the region between the point of attachment (hilum) and the basal part of the ovule (chalaza). The size and shape of this area can vary among different plant species.
In conclusion, the raphe is formed by the union of funicles with the body of the ovule. It plays a crucial role in seed development and germination by facilitating the transfer of nutrients and water.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Raphe isa)Ridge formed by union of funicles with the body of the ovule.b)Distance between chalaza and micropyle.c)Distance between hilum and micropyle.d)Area between hilum and chalaza.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















