CAT Exam > CAT Questions > Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another squa...
Start Learning for Free
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-
- a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCD
- b)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGH
- c)7.5 times the side of the square ABCD
- d)7.5 times the side of the square EFGH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining th...
To solve this problem, we need to understand the motion of Lakshman, Kanika, and Jagadeesh along the sides of the squares ABCD and EFGH.
Let's assume that the side of the square ABCD is 's' km.
1. Relative speeds of Lakshman and Kanika:
- Lakshman's speed = 'l' kmph
- Kanika's speed = 'k' kmph
Since they are traveling towards each other, their relative speed is (l + k) kmph.
2. Relative speed of Jagadeesh:
- Jagadeesh's speed = 'j' kmph
Jagadeesh is traveling along the square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction. Since the sides of squares ABCD and EFGH are parallel, Jagadeesh's speed remains constant throughout.
Now, let's analyze the motion of Lakshman, Kanika, and Jagadeesh:
- When Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H, they have already met at some point before that. Let's assume they meet at point X on side AB of square ABCD.
- Since they meet for the second time at H, they would have traveled the entire side AB twice. The distance traveled by Lakshman = 2s km and the distance traveled by Kanika = 2s km.
- The time taken by Lakshman and Kanika to meet at X can be determined using the formula: time = distance/speed.
- Time taken by Lakshman to reach X = (2s)/l hours
- Time taken by Kanika to reach X = (2s)/k hours
- Now, let's determine the distance traveled by Jagadeesh when he meets Lakshman and Kanika for the first time at point X.
- The time taken by Jagadeesh to reach X can be determined using the formula: time = distance/speed.
- Distance traveled by Jagadeesh = (2s)/j km
- Since Jagadeesh meets Lakshman and Kanika at X, they all travel the same distance.
- Distance traveled by Lakshman = 2s km
- Distance traveled by Kanika = 2s km
- Distance traveled by Jagadeesh = (2s)/j km
Now, let's compare the ratios of the distances traveled by Lakshman, Kanika, and Jagadeesh:
- Distance traveled by Lakshman : Distance traveled by Kanika : Distance traveled by Jagadeesh
= 2s : 2s : (2s)/j
= 1 : 1 : 1/j
Given that i : k : j = 1 : 3 : 5√2, we can equate the ratios:
1 : 3 : 5√2 = 1 : 1 : 1/j
From this, we can conclude that j = 1/(5√2) = √2/10.
Therefore, the distance traveled by Jagadeesh = (2s)/(√2/10) = 10√2s.
Since the side of the square ABCD is 's' km, the distance traveled by Jagadeesh is 10√2s = 10√2 × s =
Let's assume that the side of the square ABCD is 's' km.
1. Relative speeds of Lakshman and Kanika:
- Lakshman's speed = 'l' kmph
- Kanika's speed = 'k' kmph
Since they are traveling towards each other, their relative speed is (l + k) kmph.
2. Relative speed of Jagadeesh:
- Jagadeesh's speed = 'j' kmph
Jagadeesh is traveling along the square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction. Since the sides of squares ABCD and EFGH are parallel, Jagadeesh's speed remains constant throughout.
Now, let's analyze the motion of Lakshman, Kanika, and Jagadeesh:
- When Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H, they have already met at some point before that. Let's assume they meet at point X on side AB of square ABCD.
- Since they meet for the second time at H, they would have traveled the entire side AB twice. The distance traveled by Lakshman = 2s km and the distance traveled by Kanika = 2s km.
- The time taken by Lakshman and Kanika to meet at X can be determined using the formula: time = distance/speed.
- Time taken by Lakshman to reach X = (2s)/l hours
- Time taken by Kanika to reach X = (2s)/k hours
- Now, let's determine the distance traveled by Jagadeesh when he meets Lakshman and Kanika for the first time at point X.
- The time taken by Jagadeesh to reach X can be determined using the formula: time = distance/speed.
- Distance traveled by Jagadeesh = (2s)/j km
- Since Jagadeesh meets Lakshman and Kanika at X, they all travel the same distance.
- Distance traveled by Lakshman = 2s km
- Distance traveled by Kanika = 2s km
- Distance traveled by Jagadeesh = (2s)/j km
Now, let's compare the ratios of the distances traveled by Lakshman, Kanika, and Jagadeesh:
- Distance traveled by Lakshman : Distance traveled by Kanika : Distance traveled by Jagadeesh
= 2s : 2s : (2s)/j
= 1 : 1 : 1/j
Given that i : k : j = 1 : 3 : 5√2, we can equate the ratios:
1 : 3 : 5√2 = 1 : 1 : 1/j
From this, we can conclude that j = 1/(5√2) = √2/10.
Therefore, the distance traveled by Jagadeesh = (2s)/(√2/10) = 10√2s.
Since the side of the square ABCD is 's' km, the distance traveled by Jagadeesh is 10√2s = 10√2 × s =
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining th...
Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time √2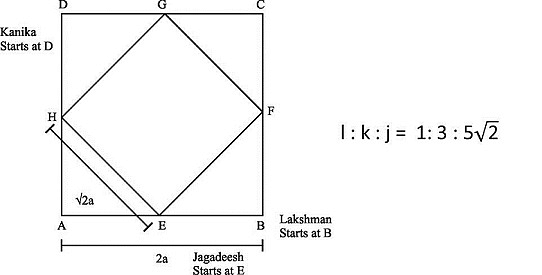

Since, i : j : k = 1 : 3 : 5√2
Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. They are at a distance of 4a from each other. Since they are at diametrically opposite points, the relative distance would be 4a irrespective of the directions they choose to travel in. So, to meet for the first time, they would have travelled a distance of 4a together.
To meet for the second time, they would have travelled a further 8a together. Essentially, between them, they would have to cover the entire perimeter of the square to meet again.
So by the time they meet for the second time, they would have covered a distance of 12a together. Their speeds are in the ratio 1: 3. So, Lakshman would have travelled 3a and Kanika would have travelled 9a.
Or, Lakshman travels in the direction BADC, while Kanika would have travelled in the direction DABC. They meet for the first time at E and the second time at H.
In the same time, Jagadeesh travels along the square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph and meets Lakshman and Kanika. While Jagadeesh meets the other two for the first time, we do not know how many laps he has completed by then.
The ratio of Lakshman’s speed to that of Jagadeesh is 1 : 5√2 so, they would have travelled distances in the same ratio as well. So, if Lakshman has travelled a distance of 3a, Jagadeesh should have travelled a distance of 3a × 5√2 to reach H.
Or, Jagadeesh travels 52a to reach H.
The answer 7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCD.
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Attention CAT Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed CAT study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in CAT.

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|
Similar CAT Doubts
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for CAT 2024 is part of CAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CAT exam syllabus. Information about Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for CAT 2024 is part of CAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CAT exam syllabus. Information about Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for CAT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CAT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider a square ABCD. EFGH is another square obtained by joining the midpoints of the sides of the square ABCD where E, F, G and H are the midpoints of AB, BC, CD and DA respectively. Lakshman and Kanika start from points B and D respectively at speeds ‘l’ kmph and ‘k’ kmph respectively and travel towards each other along the sides of the square ABCD. Jagadeesh starts from Point E and travels along the Square EFGH in the anti-clockwise direction at ‘j’ kmph. Lakshman and Kanika meet for the second time at H where Jagadeesh also meets them for the first time. If i : k : j is 1 : 3 : 5√2 then the distance travelled by Jagadeesh is:-a)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square ABCDb)7.5 × √2 times the side of the square EFGHc)7.5 times the side of the square ABCDd)7.5 times the side of the square EFGHCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice CAT tests.

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























